Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2-Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity
Uploaded by
Kayla SheltonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2-Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity
Uploaded by
Kayla SheltonCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity 1) A Cold Hard Fact: Better quality, higher productivity, lower costs, and
the ability to respond quickly to customer needs are more important than ever and the bar is getting higher. 2) Chapter Focus: This chapter focuses on three separate, but related that are vitally important to business organizations. a. Competitiveness b. Strategy c. Productivity 3) Competitiveness: Competitiveness: How effectively an organization meets the wants and needs of customers relative to others that offer similar goods or services. Organizations compete through some combination of their marketing and operations functions. o What do customers want? o How can these customers needs best be satisfied? 4) Marketings Influence: Identifying consumer wants and/or needs Pricing Advertising and promotion 5) Businesses Compete Using Operations: Product and service design Cost Location Quality Quick response Flexibility Inventory management Supply chain management Service Managers and workers
6) Why Some Organizations Fail: 1. Neglecting operations strategy 2. Failing to take advantage of strengths & opportunities &/or failing to recognize competitive threats 3. Too much emphasis on short-term financial performance at the expense of R&D 4. Too much emphasis in product and service design and not enough on process design and improvement 5. Neglecting investments in capital and human resources 6. Failing to establish good internal communications and cooperation 7. Failing to consider customer wants and needs
7) Hierarchical Planning:
8) Mission, Goals, and Strategy: Mission The reason for an organizations existence Goals Provide detail and the scope of the mission Goals can be viewed as organizational destinations Strategy A plan for achieving organizational goals Serves as a roadmap for reaching the organizational destinations 9) Mission: The reason for an organizations existence Mission statement: States the purpose of the organization The mission statement should answer the question What business are we in? 10) Fed Ex Mission Statement:
FedEx Corporation will produce superior financial returns for its shareowners by providing high value-added logistics, transportation and related information services through focused operating companies. Customer requirements will be met in the highest quality manner appropriate to each market segment served. FedEx Corporation will strive to develop mutually rewarding relationships with its employees, partners and suppliers. Safety will be the first consideration in all operations. Corporate activities will be conducted to the highest ethical and professional standards. 11) Canadian National Railway (1990):
To provide our customers distribution and transportation services for their goods in a commercial, safe, and damage-free manner.
12) GoalsThe mission statement serves as the basis for organizational goals Goals: Provide detail and the scope of the mission Goals can be viewed as organizational destinations Goals serve as the basis for organizational strategies 13) Strategy: A plan for achieving organizational goals Serves as a roadmap for reaching the organizational destinations Organizations have: Organizational strategies Overall strategies that relate to the entire organization Support the achievement of organizational goals and mission Functional level strategies Strategies that relate to each of the functional areas and that support achievement of the organizational strategy 14) Tactics and Operations:
Tactics The methods and actions taken to accomplish strategies The how to part of the process Operations The actual doing part of the process 15) Hierarchical Planning and Decision making:
16) Core Competencies: Special attributes or abilities that give an organization a competitive edge. To be effective core competencies and strategies need to be aligned 17) 3 Basic Strategies I. Low-cost leadership Low Cost Scale-based Product differentiation Newness Flexible Operations Higher Quality Service Sustainability Focus on market niche Specialization Sample Operations Strategies:
II.
III.
17)
18)
Strategy Formulation:
Effective strategy formulation requires taking into account: Core competencies Environmental scanning SWOT Successful strategy formulation also requires taking into account: Order qualifiers Order winners
19) Order qualifiers: Characteristics that customers perceive as minimum standards of acceptability for a product or service to be considered as a potential for purchase 20)Order winners: Characteristics of an organizations goods or services that cause it to be perceived as better than the competition 21) Strategy FormulationEnvironmental Scanning Environmental Scanning is necessary to identify Internal Factors: Strengths and Weaknesses External Factors: Opportunities and Threats 22) Key External Factors: Economic conditions Political conditions Legal environment 23) Key Internal Factors: 24) Human Resources Facilities and equipment Financial resources Customers Products and services Technology Suppliers Other Technology Competition Markets
Example Operations Strategies: Global Outsource Supply Chain Management Sustainability
25) Operations Strategy: The approach consistent with organization strategy that is used to guide the operations function.
