Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Algebraic Model of The Goods Market in An Open Economy
Uploaded by
Jade NguyenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An Algebraic Model of The Goods Market in An Open Economy
Uploaded by
Jade NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
An Algebraic Model of the Goods Market in an Open Economy
Exogenous Variables G, T, r, Y*, =1
Model
Endogenous Variables C, I, Y, X, IM, NX
IM = im1Y
Variable Definitions Y C I X IM G T Y* r = = = = = = = = = domestic output domestic consumption spending domestic investment spending exports imports domestic government spending domestic net taxes foreign output domestic real interest rate Parameter Definitions c0 c1 d0 d1 d2 x1 = = = = = = autonomous consumption propensity to consume autonomous investment propensity to invest sensitivity of investment to the real interest rate foreigners propensity to buy our exports propensity to import
im1 =
Demand for Domestic Goods (ZZ)
ZZ = C + I + G + NX
ZZ = [c 0 + c1 (Y T )] + [ d0 + d1Y d2 r ] + G + [ x1Y * im1Y ]
ZZ = [c 0 + d0 + G c1T d2 r + x1Y *] + (c1 + d1 im1 )Y Equilibrium Output (YE)
YE = ZZ (YE )
YE = [c 0 + d0 + G c1T d2 r + x1Y *] + (c1 + d1 im1 )YE
YE =
1 [c 0 + d0 + G c1T d2 r + x1Y *] 1 (c1 + d1 im1 )
UCSD Economics 110B
An Algebraic Model of the Goods Market in an Open Economy
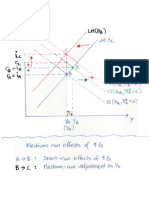
Comparative Statics I: How do changes in exogenous variables affect YE? (Assume that 0 < (c1 + d1 im1 ) < 1) An increase in G results in an increase in YE:
An increase in T results in a decrease in YE:
YE 1 = >0 G 1 (c1 + d1 im1 )
YE c1 = <0 T 1 (c1 + d1 im1 ) YE x1 = >0 Y * 1 (c1 + d1 im1 )
An increase in Y* results in an increase in YE:
Comparative Statics II: How do changes in exogenous variables affect NXE? (Assume that ) Note that: An increase in G results in a decrease in NXE :
Y NX E = im1 E < 0 G G Y NX E = im1 E > 0 T T Y NX E = x1 im1 E > 0 Y * Y *
An increase in T results in an increase in NXE :
An increase in Y* results in an increase in NXE :
UCSD Economics 110B
You might also like
- Macroeconomics: The Keynesian Cross ModelDocument22 pagesMacroeconomics: The Keynesian Cross ModelhongphakdeyNo ratings yet
- Sugerencias Técnicas para La Elección de BombaDocument15 pagesSugerencias Técnicas para La Elección de BombaHugo RoqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: The Open Economy in The Short Run: 1. Opening The Good MarketDocument21 pagesLecture 9: The Open Economy in The Short Run: 1. Opening The Good MarketSaurabh PatelNo ratings yet
- MacroC3 The Goods MarketDocument53 pagesMacroC3 The Goods MarketNguyễn Khắc Quý HươngNo ratings yet
- Fei2123PS1 SolnDocument8 pagesFei2123PS1 SolnMarco ChanNo ratings yet
- Part IIA, Paper 2 International Macroeconomics: Petra Geraats Lent 2021Document33 pagesPart IIA, Paper 2 International Macroeconomics: Petra Geraats Lent 2021IulioaraNo ratings yet
- Unit1 (Basic) - D&F6e. Chap - 3-Revisiting Keynesian Model of Income DeterminationDocument38 pagesUnit1 (Basic) - D&F6e. Chap - 3-Revisiting Keynesian Model of Income Determination2K20/BAE/44 DHWANI JAINNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Macroeconomics (Summary)Document5 pagesAssignment of Macroeconomics (Summary)Ilham Anugraha PramudityaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Expenditure Model - Open EconomyDocument27 pagesLecture 5 Expenditure Model - Open Economyshajea ali0% (1)
- Intermediate Macroeconomics 311, Professor Larry Christiano Homework 7, Due May, 2000 SOLUTIONDocument3 pagesIntermediate Macroeconomics 311, Professor Larry Christiano Homework 7, Due May, 2000 SOLUTIONBubu Teng Wan ChingNo ratings yet
