Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Outside XII 2007
Physics Outside XII 2007
Uploaded by
Satish VermaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Outside XII 2007
Physics Outside XII 2007
Uploaded by
Satish VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
1 P.T.O.
55/1
PHYSICS
-|| i-= i+n|= (= ,|i--=) -|| i-= i+n|= (= ,|i--=) -|| i-= i+n|= (= ,|i--=) -|| i-= i+n|= (= ,|i--=) -|| i-= i+n|= (= ,|i--=)
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
f=ttfa === 3 t= ft=a= = 70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one
question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five
marks. You have to attempt only one of the choice in such questions.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions, carrying one mark each.
(iv) Question numbers 6 to 12 are short answer type questions, carrying two marks each.
(v) Question numbers 13 to 24 are also short answer type questions, carrying three marks
each.
(vi) Questions numbers 25 to 27 are long answer type questions, carrying five marks each.
(vii) Use of calculators is not permitted. However, you may use log tables, if necessary.
(viii) You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary:
Mass of neutron
Boltzmann's constant
Avogadro's number
Roll No.
Series SHC
Code No.
55/1
Please check that this question paper contains 11 printed pages.
Code number given on the right hand side of the question paper should be written on the
title page of the answer-book by the condidate.
Please check that this question paper contains 27 questions.
Please write down the serial number of the question before attempting it.
j+=| =|= = n i= := +.=-+| = =i:- + 11 r +
+.=-+| = :|ir= r|| =| | i:) =) =| =-= =| =|| =-|-+i=-=| = =r|-+ + inr|+
j+=| =|= = n i= := +.=-+| = 27 +.= r+
j+=| +.= =| =-| inr|=| .|= == = +rn, +.= =| ==|= +.= inr|+
=| = . =| = . =| = . =| = . =| = .
|n =.
2 55/1
=t=t-= f=. :t =t=t-= f=. :t =t=t-= f=. :t =t=t-= f=. :t =t=t-= f=. :t
(i) =~tt := f==t= r
(ii) :=-t = === =t, f==- =rt r f= ~tt .t =t =t= == := =, at= =t =t= == :=
= t t =t =t= at=t :=t = ~ttat == f==- ==t r == :=t = t=t f.= ==
== = = === == := rt ==t r
(iii) := ===t 1 11 11 = . .. .. fa =t =-t =t = := r ,== == := == == == == == = =t r
(iv) := ===t t tt tt = 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. =t =-t =t = := r ,== == := .t .t .t .t .t =t =t r
(v) := ===t 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. = .: .: .: .: .: ~tt =t =-t =t = := r ,== == := at= at= at= at= at= =t =t r
(vi) := ===t .. .. .. .. .. = .: .: .: .: .: .tt =-t =t = := r ,== == := t t t t t =t =t r
(vii) ===== = ==t= =t ==fa =rt r attf, t=:== rt at t =t=t=t= =tft=t =t
==t= = ==a r
(viii) rt t=:== rt t f===f=f=ta ~ttfa= f==at=t = =t=t =t ==t= = ==a r
-==|= =| =ri-
=|-===|= i==-|=
|+|=|:| =| =r=|
1. In a series LCR circuit, the voltages across an inductor, a capacitor and a resistor are
30 V, 30 V and 60 V respectively. What is the phase difference between the applied
voltage and the current in the circuit ? 1
i==| ||=, +i+| = +=, =||i| -|| +i-||= = i=| + +|-=-|) ==.| 30 V, 30 V -||
60 V r+ n=|: =: +|-=-| -|| +i+| =| i+=- ||| = =|= i=-=| =n|-- r
2. Ultraviolet radiations of different frequencies and are incident on two photosensitive
materials having work functions and respectively. The kinetic energy
of the emitted electrons is same in both the cases. Which one of the two radiations will
be of higher frequency ? 1
:| +=|.|-==|r| +:|| i=== =|==n= -|| r, + +|===| i+i=| i===|
