Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.1 Definition of The Laplacetransform
Uploaded by
Nicholas MutuaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7.1 Definition of The Laplacetransform
Uploaded by
Nicholas MutuaCopyright:
Available Formats
7.
Definition of the Laplace Transform Laplace Transform
Definition 7.1.1
Let f be a function defined for t 0 . Then the integral
st { f (t )} = 0 e f (t ) dt = F ( s)
is said to be the Laplace transform of f , provided the integral converges. Notations: Lowercase letter is used to denote the function being transformed, and the corresponding uppercase letter is to denote its Laplace transform. Example: at By using the definition of the Laplace Transform, find e .
{ }
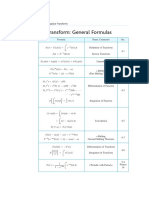
Linearity of the Laplace Transform The Laplace Transform is a linear operator, ie. for any function f (t ) and g (t ) whose Laplace transform exists, and any constants and , { f (t ) + g ( t )} = { f (t )} + { g (t )} Example: Find (refer to Table of Laplace Transform), 4 1. t 2. 3. { sinh 3t }
{ } { e }
8 t
4. { 3 t 2sin 7 t }
Reference: A First Course in Differential Equations with Modeling Applications (9th Ed) Dennis G. Zill, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company
You might also like
- Laplace and Inverse TransformsDocument40 pagesLaplace and Inverse TransformsDheerajOmprasadNo ratings yet
- Application of Laplace TransformDocument35 pagesApplication of Laplace TransformSingappuli100% (1)
- 12 - Laplace Transforms and Their Applications PDFDocument72 pages12 - Laplace Transforms and Their Applications PDFMonty100% (1)
- Definition of the Laplace TransformDocument30 pagesDefinition of the Laplace TransformkreposNo ratings yet
- Laplace transform properties and theoremsDocument14 pagesLaplace transform properties and theoremsPete BasNo ratings yet
- Title Lorem Ipsum: Laplace TransformationDocument33 pagesTitle Lorem Ipsum: Laplace TransformationQAMMER ILYASNo ratings yet
- Ch7 PDFDocument63 pagesCh7 PDF王大洋No ratings yet
- MATHSDocument11 pagesMATHSshansudar843No ratings yet
- Study of Laplace Transform AND It'S ApplicationsDocument20 pagesStudy of Laplace Transform AND It'S Applicationsjucar fernandezNo ratings yet
- Laplace by Chandra 150831190012 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument20 pagesLaplace by Chandra 150831190012 Lva1 App6892 PDFjucar fernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1pothakamuri312No ratings yet
- UNIT - IV Laplace Transformations Class 1Document77 pagesUNIT - IV Laplace Transformations Class 1ksh98No ratings yet
- Lecture Guide 3 - Laplace Transformation For Process ControlDocument17 pagesLecture Guide 3 - Laplace Transformation For Process ControlMariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformatnDocument11 pagesLaplace TransformatnOduola AtinukeNo ratings yet
- Topics From Tensoral Calculus: 1 PreliminariesDocument11 pagesTopics From Tensoral Calculus: 1 Preliminariesclark456No ratings yet
- AdvMath (Unit 2)Document24 pagesAdvMath (Unit 2)Ivan Paul SyNo ratings yet
- La Place TransformDocument8 pagesLa Place Transformreliance2012No ratings yet
- ID8565 (4)Document13 pagesID8565 (4)Firii SolomoonNo ratings yet
- LaplaceDocument43 pagesLaplaceNakuNo ratings yet
- LksmssaplaceDocument43 pagesLksmssaplaceNakuNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms Theory SolutionsDocument114 pagesLaplace Transforms Theory SolutionsHector Ledesma III100% (1)
- Laplace Transform and The Z-TransformDocument20 pagesLaplace Transform and The Z-TransformPatrick Anthony A. HipulanNo ratings yet
- EMTH202-Lecture 13 (20-03-2023)Document25 pagesEMTH202-Lecture 13 (20-03-2023)Naledi KetlogetsweNo ratings yet
- LAPLACE TRANSFORM TITLEDocument4 pagesLAPLACE TRANSFORM TITLEtingliang0831No ratings yet
- Krishna's Textbook on Mathematical MethodsDocument159 pagesKrishna's Textbook on Mathematical MethodswecharriNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Its Inverse Transform - Unit - Iii - Iv MaterialsDocument49 pagesLaplace and Its Inverse Transform - Unit - Iii - Iv MaterialsSupratim RoyNo ratings yet
- 12 - Laplace Transforms and Their ApplicationsDocument72 pages12 - Laplace Transforms and Their ApplicationsAnonymous OrhjVLXO5sNo ratings yet
- Inverse Laplace TransformDocument12 pagesInverse Laplace TransformChristian John FernandezNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Laplace Transfrom Method: Structure NoDocument46 pagesUnit 6 Laplace Transfrom Method: Structure NoJAGANNATH PRASADNo ratings yet
- Inverse LaplaceDocument12 pagesInverse LaplaceΜΙΚΕ ΖΥΡNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Title GeneratorDocument12 pagesLaplace Transform Title GeneratorJoshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Entire Course Material All Files Combined For 2011 FinalDocument191 pagesEntire Course Material All Files Combined For 2011 FinalFinian MassaNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is ADocument6 pagesAppendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is AulaganathanNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transformations 2Document26 pagesLaplace Transformations 2Soumyadeep MajumdarNo ratings yet
- LaplaceDocument13 pagesLaplaceMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Lect 22Document26 pagesLect 22itsprime747No ratings yet
- Laplace Transform by Engr. VergaraDocument88 pagesLaplace Transform by Engr. VergaraSharmaine TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PPT Slides vs3Document22 pagesChapter 6 PPT Slides vs3Sherif Aly100% (1)
