Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Service Delivery Quick Reference
Uploaded by
mrcyber100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
411 views4 pagesService Delivery Quick Reference ITIL v3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentService Delivery Quick Reference ITIL v3
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
411 views4 pagesService Delivery Quick Reference
Uploaded by
mrcyberService Delivery Quick Reference ITIL v3
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
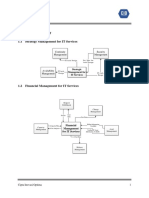
Service Level Management Financial Management for IT services Capacity Management IT Service Continuity Management Availability Management
GOALS GOALS GOALS GOALS GOALS
To maintain and gradually improve IT service quality To provide cost-effective stewardship of the IT assets To ensure that cost-justifiable IT capacity always The goal for ITSCM is to support the overall Satisfy Business objectives
trough a constant cycle of agreeing monitoring and and resources used in providing IT Services exist and that it is matched to the current and future Business Continuity Management process by Achieve sustained level of availability
reporting upon IT service achievement and identified business needs ensuring that the required IT technical and services Ensure cost effectiveness
instigation of actions to eradicate poor service or facilities can be recovered within required, and Optimize the capability of services and components
Having the appropriate IT capacity and making best agreed, business timescales
use of it
OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES
High quality, cost effective, value-adding IT services To manage the financial aspects of IT assets and
that underpin the organization’s business needs resources cost-effectively
Play a key role in ascertaining the business To account fully for the total spend on the provision
requirements of IT Services and to attribute the cost to the services
SLA is written agreement between the customer and delivered
the IT service provider, defining key targets and To advise management on IT investment matters by
responsibilities on both sides providing detailed business cases
PROCESS PROCESS PROCESS – sub-processes PROCESS PROCESS
Established Function Budgeting Business Capacity Management Stage 1- Initiation ACTIVITIES
Initial Planning activities and Implementation Setting the budget Service Capacity Management Initiate BCM determining the Availability requirements from the business for
Implement SLAs IT Accounting Resource Capacity Management Stage2 – Requirements and Strategy a new or enhanced IT Service and formulating the Availability
Compile a service catalogue Building a Cost Model Business impact analysis and recovery design criteria for the IT Infrastructure
Establish SLA structure Charging ACTIVITIES Risk assessment in conjunction with ITSCM determining the vital business
Establish overview of Service Level Requirements Setting the Price Monitoring Business Continuity Strategy functions and impact arising from IT component failure
(SLRs) Pricing methods Analysis Stage3 - implementation defining the targets for Availability, reliability and
Plan UCs and OLAs Differential Charging Tuning Organizational and implementation planning maintainability for the IT Infrastructure components
Draft and agree SLAs Billing Implementation Implement stand-by arrangements establishing measures and reporting of Availability, Reliability
Manage The Ongoing Process Storage of Capacity Management data – the CDB Develop Recovery Plans and Maintainability that reflects the business, User and IT
Monitor and report SLA achievements Demand Management Implement Risk reduction Measures support organisation perspectives
Review SLA achievements Modeling Develop Procedures monitoring and trend analysis of the Availability, Reliability
Identify Service improvements (SIP) Application sizing Initial testing and Maintainability of IT components
Periodic Reviews Producing of the capacity Plan Stage4 – Operational Management reviewing IT Service and component Availability and
Review and update SLAs, UCs and OLAs Education and awareness identifying unacceptable levels
Review SLM process for efficiency and effectiveness Review and audit investigating the underlying reasons for unacceptable
Testing Availability
producing and maintaining an Availability Plan which prioritises
Change Management
and plans IT Availability improvements.