26) Quality-Based Strategies: Strategies that focuses on quality in all phases of an organization Pursuit of such a strategy is rooted in a number of factors: Trying to overcome a poor quality reputation Desire to maintain a quality image A desire to catch up with the competition A part of a cost reduction strategy 27) Time-Based Strategies: Strategies that focus on the reduction of time needed to accomplish tasks It is believed that by reducing time, costs are lower, quality is higher, productivity is higher, time-to-market is faster, and customer service is improved Areas where organizations have achieved time reductions: Planning time Changeover time Product/service design time Delivery time Processing time Response time for complaints 28) Agile Operations: A strategic approach for competitive advantage that emphasizes the use of flexibility to adapt and prosper in an environment of change Involves the blending of several core competencies: o Cost o Reliability o Quality o Flexibility 29) The Balanced Scorecard Approach: A top-down management system that organizations can use to clarify their vision and strategy and transform them into action Develop objectives Develop metrics and targets for each objective Develop initiatives to achieve objectives Identify links among the various perspectives Finance Internal business Customer processes Learning and growth Monitor results
30)
The Balanced Scorecard:
31) Productivity: A measure of the effective use of resources, usually expressed as the ratio of output to input Productivity measures are useful for: Tracking an operating units performance over time Judging the performance of an entire industry or country 32) Why Productivity Matters: High productivity is linked to higher standards of living As an economy replaces manufacturing jobs with lower productivity service jobs, it is more difficult to maintain high standards of living Higher productivity relative to the competition leads to competitive advantage in the marketplace Pricing and profit effects For an industry, high relative productivity makes it less likely it will be supplanted by foreign industry 33) Productivity Measures: Productivity = Partial Measures: Multifactor Measures: Total Measure:
33)
Productivity Calculation Example: 5,000 $30/unit 500 hours Cost of labor: Cost of materials: Cost of overhead: $25/hour $5,000 2x labor cost
Units produced: Standard price: Labor input:
What is the multifactor productivity? 34) Solution:
What is the implication of an unitless measure of productivity? 35) U.S. Multifactor Productivity (1976 2010):
36)
Productivity Growth:
Productivi ty Growth = Current productivity - Previous productivity 100 % Previous productivity
Example: Labor productivity on the ABC assembly line was 25 units per hour in 2009. In 2010, labor productivity was 23 units per hour. What was the productivity growth from 2009 to 2010?
37)
Service Sector Productivity: Service sector productivity is difficult to measure and manage because o It involves intellectual activities o It has a high degree of variability A useful measure related to productivity is process yield o Where products are involved: Ratio of output of good product to the quantity of raw material input. Where services are involved, process yield measurement is often dependent on the particular process: o Ratio of cars rented to cars available for a given day o Ratio of student acceptances to the total number of students approved for admission.
38)
Factors Affecting Productivity:
39) o o o o o o o
Factors Affecting Productivity: Standardization Quality Differences Internet Usage Computer Viruses Control of Inputs and Outputs Scrap Rates New Workers o Safety o Lack of Skilled Workers in the Marketplace o Layoffs or Plant Closings o Labor Turnover o Workplace Design o Worker Incentive Plans
40)
Improving Productivity:
1. Develop productivity measures for all operations 2. Determine critical (bottleneck) operations 3. Develop methods for productivity improvements 4. Establish reasonable goalsWhat is a stretch goal? 5. Make it clear that management supports and encourages productivity improvement 6. Measure and publicize improvements Dont confuse productivity with efficiency
41) Dont Forget: All Goals/Projects Must Relate to the Organizational Mission, Goals, and Strategy
You might also like
- How Effectively An Organization Meets The Wants and NeedsDocument12 pagesHow Effectively An Organization Meets The Wants and Needsibraheem alsoudeNo ratings yet
- Session 2: Manufacturing Strategy and CompetitivenessDocument36 pagesSession 2: Manufacturing Strategy and CompetitivenessNikhil KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- LSCM 2 MarksDocument29 pagesLSCM 2 MarksRaja .S71% (7)
- Understanding Operations Management Through Competitive Priorities and Customer ValueDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Operations Management Through Competitive Priorities and Customer ValueDanielNo ratings yet