|+i-|=| ==.| -|| r, |+i-- r+ :|=| +=|| = ==i=- :n+=|=| =| =i-= ==|)
==|= r+ := :|=| = = i== i+i=| =| |+i-| i|= r
3 P.T.O. 55/1
3. Define the term 'activity' of radionuclide. Write its SI unit. 1
i==| i=|)i+=+ -=+n|: =| =i==-| =| +i-|||| inir|)+ :==| SI =||= inir|)+
4. An electron is moving a along +ve x-axis in the presence of uniform magnetic field along
+ve y-axis. What is the direction of the force acting on it ? 1
|=|== y--| = =i:.| )===|= =-==|= -|| =| =+i=|i- = =|: :n+=|= |=|== x--|
= =i:.| =i- = r| r+ := + =|=- =n =| i:.|| +=| r
5. What should be the length of dipole antenna for a carrier wave of frequency ? 1
|+i-| =| +|r= -= = in) i;|+ )-==| =| n-=|: i=-=| r|=| =|ir)
6. Two point charges and are separated by a distance of 1 m in air. Calculate
at what point on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero. 2
-|| = :| i=-: |+.| +|= = )=-:= = 1 m :| + i=|- r+ := :|=| |+.||
=| i=n|= +|n| r|| + == i=-: =| i=|i- +i=in- =|i=) i== + +=- i+-|+ .|-= r+
7. A voltage of 30 V is applied across a carbon resistor with first, second and third rings of
blue, black and yellow colours respectively. Calculate the value of current, in mA,
through the resistor. 2
i==| =|== +i-||=, i===| +rn|, :=| -|| -|=| +n= ==.| =|n, =|n -|| +|n +| =|
r, = i=| + 30 V =| +|-=-| n=|: =|-| r+ +i-||= = ++|ir- r|= +|n| i+=- ||| =|
=|= mA = +i=in- =|i=)+
8. A galvanometer has a resistance of It gives full scale deflection with a current of
2 mA. Calculate the value of the resistance needed to convert it into an ammeter of
range 0-0.3 A. 2
i==| =-+=|=|= =| +i-|| r+ =r 2 mA i+=- ||| = =|| +| +=|=| i+-|+| :-|
r+ := 0-0.3 A +i= = )=|= = +i+i-- == = in) |+.== +i-|| =| =|= +i=in-
=|i=)+
9. Calculate the current drawn by the primary of a transformer which steps down 200 V to
20 V to operate a device of resistance . Assume the efficiency of the transformer to
be 80%. 2
OR
An a.c. voltage of 100 V, 50 Hz is connected across a 20 ohm resistor and mH inductor
in series. Calculate (i) impedance of the circuit, (ii) rms current in the circuit.
4 55/1
== =|==|= =| +||i== =n| ;|| n| =|= +|n| i+=- ||| +i=in- =|i=) i===| =+=|=
200 V =| 20 V -= +=|=| == +i-|| =| i==| =i+ =| +=|in- == = in) i==|
=|-| r+ =|==|= =| :-|-| 80% =|i=)+
|+| |+| |+| |+| |+|
100 V, 50 Hz =| +=|+-| ||| (a.c.) +|-=-| =|, +i-||= -|| 2 mH += = ||==
==|== = i=| = =|| =|-| r+ (i) +i+| =| +i-=|||, (ii) +i+| =| +=-=|=-=n (rms) i+=-
||| +i=in- =|i=)+
10. Define resolving power of a compound microscope. How does the resolving power of a
compound microscope change when
(i) refractive index of the medium between the object and objective lens increases ?
(ii) wavelength of the radiation used is increased ? 2
==+ =-=:.|| =| i+-|:= -|=-| =| +i-|||| inir|)+ i==| ==+ =-=:.|| =| i+-|:= -|=-| =
+=| +i+-= r|-| r ==
(i) +=- -|| i-|:.== n= = =|= = =|== =| ++-=|= i|= r| =|-| r
(ii) =+=|= i=) =|= +|n i+i=|| =| -=:= =: =|-| r
11. Draw a graph showing the variation of potential energy between a pair of nucleons
as a function of their separation. Indicate the regions in which the nuclear force is
(i) attractive, (ii) repulsive. 2
-=i+n|=| = ==n =| i=|i-= ==| = +i+-= =| -=i+n|=| = +|== =| =n= =|== =|=
r||i=)+ :== +r -|| :i=- =|i=) =r| =|i-|=|= =n (i) |=||, (ii) +i-=|| r+
12. Two semiconductor materials X and Y shown in the given figure, are made by doping
germanium crystal with indum and arsenic respectively. The two are joined end to end
and connected to a battery as shown.
(i) Will the junction be forward biased or reverse biased ?
(ii) Sketch a V-I graph for this arrangement. 2
5 P.T.O. 55/1
i=| = :.||) :| |=|n= +:||| X -|| Y =| ==i=== i===n =| ==.| :i== -|| |=i==
= =|| +i=i- == ==|=| ==| r+ i=| = :.||) ==| :-r )= = i= =| := = i= =
=|= i==| ==| = ==|i=- i==| ==| r+
(i) +=| =r =i| =i:i.|= =|=i=- r|=| |+| +.=i:i.|= =|=i=-
(ii) := +=|| = in) V - I =|= r||i=)+
13. State Gauss's theorem in electrostatics. Apply this theorem to derive an expression for
electric field intensity at a point near an infinitely long straight charged wire. 3
i=| i+=i-=| = =|== +== inir|)+ := +== =| =+=|= =-- n-=|: = =|| |+i.|-
-| = i=== i==| i=-: + i+= - --| | =| -|+ -| = in) = == = + == = in)
=|i=)+
14. Explain the underlying principle of working of a parallel plate capacitor.
If two similar plates, each of area A having surface charge densities and are
separated by a distance d in air, write expressions for
(i) the electric field at points between the two plates.
(ii) the potnetial difference between the plates.
(iii) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed. 3
==|-- +i===| =||i| =| =|=i+i| =| |||-|- i=,|-- =+= =|i=)+
=i: :| ==|= +i===|) i=== +== =| -||=n A, +|= |+.| |=+ -|| -|| +|=
= +|== :| d r, -| i=-=inir|- = in) === inir|)
(i) :|=| +i===|| = =|= = i=-:| + i+=---||+
(ii) +i===|| = =|= i+-|+|--+
(iii) := +=| == =||i| =| ||i-|+
6 55/1
15. For the potentiometer circuit shown in the given figure, points X and Y reprensent the
two terminals of an unknown emf E'. A student observed that when the jockey in moved
from the end A to the end B of the potentiometer wire, the deflection in the
galvanometer remains in the same direction.
What may be the two possible faults in the circuit that could result in this
obsevation ?
If the galvanometer deflection at the end B is (i) more, (ii) less, than that at the end
A, which of the two faults, listed above, would be there in the circuit ?
Give reasons in support of your answer in each case. 3
OR
The given figure shows a network of resistances R
1
, R
2
, R
3
and R
4
.
Using Kirchhoff's laws, establish the balance condition for the network.
7 P.T.O. 55/1
:.||) =) +|=i-.|=|=|= +i+| = i=-: X -|| Y i==| n|- i+.+|.=n. (emf) E' = :| =i==n|
=| i==i+- =- r+ =|: i+=||| =r +-|| =-| r i= == =|=| =| +|=i-.|=|=|= -| = i=
A = i= B =| | n =|- r, -| =-+=|=|= = i+-|+| )= r| i:.|| = r-| r+
+i+| = + =|==| :| =-|+ |i==| r| ==-| r i=== +i||==+=+ =r +-|| i=n-| r
=i: =-+=|=|= = i= B + i+-|+| i= A =| -n=| = (i) i|=, (ii) == r, -| =+ :| =: :| |i==|
= = +i+| = =|==| |i= r
+== +=| = += =-| =| +i= =|| := =|i=)+
|+| |+| |+| |+| |+|
i:) =) +i+| = +i-||| R
1
, R
2
, R
3
-|| R
4
=| )= ==+= :.||=| ==| r+
i=r||= = i===| =| =+=|= ==, := ==+= = =-n= = in) .|- =||i+- =|i=)+
8 55/1
16. What is Seebeck effect ? Plot a graph showing the variation of thermo emf with
temperature of hot junction (keeping cold junction at 0C) of a thermocouple. How will
the (i) neutral temperature, (ii) inversion temperature of a thermocouple change when
the temperature of cold junction is increased ? 3
=|== (===) +-||+ +=| r i==| -|++=- == = in) == =i| = -|+ = +i+-= = =||
-|+-i+=--+|r= =n = r|= +|n +i+-= (==i= | =i| =| -|+ 0C r|| ==| r) =| :.||=
= in) =|= r||i=)+ i==| -|++=- == = (i) =:|=|= -|+, (ii) === -|+ = | =i| = -|+
= +i, == =| +=| +-||+ r|-| r
17. Name the following constituent radiations of electromagnetic spectrum which
(i) produce intense heating effect.
(ii) is absorbed by the ozone layer in the atmosphere.
(iii) is used for studying crystal structure.
Write one more application forr each of these radiations. 3
i+=--=-==|= =++== = == i=-=inir|- +=+| i+i=|| = =|= inir|) =|
(i) -|+ ==|= +-||+ =+ =- r+
(ii) +|==n =| |=|= +- ;|| +.||i|- = in) =|- r+
(iii) i===n|= ===| = === = +=+ r|- r+
:== = +== i+i=| =| )= -= =+=|= inir|)+
18. A double convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.6 has its both surfaces of equal radii
of curvature of 30 cm each. An object of height 5 cm is placed at a distance of 12.5 cm
from the lens. Calculate the size of the image formed. 3
.c ++-=|= = =|= = == i==| =-|=|-|n n= = :|=| +| =| +=-| i|=|) ==|= | +==
30 cm =| r+ 5 cm ==|: =| =|: +=- := n= = 12.5 cm :| + r|| =: r+ === +|n +i-i=-=
=| |=|+ +i=in- =|i=)+
19. Draw a schematic diagram of the experimental arrangement used by Davisson and
Germer to establish the wave nature of electrons. Explain briefly how the de-Broglie
relation was experimentally verified in case of electrons. 3
:n+=|=| =| -= +ji- =| =||i+- == = in) i+== -|| == ;|| =+=|= = n|: =:
+|=|i== =+=|| =| =+=|| |r| r||i=)+ :n+=|=| = +=| = :-=|n| ==| =| +|=|i==
==|+= i== +=| i==| ==|, =-|+ = =+= =|i=)+
9 P.T.O. 55/1
20. Draw the graph to show variation of binding energy per nucleon with mass number of
different atomic nuclei. Calculate binding energy/nucleon of nucleus. 3
Given :
mass of
mass of proton = 1.007825 u
mass of neutron = 1.008665 u
and 1 u = 931 MeV/C
2
i+i-| +=|| =|i-|=| =| :==|= =r=| = +i+-= = =|| +i- -=i+n|= =-|= ==|
= r|= +|n +i+-= =| :.||= = in) =|= r||i=)+ =|i-|= =| =-|= ==|-=i+n|=
+i=in- =|i=)+
i:=| ==| r
=| :==|= = 39.962589 u
+|=|= =| :==|= = 1.007825 u
-==|= =| :==|= = 1.008665 u
-|| 1 u = 931 MeV/C
2
21. Draw the circuit diagram of a common emitter amplifier using n-p-n transistor. What is
the phase differnece between the input signal and output voltage ? State two reasons
why a common emitter amplifier is preferred to a common base amplifier. 3
n-p-n =|i=== =| =+=|= == =-|=i= ==== ++|= =| +i+| |r| r||i=)+ i=+.||
i==n -|| i==- +|-=-| = =|= =n|-- +=| r =-|=i= ||| ++|= =| -n=| =
=-|=i= ==== ++|= =| i|= +=-: +=| i==| =|-| r, :| =|| inir|)+
22. Explain the formation of energy band in solids. Draw energy band diagram for (i) a
conductor, (ii) an intrinsic semiconductor. 3
|=| = ==|-= ===| =+= =|i=)+ (i) i==| =|n=, (ii) i==| == |=|n= = in) ==|-=
| r| r|| i=)+
23. What is modulation ? Explain the need of modulating a low frequency information signal.
With the help of diagrams, differentiate between PAM and PDM. 3
=|n= +=| r i==| i=-= |+i-| ===| i==n =| =|in- == =| |+.==-| =+= =|i=)+
i=|| =| =r|=-| =, PAM -|| PDM = -|: =|i=)+
24. Write the acronym LASER in expanded form. State any four reasons for preferring diode
lasers as light sources for optical communication links. 3
+i+|| .|: LASER =| i+=-|i- =+ inir|)+ +=|i.|= ==| =-+=| = in) +=|.| =|-| = =+
= |=| n= =| i|= +=-: i=) =|= = =|: =| =|| inir|)+
10 55/1
25. Explain, with the help of a labelled diagram, the principle and construction of a
cyclotron.
Deduce an expression for the cyclotron frequency and show that it does not depend on
the speed of the charged particle. 5
OR
Distinguish the magnetic properties of dia, para- and ferro-magnetic substances in
terms of (i) susceptibility, (ii) magnetic permeability and (iii) coercivity. Give one
example of each of these materials.
Draw the field lines due to an external magnetic field near a (i) diamagnetic,
(ii) paramagnetic substance.
=|=|i=- |r| =| =r|=-| = =|:+n|=|= =| ===| -|| i=,|-- =+= =|i=)+
=|:+n|=|= |+i-| = in) === =+ =|i=) -|| :.||:) i= =r |+i-| |+i.|- =| =| =|n
+ i=-| =r| =-|+
|+| |+| |+| |+| |+|
(i) ==|ir-|, (ii) =-==|= +|=-=-| -|| (iii) i==|ir-| = +:| = +i--, =- -|| n|r-=-==|=
+:||| = =-==|= =|| = -|: =|i=)+ := +:||| = +== =| )=-)= =:|r| inir|)+
(i) +i-=-==|=, (ii) ==-==|= +:|| = i=== i==| =|n =-==|= -|| = =|| -|| r||)
r|| i=)+
26. Explain the term 'inductive reactance'. Show graphically the variation of inductive
reactance with frequency of the applied alternating voltage.
An a.c. voltage is applied across a pure inductor of inductance L. Show
mathematically that the current flowing through it lags behind the applied voltage by aphase
angle of . 5
OR
Explain the term 'capacitive reactance'. Show graphically the variation of capacitive
reactance with frequency of the applied alternating voltage.
An a.c. voltage is applied across a pure capacitor of capacitance C. Show
mathematically that the current flowing through it leads the applied voltage by a phase angle
of .
+i|= +i-||- =| =+= =|i=)+ =+=+ +=|+-| +|-=-| =| |+i-| = +i+-= = =|| +i|=
+i-||- = +i+-= =| =|= r||== :.||:)+
L +| = i==| |:.| += = i=| + =|: +=|+-| ||| (a.c.) +|-=-| =+=+
=| =|-| r+ =i|-|= =+ = =r :.||:) i= :== ++|ir- r|= +|n| i+=- ||| =+=+ +|-=-|
= =n| =|| ;|| +.= r|-| r+
|+| |+| |+| |+| |+|
||i-| +i-||- =| =+= =|i=)+ =+=+ +=|+-| +|-=-| =| |+i-| = +i+-= = =|| ||i-|
+i-||- = +i+-= =| =|= r||== :.||:)+
C ||i-| = i==| |:.| =||i| = i=| + =|: +=|+-| ||| (a.c.) +|-=-|
=+=+ =| =|-| r+ =i|-|= =+ = =r :.||:) i= :== ++|ir- r|= +|n| i+=- ||| =+=+
+|-=-| = =n| =|| ;|| = r|-| r+
11 P.T.O. 55/1
27. State the essential condition for diffraction of light to take place.
Use Huygen's principle to explain diffraction of light due to a narrow single slit and
the formation of a patern of fringes obtained on the screen. Sketch the pattern of
fringes formed due to diffraction at a single slit showing variation of intensity with
angle . 5
OR
What are coherent sources of light ? Why are coherent sources required to obtain
sustained interference pattern ?