- Engineering Mathematics 1 Transform Functions: QuestionsDocument20 pagesEngineering Mathematics 1 Transform Functions: QuestionsSyahrul SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Transforms and Moment Generating Functions ExplainedDocument12 pagesTransforms and Moment Generating Functions Explainedladida1234567No ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Review: ExampleDocument3 pagesLaplace Transform Review: ExampleSandhyaNo ratings yet
- P1 MT (Abr)Document5 pagesP1 MT (Abr)fikrianyNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Inverse Laplace TransformDocument96 pagesLaplace and Inverse Laplace Transformgtewszc123No ratings yet
- Calculus For Engineers: Chapter 16 - Laplace TransformsDocument41 pagesCalculus For Engineers: Chapter 16 - Laplace TransformsscreamNo ratings yet
- MAT231BT - Laplace TransformsDocument25 pagesMAT231BT - Laplace TransformsRochakNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Definition of Laplace Transform Objectives:: FT Me TTDocument11 pages4.1 Definition of Laplace Transform Objectives:: FT Me TTKhaled HassanNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform GuideDocument10 pagesLaplace Transform Guideariana_kardiamouNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: Michelle T. Panganduyon, PHDDocument133 pagesDifferential Equations: Michelle T. Panganduyon, PHDBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- LaplaceDocument4 pagesLaplacebelleblackNo ratings yet
- Laplace Periodic SolutionsDocument4 pagesLaplace Periodic SolutionsasbadgNo ratings yet
- The Laplace Transform Review: ECE 382 Fall 2012Document15 pagesThe Laplace Transform Review: ECE 382 Fall 2012ljjbNo ratings yet
- The Fourier Transform ExplainedDocument35 pagesThe Fourier Transform ExplainedThanatkrit KaewtemNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms ExplainedDocument38 pagesLaplace Transforms ExplainedBantu AadhfNo ratings yet
- Convolution and Equidistribution: Sato-Tate Theorems for Finite-Field Mellin Transforms (AM-180)From EverandConvolution and Equidistribution: Sato-Tate Theorems for Finite-Field Mellin Transforms (AM-180)No ratings yet
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument7 pagesSampleNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Journal of International: Academic Research For MultidisciplinaryDocument9 pagesJournal of International: Academic Research For MultidisciplinaryNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- BSC BioinfoDocument7 pagesBSC BioinfoNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document35 pagesChapter 13Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Dean requests assistance for students who missed graduationDocument66 pagesDean requests assistance for students who missed graduationNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- T4Document23 pagesT4Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Year 1Document2 pagesYear 1Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- XCVZDocument25 pagesXCVZNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Important Module1 Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument11 pagesImportant Module1 Solving Quadratic EquationsNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - Practice TestDocument6 pagesQuadratic Equations - Practice TestNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Differential Continuity Equation: Eynolds Ransport HeoremDocument5 pagesDifferential Continuity Equation: Eynolds Ransport HeoremNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula: B B Ac X A X XDocument1 pageSolving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula: B B Ac X A X Xliangp28No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument49 pagesSyllabusNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- M 24Document2 pagesM 24Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.3 1 of 5Document5 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.3 1 of 5Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Model For Estimating Distillate Yield in Large Solar StillsDocument14 pagesA Simplified Model For Estimating Distillate Yield in Large Solar StillsNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Surds, Indices and Logarithms Classwork: Ab A B A A B BDocument6 pagesTopic 3: Surds, Indices and Logarithms Classwork: Ab A B A A B BNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1S - DR Paul May: Calculus Question For January Exam 2007Document2 pagesChemistry 1S - DR Paul May: Calculus Question For January Exam 2007masyuki1979No ratings yet
- Calc 3 Lecture Notes Section 12.4 1 of 7Document7 pagesCalc 3 Lecture Notes Section 12.4 1 of 7Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Portal Provides Free Books, Papers and ResourcesDocument64 pagesCivil Engineering Portal Provides Free Books, Papers and ResourcesCiutac Ionut CristianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1S Exam Calculus QuestionDocument3 pagesChemistry 1S Exam Calculus Questionmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry: DC ABDocument13 pagesAnalytical Geometry: DC ABbd87glNo ratings yet
- 11106Document3 pages11106bd87glNo ratings yet
- 480 Final F04Document13 pages480 Final F04Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument67 pagesArtificial Intelligencerajarajkumar543No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document18 pagesChapter 10Nicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- Area and Arc Length For Polar CurvesDocument1 pageArea and Arc Length For Polar CurvesNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- 08 Nonlinear ODEDocument9 pages08 Nonlinear ODENicholas MutuaNo ratings yet
- 7.5 Dirac Delta FunctionDocument1 page7.5 Dirac Delta FunctionNicholas MutuaNo ratings yet