- 2013 Business Studies NotesDocument20 pages2013 Business Studies NotesJim Sinclair-AndersonNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role and Objectives of Operations/ Production: Henky S. Nugroho Bambang P. PriantoDocument27 pagesThe Strategic Role and Objectives of Operations/ Production: Henky S. Nugroho Bambang P. Priantoteknikpembakaran2013No ratings yet
- MACS Assess Performance Across Value ChainDocument51 pagesMACS Assess Performance Across Value ChainRandy CavaleraNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy and CompetitivenessDocument35 pagesOperations Strategy and CompetitivenessJeewika PareekNo ratings yet
- Om Chapter TwoDocument30 pagesOm Chapter TwoBETTYNo ratings yet
- MBA 290-Strategic AnalysisDocument110 pagesMBA 290-Strategic AnalysisAbhishek SoniNo ratings yet
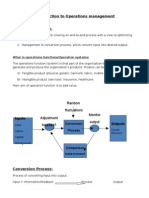
- Introduction To Operations Management: Random Fluctuations Monitor Output Adjustment Needed?Document11 pagesIntroduction To Operations Management: Random Fluctuations Monitor Output Adjustment Needed?Shweta Yadav100% (1)
- Module 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesModule 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementBharathKumarM86% (14)
- Operation ManagementDocument79 pagesOperation ManagementSumama IkhlasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations StrategyDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Operations StrategySunil HansuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Strategic ManagementDocument110 pagesAdvanced Strategic ManagementDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Cu Is Not Sponsored or Endorsed by Any College or UniversityDocument26 pagesCu Is Not Sponsored or Endorsed by Any College or Universityirna darlinNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument40 pagesQuality Function DeploymentVaswee Dubey100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2Dilara GuntayNo ratings yet
- Bank Operations Manager Manufacturing Operations ManagerDocument6 pagesBank Operations Manager Manufacturing Operations ManagerLauren StuartNo ratings yet
- CareerPath SupplyChainDocument27 pagesCareerPath SupplyChainShobhit PareekNo ratings yet
- Customer Fulfillment Strategies for Supply Chain SuccessDocument66 pagesCustomer Fulfillment Strategies for Supply Chain SuccessAli HusnaenNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument25 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementPriAnca GuptaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Canadian 5th Edition Stevenson Test BankDocument40 pagesOperations Management Canadian 5th Edition Stevenson Test BankNatalieWilsondrsai100% (12)
- MBA 290-Strategic AnalysisDocument110 pagesMBA 290-Strategic AnalysisAllan YeungNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument16 pagesOperations Managementalthafap02No ratings yet
- Management Processes CatDocument6 pagesManagement Processes CatSteve OgolaNo ratings yet
- Operations StrategyDocument37 pagesOperations StrategyDinesh GannerllaNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementUpdatedDocument107 pagesOperations ManagementUpdatedNikita Kossolapov100% (1)
- Bản sao của chapter 9Document8 pagesBản sao của chapter 9Phương AnhhNo ratings yet
- M Strategy3Document21 pagesM Strategy3Mohammad AlfatehNo ratings yet
- Summary Covers Exam MaterialDocument30 pagesSummary Covers Exam MaterialWriting ServiceNo ratings yet
- Core of ITILDocument15 pagesCore of ITILRajNo ratings yet
- Mb0044 Unit 03 SLMDocument22 pagesMb0044 Unit 03 SLMRahul ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Two: Competitiveness, Strategies, and Productivity in OperationsDocument63 pagesChapter-Two: Competitiveness, Strategies, and Productivity in OperationsChernet AyenewNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Individual Assignment (20%)Document7 pagesOperations Management: Individual Assignment (20%)AddiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document32 pagesChapter 02MathewNo ratings yet
- AE 27 Lesson 2Document36 pagesAE 27 Lesson 2Ces GarceraNo ratings yet
- Karnavati University Gandhinagar Gujarat-3Document12 pagesKarnavati University Gandhinagar Gujarat-3Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals: Chapter 7 (Lecture Notes)Document6 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals: Chapter 7 (Lecture Notes)Peishi OngNo ratings yet
- Production Operations Management - Lecture 2Document23 pagesProduction Operations Management - Lecture 2Hassan ElbayyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Operations Strategy & CompetitivenessDocument30 pages2 Operations Strategy & CompetitivenessPALLAVI BHISENo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument91 pagesOperations ManagementAnup MamenNo ratings yet
- MGMT 314 Sustainable Strategy OperationsDocument16 pagesMGMT 314 Sustainable Strategy OperationsLini VargheseNo ratings yet
- Term Report Trends in Operation ManagementDocument11 pagesTerm Report Trends in Operation ManagementAhsan SaeedNo ratings yet
- wk1 Strategy-NewDocument34 pageswk1 Strategy-NewAnu DNo ratings yet