Training
Assurance
DEFS DEFS INPUTS Recovery Types INPUTS
Service Catalog: defines services with default levels Cost Model: by service, location, customer (for Technology Do nothing - Few, if any, organisations can function Business availability requirements
and options. Gives a profile of IT service provider to charging) SLA, SLR and Service Catalogue effectively without IT Services. Even if there is a Business impact assessment
org. and overview of services provided to users. Cost Types: HW, SW, People, Accommodation, Business plans and strategy requirement for stand-alone PC processing, there is Availability, Maintainability and Reliability requirements
SLR-Service Level Requirements: list of clients reqs. External services, Transfer costs IS/IT plans and strategy still a need for recovery to be supported. Impact assessment for Vital Business Functions
OLA-Operational Level Agreements: Between 2 Cost Elements: Sub elements of Cost Types, like HW = Operational schedules Manual Work-arounds - manual Work-arounds can Incident and problem data
intern IT departments NW, Server, Office Deployment and development plans and programs be an effective interim measure until the IT Service is Configuration and monitoring targets
UC-Underpinning Contract: With an external Cost Category resumed wherever they are practical and possible.
Forward schedule of change Service Level Targets
supplier. Capital or Operational Reciprocal arrangements - Entering into an
Incidents and problems
SLA Direct/Indirect agreement with another organisation using similar
Service reviews
SIP-Service Improvement Program: SLM with PM Absorbed/Unabsorbed Indirect technology. Benefits can exist, in maintaining some
SLA breaches
and AM starts a formal project focusing on user Fixed/Variable reciprocal arrangements, for example, in the off-site
Budget
satisfaction storage of backups and other critical information.
Service Catalog Contents CHARGING OUTPUTS Gradual Recovery (cold standby) - up to 72 hours, OUTPUTS
Version number, date created, date amended; TOC; Notional (Invoiced, not payed), Communication of Info Capacity plan without a re-establishment of full IT facilities. Availability and recovery design criteria
Foreword from CIO; IT Service provider profile; Service (customer informed of charges to be aware), Pricing CDB Accommodation fully equipped with power and local Agreed targets of availability, rel., maintainability
times and accessibility of IT Service Provider; Overview Flexibility (Rates charged annually) network cabling Infrastructure, telecom connections.
Baselines and profiles Reports on achieved A.R.M
of services and products; Customer focused Fixed or portable facility.
Thresholds and alarms Availability monitoring
service/product description; Specs; Deliverables; Service Pricing Method/Policy When opting for a gradual recovery, consideration
Capacity reports (regular, at hock and Exception) Availability improvements plans
times; Maintenance times; Support times; Delivery Cost Plus – cost + profit rate must be given to highly customised items of
SLA and SLR recommendations hardware or equipment that will be difficult, if not
times; Quality targets (availability, usability, reliability, Going Rate – comparable to other dept services Costing and Charging recommendations
priority); Requirements; Request & Change procedure; impossible, to replace.
Market Price – match external supplier price Proactive changes and service improvements
Contigency policy; Pricing & Charging; Index & Negotiated Contract Price Intermediate Recovery (warm standby) 24 to 72 hour
Revised operational schedule period. It is usually far away (logistics) and shared
Definitions
Effectiveness reviews with 20 to 30 other companies. Use 6-12 weeks. Can
Audit reports be portable, in a trailer.
Immediate Recovery (hot standby) provides for
immediate restoration. Application systems and
communications already available and data mirrored
from the operational servers. In the event of a system
failure, the Customers can immediately switch to the
backup facility with little or no loss of service.
System can be used as backup and reporting resource.
