Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stem Cells
Uploaded by
yo_dawg17Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stem Cells
Uploaded by
yo_dawg17Copyright:
Available Formats
Lauren Slater 2
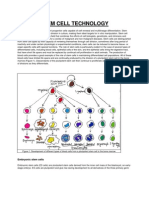
STEM CELLS Stem cells are cells that have the potential to develop into many different cell types in the body and in many tissues they serve as a repair system, dividing without limit to replenish other cells as long as the organism is still alive. When a stem cell divides, each new one either remains a stem cell or becomes another type of cell with a specialized function, such as a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a brain cell. The 3 main areas in stem cell research are adult, embryonic, and reprogrammed cells known as iPS stem cells. iPS, which stands for induced pluripotent stem cells, are reprogrammed adult skin cells changed to behave like embryonic stem cells so that scientists can bypass using embryos altogether. Embryonic stem cells are taken from a growing embryo at the blastocyst stage, killing the developing human life. Adult stem cells, on the other hand, are found in all tissues of a growing human being and, also have the potential to change themselves into practically all other cell types. Stem cells are important because they have regenerative abilities, which could help treat diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, or could replace damaged or destroyed tissues.
You might also like
- Biology Assignment (Stem Cells)Document3 pagesBiology Assignment (Stem Cells)Dwayne CoelhoNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem Cells?Document5 pagesWhat Are Stem Cells?beverly brittoNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Get Rid of Stem Cell Treatments Situation Once and For AllmhjkzDocument3 pagesGet Rid of Stem Cell Treatments Situation Once and For Allmhjkzturtlegender64No ratings yet
- Note On Stem Cell and Others - 051733Document10 pagesNote On Stem Cell and Others - 051733patmarys247No ratings yet
- Stem Cell TreatmentsDocument9 pagesStem Cell TreatmentsTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Precisely Why Stem Cells Is Your Most Severe Opponent 9 Tips To Defeat ItponzeDocument3 pagesPrecisely Why Stem Cells Is Your Most Severe Opponent 9 Tips To Defeat Itponzebronzemakeup0No ratings yet
- 2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461Document34 pages2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461Eka DevianyNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem CellsDocument8 pagesWhat Are Stem CellsPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell IsscrDocument8 pagesStem Cell Isscrcazzy_luvNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem Cells?Document7 pagesWhat Are Stem Cells?CherishtheLoveNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: The Key To Prolonged LifeDocument8 pagesStem Cells: The Key To Prolonged LifeLeslie EdensNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument7 pagesStem CellbaharNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: Vitro and in VivoDocument14 pagesStem Cells: Vitro and in VivoSamsonNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stem Cell?: Cell Red Blood CellsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Stem Cell?: Cell Red Blood CellsLouisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsALNAKINo ratings yet
- The Difference of Stem Cell ProductDocument12 pagesThe Difference of Stem Cell ProductIsmail Tidak Ada KepanjanganNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument2 pagesStem CellsKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- New Future For MedicineDocument2 pagesNew Future For MedicineJason BentleyNo ratings yet
- ISSCR 11 StemCellFactBrch FNLDocument8 pagesISSCR 11 StemCellFactBrch FNLНваневу СильванусNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells EssayDocument3 pagesStem Cells Essayapi-248018975No ratings yet
- Stem Cells:What Are They?why Are They Important?: by Mateus FrancoDocument12 pagesStem Cells:What Are They?why Are They Important?: by Mateus FrancoMateus FrançaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell CultureDocument78 pagesStem Cell CulturechasrodzNo ratings yet
- StemcellsDocument41 pagesStemcellsN CH MadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissue Trial ExamDocument24 pagesCells and Tissue Trial ExamReno Miranda EnticoNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Are A ClassDocument8 pagesStem Cells Are A ClassPrashant JadhavNo ratings yet
- Introducing Stem Cells: Prepared By: Ahmad Jaabo Grade: 6 BDocument6 pagesIntroducing Stem Cells: Prepared By: Ahmad Jaabo Grade: 6 Biman zeineddineNo ratings yet
- Sources of Stem CellsDocument13 pagesSources of Stem CellsAnshi AroraNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument9 pagesStem CellsSayaNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument16 pagesStem CellWindiNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Cellula PrecursoriaDocument26 pagesStem Cell: Cellula PrecursoriaYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsurmumgaeNo ratings yet
- Problems in Biology of Stem CellDocument7 pagesProblems in Biology of Stem CellBharti RuberNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem Cells and Where Do They Come FromDocument4 pagesWhat Are Stem Cells and Where Do They Come FromjaniellegbNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument4 pagesStem CellZeth VargasNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument31 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument12 pagesStem Cellapi-121232177No ratings yet
- Assignment On Cells and Stem CellsDocument10 pagesAssignment On Cells and Stem CellsMohammad MashhoodNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Mihai - Cristian BAGHINA Seria A Grupa 2Document9 pagesStem Cell: Mihai - Cristian BAGHINA Seria A Grupa 2Mihai NycromNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: What They Are and What They Do: International Journal of Biology SciencesDocument3 pagesStem Cells: What They Are and What They Do: International Journal of Biology SciencesKolawole Adesina KehindeNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFVelmuruganNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFharithrra vNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFharithrra vNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFIlincaNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument13 pagesStem CellsMarcus GohNo ratings yet
- 11-Cloning and Stem Cell TechDocument41 pages11-Cloning and Stem Cell TechCHUAH CHANG HONGNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Background Webquest Docx 1Document3 pagesStem Cell Background Webquest Docx 1api-301503657No ratings yet
- Stem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Document13 pagesStem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Harshal GohilNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument4 pagesStem Cellsapi-326952599No ratings yet
- Take NotesDocument2 pagesTake NotesRickyvhoy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Navigation SearchDocument14 pagesStem Cell: Navigation Searchanon-589691No ratings yet
- Summary of Stem CellsDocument2 pagesSummary of Stem CellsjohnNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument8 pagesStem CellHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell BasicsDocument5 pagesStem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell BasicsAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Harriette M. Flores Introduction: What Are Stem Cells, and Why Are They Important?Document3 pagesStem Cell: Harriette M. Flores Introduction: What Are Stem Cells, and Why Are They Important?Harriette Marilla FloresNo ratings yet
- Week 12-13 - Part2 - StemCellTherapyDocument29 pagesWeek 12-13 - Part2 - StemCellTherapyLouise San BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument9 pagesStem CellDulce UribeNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument7 pagesAbstractLiviu GogataNo ratings yet
- Stemcellresearchpaper Isabellaterrell Mod1bDocument4 pagesStemcellresearchpaper Isabellaterrell Mod1bapi-296790347No ratings yet