- Exam Content Manual: PreviewDocument5 pagesExam Content Manual: PreviewPunit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Name: Kumail Mehdi. (5B) BBA 201096Document5 pagesManagement Information System: Name: Kumail Mehdi. (5B) BBA 201096Saad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1+2: 1. (A) Differentiate Between Operations Management and Production Management. 05 Chapter 1Document96 pagesChapter 1+2: 1. (A) Differentiate Between Operations Management and Production Management. 05 Chapter 1Zubayer HassanNo ratings yet
- BPR Lecture Introduction to Business Process ReengineeringDocument21 pagesBPR Lecture Introduction to Business Process ReengineeringMariaNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Organizational Structures for International BusinessDocument50 pagesStrategies and Organizational Structures for International BusinessSena TranNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions of Advance Management Accounting (CA Final)Document7 pagesTheory Questions of Advance Management Accounting (CA Final)Lawrence Maretlwa33% (3)
- RatewalDocument32 pagesRatewalAnonymous wdtORXGydWNo ratings yet
- Competition in Manufacturing StrategyDocument16 pagesCompetition in Manufacturing StrategyAAYUSH ANANDNo ratings yet
- Ipcc SMDocument9 pagesIpcc SMRaghu SethNo ratings yet
- Operations StrategyDocument4 pagesOperations Strategyjth55936zwohocomNo ratings yet
- Strategic Profitability AnalysisDocument76 pagesStrategic Profitability Analysisvkfzr100% (1)
- The Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesFrom EverandThe Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- CH 4 Int'l Acct.'ing HWDocument2 pagesCH 4 Int'l Acct.'ing HWKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Chi-square goodness of fit test grades time StatCrunchDocument1 pageChi-square goodness of fit test grades time StatCrunchKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Review GuideDocument3 pagesExam 1 Review GuideKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Your Order Has Been Received!Document2 pagesYour Order Has Been Received!Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- CH 1 SolDocument7 pagesCH 1 SolHanu ChristianNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Chapter 1 OverviewDocument31 pagesStrategic Management Chapter 1 OverviewKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7 – 13 Essay QuestionsDocument26 pagesChapters 7 – 13 Essay QuestionsKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- F Years of Service That Qualify For Pension Credit, Subject To A Maximum of 30 YearsDocument3 pagesF Years of Service That Qualify For Pension Credit, Subject To A Maximum of 30 YearsKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 QuizDocument2 pagesChapter 22 QuizKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Final DraftDocument3 pagesFinal DraftKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- In Class ProblemDocument1 pageIn Class ProblemKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- FIRE 416 Review Summer 2014Document5 pagesFIRE 416 Review Summer 2014Kayla Shelton0% (1)
- Selecting Appropriate Construction Contract Accounting MethodDocument11 pagesSelecting Appropriate Construction Contract Accounting MethodKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6Document1 pageExercise 6Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7-13 Essay Questions SummaryDocument23 pagesChapters 7-13 Essay Questions SummaryKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument8 pagesStrategic ManagementKayla Shelton100% (1)
- Definitions For FIRE 312Document2 pagesDefinitions For FIRE 312Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis and CVP Calculations for Multiple CompaniesDocument2 pagesBreak-Even Analysis and CVP Calculations for Multiple CompaniesKayla Shelton0% (1)
- Managers' Bonus CalculationsDocument1 pageManagers' Bonus CalculationsKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Test 4 UpdatedDocument8 pagesCheat Sheet For Test 4 UpdatedKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Variable Definitions For VariancesDocument2 pagesVariable Definitions For VariancesKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Contract LawDocument46 pagesContract LawKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Kinney 8e - IM - CH 07Document21 pagesKinney 8e - IM - CH 07Kayla Shelton0% (1)
- Relevant CostingDocument13 pagesRelevant CostingKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- MGMT 302: Business Statistics II Snead Hall B2113, Fall 2013Document8 pagesMGMT 302: Business Statistics II Snead Hall B2113, Fall 2013Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing (ABC)Document2 pagesActivity Based Costing (ABC)Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Exam Sample AbsorbtionDocument12 pagesExam Sample AbsorbtionMa Joyce Imperial100% (1)
- Variable CostingDocument80 pagesVariable CostingKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Cpa Questions Part XDocument10 pagesCpa Questions Part XAngelo MendezNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing (ABC)Document2 pagesActivity Based Costing (ABC)Kayla SheltonNo ratings yet