- Year # of Hkust Freshmen Price (Tuition: HK$) Nominal GDP Real GDP (In 1990 $) Real GDP (In 2000 $)Document4 pagesYear # of Hkust Freshmen Price (Tuition: HK$) Nominal GDP Real GDP (In 1990 $) Real GDP (In 2000 $)Vianna NgNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For Chapter 11: Foundations of Modern MacroeconomicsDocument8 pagesProblem Set For Chapter 11: Foundations of Modern Macroeconomicstegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- Input-Output Models: LC Abueg: Mathematical EconomicsDocument33 pagesInput-Output Models: LC Abueg: Mathematical EconomicsArpit JainNo ratings yet
- C/ (1-C) C 1/ (1-C) (C Is MPC)Document6 pagesC/ (1-C) C 1/ (1-C) (C Is MPC)ragini pathakNo ratings yet
- Consumption and InvestmentDocument59 pagesConsumption and InvestmentPuspita Fiona rekaNo ratings yet
- Open Economy MacroeconomicsDocument15 pagesOpen Economy MacroeconomicssrpsinghNo ratings yet
- C OnsumsiDocument45 pagesC OnsumsiDwiMariaUlfahNo ratings yet
- The Keynesian Model: Intermediate MacroeconomicsDocument23 pagesThe Keynesian Model: Intermediate MacroeconomicsAbeeraKhanGhaznaviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - National Income DeterminationDocument21 pagesLecture 3 - National Income DeterminationPia Tanya UyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Keynes - 4 SectorDocument16 pagesModule 4 Keynes - 4 SectorPrashastiNo ratings yet
- Macro Theory Solutions - BenassyDocument177 pagesMacro Theory Solutions - BenassyazabekNo ratings yet
- Consumption and InvestmentDocument49 pagesConsumption and InvestmentPuspita Fiona reka100% (1)
- ECN 403 Lecture NoteDocument26 pagesECN 403 Lecture Noteveronicakaren404No ratings yet
- EC201 Tutorial Exercise 3 SolutionDocument6 pagesEC201 Tutorial Exercise 3 SolutionPriyaDarshani100% (1)
- Economics Notes Unit 6Document5 pagesEconomics Notes Unit 6Hritwik GhoshNo ratings yet
- Section 6Document8 pagesSection 6Tango BrillanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Power PointDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Power PointJacqueline Sabrina FernandezNo ratings yet
- ECS1601 Formula SheetDocument1 pageECS1601 Formula Sheetmacedakamogelo16No ratings yet
- Three-Sector ModelDocument72 pagesThree-Sector ModelJamesNo ratings yet
- ExamUZH FS21 FinalDocument5 pagesExamUZH FS21 FinalLudovico CalvettiNo ratings yet
- 4 - 5 Consumption and Investment - Week04-05Document39 pages4 - 5 Consumption and Investment - Week04-05Aldo Situmorang100% (1)
- Session 5 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From The Text Material: Chapter 2 - Page 34 Chapter 3 - Page 47 - 60Document17 pagesSession 5 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From The Text Material: Chapter 2 - Page 34 Chapter 3 - Page 47 - 60AkshitSoniNo ratings yet
- ECON 2123 Problem Set 1 SolutionDocument6 pagesECON 2123 Problem Set 1 SolutionNgsNo ratings yet
- Economics 302 (Sec. 001) Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Theory and PolicyDocument31 pagesEconomics 302 (Sec. 001) Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Theory and Policytai2000No ratings yet
- Session 2Document73 pagesSession 2Sankit Mohanty100% (1)
- Determination of National Income in Open Economy: Surinder Meena Pantea Rodd Pradeep Tahilyani Tasleem AliDocument26 pagesDetermination of National Income in Open Economy: Surinder Meena Pantea Rodd Pradeep Tahilyani Tasleem AliSurinder MeenaNo ratings yet
- PracticeDocument3 pagesPracticeAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Econ 101b Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesEcon 101b Lecture NotesSmi AndleebNo ratings yet
- Ekonomi MakroDocument24 pagesEkonomi MakroNovi NurainiNo ratings yet
- (ECON1266) Topic Notes - 2Document8 pages(ECON1266) Topic Notes - 2Nguyễn TùngNo ratings yet
