Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Format Ready To Print
Uploaded by
may_hisolerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Format Ready To Print
Uploaded by
may_hisolerCopyright:
Available Formats
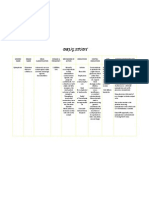
DRUG STUDY
GENERIC NAME BRAND NAME DRUG CLASSIFFICATION DOSAGE & FREQUENCY MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRA INDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Terbutaline Sulfate
Bricanyl Turbuhaler
Produces bronchodilation by relaxing bronchial smooth muscle through beta 2 receptor stimulation
PO 5 mg 3 times daily, at 6 h intervals during waking hours (max, 15 mg/day). Decrease dosage to 2.5 mg 3 times daily if intolerable adverse reactions occur.
Block bronchodilator effect of terbutaline. Patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances (eg, as prophylaxis after MI), there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of betablocking agents in patients with asthma. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
For prevention and reversal of bronchospasm associated with asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema.
Acute and maintenance tocolysis (oral) or prolonged tocolysis (injection); hypersensitivity to sympathomimet ic amines or any component of the product.
Palpitations (23%); tachycardia (4%); ventricular extrasystoles (2%); vasodilations (1%).
Advise patient to take tablets with food to avoid GI upset. Inform patient that the drug can stop working over time. If this is noted, advise the patient to notify their health care provider at once. Instruct patient to report these symptoms to health care provider: chest pain, dizziness or headache, palpitations, persisting symptoms of asthma. Advise patients not to use terbutaline more often than prescribed. If symptoms persist, promptly consult a health care provider.
You might also like
- 5 PR OrientationDocument1 page5 PR Orientationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- 7 PR TerminationDocument1 page7 PR Terminationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- 6 PR WorkingDocument1 page6 PR Workingmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- World PeaceDocument8 pagesWorld Peacemay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format Ready To PrintDocument1 pageDrug Study Format Ready To Printmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- 14ncp3Document2 pages14ncp3may_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format Ready To PrintDocument2 pagesDrug Study Format Ready To Printmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Miyat PresentationDocument73 pagesMiyat Presentationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Anemia Inpatient With Breast CancerDocument2 pagesAnemia Inpatient With Breast Cancermay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan: MedicationDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan: Medicationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Miyat PresentationDocument73 pagesMiyat Presentationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument7 pagesNCP Cvamay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Buerger's DiseaseDocument11 pagesBuerger's Diseasemay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument14 pagesShockmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathophysiology Breast CancerDocument1 pageEtiology and Pathophysiology Breast Cancermay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Pott's DiseaseDocument13 pagesPott's DiseaseLino Jr GordoncilloNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathophysiology Breast CancerDocument1 pageEtiology and Pathophysiology Breast Cancermay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Breast CompositionDocument1 pageBreast Compositionmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathophysiolog1Document2 pagesEtiology and Pathophysiolog1may_hisolerNo ratings yet
- CuesDocument2 pagesCuesmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument2 pagesCranial Nervemay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Card It IsDocument3 pagesCard It Ismay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bronsted QA Set C Bio 1 GuideDocument8 pagesBronsted QA Set C Bio 1 GuideBaguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- Pil 7666Document8 pagesPil 7666Paskalis HarrisNo ratings yet
- Elevation of Cortisol Levels by Ingesting LiquoriceDocument4 pagesElevation of Cortisol Levels by Ingesting LiquoriceasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Oia PDF Complaint FormDocument11 pagesOia PDF Complaint FormSolomon AndrewNo ratings yet
- WGI Benefit GuideDocument32 pagesWGI Benefit GuideSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- MeropenemDocument3 pagesMeropenemJasmin T LarizaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Melanoma of Oral Cavity PDFDocument3 pagesMalignant Melanoma of Oral Cavity PDFahmed shimalNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan ADocument27 pagesDiagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan AJoan Alde PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Shatavari - Benefits, Precautions and DosageDocument13 pagesShatavari - Benefits, Precautions and Dosagenvenkatesh485No ratings yet
- Exemption Request: Rajamuthu Thiruppathirajan Rajamuthu ThiruppathirajanDocument1 pageExemption Request: Rajamuthu Thiruppathirajan Rajamuthu ThiruppathirajanThiruppathirajanNo ratings yet
- Richard McCarty - Stress, Health, and Behavior-The Guilford Press (2023)Document355 pagesRichard McCarty - Stress, Health, and Behavior-The Guilford Press (2023)Mustafa ŞEKERNo ratings yet
- PWKI Art 23954-10Document5 pagesPWKI Art 23954-10Oeij Henri WijayaNo ratings yet
- Liver Trauma: WSES 2020 Guidelines: Review Open AccessDocument15 pagesLiver Trauma: WSES 2020 Guidelines: Review Open AccessMayra HernandezNo ratings yet
- Methods To Study BiopsychologyDocument11 pagesMethods To Study BiopsychologyDisha ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- Studying Rubrics Representing Arsenic Album For Allergic Rhinitis in Kent'S Repertory Through Clinical Cases An Experimental StudyDocument19 pagesStudying Rubrics Representing Arsenic Album For Allergic Rhinitis in Kent'S Repertory Through Clinical Cases An Experimental Studyuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 05 - Summary NotesNlh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Truth About Detox Detox 101 A Step by Step GuideDocument31 pagesThe Truth About Detox Detox 101 A Step by Step GuideBert Pringi100% (1)
- Gender Dysphoria and Social AnxietyDocument9 pagesGender Dysphoria and Social AnxietyJellybabyNo ratings yet
- Development of Medical Services in GeorgiaDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Medical Services in GeorgiaTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Lac Caninum: by David LilleyDocument4 pagesLac Caninum: by David LilleyVladimir Komarov100% (1)
- Health Psychology Chapter 2 SummaryDocument6 pagesHealth Psychology Chapter 2 SummaryZakariaNo ratings yet
- Health Condition and Problems Nursing Problems Supporting Data / Cues D A T E Identified ResolvedDocument2 pagesHealth Condition and Problems Nursing Problems Supporting Data / Cues D A T E Identified ResolvedLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Agglutination Is The Process by Which Particulate Antigens Such As Cells Aggregate To Form Larger Complexes When A Specific Antibody Is PresentDocument2 pagesAgglutination Is The Process by Which Particulate Antigens Such As Cells Aggregate To Form Larger Complexes When A Specific Antibody Is PresentKorina EclarNo ratings yet
- Clauneta MondlaneDocument7 pagesClauneta MondlaneMiguelOriellNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 11Document6 pagesĐỀ 11Hoàng AnNo ratings yet
- Kenya Medical Cities - Model Research Hospitals - 032023 - 1P - PPTDocument195 pagesKenya Medical Cities - Model Research Hospitals - 032023 - 1P - PPTPépo TákátífúNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Rationale: Increasing Paco2 andDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Rationale: Increasing Paco2 andSean Menard FloresNo ratings yet
- Labor Law 1 Case DigestsDocument11 pagesLabor Law 1 Case DigestsDennis Jay Dencio ParasNo ratings yet
- AZ ACOG Antepartum RecordDocument6 pagesAZ ACOG Antepartum RecordAvilla Ane LukitoNo ratings yet
- TRIMBOW® 100/6/10 and 200/6/10: What Is in This Leaflet Before You Use TrimbowDocument6 pagesTRIMBOW® 100/6/10 and 200/6/10: What Is in This Leaflet Before You Use TrimbowShauna DunnNo ratings yet