Service Level Management Financial Management for IT services Capacity Management IT Service Continuity Management Availability Management
BENEFITS BENEFITS BENEFITS BENEFITS BENEFITS
Customer and IT service provider have a clearer Increased Confidence in budgets Minimize risk of failing to meet SLAs and SLRs The annual spend on ITSM can be controlled A single point of accountability for availability is established
view of requirements and responsibilities Accurate information supplied for investment and More confident forecasting Cost justifiable risk reduction measures can be within the organization
Commitment on both sides TCO purposes Value to the applications lifecycle implemented IT Services are designed to meet the IT Availability
Specific targets to aim for Increased professionalism and efficiency Increased efficiency The ability to recover in a controlled manner requirements of the business
Week areas will be identified Warning over or under usage of service Cost savings and cost avoidance All staff aware of their role relating to ITSCM the levels of IT Availability provided are cost justified
Supports supplier management (internal and Sound business method of balancing IT service Timely enhancements and upgrades Potential lower insurance premiums the levels of Availability required are agreed, measured and
external) provision with business requirements Meetings regulatory requirements monitored to fully support Service Level Management
Demonstrable performance indicators The cost of doing or not doing a Change Better business relationships shortfalls in the provision of the required levels of Availability
Gradual improvements in service quality Positive marketing of contingency capabilities are recognised and appropriate corrective actions identified and
Better forward planning / both customers and IT Organizational credibility implemented
Will show where customer/user actions are causing Competitive advantage a business and User perspective of IT Service Availability is
difficulty and identify where working practice need taken to ensure optimal usage and performance of the IT
to be improved Infrastructure is achieved to deliver maximum benefit
IT service will be defined to meet Service Level the frequency and duration of IT Service failures is reduced
Requirements over time
SLAs can be used as a basis for charging IT support organisation mindset moves from error correction to
Improved communication between IT and customers service enhancement; from reactive to proactive attitude
Better value for money the IT support organisation is seen to 'add value' to the
business.
PROBLEMS PROBLEMS PROBLEMS Contingency Plan PROBLEMS
ensuring targets are achievable (use existing Lack of understanding leading to inefficient, overlay Unrealistic expectations IT infrastructure, comprising the replacement system, Defining availability levels that are meaningful to the business
achievements if known) expensive or over-complex systems Vendor influence plus contracts/agreements necessary for recovery Managing internal and external providers is made difficult by
verifying targets prior to agreement (prior Monitoring tools inaccurate or too expensive Lack of accurate information IT Infrastructure Management and operating lack of agreed availability targets
monitoring, pilot SLAs) Delay in obtaining, or inaccurate, information - business data agreements/procedures during a disaster Assessing achievable and cost-effective levels of IT service
Monitoring of actual achievement (only agree what Difficulty in recruiting staff with accountancy and IT - technical data Personnel - details of those needed at contingency availability
can be monitored) skills Distributed environments site plus accommodation required New services are implemented without full consideration of
Inadequate resources and time (process must be Unable to respond to changes quickly enough Level of monitoring to be implemented Security instructions, emergency contacts and items availability requirements
properly staffed and resourced Lack of management understanding and support for home site Loss of business and reputation due to unstable IT services
Lack of understanding (educations) Contingency site: location, people, facilities, security Lack of accountability
Differences in perceptions within the customer and transport arrangements
community (need to agree relevant targets at all Return to normal - dependencies affecting the return
levels)
Not enough seniority (give Service Level Manager
the appropriate authority)
SLA may not be supported by adequate underpinning
agreements/contracts (review OLAs and contracts)
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS DEFINITIONS
what number or percentage of Services are covered Overall cost of delivery per customer Resource forecasts Percentage of Vital Business Functions covered by IT Availability – Ability of an IT Service or CI to perform its
by SLAs Percentage of IT costs not accounted for - timely production of forecasts Service Continuity Plans required function at a stated instant or over a stated period of time
are Underpinning contracts and OLAs in place for all Dollar value of budget variances/adjustments - accurate forecasts if trends in resource util. Percentage of Vital Business Functions covered by Reliability – freedom from operational failure. Rel. of an IT
SLAs and for what percentage? Percentage of IT financial objectives met - incorporation of business plans into cap. plan annual IT Continuity tests service is determined by rel. of each component delivering the
are SLAs being monitored and are regular reports IT Service Headcount Technology Number of annual IT Service Continuity Plan testing service.
being produced? - ability to monitor perf and troughput failures Maintainability – ability of a CI to be kept in, or to be restored to
are review meetings being held on time and correctly - impl. Of new tech. in line with business Number of 3rd party recovery support contracts not an operational state.
minuted? requirements (time cost functionality) agreed Serviceability – describes contractual arrangements made with 3rd
is there documentary evidence that issues raised at - use of old technology does not result in breached Number of audits performed on IT Service party IT service providers to assure Avail., Rel. and
reviews are being followed up and resolved (e.g. via SLa due to problems Continuity Plan Maintainability. of IT services and their CIs.
an SIP) Cost effectiveness Number of business issues logged against IT Service Resilience – capacity of an IT service to allow continued operation
what number or percentage of Service targets are - a reduction in panic buying Continuity. of IT despite the failure of one or more sub-systems.
being met and what is the number and severity of - not significant over-capacity Vital Business Function – business critical element of business
service breaches? - accurate forecasts of planned expenditure process.
Plan and implement the appropriate IT capacity to Security – deals with confidentiality, integrity and availability of
are service breaches being followed up effectively?
match business needs data.
are service level achievements improving
- reduction in lost reduction in the incidents due to AMDB – record & store info reqd. for support of key activities:
are Customer perception statistics improving?
poor performance reporting, analysis and availability forecasting...
are IT costs decreasing for services with stable Service Window – period in which maintenance can be completed
(acceptable but not improving) service level - reduction in lost business due to inadequate
capacity on a service
achievements?
- new services are implemented which match SLR
are SLAs, OLAs and underpinning contracts current
-recommendation made by capacity mgt. are acted
and what percentage are in need of review and
upon
update?
CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS
Meeting Customer Needs And Priorities Effective stewardship over IT finances Accurate business forecasts Ensuring IT Service Recovery Within Agreed
Adherence To Service Levels Establishing Process knowledge of IT strategy and plans, and that the Timescales
Providing Services Cost Effectively Planning plans are accurate
Controlling Service Delivery Implementation an understanding of current and future technologies
Maintaining Recognized Industry Acceptance For IT Operational an ability to demonstrate cost effectiveness
Quality Managing change interaction with other effective Service Management
Maintaining An IT Service Culture processes
Managing variances
an ability to plan and implement the appropriate IT
Capacity to match business need
Service Level Management Financial Management for IT services Capacity Management IT Service Continuity Management Availability Management
RESPONSIBILITIES SLMgr RESPONSIBILITIES RESPONSIBILITIES RESPONSIBILITIES ITSC Manager RESPONSIBILITIES (A. Manager)
creates and maintains a catalogue of existing Budgeting: ensures that appropriate levels of monitoring of Develop and manage the ITSCM Plan to ensure that, to be accountable for the deployment of the AM process and
Services manage the IT organisation budget resources and system performance are set, and that at all times, the recovery objectives of the business associated methods and techniques
formulates, agrees and maintains an appropriate SLM prepare budget forecasts and assist Customers in the information recorded in a CBD is kept up-to-date can be achieved. to be responsible for ensuring the AM process is regularly
structure (SLA, OLA, Contracts, accommodating preparing IT elements of their budgets and used by all parts of the Capacity Management Ensure that all IT Service areas are prepared and able reviewed and audited, and that all of these are subject to cont.
service improvement plan within SLM) report regularly to IT managers and Customers on process to respond to an Invocation of the Continuity plans. improvement and remain fit for purpose
negotiates, agrees and maintains the Service Level conformance to budgets produces Capacity Plans in line with the Maintain a comprehensive IT testing schedule. to be responsible for determining the Av. requirements from the
Agreements with the Customer Accounting: organisation's business planning cycle, identifying Undertake quality reviews of all procedures and business for new or enhanced IT Services
negotiates, agrees and maintains the Operational select suitable tools and processes for gathering Cost Capacity requirements early enough to take account ensure that these are incorporated into the testing to be responsible for the creation of A and recovery design
Level Agreements with the IT provider data of procurement lead times schedule. criteria to be applied to new or enhanced Infrastructure design
negotiates and agrees with both the Customer and IT develop suitable cost models documents the need for any increase or reduction in Communicate and maintain awareness of ITSCM to be responsible for ensuring the levels of IT A. required are
Provider any Service Level Requirements for any agree suitable IT Accounting policies, e.g. hardware based on SLRs and cost constraints objectives within the business areas supported and IT cost justified
proposed new/developing services Depreciation produces regular management reports which include Service areas. defining the targets of A. required for the IT Infrastructure and
analyses and reviews service performance against the assist in developing cost-benefit cases for IT current usage of resources, trends and forecasts Undertake regular reviews, at least annually, of the its components that underpin a new or enhanced IT Service as
SLAs and OLAs investments sizes all proposed new systems to determine the Continuity plans with the business areas to ensure the basis for an SLA
produces regular reports on service performance and advise senior management on the cost-effectiveness computer and network resources required, to that they accurately reflect the Business processing establishment of measures and reporting that reflect business,
achievement of IT solutions determine hardware utilisation, performance service Environment. User and IT support org. requirements
organizes and maintains the regular Service Level Charging: levels and cost implications Negotiate and manage contracts with providers of responsible for the monitoring of actual IT A. achieved vs
review process identify methods of charging within the organisations recommends resolutions to performance-related third party recovery services. targets and to ensure shortfalls are addressed
initiates any actions required to maintain or improve charging policy Incidents and Problems Manage the IT Service delivery during times of crisis to be responsible for the production and maintenance of an A.
service levels provide justifications and comparisons for charges recommends to IT management when to employ including: Plan which prioritises and plans IT A. improvements
conducts annual (as appropriate) reviews of the entire prepare regular bills for Customers
Demand Management, to dampen Customer o Co-ordination with the crisis control team to promote AM awareness and understanding within the IT
Service Level process and negotiates, agrees and demands on systems o Invocation of the appropriate recovery support organisation
prepare a price list of Services, if required
controls any amendments necessary carries out ad-hoc performance and Capacity studies facilities to maintain an awareness of technology advancements and IT
acts as co-ordination point for any temporary on request from IT management o Resource management, direction and best practice, e.g. ITIL.
Changes to service levels required is represented on the CAB, assessing and authorising arbitration
Changes o Recovery site management.
ensures that regular and ad hoc audits are carried out
on the Capacity Management process
SMART: Specific- Measurable- Achievable- Realistic - INTERFACES INTERFACES INTERFACES INTERFACES
Time based CfgM: IM- scripts for diagnostics SD, IM, PM ChM
SLA STRUCTURES - manages assets and cost information - performance counters - Provides historical data - Input from AM is details of the planed maintenance regime
Customer Based – With a customer group SLM : PM- scripts for diagnostics - Customer liaison - input to AM is schedule of planned maintenance activities
Service Based – For customers of a service (e-mail) - cost provision impacts service..; - performance counters ChM SLM
Multi-Level SLAs - Supplied with cost of meeting current and new ChM- assist in CAB assessing business impact - Ensures the on-going accuracy of continuity plans - provide information what is availability of the system for SLA
Corporate Level – cover generic SLM issues requirements - raise RFC if needed - - SLR provide availability requirements
Customer Level CM, AM: RM- helps with distribution strategy (network CfgM FM
Service Level - Supplied with cost of meeting cap. and avail. bandwidth,..) - Identifies the core infrastructure - input to FM is cost of nonavailability
- some data shared – e.g. Machine data sharing - after distribution capacity audits - output from FM cost associated with proposed upgrades to the
Meeting Customer Needs and Priorities: Customer
CfgM- gets information about CIs SLM infrastructure
satisfaction score/rating ; Average time to implement
SLA requests ; Number of SLAs in renegotiation ; - stores capacity information in CMDB - understands the obligations of IT service provision ITSCM
Number of SLAs requiring changes (targets not SLM - Perf. And capacity targets FM - output from ITSCM is business impact assessment
attainable, etc.) ; Number of SLA issues logged - assist SLM drafting OLAs - - Input from AM is the availability and design criteria tom
Adherence To Service Levels: Number of SLA targets FM - cost summary as part of capacity plan CM maintain “business as usual” by preventing or minimizing
missed ; Number of SLA targets threatened - resource utilization basis for charging - ensure business requirements are fully supported impact of failure by use CFIA
Providing Services Cost Effectively: Current cost per ITSCM - capacity needed for recovery options used trough the appropriate IT hardware resources CM
customer for delivery of services ; Percentage - maintain ITSCM capacity requirements in line with AM - input from AM is completed CFIA
improvement in delivery cost per customer production - delivers risk reduction measures to maintain - input from CM is capacity plan
Controlling Service Delivery: Number of OLA issues AM - Share common goal slow performance is business-as-usual
logged ; Number of Underpinning Contract issues effectively the same as unavailability
logged Cost types: AM methods and techniques
Maintaining Recognized Industry Acceptance For IT Hardware, Software, Employment, Accommodation, Redundancy and resilience
Quality: Number of ITs articles/white papers published ; External services and Transfer Component Failure Impact analysis (CFIA)
Percentage IT Operations staff in industry (i.e; itSMF) Cost Elements: Fault tree Analysis (FTA)
programs ; Percentage progress towards industry Breakdown of cost types (HW/ server/ NT/ HR server…) CCTA Risk Analysis & Management Method (CRAMM)
certification (i.e; ISO9000) ; Dollars spent on external Service Outage Analysis (SOA)
communications activities
Technical Observation Post (TOP)
Maintaining an IT Service Culture: Percentage of IT
Incident Lifecycle Management
Operations staff ITIL-aware ; Number of IT Operations
staff ITIL certified ; Number of IT Operations staff with Continuous Improvements
advanced ITIL certification ; Number Of Agreed SLAs
Not Supported By OLAs/UCs
SLA Content ELEMENTS of fin. management
General details Budgeting
Service hours Accounting
Roles and responsibilities Charging
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability & Fin Management Cycle
Serviceability Planning annual:
Service Performance Budgeting (agree overall expenditure)
Customer Support IT Accounting (Establish standard unit cost for each
Example incident targets IT resource)
Printing Charging (Establish Pricing policy, Publish price list)
IT Service Continuity Operational monthly:
Security Budgeting (take actions to manage budget
Change management Procedures expectations or charged costs)
Charging IT Accounting (Monitor Expenditure by cost-centre)
Quality / Customer perception Charging (Compile and issue bills)
Administration (Reporting, service reviews,..) http://itservicemngmt.blogspot.com/
You might also like
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDocument1 pageItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Ola TemplateDocument8 pagesOla Templatetoto_falaNo ratings yet
- ITSM Reference Architecture - ITSM - Whitepaper PDFDocument21 pagesITSM Reference Architecture - ITSM - Whitepaper PDFBensito CastilloNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapAllanNo ratings yet
- ITSMS Service Catalog TemplateDocument13 pagesITSMS Service Catalog TemplateMustafa AnisNo ratings yet
- Example Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateDocument13 pagesExample Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Poster 1Document1 pageITIL v3 Poster 1Andrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- ITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5Document38 pagesITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5danrodd100% (1)
- Business Communication TodayDocument39 pagesBusiness Communication TodaymzNo ratings yet
- ITIL Capacity Management: Much More Than Charts Over CoffeeDocument44 pagesITIL Capacity Management: Much More Than Charts Over CoffeeGary ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryDocument2 pagesITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryhyrtksnNo ratings yet
- ABC's IT Services CatalogDocument14 pagesABC's IT Services CatalogManav Patel100% (1)
- It Services and ManagementDocument18 pagesIt Services and ManagementAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Service Transition and SupportDocument14 pagesService Transition and SupportGopinath Akundy100% (1)
- Non-Functional Requirements SpecificationsDocument7 pagesNon-Functional Requirements SpecificationsAmr M. AminNo ratings yet
- Itil and The CMDBDocument5 pagesItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Guideline To Complete The Manual Balanced Scorecard TemplateDocument12 pagesGuideline To Complete The Manual Balanced Scorecard TemplateGheorg Armani OkparaNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Design MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Design MindmapIgor100% (3)
- Service DesignDocument55 pagesService DesignAniela OlteanuNo ratings yet
- WI WP ITSM ImplemetationWhite PaperDocument9 pagesWI WP ITSM ImplemetationWhite PaperalexandruNo ratings yet
- Be An IT Services Broker: HP Service Integration and ManagementDocument15 pagesBe An IT Services Broker: HP Service Integration and ManagementRamón AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Release and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MapDocument15 pagesRelease and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MappjoseptNo ratings yet
- ITSM Process Model v.1.0Document17 pagesITSM Process Model v.1.0DaptarDoangNo ratings yet
- Director IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusDocument2 pagesDirector IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusBurke MeanusNo ratings yet
- ITIL KPIs Service DesignDocument6 pagesITIL KPIs Service DesignAtaliba Lima100% (1)
- CA Service Catalog Advanced ConceptsDocument23 pagesCA Service Catalog Advanced Conceptsumairakhlaque78No ratings yet
- Service Delivery ManagerDocument3 pagesService Delivery Managervihusan68No ratings yet
- Process Improvement Calculations ToolsDocument65 pagesProcess Improvement Calculations ToolsNevets Nonnac100% (1)
- Achieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementDocument1 pageAchieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementgringoricanNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Introducing Service Design PDFDocument17 pagesITIL - Introducing Service Design PDFKumar Soubhagya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Account Based Marketing (Abm) : Logo Name Description Contact Details Accuracy PricingDocument3 pagesAccount Based Marketing (Abm) : Logo Name Description Contact Details Accuracy PricingKUSHAGRA ARORA100% (1)
- CAP Mindmap v4Document1 pageCAP Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Service Catalog Template DocDocument3 pagesService Catalog Template DocBabul BhattNo ratings yet
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- IT Service Catalog Template Provides Standard Development Laptop DetailsDocument3 pagesIT Service Catalog Template Provides Standard Development Laptop Detailspasc colcheteNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management (ITSM)Document4 pagesIT Service Management (ITSM)Saikat BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ITIL PresentationDocument16 pagesITIL PresentationEd Marshall100% (1)
- From Help Desk To Service DeskDocument57 pagesFrom Help Desk To Service DeskteacherignouNo ratings yet
- ITIL-Service StrategyDocument11 pagesITIL-Service StrategyTùng Phạm100% (1)
- ITIL Planning To Implement Service ManagementDocument12 pagesITIL Planning To Implement Service ManagementyellowsteelNo ratings yet
- Process Vs PraticesDocument1 pageProcess Vs PraticesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Core of ITILDocument15 pagesCore of ITILRajNo ratings yet
- Training ServicesDocument12 pagesTraining ServicesSanjay ParmarNo ratings yet
- ITIL+Service Operation 1203Document49 pagesITIL+Service Operation 1203Андрей ИвановNo ratings yet
- Service CatalogDocument10 pagesService Catalogmarcelorgs100% (2)
- Devops & Itsm:: Defining Value From Two Sides of The Same CoinDocument12 pagesDevops & Itsm:: Defining Value From Two Sides of The Same CoinAshish JainNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Service Request ManagementDocument3 pagesITIL v3 Service Request ManagementAbhirup SarkarNo ratings yet
- Service Delivery ManagerDocument4 pagesService Delivery Managerparadescartar100% (1)
- The CMDB As The Brain of ITDocument4 pagesThe CMDB As The Brain of ITmojo_92No ratings yet
- A Guide To Service Desk Concepts, Fourth EditionDocument328 pagesA Guide To Service Desk Concepts, Fourth EditionDSunte WilsonNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Transition - Invensis LearningDocument21 pagesITIL Service Transition - Invensis LearningInvensislearningNo ratings yet
- Sample Metrics For ITIL ProcessesDocument3 pagesSample Metrics For ITIL ProcessessantuchetuNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management (1) .A Companion To ITILDocument59 pagesIT Service Management (1) .A Companion To ITILYoshie Adi Purnama100% (2)
