Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Cholecystitis
NCP For Cholecystitis
Uploaded by
Henry Salvador ParzaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP For Cholecystitis
NCP For Cholecystitis
Uploaded by
Henry Salvador ParzaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Preoperative NCP 1.
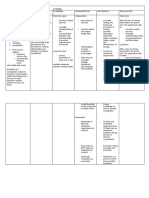
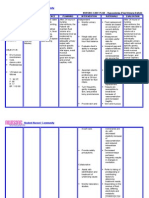
Acute Pain Cues Nursing Diagnosis S Acute pain related to O inflammation -pain scale and of 7/10 distortion of -difficulty the in moving gallbladder as as evidenced manifested by verbal by facial reports of grimaces pain. -(+) pallor -(+) muscle guarding -RR - 30 -BP - 140/90 Scientific Explanations Due to the presence of stones in the gallbladder it causes some obstruction in the cystic duct which in turn causes a sharp acute pain on the right part of the abdomen. Objectives After 4 hours of nursing intervention the patient will report relieve of pain. Nursing Interventions 1.Observe and document location, severity (010 scale),and character of pain (e.g., steady, intermittent, colicky). 2. Promote bedrest, allowing patient to assume position ofcomfort. 3. Control environmental temperature. 4. Encourage use of relaxation techniques, e.g., guidedimagery, visualization, deep-breathing exercises. Providediversional Rationale - Assists in differentiating cause of pain, and providesinformation about disease progression/resolution,development of complications, and effectiveness ofinterventions. - Bedrest in low-Fowlers position reduces intra-abdominalpressure; however, patient will naturally assume leastpainful position. - Cool surroundings aid in minimizing dermal discomfort. - Promotes rest, redirects attention, may enhance coping. - Helpful in alleviating anxiety and refocusing attention,which can relieve pain. - Relief of pain facilitates cooperation with othertherapeutic interventions, Evaluation Is there a change on the patients;a.Pain scaleb.RRc.BPd.Reports of paine.Facial expressions.
activities. 5. Make time to listen to and maintain frequent contact withpatient.6. Administer analgesics as indicated
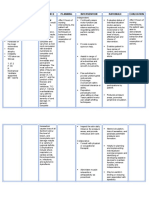
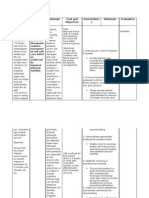
2. Fluid Volume deficient Cues S O -(+) pallor -(+) body weakness -(+) vomiting -with poor skin turgor -(+) dry skin -(+) dry mouth Nursing Diagnosis Fluid Volume Deficient related to vomiting Scientific Explanations Because of vomiting excessive losses through normal routes occur thus causes Fluid Volume Deficient Objectives After series of NI the pt. will maintain adequate fluid volume as evidenced by moist mucous membranes and good skin turgor Nursing Interventions 1. Maintain accurate record of I&O, noting output less thanIntake, increased urine specific gravity. Assessskin/mucous membranes, peripheral pulses, and capillaryrefill. 2. Perform frequent oral hygiene 3. Provide skin and mouth care 4. Increase fluid intake 5. Ascertain patients beverage preferences, and Rationale Evaluation
- Provides information Is there still about fluid the presence status/circulatingvolume of; and replacement needs. a.vomiting - Decreases dryness of oral mucous b.dry skin membranes; reducesrisk of oral bleeding. c.dry mouth - Skin and mucous membranes are dry, with decreasedelasticity, because of vasoconstriction and reducedintracellular water. d.poor skin turgor e.body weakness
set up a 24-hr schedule for fluid intake. Encourage foods with highfluid content.
6. Administer antiemetics, e.g., prochlorperazine(Compazine) as ordered by the physician. - Reduces nausea and prevents vomiting.
- promotes hydration.Relieves thirst and discomfort of dry mucous membranesand augments parenteral replacement.
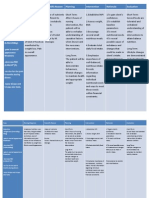
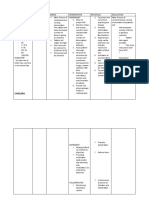
Post-operative NCP 3. Knowledge Deficit Cues S pwede bang maulit ang sakit ko as verbalized by the patient O -Frequently asking question about his condition, treatment and diet -With worried gaze Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanations Deficient There is this knowledge related presence of to knowledge condition,prognosis, deficit due to treatment, selfsome care, and discharge unfamiliar needs information that causes some confusion to the client that needs to be discussed. Objectives Nursing Interventions After an hour of 1. Provide nurse-patient explanations interaction the of/reasons for test patient will procedures Verbalize andpreparation understanding needed. of disease process, 2. Review disease prognosis, and process/prognosis. potential Discuss complications. hospitalizationand prospective treatment as indicated. Encouragequestions, expression of concern. 3. Review drug regimen, possible side effects. 4. Instruct patient to avoid food/fluids high in fats (e.g.,whole milk, ice cream, butter, fried foods, nuts, Rationale - Information can decrease anxiety, thereby reducingsympathetic stimulation. - Provides knowledge base from which patient can makeinformed choices. Effective communication and supportat this time can diminish anxiety and promote healing. - Gallstones often recur, necessitating long-term therapy. - Prevents/limits recurrence of gallbladder attacks. Evaluation -Does the patient understands and could recall all the teachings given? -Is there a significant changes that occur on the patients knowledge regarding; a.disease condition
b.diet - Promotes gas formation, which can increase c.treatment gastricdistension/discomfort. d.medication e.self-care needs
gravies,pork), gas producers (e.g., cabbage, beans, onions,carbonated beverages), or gastric irritants (e.g., spicyfoods, caffeine, citrus). 5. Suggest patient limit gum chewing, sucking on straw/hardcandy, or smoking.
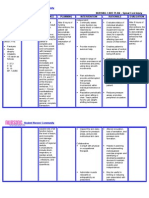
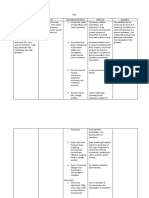
b.Drug Study Name of Drug GN: H2Bloc (Pepcidine)BN: Famotidine Date Ordered Route/ Dosage and Frequency PO20 mg tab at bedtime Action - Anti-ulcercompetitively inhibits action of histamine on the H2 at receptor sites of parietal cells, decreasing gastric acid secretion Indication -for short term treatment of duodenal ulcer Adverse Reaction - headache, dizziness, malaise, dry mouth Nursing Consideration 1. Check for doctors order2. not to be given in patients hypersensitive to drugs3. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug4. Instruct patient to take drug with food5. Advised patient to take drug once
GN: CefuroximeBN: Zinacef
IV750 mg every 8 o prior to OR (30 to 60 minutes before)
- anti-infective- a 2 nd generation cephalosporin that inhibits cell -wall synthesis, promoting osmotic instability
- perioperative prophylaxis
- Nausea and Vomiting
GN: Clomipramine HClBN: Placil
PO10 mg tab, at 6 am
- Anti-depressants
- for depression and chronic pain
- headache, dizziness, malaise, dry mouth
GN: Gentamicin DulfateBN:
IV80 mg amp, every 8
- Anti-infectiveinhibits protein
- endocarditis prophylaxis for GI
- Nausea and Vomiting,
daily usually at bed time6. Advise patient to report abdominal pain or blood in stools or is vomiting 1. Check for doctors order2. Perform ANST prior to admission3. Should not be given if positive skin test4. Slow IV push5. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug6. Advise patient to report any discomfort on the IV insertion site 1. Check for doctors order2. not to be given in patients hypersensitive to drugs3. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug 1. Check for doctors order
Genticin
synthesis
or GU procedure or surgery
headache, dizziness
GN: AmpicillinBN: Omnipen
IV1 g amp, every 8 0
- Anti-infectiveinhibits protein synthesis
- endocarditis prophylaxis for GI or GU procedure or surgery
- Nausea and Vomiting, headache, dizziness
2. Perform ANST prior to admission 3. Should not be given if positive skin test 4. Slow IV push 5. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug 6. Advise patient to report any discomfort on the IV insertion site 7. Monitor urine output, specific gravity, U/A, BUN and creatinine levels 1. Check for doctors order2. Perform ANST prior to admission3. Should not be given if positive skin test4. Slow IV push5. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug6. Advise patient to report any discomfort on