- Sebenta MacroeconomiaDocument27 pagesSebenta MacroeconomiaAAA ANo ratings yet
- Foreign Trade Multiplier: - A Simple Keynesian Model For An Open EconomyDocument10 pagesForeign Trade Multiplier: - A Simple Keynesian Model For An Open Economykunal singhNo ratings yet
- GDP-NI Framewok-Fall-2016Document4 pagesGDP-NI Framewok-Fall-2016سعد احمد خاںNo ratings yet
- C3 - APE and Fiscal PolicyDocument45 pagesC3 - APE and Fiscal PolicyAnh Ôn KimNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Inflexibility Assumptions:: W - Inflexible P - Inflexible I - InflexibleDocument48 pagesFundamental Inflexibility Assumptions:: W - Inflexible P - Inflexible I - InflexiblehongphakdeyNo ratings yet
- Simple Keynesian ModelDocument7 pagesSimple Keynesian Modelloving_girl165712No ratings yet
- National Income Determination in Four Sector EconomyDocument32 pagesNational Income Determination in Four Sector Economyutsav100% (1)
- 01 - Investment Analysis - StudentDocument12 pages01 - Investment Analysis - StudentVương TùngNo ratings yet
- Adding Government and Trade To The Simple Macro ModelDocument27 pagesAdding Government and Trade To The Simple Macro Modelaamitabh3No ratings yet
- 14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Fall 2005 Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Fall 2005 Quiz 1 SolutionsNguyen Thi Thu HaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand in An Economy With Leakages in The Income-Expenditure StreamDocument2 pagesAggregate Demand in An Economy With Leakages in The Income-Expenditure StreamArinjay JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Real Business Cycles: Tiago CavalcantiDocument42 pagesLecture 3: Real Business Cycles: Tiago CavalcantiJanice OwnNo ratings yet
- Homework 07Document2 pagesHomework 07Mehdi Ben SlimaneNo ratings yet
- Macro Econ FormulasDocument4 pagesMacro Econ FormulasChristina LeeNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument4 pagesNational Incomepratik_ronoNo ratings yet
- Keseimbangan Pendapatan Nasional (Income Equilibrium)Document15 pagesKeseimbangan Pendapatan Nasional (Income Equilibrium)Mohammad Rian ArifinNo ratings yet
- 11.5 Closed Economy Is Curve DerivationDocument6 pages11.5 Closed Economy Is Curve Derivation周杨No ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Econometrics Chapter 4Document5 pagesEconometrics Chapter 4Jade NguyenNo ratings yet
- How Does A Change in Expected Inflation Shift The Is CurveDocument1 pageHow Does A Change in Expected Inflation Shift The Is CurveJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Real Vs Nominal Interest Rate HandoutDocument2 pagesReal Vs Nominal Interest Rate HandoutJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Expected Present Discounted Value HandoutDocument2 pagesExpected Present Discounted Value HandoutJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and ExpectationsDocument10 pagesFinancial Markets and ExpectationsJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 MR Increase in GDocument1 pageChapter14 MR Increase in GJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 MR Increase in MDocument1 pageChapter 14 MR Increase in MJade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Homework1 E3 10Document4 pagesHomework1 E3 10Jade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Homework-E4-8 and E4-15Document12 pagesHomework-E4-8 and E4-15Jade NguyenNo ratings yet
- Dalit CapitalDocument2 pagesDalit CapitalVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- An Essay On Education - Analysis of Education System in India. What We Need To Modify?Document47 pagesAn Essay On Education - Analysis of Education System in India. What We Need To Modify?Amit Bhushan89% (9)
- Dampak Free Trade Arrangements (Fta) Terhadap Ekonomi Makro, Sektoral, Regional, Dan Distribusi Pendapatan Di IndonesiaDocument3 pagesDampak Free Trade Arrangements (Fta) Terhadap Ekonomi Makro, Sektoral, Regional, Dan Distribusi Pendapatan Di IndonesiaRizkyNo ratings yet
- Home Office and Branch Accounting OutlineDocument2 pagesHome Office and Branch Accounting OutlineKate Alvarez100% (1)
- Stuvia 2485683 dsc1520 Assignment 1 Complete Answers Semester 1 2024 158619 Due 1 March 2024Document34 pagesStuvia 2485683 dsc1520 Assignment 1 Complete Answers Semester 1 2024 158619 Due 1 March 2024Haat My LaterNo ratings yet
- Revenue Status Report FY 2011-2012 - General Fund 20111231Document19 pagesRevenue Status Report FY 2011-2012 - General Fund 20111231Infosys GriffinNo ratings yet
- Brickley Zimmerman SmithDocument15 pagesBrickley Zimmerman SmithAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 2Document7 pagesPractice Problem Set 2AkshayNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight: Cost Allocation: PracticesDocument20 pagesChapter Eight: Cost Allocation: Practicesmuudey sheikhNo ratings yet
- The Proprietary Theory and The Entity Theory of Corporate Enterpr PDFDocument242 pagesThe Proprietary Theory and The Entity Theory of Corporate Enterpr PDFAnusha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Chap 007Document19 pagesChap 007charlie simoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 1060: Economics (History of Economic Thought)Document8 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 1060: Economics (History of Economic Thought)Neeti JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Strategic Situation of KepakDocument5 pagesA Review of The Strategic Situation of KepakasdefenceNo ratings yet
- Alternative Investments - Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesAlternative Investments - Cheat SheetUchit MehtaNo ratings yet
- An Mit Study Has Estimated Costs For Producing Steel WithDocument1 pageAn Mit Study Has Estimated Costs For Producing Steel Withtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- OligopolyDocument5 pagesOligopolyFazil DamryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Public GoodsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Public Goodsbest videosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Pricing StrategyDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Pricing Strategyuser 123No ratings yet
- The Regulation of Technology and The Technology of RegulationDocument18 pagesThe Regulation of Technology and The Technology of RegulationCecilia SelaruNo ratings yet
- Price Control The Consumer and LawDocument53 pagesPrice Control The Consumer and LawAnika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Micro Module 1 Package 1Document5 pagesMicro Module 1 Package 1Fire burnNo ratings yet
- Phelps Lecture2006Document26 pagesPhelps Lecture2006Tuan HoangNo ratings yet
- Rapaport Research Report July 2011Document8 pagesRapaport Research Report July 2011Fevi AbejeNo ratings yet
- The Internal Factor Evaluation IFE MatriDocument4 pagesThe Internal Factor Evaluation IFE MatridominicNo ratings yet
- SPACE MATRIX NishatDocument4 pagesSPACE MATRIX NishatMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Agency TheoryDocument5 pagesAgency TheoryChiah ChyiNo ratings yet
- Dividend Decision NotesDocument6 pagesDividend Decision NotesSavya SachiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 DanDocument16 pagesGrade 9 DanRoi SorianoNo ratings yet
- Cal vs. CML vs. SML: Posted by Bill Campbell III, CFA On September 29, 2013Document4 pagesCal vs. CML vs. SML: Posted by Bill Campbell III, CFA On September 29, 2013IMZNNo ratings yet
- 07 Macro GDP GDPDeflator CPI InflationDocument6 pages07 Macro GDP GDPDeflator CPI InflationAaryan ModiNo ratings yet