- 03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue JourneyDocument28 pages03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue Journeyarsman1100% (1)
- FNAL OLA TemplateDocument23 pagesFNAL OLA Templatehallarmemon0% (1)
- Problem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, BenefitsDocument26 pagesProblem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, Benefits1buckeyeNo ratings yet
- ITIL - An Example Schedule of Change PDFDocument1 pageITIL - An Example Schedule of Change PDFlemo100% (1)
- Lampiran 3 - Tatacara Penggunaan IDB Analyzer PDFDocument11 pagesLampiran 3 - Tatacara Penggunaan IDB Analyzer PDFzulhariszan abd mananNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Unit-VDocument41 pagesVlsi Unit-VJay SubbareddyNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Solved by FactorizationDocument131 pagesQuadratic Equations Solved by Factorizationsujaritha sureshNo ratings yet
- D Sub 50 PinDocument4 pagesD Sub 50 PinAhmed AyoupNo ratings yet
- Epson Error Codes - Quick GuideDocument3 pagesEpson Error Codes - Quick GuideJavier M. Garcia PérezNo ratings yet
- Agfa Drystar 5300 - Software Paches PDFDocument18 pagesAgfa Drystar 5300 - Software Paches PDFjamesNo ratings yet
- TBL-31-E-GMA - ED80-DL-113-EN-1-Wiring and Interconnection Diagram-Waste Water Central Monitoring BasinDocument6 pagesTBL-31-E-GMA - ED80-DL-113-EN-1-Wiring and Interconnection Diagram-Waste Water Central Monitoring BasinAjeng InsaniNo ratings yet
- Bayesian framework for building kinetic modelsDocument23 pagesBayesian framework for building kinetic modelsSHIVAM CHATURVEDI IET Lucknow StudentNo ratings yet
- Wheel Corner Module Technology and Concept AnalysisDocument83 pagesWheel Corner Module Technology and Concept AnalysisРуслан ИсмуллинNo ratings yet
- White3 ManualDocument22 pagesWhite3 ManualFaustoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft EPSDocument3 pagesMicrosoft EPSvikas kunduNo ratings yet
- No - Hands-On Assignment Topics Covered StatusDocument2 pagesNo - Hands-On Assignment Topics Covered StatusSHIVANo ratings yet
- NET201 Lab Experiment # 5 - Configuring IPv6 Static and Default RoutesDocument19 pagesNET201 Lab Experiment # 5 - Configuring IPv6 Static and Default RoutesJasmin Cez MabilanganNo ratings yet
- Introduction to VLSI Design FlowDocument3 pagesIntroduction to VLSI Design FlowManjunath B MNo ratings yet
- Spring Boot: Working With Application Runner: - by RAGHU SIR, Naresh ITDocument4 pagesSpring Boot: Working With Application Runner: - by RAGHU SIR, Naresh ITVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assessment Types - Daniel MiesslerDocument11 pagesInformation Security Assessment Types - Daniel Miesslersyed muffassirNo ratings yet
- Informatica: Import Source File - StoreDocument11 pagesInformatica: Import Source File - StoreDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is New in PTV Vissim/Viswalk 11Document20 pagesWhat Is New in PTV Vissim/Viswalk 11Billy BrosNo ratings yet
- FoxPro Programming Using FoxPro 2.6 or HigherDocument82 pagesFoxPro Programming Using FoxPro 2.6 or HigherARIN PERNES40% (5)
- Splunk Fun 2 w o answersDocument23 pagesSplunk Fun 2 w o answersfatouNo ratings yet
- Hassinen TarmoDocument77 pagesHassinen TarmoSibusiso Charlie OlyphantNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument105 pagesChapter IVaira catubagNo ratings yet
- Db4o 4.5 Tutorial JavaDocument156 pagesDb4o 4.5 Tutorial JavanyellutlaNo ratings yet
- Citroenforum hr-MIRASCRIPT PDFDocument6 pagesCitroenforum hr-MIRASCRIPT PDFNemanja BoricNo ratings yet
- Smart Energy Consumption Monitoring System (E-Save) ProposalDocument10 pagesSmart Energy Consumption Monitoring System (E-Save) ProposalMichael GaladoNo ratings yet
- Shpakova GamificationandinnovationDocument21 pagesShpakova GamificationandinnovationLena KremmerNo ratings yet
- IpcDocument41 pagesIpcAnonymous ZCrVvMdNo ratings yet
- User Manual For PileGroupDocument120 pagesUser Manual For PileGroupmyplaxisNo ratings yet
- Global Threat Report by CrowdStrike 2023Document42 pagesGlobal Threat Report by CrowdStrike 2023Chris Lemieux100% (1)