GN: MgSO4
IV0.03% 7ml every 12
-anti-convulsant -replaces magnesium and maintains magnesium level
- magnesium supplementation
- drowsiness, hypotension
GN: Ketorolac TromethamineBN: Toradol
IV30 mg amp, every 6
- Antiinflammatory inhibits prostaglandin synthesis
- short term management of moderately severe, acute pain
- dizziness, sedation, headache, flatulence, nausea and vomiting
the IV insertion site 1. Use parenteral magnesium with extreme caution in patients with impaired renal function2. Test knee jerk and patellar reflexes before each additional dose3. check magnesium level after repeated doses4. Monitor fluid intake and output5. Monitor renal function 1. Check for doctors order 2. Perform ANST prior to admission 3. Should not be given if positive skin test 4. Slow IV push 5. Inform the patient about the possible side effect of the drug 6. Advise patient to report any discomfort on the
IV insertion siteAnesthetic drug
Anesthetic drug Action GN: Lidocaine HCl IV Anesthetic drugs Adverse Reaction -lethargy, hypotension Nursing Consideration 1. Monitor BP, PR, and RR before and after giving the medication2. Monitor patient for toxicity
You might also like
- The Fentanyl Story: Theodore H. StanleyDocument12 pagesThe Fentanyl Story: Theodore H. StanleyRafael GaytanNo ratings yet
- Explain The Importance of Medication Safety Concerning Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesExplain The Importance of Medication Safety Concerning Nursing Practicechinthaka18389021No ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationFaith Bingan Remiscal67% (6)
- Wataru Tsurumi - (Do Not Commit Suicide, Read Description) The Complete Manual of SuicideDocument86 pagesWataru Tsurumi - (Do Not Commit Suicide, Read Description) The Complete Manual of SuicideNico LejeuneNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument6 pagesAcute Pain NCPPesky Pescante-MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Dual Miasms and Nitric Acid As An Intercurrent Remedy in Homeopathy RevDocument12 pagesDual Miasms and Nitric Acid As An Intercurrent Remedy in Homeopathy Revmikembad100% (2)
- NCP - CholelithiasisDocument7 pagesNCP - CholelithiasisJustine Reino Flores100% (3)
- Roles of Different Pharmacy Workforce (Pharmacy Supportive Personnel)Document23 pagesRoles of Different Pharmacy Workforce (Pharmacy Supportive Personnel)Tata Leizel GanzonNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2Document4 pagesNCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2ejoanbNo ratings yet
- NCP CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesNCP CholelithiasisWendy Hingpit RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Acutepain RevisedDocument3 pagesAcutepain RevisedAndrea AutorNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesNCP Gastric CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (4)
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- DMSO - DimethylsulphoxideDocument135 pagesDMSO - DimethylsulphoxideDukof Fokud100% (3)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was SeenDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was Seenkaren kate ablesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNo ratings yet
- NCP DiverticulitisDocument6 pagesNCP DiverticulitisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Cholecystitis NCPDocument5 pagesCholecystitis NCPtsukino143No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- NCP Pancreatic MassDocument4 pagesNCP Pancreatic MassAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR78% (9)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute Cholecystitisnarucute01224100% (3)
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisDocument9 pagesNCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisJavie100% (7)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losanta100% (2)
- Medicinal Chemistry Unit IVDocument57 pagesMedicinal Chemistry Unit IVPankaj Chaurasiya100% (2)
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionRene John Francisco50% (4)
- Cholecystitis NCPDocument4 pagesCholecystitis NCPdark-canales50% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanANGELICA JANE FLORENDONo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceMaze Reyes40% (5)
- NCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityDocument5 pagesNCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- NCP CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesNCP CholelithiasisAllan Macacapagal0% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCP TractionDocument9 pagesNCP TractionAnneSitjar100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- NCP PottsDocument3 pagesNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraNo ratings yet
- NCP MCMC Post OperativeDocument3 pagesNCP MCMC Post OperativeKristiyanong KabataanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocument3 pagesAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument3 pagesAssessmentJemma GandaNo ratings yet
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPcy belNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficient Cues SDocument6 pagesFluid Volume Deficient Cues SjedrickNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument15 pagesAPPENDICITISTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Urinary Tract Infection 2Document23 pagesA Case Study of Urinary Tract Infection 2Jenyl BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of MRS New PageDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan of MRS New PageWAHEED JUBRILNo ratings yet
- Ncma 2Document6 pagesNcma 2Hilario AndreaNo ratings yet
- NCP1Document3 pagesNCP1Alissa MaghopoyNo ratings yet
- "I Don't Have An Infection in My Gallbladder Which Is Good, But I Do Feel The Pain," As Verbalized by TheDocument2 pages"I Don't Have An Infection in My Gallbladder Which Is Good, But I Do Feel The Pain," As Verbalized by Theunnamed person100% (1)
- Price List For Packsize AdditionDocument5 pagesPrice List For Packsize Additionanoushia alviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsDocument20 pagesLecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsJedoNo ratings yet
- Combretum Leprosum Usada para AsmaDocument26 pagesCombretum Leprosum Usada para AsmamarcosmenesesprNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anemia Antiplatelete MalariaDocument5 pagesMCQ Anemia Antiplatelete Malariasherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- Exiben by Kamruzzaman 2018Document13 pagesExiben by Kamruzzaman 2018md. kamruzzamanNo ratings yet
- Medication SafeDocument10 pagesMedication SafedenzkissaieNo ratings yet
- Light Sensitive Drug-02Document6 pagesLight Sensitive Drug-02abutalibNo ratings yet
- PCAL ReviewerDocument10 pagesPCAL ReviewerTOLENTINO Neil Justin M.No ratings yet
- The Quest For Beauty. IeltsDocument5 pagesThe Quest For Beauty. Ieltstunik.yarosav01No ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Drug Use in Australian Society Second Edition All Chapter PDF Docx KindleDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Drug Use in Australian Society Second Edition All Chapter PDF Docx Kindlebobbi.foster487100% (35)
- A Review On Herbal Antidiabetic Drugs EditedDocument31 pagesA Review On Herbal Antidiabetic Drugs EditedVala TejalNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Alopecia Areata TreatmentDocument185 pagesHandbook of Alopecia Areata TreatmentPAULO CELSO BUDRI FREIRENo ratings yet
- 2.review of LiteratureDocument20 pages2.review of LiteratureMjd ObiedNo ratings yet
- Standards of Care in Diabetes - 2023Document12 pagesStandards of Care in Diabetes - 2023Menethil Terenas ElijiahNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics-An Investigatory ProjectDocument20 pagesAntibiotics-An Investigatory ProjectAdiJaijan100% (2)
- Veltri Drug Cards - Quiz 1Document1 pageVeltri Drug Cards - Quiz 1starobinNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Pain Management - Pediatric Pain ManagementDocument12 pagesModule 6 Pain Management - Pediatric Pain Managementfuka priesleyNo ratings yet
- Ebook Campbell Walsh Wein Handbook of Urology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Campbell Walsh Wein Handbook of Urology PDF Full Chapter PDFfrank.daniels751100% (31)
- New Developments in Tuberculosis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument15 pagesNew Developments in Tuberculosis Diagnosis and TreatmentannewidiatmoNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate Syrup InsertDocument6 pagesFerrous Sulfate Syrup InsertPrincess TiongsonNo ratings yet
- AlendronateDocument3 pagesAlendronateAdhaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument48 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet