Professional Documents
Culture Documents
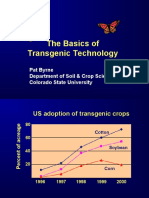
Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer
Uploaded by
anirbanmanna88320Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer
Uploaded by
anirbanmanna88320Copyright:
Available Formats
Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer
We need to make a segment of DNA that contains a selectable marker and a gene of interest to look like a T-DNA. Next, we need to get this T-DNA into an Agrobacterium cell so that it can be mobilized by the vir genes. Lastly, we have to produce and find transformed plant cells that can be regenerated into normal, fertile plants. Requirements - a transfer cassette bounded by functioning borders - ways to get this cassette into Agrobacterium - disarmed Ti plasmids that retain functional vir genes Advantages and disadvantages of Agrobacterium as a gene transfer tool advantages - technically simple - yields relatively uncomplicated insertion events (low copy number, minimal rearrangements) - unlimited size of foreign DNA - efficient (for most plants) - adaptable to different cell types, culture procedures (protoplasts, tissue sections, non-culture methods) - transformants are mitotically and meiotically stable Disadvantages - host range is limited: not all plants may be susceptible to Agrobacterium - with susceptible plants, accessible culture/regeneration systems must be adaptable to Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer (add the importance with these points)
You might also like
- Gene Transfer in PlantsDocument26 pagesGene Transfer in Plantsanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Agrobacterium Mediated TransformationDocument6 pagesAgrobacterium Mediated TransformationMuhammad Ibrahim AslamNo ratings yet
- Binary and Co Integrative VectorsDocument25 pagesBinary and Co Integrative VectorsSakshi BuchkeNo ratings yet
- Genetic TransformationDocument7 pagesGenetic TransformationADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Genetic Transformation of PlantsDocument91 pagesChapter 11 Genetic Transformation of Plantsrajiv pathakNo ratings yet
- Cloning Vectors For Higher PlantsDocument18 pagesCloning Vectors For Higher PlantsDarshan Marjadi100% (1)
- TransgenicDocument7 pagesTransgenicGopalNo ratings yet
- Basics of Genetic Trasgenic Plants DefinitionDocument36 pagesBasics of Genetic Trasgenic Plants DefinitionKeyru LaillampNo ratings yet
- Indirect and Direct Methods of Gene TransferDocument4 pagesIndirect and Direct Methods of Gene TransferOrpita Das100% (2)
- Mansi Potinde NOTESDocument5 pagesMansi Potinde NOTESPrasanna SankheNo ratings yet
- 2-Plant Genetic Transformation 28.02.13Document42 pages2-Plant Genetic Transformation 28.02.13vishalNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant Transformation MethodsDocument31 pages3 Plant Transformation MethodsVenkateswarlu Yadavalli100% (2)
- Lecture 4Document15 pagesLecture 4aya manoliaNo ratings yet
- Process of Developing Genetically Modified (GM) CropsDocument5 pagesProcess of Developing Genetically Modified (GM) Cropsdaeng ngunjungNo ratings yet
- Ti Plasmid Derived Vector SystemDocument4 pagesTi Plasmid Derived Vector Systemswaroopsanket100% (1)
- Methods of Gene Transfer in PlantsDocument29 pagesMethods of Gene Transfer in PlantsTara TAHIRNo ratings yet
- Bty443 Unit IIDocument61 pagesBty443 Unit IImanisha prasadNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer & VectorDocument27 pagesGene Transfer & VectorGopi ShankarNo ratings yet
- 71830-Article Text-155973-1-10-20111109 PDFDocument8 pages71830-Article Text-155973-1-10-20111109 PDFMuktanand DhurveNo ratings yet
- Transformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aDocument19 pagesTransformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Plants and Plant Biotechnology: Presented by Amith Reddy Eastern New Mexico UniversityDocument52 pagesTransgenic Plants and Plant Biotechnology: Presented by Amith Reddy Eastern New Mexico UniversityamitrameshwardayalNo ratings yet
- Application of Biotechnology For Improvement of Ornamental CropsDocument92 pagesApplication of Biotechnology For Improvement of Ornamental Cropspavani100% (8)
- Plant Metabolic EngineeringDocument32 pagesPlant Metabolic Engineeringvamshibommi3477100% (1)
- Lecture 11 Digital Signals SystemsDocument11 pagesLecture 11 Digital Signals Systemsraguraj8No ratings yet
- The Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeDocument25 pagesThe Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeRoma Amor Gilhang SauraneNo ratings yet
- PPCB Lab Presentation PDFDocument13 pagesPPCB Lab Presentation PDFAdithya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2017 PGE Day 6Document43 pages2017 PGE Day 6Mamila TadNo ratings yet
- Plant Transformation TechniquesDocument39 pagesPlant Transformation TechniquesHassaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3 Transgenic PlantsDocument43 pages3 Transgenic Plantseziest123No ratings yet
- Transgenic Plant 1. Introduction To DNA: Voet, Donald 1995 BiochemistryDocument4 pagesTransgenic Plant 1. Introduction To DNA: Voet, Donald 1995 BiochemistryDitta Ria AriniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Genetic Engineering of Plants: Methodology: Agrobacterium TumefaciensDocument16 pagesChapter 18-Genetic Engineering of Plants: Methodology: Agrobacterium Tumefaciensit fapertaNo ratings yet
- Gene Editor PromegaDocument28 pagesGene Editor PromegaJuliana SouzaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Rdna Technology in AgricultureDocument14 pagesApplications of Rdna Technology in AgricultureDhanya RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Techniques 2Document23 pagesGene Transfer Techniques 2Cecilia MukototsiNo ratings yet
- T-DNA Mediated Gene Transfer in PlantsDocument26 pagesT-DNA Mediated Gene Transfer in PlantsSathiyaraj91% (11)
- Plant Gene ExpressionDocument3 pagesPlant Gene ExpressionArun SendhilNo ratings yet
- The Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeDocument25 pagesThe Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeSharang AhujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two New Curr - For Pres Ed2pptxDocument52 pagesChapter Two New Curr - For Pres Ed2pptxfiker tesfaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Unit 1 Use of PCR For GMO Identification SDocument9 pagesPaper 2 Unit 1 Use of PCR For GMO Identification SSandeep GupteNo ratings yet
- Safety of Genetically Engineered FoodsDocument18 pagesSafety of Genetically Engineered FoodsMd. Sazzad HossainNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 14Document11 pagesLecture - 14Asad ullahNo ratings yet
- Direct Methods of Gene Transfer in PlantsDocument17 pagesDirect Methods of Gene Transfer in PlantsAYUSHI MATHURNo ratings yet
- Module 5bDocument24 pagesModule 5bMing YanNo ratings yet
- Plantbio - Week9handout-2003Document4 pagesPlantbio - Week9handout-2003Abraham WalkthewokNo ratings yet
- HBC 410 Agrobacterium Mediated TransformationDocument20 pagesHBC 410 Agrobacterium Mediated TransformationArthur Derman Sith-leeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme TechnologyDocument61 pagesEnzyme TechnologyLinnuha Ulin100% (1)
- Transgenic CropsDocument4 pagesTransgenic CropsfinnandzestzuNo ratings yet
- Plant Transformation Methods - Insiya Tankiwala - 13bbt0201Document11 pagesPlant Transformation Methods - Insiya Tankiwala - 13bbt0201InsiyaTankiwalaNo ratings yet
- Production of BT CornDocument6 pagesProduction of BT CornJustin Daniel Ng SuyNo ratings yet
- Transgenik TeknologiDocument58 pagesTransgenik Teknologiit fapertaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering in TomatoDocument51 pagesGenetic Engineering in TomatoSandeep kumar SathuaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Gene TransferDocument19 pagesMethods of Gene TransferSudarshini BorugaddaNo ratings yet
- Transgenicplants PPT 170509172214 PDFDocument31 pagesTransgenicplants PPT 170509172214 PDFKishore KaranNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument34 pagesGenetic EngineeringTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Expression Systems & VectorsDocument9 pagesExpression Systems & VectorsSwetha SundarNo ratings yet
- What Is genetic-WPS OfficeDocument16 pagesWhat Is genetic-WPS OfficeShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- AgrobacteriumDocument38 pagesAgrobacteriumAkshay ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Primary and Stem Cells: Gene Transfer Technologies and ApplicationsFrom EverandPrimary and Stem Cells: Gene Transfer Technologies and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Plant Omics: Advances in Big Data BiologyFrom EverandPlant Omics: Advances in Big Data BiologyHajime OhyanagiNo ratings yet
- Akira TLRDocument7 pagesAkira TLRaishwaryadashNo ratings yet
- Adiponectin JBC PDFDocument5 pagesAdiponectin JBC PDFanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Explosive Cell LysisDocument13 pagesExplosive Cell Lysisanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Small Interfering RNADocument6 pagesSmall Interfering RNAanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Targeting The NLRP3 Inflammasome To Reduce Diet-Induced Metabolic Abnormalities in MiceDocument39 pagesTargeting The NLRP3 Inflammasome To Reduce Diet-Induced Metabolic Abnormalities in Miceanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Janeway's Immunobiology: Seventh EditionDocument12 pagesJaneway's Immunobiology: Seventh Editionanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- BiopsyDocument4 pagesBiopsyanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2007) 127, 2525-2532: Doi:10.1038/sj - Jid.5700865Document1 pageJournal of Investigative Dermatology (2007) 127, 2525-2532: Doi:10.1038/sj - Jid.5700865anirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Course: MSC BT Semester: Iii Subject Code: MBT 305 Subject Name: Computational Biology Unit Number: 1 Unit Title: Introduction To BioinformaticsDocument19 pagesCourse: MSC BT Semester: Iii Subject Code: MBT 305 Subject Name: Computational Biology Unit Number: 1 Unit Title: Introduction To Bioinformaticsanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Result of Online Entrance Examination 2015 of M.Sc. Life ScienceDocument2 pagesResult of Online Entrance Examination 2015 of M.Sc. Life Scienceanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Schedule For Online Entrence Examination-2015-2016: S.No. Course Code Date Shift TimingDocument3 pagesSchedule For Online Entrence Examination-2015-2016: S.No. Course Code Date Shift Timinganirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Adherens and Tight Junctions: Structure, Function and Connections To The Actin CytoskeletonDocument10 pagesAdherens and Tight Junctions: Structure, Function and Connections To The Actin Cytoskeletonanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Acid Dissociation ConstantDocument15 pagesAcid Dissociation Constantanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University: (A Central University) LucknowDocument16 pagesBabasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University: (A Central University) Lucknowanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- SMMTR PaperDocument11 pagesSMMTR Paperanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- 3 Clinical significance: Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as catabolin, isDocument4 pages3 Clinical significance: Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as catabolin, isanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- 1 Types: 2.3 Diagnostic RelevanceDocument3 pages1 Types: 2.3 Diagnostic Relevanceanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- CRISPRDocument15 pagesCRISPRanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- CRISPRDocument15 pagesCRISPRanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- ICMR JRF Entrance Examination 2015: Information BrochureDocument18 pagesICMR JRF Entrance Examination 2015: Information BrochureNayan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai - 400 076 Admission To Postgraduate/ Ph.D. Programme Autumn Semester, Academic Year: 2015 16Document2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai - 400 076 Admission To Postgraduate/ Ph.D. Programme Autumn Semester, Academic Year: 2015 16Kiran Kumar KandregulaNo ratings yet
- BET CertificateDocument1 pageBET Certificateanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Targeting The IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Disease: Pierre MiossecDocument1 pageTargeting The IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Disease: Pierre Miossecanirbanmanna88320100% (1)
- South Asian University: Admission FormDocument3 pagesSouth Asian University: Admission Formanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- ButrflyDocument1 pageButrflyanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Katha o KahiniDocument95 pagesKatha o Kahinianirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument1 pagePlant Cellanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Ribo SwitchDocument1 pageRibo Switchanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Content Agriculture BiotechDocument5 pagesContent Agriculture Biotechanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- 408 Pooja Shinde PROJECTDocument35 pages408 Pooja Shinde PROJECTPooja ShindeNo ratings yet
