Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap012 The Demand For Resources
Uploaded by
alaina_alfaroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap012 The Demand For Resources
Uploaded by
alaina_alfaroCopyright:
Available Formats
12
The Demand for Resources
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Resource Pricing
Firms demand resources Focus on labor Resource prices are important Money-income determination Cost minimization Resource allocation Policy issues
LO1
12-2
Resource Demand
All markets are competitive
(good and resource)
Derived demand depends on: Productivity of resource (MP) Price of the good it helps produce (P) Marginal revenue product (MRP) Change in TR resulting from unit
change in resource (labor)
LO1
12-3
Resource Demand
Rule for employing resources: MRP = MRC
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
Marginal Revenue Product
Change in Total Revenue Unit Change in Resource Quantity
Marginal Resource Cost (MRC)
Marginal Resource Cost
Change in Total (Resource) Cost Unit Change in Resource Quantity
12-4
LO1
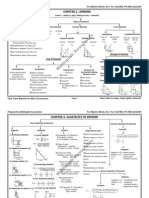
MRP as Resource Demand
(1) (2) Units of Total Product Resource (Output) (3) Marginal Product (MP) (4) Product Price (5) Total Revenue, (2) X (4) (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0] 7] 13 ] 18 ] 22 ] 25 ] 27 ] 28
$18 16
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
$2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
$0 14 26 36 44 50 54 56
] ] ] ] ] ] ]
$14 12 10 8 6 4 2
Purely Competitive Firms Demand for A Resource
LO1
Resource Wage (Wage Rate)
14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
D=MRP
Quantity of Resource Demanded
12-5
MRP as Resource Demand
(1) (2) Units of Total Product Resource (Output) (3) Marginal Product (MP) (4) Product Price (5) Total Revenue, (2) X (4) (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0] 7] 13 ] 18 ] 22 ] 25 ] 27 ] 28
$18 16
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
$2.80 2.60 2.40 2.20 2.00 1.87 1.75 1.65
$ 0.00 18.20 31.20 39.60 44.00 46.25 47.25 46.20
] ] ] ] ] ] ]
$18.20 13.00 8.40 4.40 2.25 1.00 -1.05
Imperfectly Competitive Firms Demand for A Resource
LO1
Resource Wage (Wage Rate)
14 12
D=MRP (Pure Competition)
10
8 6 4 2 0
D=MRP (Imperfect Competition)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
-2
Quantity of Resource Demanded
12-6
Determinants of Resource Demand
Changes in product demand Changes in productivity Quantities of other resources Technological advance Quality of the variable resource
LO2
12-7
Determinants of Resource Demand
Changes in the price of substitute
resources Substitution effect Output effect Net effect Changes in the price of complementary resources
LO2
12-8
Occupational Employment Trends
Rising employment Services Health care Computers Declining employment Labor saving technological change Textiles
LO2
12-9
Elasticity of Resource Demand
Erd =
Percentage Change in Resource Quantity Percentage Change in Resource Price
Ease of resource substitutability Elasticity of product demand Ratio of resource cost to total cost
LO2
12-10
Optimal Combination of Resources
All resource inputs are variable Choose the optimal combination Minimize cost of producing a given
output
Maximize profit
LO3
12-11
The Least Cost Rule
Minimize cost of producing a given
output Last dollar spent on each resource yields the same marginal product
Marginal Product Of Labor (MPL) Marginal Product Of Capital (MPC) Price of Capital (PC)
Price of Labor (PL)
LO3
12-12
Profit Maximizing Rule
MRP of each resource equals its
price
PL = MRPL and PC = MRPC
MRPL PL MRPC PC
=1
LO3
12-13
Income Distribution
Paid according to value of service Workers Resource owners Inequality Productive resources unequally
LO3
distributed Market imperfections
12-14
Income Distribution
Numerical Illustration Data for finding the least-cost and
profit-maximizing combination of labor and capital
12-15
You might also like
- Demand Driven Material Requirements Planning (DDMRP): Version 3From EverandDemand Driven Material Requirements Planning (DDMRP): Version 3Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Managerial Economics (Chapter 6)Document39 pagesManagerial Economics (Chapter 6)api-370372490% (10)
- The Demand For Resources and Wage DeterminationDocument24 pagesThe Demand For Resources and Wage Determinationivyling29No ratings yet
- Factor Market and Production MarketDocument43 pagesFactor Market and Production MarketMmapontsho Tshabalala100% (1)
- ECON 201 Macroeconomics: The Demand For ResourcesDocument59 pagesECON 201 Macroeconomics: The Demand For ResourcesKylie smithNo ratings yet
- 2P The Demand For ResourcesDocument32 pages2P The Demand For ResourcesBett WesleyNo ratings yet
- Economics: Factor Markets and The Production FunctionDocument43 pagesEconomics: Factor Markets and The Production FunctionbaskarumaNo ratings yet
- FridayDocument10 pagesFridayapi-341056627No ratings yet
- The Theory of Factor PricingDocument12 pagesThe Theory of Factor Pricinglali6275% (4)
- Lecture # 14 Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument13 pagesLecture # 14 Principles of MicroeconomicsumarNo ratings yet
- (Lesson Part-II) - Chapter 5. Producer Behavior TheoryDocument55 pages(Lesson Part-II) - Chapter 5. Producer Behavior TheoryШохрух МаджидовNo ratings yet
- Macro-notesDocument28 pagesMacro-notesrauskalina2No ratings yet
- Chap 010Document16 pagesChap 010Wendors WendorsNo ratings yet
- The Demand of Labor: Presented By: Hina Shahzadi Session 2020-2023 Government College University FaisalabadDocument27 pagesThe Demand of Labor: Presented By: Hina Shahzadi Session 2020-2023 Government College University FaisalabadGreat Wall Of FactsNo ratings yet
