Chapter 7: Microprogrammed Control
Dr. Loai
Tawalbeh
cpe 252: Computer Organization
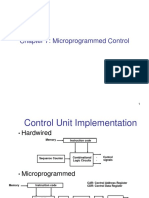
�Control Unit Implementation
Hardwired
Memory Instruction code
Sequence Counter
Combinational Logic Circuits
. .
Control signals
Microprogrammed
Memory Instruction code CAR: Control Address Register CDR: Control Data Register
Next Address Generator (sequencer)
CA R
Control Memory
CDR
Decoding Circuit
. .
Control signals
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Microprogrammed Control Unit
Control signals
Group of bits used to select paths in multiplexers, decoders, arithmetic logic units
Control variables
Binary variables specify microoperations
Certain microoperations initiated while others idle
Control word
String of 1s and 0s represent control variables
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Microprogrammed Control Unit
Control memory
Memory contains control words
Microinstructions
Control words stored in control memory Specify control signals for execution of microoperations
Microprogram
Sequence of microinstructions
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Control Memory
Read-only memory (ROM) Content of word in ROM at given address specifies microinstruction Each computer instruction initiates series of microinstructions (microprogram) in control memory These microinstructions generate microoperations to
Fetch instruction from main memory Evaluate effective address Execute operation specified by instruction Return control to fetch phase for next instruction
Address
Control memory (ROM)
cpe 252: Computer Organization
Control word (microinstruction)
5
�Microprogrammed Control Organization
External input Next Address Generator (sequencer) CA R Control Memory (ROM) CDR Control word
Control memory
Contains microprograms (set of microinstructions) Microinstruction contains
Bits initiate microoperations Bits determine address of next microinstruction
Control address register (CAR)
Specifies address of next microinstruction
cpe 252: Computer Organization 6
�Microprogrammed Control Organization
Next address generator (microprogram sequencer)
Determines address sequence for control memory
Microprogram sequencer functions
Increment CAR by one Transfer external address into CAR Load initial address into CAR to start control operations
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Microprogrammed Control Organization
Control data register (CDR)- or pipeline register
Holds microinstruction read from control memory Allows execution of microoperations specified by control word simultaneously with generation of next microinstruction
Control unit can operate without CDR
External input Next Address Generator (sequencer) Control Memory (ROM)
CA R
Control word
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Microprogram Routines
Routine
Group of microinstructions stored in control memory
Each computer instruction has its own microprogram routine to generate microoperations that execute the instruction
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Microprogram Routines
Subroutine
Sequence of microinstructions used by other routines to accomplish particular task
Example
Subroutine to generate effective address of operand for memory reference instruction
Subroutine register (SBR)
Stores return address during subroutine call
cpe 252: Computer Organization
10
�Conditional Branching
Branching from one routine to another depends on status bit conditions Status bits provide parameter info such as
Carry-out of adder Sign bit of number Mode bits of instruction
Info in status bits can be tested and actions initiated based on their conditions: 1 or 0 Unconditional branch
Fix value of status bit to 1
cpe 252: Computer Organization 11
�Mapping of Instruction
Each computer instruction has its own microprogram routine stored in a given location of the control memory Mapping
Transformation from instruction code bits to address in control memory where routine is located
cpe 252: Computer Organization
12
�Mapping of Instruction
Example
Mapping 4-bit operation code to 7-bit address
OP-codes of Instructions ADD 0000 AND 0001 LDA 0010 Mapping bits
0 xxxx 00
Control memory
Address 0 0000 00 0 0001 00 0 0010 00 ADD Routine
AND Routine
LDA Routine 13
cpe 252: Computer Organization
�Address Sequencing
Address sequencing capabilities required in control unit
Incrementing CAR Unconditional or conditional branch, depending on status bit conditions Mapping from bits of instruction to address for control memory Facility for subroutine call and return
cpe 252: Computer Organization 14
�Address Sequencing
Instruction code Mapping
logic
Status bits
Branch logic
MUX select
Multiplexers Subroutine Register (SBR) Incrementer
Control Address Register
(CAR)
Control memory (ROM) select a status bit Branch address Microoperations
cpe 252: Computer Organization
15
�Microprogram Example
MUX
Computer Configuration
10 AR
0 Address Memory 2048 x 16
10 PC
MUX 6 SBR 0 6 CAR 0 15 DR 0
Control memory 128 x 20 Control unit cpe 252: Computer Organization
Arithmetic logic and shift unit 15 AC 0 16
�Microprogram Example
Computer instruction format
15 14 11 10 Opcode I 0
Address
Four computer instructions
Symbol ADD BRANCH STORE EXCHANGE OP-code 0000 0001 0010 0011 Description AC AC + M[EA] if (AC < 0) then (PC EA) M[EA] AC AC M[EA], M[EA] AC EA is the effective address
Microinstruction Format
3 F1 3 F2 3 F3 2 CD 2 BR 7 AD
F1, F2, F3: Microoperation fields CD: Condition for branching BR: Branch field AD: Address field
cpe 252: Computer Organization
17
�Microinstruction Fields
F1 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 Microoperation None AC AC + DR AC 0 AC AC + 1 AC DR AR DR(0-10) AR PC M[AR] DR Symbol NOP ADD CLRAC INCAC DRTAC DRTAR PCTAR WRITE F2 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 Microoperation None AC AC - DR AC AC DR AC AC DR DR M[AR] DR AC DR DR + 1 DR(0-10) PC Symbol NOP SUB OR AND READ ACTDR INCDR PCTDR
F3 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111
Microoperation None AC AC DR AC AC AC shl AC AC shr AC PC PC + 1 PC AR Reserved
Symbol NOP XOR COM SHL SHR INCPC ARTPC
cpe 252: Computer Organization
18
�Microinstruction Fields
CD 00 01 10 11 Condition Always = 1 DR(15) AC(15) AC = 0 Symbol U I S Z Comments Unconditional branch Indirect address bit Sign bit of AC Zero value in AC
BR 00 01 10 11
Symbol JMP CALL RET MAP
Function CAR AD if condition = 1 CAR CAR + 1 if condition = 0 CAR AD, SBR CAR + 1 if condition = 1 CAR CAR + 1 if condition = 0 CAR SBR (Return from subroutine) CAR(2-5) DR(11-14), CAR(0,1,6) 0
cpe 252: Computer Organization
19
�Symbolic Microinstruction
Sample Format
Label:
Micro-ops
CD
BR
AD
Label
may be empty or may specify symbolic address terminated with colon
Micro-ops consists of 1, 2, or 3 symbols separated by commas CD one of {U, I, S, Z} U: Unconditional Branch I: Indirect address bit S: Sign of AC Z: Zero value in AC one of {JMP, CALL, RET, MAP} one of {Symbolic address, NEXT, empty}
cpe 252: Computer Organization 20
BR AD
�Fetch Routine
Fetch routine
- Read instruction from memory - Decode instruction and update PC
Microinstructions for fetch routine:
AR PC DR M[AR], PC PC + 1 AR DR(0-10), CAR(2-5) DR(11-14), CAR(0,1,6) 0
Symbolic microprogram for fetch routine:
FETCH:
ORG 64 PCTAR READ, INCPC DRTAR U JMP NEXT U JMP NEXT U MAP
Binary microporgram for fetch routine:
Binary address 1000000 1000001 1000010 F1 110 000 101 F2 000 100 000 F3 000 101 000 CD 00 00 00 BR 00 00 11 AD 1000001 1000010 0000000
cpe 252: Computer Organization
21
�Symbolic Microprogram
Control memory: First 64 words: Last 64 words: Mapping: 128 20-bit words Routines for 16 machine instructions Used for other purpose (e.g., fetch routine and other subroutines) OP-code XXXX into 0XXXX00, first address for 16 routines are 0(0 0000 00), 4(0 0001 00), 8, 12, 16, 20, ..., 60
Partial Symbolic Microprogram
Label
ADD:
Microops
ORG 0 NOP READ ADD ORG 4 NOP NOP NOP ARTPC ORG 8 NOP ACTDR WRITE ORG 12 NOP READ ACTDR, DRTAC WRITE ORG 64 PCTAR READ, INCPC DRTAR READ DRTAR cpe
CD
I U U S U I U I U U I U U U
BR
CALL JMP JMP JMP JMP CALL JMP CALL JMP JMP CALL JMP JMP JMP
AD
INDRCT NEXT FETCH OVER FETCH INDRCT FETCH INDRCT NEXT FETCH INDRCT NEXT NEXT FETCH
BRANCH: OVER:
STORE:
EXCHANGE:
FETCH: INDRCT:
252:
U JMP NEXT U JMP NEXT U MAP U JMP NEXT Computer Organization U RET
22
�Binary Microprogram
Micro Routine ADD Address Decimal Binary 0 0000000 1 0000001 2 0000010 3 0000011 4 0000100 5 0000101 6 0000110 7 0000111 8 0001000 9 0001001 10 0001010 11 0001011 12 0001100 13 0001101 14 0001110 15 0001111 64 65 66 67 68 1000000 1000001 1000010 1000011 1000100 F1 000 000 001 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 111 000 000 001 100 111 110 000 101 000 101 Binary Microinstruction F2 F3 CD 000 000 01 100 000 00 000 000 00 000 000 00 000 000 10 000 000 00 000 000 01 000 110 00 000 000 01 101 000 00 000 000 00 000 000 00 000 000 01 000 000 00 101 000 00 000 000 00 000 100 000 100 000 000 101 000 000 000 00 00 00 00 00 BR 01 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 01 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 11 00 10 AD 1000011 0000010 1000000 1000000 0000110 1000000 1000011 1000000 1000011 0001010 1000000 1000000 1000011 0001110 0001111 1000000 1000001 1000010 0000000 1000100 0000000
BRANCH
STORE
EXCHANGE
FETCH
INDRCT
cpe 252: Computer Organization
23
�Design of Control Unit
microoperation fields
F1 F2 F3
3 x 8 decoder 7 6 54 3 21 0 3 x 8 decoder 7 6 54 3 21 0 3 x 8 decoder 76 54 3 21 0
AND ADD
DRTAC
PCTAR DRTAR From From PC DR(0-10) 0 1 Multiplexers
Arithmetic logic and shift unit
AC DR
Load
AC
Select
Load
AR
Clock
cpe 252: Computer Organization
24
�Microprogram Sequencer
External (MAP) L
I Input I 0 logic 1 T
3 2 1 0 S1 MUX1 S0
SBR
Load
1 I S Z
Incrementer MUX2 Select Test Clock CAR
Control memory Microops CD BR AD
...
...
cpe 252: Computer Organization
25
�Input Logic for Microprogram Sequencer
From I CPU S
1 MUX2 Select Z Test
L BR field of CS
T Input I0 logic I
1
L(load SBR with PC) for subroutine Call S0 for next address S1 selection
CD Field of CS
Input Logic
I1I0T 000 001 010 011 10x 11x Meaning Source of Address In-Line JMP In-Line CALL RET MAP CAR+1 CS(AD) CAR+1 CS(AD) and SBR <- CAR+1 SBR DR(11-14) S1S0 00 01 00 01 10 11 L 0 0 0 1 0 0
S1 = I1 S0 = I0I1 + I1T L = I1I0T
cpe 252: Computer Organization 26