- Hairy Root Culture and Transient ExpressionDocument5 pagesHairy Root Culture and Transient Expressionautumn333No ratings yet
- Agrobacterium MorgellonsDocument9 pagesAgrobacterium MorgellonsRui Baptista PereiraNo ratings yet
- Plant Breeding and Transformation: NST PMS 1B: Origins of Modern AgricultureDocument13 pagesPlant Breeding and Transformation: NST PMS 1B: Origins of Modern AgricultureDio ShinNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsDocument9 pagesGene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Transgenic PlantDocument20 pagesTransgenic Plantsabiha khanNo ratings yet
- Morgellons Disease The Mystery Unfolds Virginia R Savely and Raphael B StrickerDocument12 pagesMorgellons Disease The Mystery Unfolds Virginia R Savely and Raphael B Strickersisterrosetta100% (1)
- tmpECC3 TMPDocument13 pagestmpECC3 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology of Indonesian Natural Orchids: Endang SemiartiDocument46 pagesBiotechnology of Indonesian Natural Orchids: Endang Semiartisahul sunuNo ratings yet
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Document73 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Bikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Plant Transformation TechniquesDocument39 pagesPlant Transformation TechniquesHassaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Food Biotechnology PDFDocument44 pagesFood Biotechnology PDFRaviNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Plasmid DNA From Agrobacterium Using The QIAprep® Spin Miniprep Kit Spin ProcedureDocument3 pagesIsolation of Plasmid DNA From Agrobacterium Using The QIAprep® Spin Miniprep Kit Spin Procedure于连升No ratings yet
- (David C. Sigee) Bacterial Plant Pathology Cell A (B-Ok - Xyz)Document340 pages(David C. Sigee) Bacterial Plant Pathology Cell A (B-Ok - Xyz)mksbhu50% (2)
- KytokininesDocument12 pagesKytokinines123456No ratings yet
- tmp7AB9 TMPDocument10 pagestmp7AB9 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Chen Et Al. (2022) Crop Transformation TechnologiesDocument9 pagesChen Et Al. (2022) Crop Transformation TechnologiesFreddy Colmenarez-BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Genetic Manipulation in Plants: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Asmah Awal Faculty of Plantation & Agrotechnology Asmah138@uitm - Edu.myDocument31 pagesGenetic Manipulation in Plants: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Asmah Awal Faculty of Plantation & Agrotechnology Asmah138@uitm - Edu.myXwag 12No ratings yet
- Rapid and Efficient Agrobacterium Mediated Transformation in RiceDocument6 pagesRapid and Efficient Agrobacterium Mediated Transformation in RiceAbdul Zaheer KhanNo ratings yet
- Agrobacterium Tumefaciens: and Plant Cell Interactions and Activities Required For Interkingdom Macromolecular TransferDocument29 pagesAgrobacterium Tumefaciens: and Plant Cell Interactions and Activities Required For Interkingdom Macromolecular Transfercowpea2009No ratings yet
- United States Plant Patent: Firoozbadly Et Al. Aug. 4, 2015Document19 pagesUnited States Plant Patent: Firoozbadly Et Al. Aug. 4, 2015ALxiitoo SancHez NtsNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Biotechnology ScriptDocument18 pagesMicrobiology and Biotechnology ScriptDavid RăscuţoiNo ratings yet
- Invasive Fungal SpeciesDocument2 pagesInvasive Fungal SpeciescmagdanganNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For BiotechnologyDocument42 pagesLaboratory Manual For BiotechnologySanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- History of BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesHistory of BiotechnologySanjiban ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- TTPB23 Abridged 24Document24 pagesTTPB23 Abridged 24AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Biotechnology Applications Read Chapter 10Document27 pagesPlant and Animal Biotechnology Applications Read Chapter 10Sheetal PimparwarNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Methods MHRD NotesDocument38 pagesGene Transfer Methods MHRD Notessrinivas ceoNo ratings yet
- Transformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aDocument19 pagesTransformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Plants and Plant Biotechnology: Presented by Amith Reddy Eastern New Mexico UniversityDocument52 pagesTransgenic Plants and Plant Biotechnology: Presented by Amith Reddy Eastern New Mexico UniversityamitrameshwardayalNo ratings yet