- Macro NotesDocument43 pagesMacro Notes266818No ratings yet
- 1.7 Resource Markets APDocument22 pages1.7 Resource Markets APJellane SeñoraNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Resource Demand Changes in Product DemandDocument4 pagesDeterminants of Resource Demand Changes in Product DemandAreej Choudhry 5348-FMS/BBA/F18No ratings yet
- Production Cost Analysis in 40 CharactersDocument37 pagesProduction Cost Analysis in 40 CharactersSurya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 & 12 Cost Analysis & Factors of Production: Dr. Qais AslamDocument32 pagesLecture 11 & 12 Cost Analysis & Factors of Production: Dr. Qais Aslamtitan abcdNo ratings yet
- Principle of Factor Substitution - Principle of Product SubstitutionDocument19 pagesPrinciple of Factor Substitution - Principle of Product SubstitutionKIRUTHIKANo ratings yet
- Introduction and Micro ReviewDocument20 pagesIntroduction and Micro ReviewBrett FerchNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Resource DemandDocument3 pagesDeterminants of Resource DemandSherazButtNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor ProduksiDocument29 pagesFaktor-Faktor ProduksiFauzi FarchanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Factor Pricing TheoryDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Factor Pricing TheoryRohitPatialNo ratings yet
- Short Run and Long Run Demand For LaborDocument18 pagesShort Run and Long Run Demand For LaborJohnTangog100% (2)
- MicroeconomicsDocument10 pagesMicroeconomicsVishal Gattani100% (5)
- Learning Objectives: Cost: The Price of Value CreationDocument17 pagesLearning Objectives: Cost: The Price of Value Creationbarca411No ratings yet
- Microeconomics Assignment 3Document8 pagesMicroeconomics Assignment 3Momina HaroonNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics of Product Markets and Consumer BehaviorDocument18 pagesMicroeconomics of Product Markets and Consumer BehaviorWendors WendorsNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Ninth Canadian EditionDocument57 pagesMacroeconomics: Ninth Canadian EditionUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 5 NotesDeeana SioufiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Production Functions and CostDocument55 pagesChapter 2 Production Functions and CostLemi GonfaNo ratings yet
- Production and Cost TheoryDocument79 pagesProduction and Cost TheoryMaria DatingalingNo ratings yet
- Performance - Aesthetics - Special Features - Conformance - Reliability - Durability - Perceived Quality - Serviceability - ConsistencyDocument73 pagesPerformance - Aesthetics - Special Features - Conformance - Reliability - Durability - Perceived Quality - Serviceability - ConsistencyAnkit MathurNo ratings yet
- Target Costing, Relevant Costs For Decision Making, Transfer Pricing and Balanced Scorecard PDFDocument103 pagesTarget Costing, Relevant Costs For Decision Making, Transfer Pricing and Balanced Scorecard PDFArnab SahaNo ratings yet
- AP Micro 5-3 Perfectly Competative LaborDocument20 pagesAP Micro 5-3 Perfectly Competative Laborkjs1031No ratings yet
- Aerospace Lean Manufacturing Metrics GuideDocument2 pagesAerospace Lean Manufacturing Metrics GuideMani Rathinam RajamaniNo ratings yet
- BEC Demo CompanionDocument23 pagesBEC Demo Companionalik711698100% (1)
- Production and Cost FunctionDocument42 pagesProduction and Cost FunctionHealthEconomics_USaNNo ratings yet
- AP Micro 5-5 Unit SummaryDocument66 pagesAP Micro 5-5 Unit SummaryKim TividadNo ratings yet
- Alternatives to Replace Coal Power Plant CapacityDocument38 pagesAlternatives to Replace Coal Power Plant Capacitylennahfe19No ratings yet
- Production FunctionDocument81 pagesProduction Functionsurbhi guptaNo ratings yet
- Production FunctionDocument81 pagesProduction FunctionRashmeet AroraNo ratings yet
- Markets Factors ProductionDocument44 pagesMarkets Factors ProductionSunita PatilNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 ProductivityDocument15 pagesBab 3 ProductivityDymm ErieyNo ratings yet
- Material Requirements Planning in A Demand-Driven World 2Document52 pagesMaterial Requirements Planning in A Demand-Driven World 2Him Kung100% (2)
- The Theory of Income DistributionDocument5 pagesThe Theory of Income DistributionVarin Edwards100% (1)
- Bahan Matrikulasi MMDocument28 pagesBahan Matrikulasi MMAhmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives: The Organization of ProductionDocument6 pagesLecture Objectives: The Organization of Productiondayah3490No ratings yet
- Production Analysis (SR)Document13 pagesProduction Analysis (SR)entertainmentcubeNo ratings yet
- ACC212 Final Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesACC212 Final Exam ReviewVictoria PecicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document10 pagesChapter 5nourhankawiiNo ratings yet
- Production Cost Short-RunDocument42 pagesProduction Cost Short-RunRichi KothariNo ratings yet
- Costs and Production AnalysisDocument31 pagesCosts and Production AnalysisRajan NandolaNo ratings yet
- Cost and BenefitsDocument19 pagesCost and BenefitsraghurmiNo ratings yet
- Indutrial Engineering Unit I - ProductivityDocument42 pagesIndutrial Engineering Unit I - Productivityankitdoshi93No ratings yet
- IIIa-DEMAND FOR LABOR-1Document8 pagesIIIa-DEMAND FOR LABOR-1elsamarselaputri25No ratings yet
- Materials Handling Equipment Wholesale Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandMaterials Handling Equipment Wholesale Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet