Professional Documents
Culture Documents
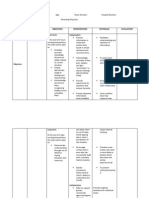
Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent
Uploaded by
Christy BerryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent
Uploaded by
Christy BerryCopyright:
Available Formats
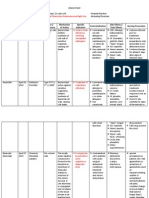
Name of Patient: Diagnosis/Impression: NURSING CARE PLAN CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia
Age:
Room Number: Attending Physician:
Hospital Number:
OBJECTIVES Short term
INTERVENTIONS Independent Identify underlying cause (e.g excessive heat production such as hyperthyroid state, malignant hyperperexia, dehydration, infection, pelvic laparotomy surgery.) Monitor core temperature.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective
After 4 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: To determine ways how to increase heat loss Identify underlying cause/contribu ting factors and importance of treatment, as well as signs and symptoms requiring further evaluation and intervention. Demonstrate behaviours to
To assess causative and contributing factors.
Objective
To evaluate effects and degree of hyperthermia. Evaporation is decreased by environmental fdactors of high humidity and high ambient temperature as
Note presence and absence of sweating as body attempts to increase heat loss by evaporation,
monitor or promote normothermia or or temperature within normal range. Long term After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: Maintain core temperature within normal range Be free of complications such as irreversible brain/ neurologic damage and acute renal failure. Be free of seizure activity.
conduction, and diffusion.
well as body factors producing loss of ability to sweat or sweat gland dysfunction (e.g dehydration, vasoconstriction) To assist with measures or reduce body temperature and restore normal body and organ function.
Promote surface cooling by means of undressing (heat loss by radiation and conduction);cool environment and or fans (heat loss by convection); cool tepid sponge bath or immersion (heat loss by evaporation and conduction); local ice packs, especially in groinand axillae (areas og high blood flow); and or use of hypothermia blanket. Wrap extremities with bath towel
To minimize shivering.
when hypothermia blanket is used.
Maintain bed rest
To reduce metabolic demands/oxygen consumption. To prevent dehydration.
Discuss importance of adequate fluid intake.
Dependent: Administer replacement fluids and electrolytes. Administer medications (e.g diazepam and chlorpromazine) as ordered Administer antipyretics (e.g paractemol)
To support circulating volume and tissue perfusion. To control shivering and seizures
To assist with measures or reduce body temperature and restore normal body and organ function
You might also like
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasNo ratings yet
- Environmental Emergencies ParamedicDocument90 pagesEnvironmental Emergencies ParamedicPaulhotvw67100% (2)
- Environmental Emergencies Heat Exhaustion HeatstrokeDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Emergencies Heat Exhaustion HeatstrokepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument17 pagesPneumoniajustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPclaidelynNo ratings yet
- Environmental EmergenciesDocument38 pagesEnvironmental EmergenciesIshaBrijeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument5 pagesHyperthermia NCPJayson John Domingo89% (9)
- Eighteen: Environmental EmergenciesDocument66 pagesEighteen: Environmental EmergenciesLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pneumonia PatientsDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pneumonia Patientsha,hr12480% (5)
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument37 pagesPeritoneal Dialysisger668No ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument7 pagesNursing DiagnosisMariya Mikaela Garcia SoledadNo ratings yet
- NCP PleuralDocument5 pagesNCP Pleuraljanine_valdezNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesHyperthermiaSäbïná D. GabätöNo ratings yet
- NCP TahbsoDocument18 pagesNCP TahbsoKe EjieNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- PRINCIPLES OF ENVIRONMENTAL DISEASESDocument27 pagesPRINCIPLES OF ENVIRONMENTAL DISEASESSHIHAB UDDIN KAZINo ratings yet
- MJDocument1 pageMJ031492mjNo ratings yet
- Vtal Signs LectureDocument89 pagesVtal Signs LectureHazel Romerosa AmatosNo ratings yet
- Heat StrokeDocument22 pagesHeat StrokeCrizza Maglasang100% (1)
- Simulation Lab 20 Instructions With AnswersDocument5 pagesSimulation Lab 20 Instructions With AnswersChristine Mccombs100% (3)
- NCP Cardio PrintDocument7 pagesNCP Cardio PrintNicole MapiliNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument4 pagesVital SignsPauline israelNo ratings yet
- General MedicineDocument23 pagesGeneral MedicineRefad MahimNo ratings yet
- HYPERTHERMIADocument5 pagesHYPERTHERMIAJerwelyn JoyNo ratings yet
- How to treat hypothermiaDocument6 pagesHow to treat hypothermiaRonald Silva CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Risk For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument9 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Risk For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDoj Deej Mendoza GambleNo ratings yet
- C C C CC CC: Yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy YDocument5 pagesC C C CC CC: Yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy YMitch Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Case StudyDocument28 pagesHyperthermia Case StudyJanelle GimenezNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument74 pagesVital SignsSofyan Hadi Saputra100% (1)
- Hypothermia GuideDocument9 pagesHypothermia GuideLani Afriani PohanNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceJill Catherine CabanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Inference Nursing Diagnosis Goal/Plan Intervention/Plan Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument1 pageAssessment Inference Nursing Diagnosis Goal/Plan Intervention/Plan Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataAR JINo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument90 pagesVital SignsAngelina CoffieNo ratings yet
- Tepid SpongingDocument3 pagesTepid SpongingNrs Sani Sule MashiNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument85 pagesVital SignsSara SabraNo ratings yet
- Erickson's stages of development and elderly careDocument44 pagesErickson's stages of development and elderly careJazzmyne T.No ratings yet
- Hy Per Ther Mi A: Learn To PronounceDocument2 pagesHy Per Ther Mi A: Learn To PronounceReia DagohoyNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument9 pagesNCP PTBecbarticanNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Fluid Balance: Assessing Intake and OutputDocument8 pagesMaintaining Fluid Balance: Assessing Intake and OutputNurul HendrianiNo ratings yet
- NCP LatestDocument6 pagesNCP LatestThirdy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs1Document65 pagesVital Signs1Rosemary DelaliNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Maintain Vital Signs - Part 01Document94 pagesMaintain Vital Signs - Part 01Disala RanaweeraNo ratings yet
- Nur 111 Session 21 Sas 1Document8 pagesNur 111 Session 21 Sas 1Zzimply Tri Sha UmaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nursing Practice: M.Sc. Degree Course in NursingDocument58 pagesAdvanced Nursing Practice: M.Sc. Degree Course in NursingEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: Measurements of Basic Body FunctionsDocument175 pagesVital Signs: Measurements of Basic Body FunctionsrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Heat DisorderDocument8 pagesJurnal Heat DisorderDiatri Eka DentaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale SubjectiveDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjectivemacloy21No ratings yet
- ThyroidectomyDocument11 pagesThyroidectomySherina W. EddingNo ratings yet
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocument4 pagesIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771No ratings yet
- Vital Signs-Temp, PRDocument54 pagesVital Signs-Temp, PRmags_abad09No ratings yet
- Preoperative and Postoperative Management - 2Document21 pagesPreoperative and Postoperative Management - 2Sameeha AbbassNo ratings yet
- General Nursing AssignmentsDocument12 pagesGeneral Nursing AssignmentsBia BlancaNo ratings yet
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocument10 pagesReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fever: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Fever: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareTele NursingNo ratings yet
- Ethos GRP 1Document6 pagesEthos GRP 1Rinae MutandanyiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllsreekalaNo ratings yet
- Hydrotherapy: 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyFrom EverandHydrotherapy: 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument39 pagesHypertensionChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- DevolutionDocument10 pagesDevolutionChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- BemoncDocument84 pagesBemoncJUANJOSEFOX100% (1)
- Maternal & Neonatal RelatedDocument15 pagesMaternal & Neonatal RelatedChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Emonc Protocol (Philhealth-DOH)Document38 pagesEmonc Protocol (Philhealth-DOH)Sandra BaileyNo ratings yet
- Global Elimination of Dog-Mediated Human RabiesDocument42 pagesGlobal Elimination of Dog-Mediated Human RabiesChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- HTN Slide Deck NewDocument27 pagesHTN Slide Deck NewChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Philippine Practice Guidelines Group in Infectious Diseases-Task Force On Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument28 pagesPhilippine Practice Guidelines Group in Infectious Diseases-Task Force On Urinary Tract InfectionsSirias_blackNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Assist with ambulation, transfers, positioning, and hygiene as neededDocument2 pagesAssist with ambulation, transfers, positioning, and hygiene as neededChristy Berry100% (1)
- GCP NF - AssessmentDocument17 pagesGCP NF - AssessmentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Nursing Coomunity Health NursingDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Nursing Coomunity Health NursingChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- GCP NCPDocument7 pagesGCP NCPChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Document3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNo ratings yet
- NoncomplianceDocument3 pagesNoncomplianceChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Approach To SymptomsDocument23 pagesApproach To SymptomsChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Ineffective AirwayDocument3 pagesIneffective AirwayChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Deficient KnowledgeChristy Berry100% (1)
- Assist with ambulation, transfers, positioning, and hygiene as neededDocument2 pagesAssist with ambulation, transfers, positioning, and hygiene as neededChristy Berry100% (1)
- Teaching Learning GuideDocument3 pagesTeaching Learning GuideChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- NoncomplianceDocument3 pagesNoncomplianceChristy Berry100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Deficient KnowledgeChristy Berry100% (1)
- Doh ProgramsDocument3 pagesDoh ProgramsitsmyhavenNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Care DeficitChristy BerryNo ratings yet