State three characteristic features which distinguish the interference pattern due to two
coherently illuminated sources as compared to that observed in a diffraction pattern
due to a single slit.
+=|.| = i++-= = in) |+.== .|- inir|)+
r|:=-= = i=,|-- =| =+=|= == i==| ==|| )=n i=| = =|| +=|.| =| i++-= -|| +:
+ +|- i==| = +== =| ===| =+= =|i=)+ =|| = =|| -|+-| = +i+-= =| :.||- r)
i==| )=n i=| + i++-= = =|| == i== +== =| r||i=| r||i=)+
|+| |+| |+| |+| |+|
+=|.| = =n|==, =|- +=| r|- r +i-+|in- =i-=| +== +|- == = in) =n|==, =|-|
=| |+.==-| +=| r|-| r
)= -|= i+i.|= n-|| inir|) i=== ;|| :| =n|==, :|- =|-| = =|| +|- =i-=| +==
=| -n=| = )=n i=| = =|| +i-|- i++-= +== = -|: i==| =| ==+
You might also like
- Ajc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2011 PhysicsDocument11 pages2011 PhysicsVelliyotu ValappilNo ratings yet
- Del X Science 31-1-1Document8 pagesDel X Science 31-1-1simimmehaboobNo ratings yet
- 55-2-2 PhysicsDocument16 pages55-2-2 PhysicsK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- 55-2-3 PhysicsDocument16 pages55-2-3 PhysicsK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- Physics (ISS) Set - A 2010Document7 pagesPhysics (ISS) Set - A 2010rahulrana810No ratings yet
- Mathematics Foreign XII 2007Document11 pagesMathematics Foreign XII 2007dannycbsNo ratings yet
- Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) KfurdDocument6 pagesTho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) Kfurd Tho Fokku LS) KfurdRohan RaoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Leader, Achiever & Enthusiast CourseDocument25 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Leader, Achiever & Enthusiast CourseManish MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 - Microwave Network AnalysisDocument21 pages1 - Microwave Network Analysis12user123No ratings yet
- PaperDocument35 pagesPaperRashmi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5.61 Physical Chemistry 24 Pauli Spin MatricesDocument8 pages5.61 Physical Chemistry 24 Pauli Spin MatricesTechnological AssetsNo ratings yet
- Currents in A Single-Phase FWaveDocument8 pagesCurrents in A Single-Phase FWaveAswathy CjNo ratings yet
- A rA r r B A: To find B, and hence the magnetic field H = B/ μ, we take the curl of A. In spherical coordinatesDocument14 pagesA rA r r B A: To find B, and hence the magnetic field H = B/ μ, we take the curl of A. In spherical coordinatesAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current Theory - EDocument12 pagesAlternative Current Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- Ee224 Laboratory 1Document8 pagesEe224 Laboratory 1Jericho RamirezNo ratings yet
- TM2401 FourierDocument58 pagesTM2401 FourierDenise Isebella LeeNo ratings yet
- J 88 12 (Elec Science)Document8 pagesJ 88 12 (Elec Science)akv_303No ratings yet
- Model Question Paper of Science Xii of Bihar State BoardDocument168 pagesModel Question Paper of Science Xii of Bihar State BoardAkshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Paper-Ii Electronic Science: Instructions For The CandidatesDocument8 pagesPaper-Ii Electronic Science: Instructions For The CandidatesKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- skf2133 Chapter5nDocument26 pagesskf2133 Chapter5nsamandondonNo ratings yet
- Yjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesYjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
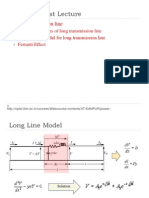
- Review of Last Lecture: Long Transmission LineDocument19 pagesReview of Last Lecture: Long Transmission Linennvpratap100% (1)
- EquationsDocument5 pagesEquationsBernadette Bithao AnonoyNo ratings yet
- Problema LevasDocument5 pagesProblema LevasCarlos A. Iriarte Martinez100% (1)
- EE644 - Discrete Time Systems Spring 2009 Midterm Exam #2 With Solutions Problem 1. Polyphase RepresentationsDocument5 pagesEE644 - Discrete Time Systems Spring 2009 Midterm Exam #2 With Solutions Problem 1. Polyphase RepresentationsDecker JamesNo ratings yet
- Bee332 HW8S 2011Document2 pagesBee332 HW8S 2011hooj08No ratings yet
- Fast Transients Analysis of Non-Uniform Multiconductor Transmission Lines Excited by Incident FieldDocument6 pagesFast Transients Analysis of Non-Uniform Multiconductor Transmission Lines Excited by Incident FieldItalo ChiarellaNo ratings yet
- An Optimal Balancing Structure For Small and Medium Electrical Machine RotorsDocument9 pagesAn Optimal Balancing Structure For Small and Medium Electrical Machine Rotorsikram09568519No ratings yet
- EM Fields ReferenceDocument1 pageEM Fields Referencefaeros9998575No ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document7 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
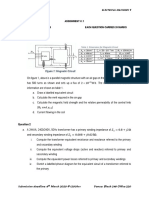
- EEB 344 - 2020 - Assignment 1Document1 pageEEB 344 - 2020 - Assignment 1Tiro RamatlakadibeNo ratings yet
- Ecse 353 Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Formulas: V) V + V V V V 0Document6 pagesEcse 353 Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Formulas: V) V + V V V V 0Eileen FuNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document9 pagesProblem Set 3Biren PatelNo ratings yet
- Voltages Balancing in Neutral-Point-Clamped Active Rectifiers Based On Current Harmonic DistortionDocument9 pagesVoltages Balancing in Neutral-Point-Clamped Active Rectifiers Based On Current Harmonic DistortionMohamed BerririNo ratings yet
- Network TheoremsDocument6 pagesNetwork TheoremssvijiNo ratings yet
- Solutions: S - 1 Electrical Circuits (November/December-2012, R09) JNTU-HyderabadDocument19 pagesSolutions: S - 1 Electrical Circuits (November/December-2012, R09) JNTU-HyderabadnbprNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Ac CircuitDocument26 pagesEe602 Ac CircuitArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- EEE222 ECA-2 Lab 6, FA20-BEE-3C-146Document8 pagesEEE222 ECA-2 Lab 6, FA20-BEE-3C-146Souban JavedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument28 pagesUnit 3: Electromechanical Energy ConversionskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Ec Lab: Course Name: Electrical Circuit Lab Course Code: CSE 133Document4 pagesEc Lab: Course Name: Electrical Circuit Lab Course Code: CSE 133Tarif Al MozahedNo ratings yet
- BG31005 Tutorial PartI SolutionDocument27 pagesBG31005 Tutorial PartI Solutionasvini001No ratings yet
- Physics Paper IIIDocument3 pagesPhysics Paper IIItadepalli patanjaliNo ratings yet
- Mid Term2 Marking Guide - Physics - Level 3Document5 pagesMid Term2 Marking Guide - Physics - Level 3jolieprincesseishimweNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled Networks: Learning GoalsDocument26 pagesMagnetically Coupled Networks: Learning GoalsTegar Ari Satria KurniawanNo ratings yet
- JNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFDocument32 pagesJNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFkarthiha12No ratings yet
- Trocio, Joshua ECE 412 Exp1Document6 pagesTrocio, Joshua ECE 412 Exp1Joshua TrocioNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation TablesDocument6 pagesPhysics Equation TablesSangram NalawadeNo ratings yet
- TransmissionLine Model and Performance ReDocument10 pagesTransmissionLine Model and Performance ReMushtaq Najeeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Be First Year Engineering Semester 1 2017 May Basic Electrical Engineering CbcgsDocument24 pagesBe First Year Engineering Semester 1 2017 May Basic Electrical Engineering CbcgsAzhagae ManiNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementFrom EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNo ratings yet