Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Credit Transactions (Di Ko Xur)
Uploaded by
Crislene Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document discusses different types of redemption in credit transactions and distinguishes between related concepts:
1. There are two types of redemption - equity of redemption which allows the mortgagor to redeem the mortgaged property before sale in cases of judicial foreclosure, and right of redemption which allows redemption within one year of registration of the certificate of sale in cases of extrajudicial foreclosure.
2. Guaranty and suretyship are distinguished: in guaranty the guarantor is primarily liable while the surety is secondarily liable, and the guarantor insures the debtor's solvency while the surety insures the debt.
3. Commodatum and mutuum are
Original Description:
its all about credit transaction
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of redemption in credit transactions and distinguishes between related concepts:
1. There are two types of redemption - equity of redemption which allows the mortgagor to redeem the mortgaged property before sale in cases of judicial foreclosure, and right of redemption which allows redemption within one year of registration of the certificate of sale in cases of extrajudicial foreclosure.
2. Guaranty and suretyship are distinguished: in guaranty the guarantor is primarily liable while the surety is secondarily liable, and the guarantor insures the debtor's solvency while the surety insures the debt.
3. Commodatum and mutuum are
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCredit Transactions (Di Ko Xur)
Uploaded by
Crislene CruzThe document discusses different types of redemption in credit transactions and distinguishes between related concepts:
1. There are two types of redemption - equity of redemption which allows the mortgagor to redeem the mortgaged property before sale in cases of judicial foreclosure, and right of redemption which allows redemption within one year of registration of the certificate of sale in cases of extrajudicial foreclosure.
2. Guaranty and suretyship are distinguished: in guaranty the guarantor is primarily liable while the surety is secondarily liable, and the guarantor insures the debtor's solvency while the surety insures the debt.
3. Commodatum and mutuum are
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
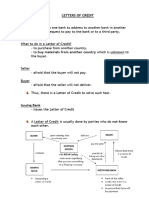
Civil code- credit transactions?? naa pud sa Commercial Law???
1.What are the kinds of redemption?
Category: Credit Transactions 1. Equity of redemption right of mortgagor to redeem the mortgaged property after his default in the performance of the conditions of the mortgage but before the sale of the mortgaged property or confirmation of sale. It applies in case of judicial foreclosure.
1. Right of redemption right of the mortgagor to redeem the mortgaged property within one year from the date of registration of the certificate of sale. It applies in case of extrajudicial foreclosure.
2.
Difference Between Guarantee and Suretyship
Category: Credit Transactions
What is the distinction between Guaranty and Suretyship?
1. Guaranty is collateral while Surety is an original promissory undertaking. 2. In guaranty, the guarantor is primarily liable while in suretyship, the surety is secondarily available. 3. The guarantor binds himself to pay if the principal cannot pay. The surety undertakes to pay if the principal does not pay. 4. The guarantor is the insurer of the solvency of the debtor. The surety is the insurer of the debt.
5. The guarantor can avail of the benefit of excussion and division in case the creditor proceeds against him. The surety cannot avail of the benefit of excussion and division.
3.Distinguish Commodatum from Mutuum
Category: Credit Transactions
Distinction Between Commodatum and Mutuum
1. The object of commodatum are Non-consumable (Non-fungible); in Mutuum Consumable goods. 2. The cause for commodatum is Gratuitous otherwise it is a lease; in Mutuum it may or may not be gratuitous. 3. The purpose in commodatum is for use or temporary possession; in mutuum it is for consumption. 4. The subject matter in commodatum is real or personal property while it is only personal property in mutuum. 5. The ownership of the thing is retained by the the bailor in commodatum while in mutuum, it passes to the debtor. 6. The thing to be returned in commodatum is the exact thing loaned while in mutuum, it is a thing of equal amount of the same kind and quality. 7. In commodatum, it is the bailor who bears the risk of loss; while in mutuum, it is the debtor. 8. In commodatum, the thing maybe returned even before the expiration of the term in urgent cases; however, in mutuum, it must be after the expiration of the term. 9. Commodatum is a contract of use while mutuum is a contract of consumption.
You might also like
- Recovery in Credit GrantedDocument21 pagesRecovery in Credit GrantedMaria Ysabella Yee80% (5)
- CREDIT TRANSACTIONS GUIDEDocument12 pagesCREDIT TRANSACTIONS GUIDESean Asco Ruma75% (4)
- Cybercrimes Under The Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012Document6 pagesCybercrimes Under The Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Cridit Managment: MBA Banking & Finance 3 TermDocument24 pagesCridit Managment: MBA Banking & Finance 3 Term✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- Understand Charges and SecuritiesDocument17 pagesUnderstand Charges and SecuritiesTharani BalajiNo ratings yet
- Commodatum and MutuumDocument1 pageCommodatum and MutuumMary Joy DomantayNo ratings yet
- Unit III Contract of Pledge and PawnDocument16 pagesUnit III Contract of Pledge and PawnHemanta PahariNo ratings yet
- Commercial Credits & Sale of GoodsDocument109 pagesCommercial Credits & Sale of GoodsRomsamBla100% (2)
- Business LawsDocument106 pagesBusiness Lawsaakanshatyagi030303No ratings yet
- Synopsis of Law On PledgeDocument3 pagesSynopsis of Law On PledgeBrian JavierNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions, Loans, First Part of Commodatum and MutuumDocument12 pagesCredit Transactions, Loans, First Part of Commodatum and MutuumJohn Lexter Macalber50% (2)
- Contract of LoanDocument5 pagesContract of LoanzellyNo ratings yet
- Securities For AdvancesDocument3 pagesSecurities For AdvancesWaqas TariqNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions NotesDocument3 pagesCredit Transactions NotesAlyk Tumayan CalionNo ratings yet
- Credit TransDocument45 pagesCredit TransliboaninoNo ratings yet
- Bailment Pledge & MortgageDocument6 pagesBailment Pledge & MortgageAyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- LAB question Bank 2024Document11 pagesLAB question Bank 2024SharvariNo ratings yet
- Law ReviewerDocument16 pagesLaw ReviewerAngel AsisNo ratings yet
- Ijara-Based Financing: Definition of Ijara (Leasing)Document13 pagesIjara-Based Financing: Definition of Ijara (Leasing)Nura HaikuNo ratings yet
- Bailment & Pledge-FinalDocument11 pagesBailment & Pledge-FinalAbhishek JainNo ratings yet
- Bailment and PledgeDocument8 pagesBailment and Pledgemuazzamali533100% (1)
- Handout - BAILMENTDocument7 pagesHandout - BAILMENTaanyaNo ratings yet
- Contract of IndemnityDocument21 pagesContract of IndemnitysaadRaulNo ratings yet
- Indemnity & Guaranty, Contract of Bailment and Contract of AgencyDocument10 pagesIndemnity & Guaranty, Contract of Bailment and Contract of Agencyahmad rezaNo ratings yet
- What Is Mortgage Markets?Document8 pagesWhat Is Mortgage Markets?Hades RiegoNo ratings yet
- Meaning of a MortgageDocument8 pagesMeaning of a MortgageSurendrasingh ZalaNo ratings yet
- Mba Iii - T N Rao - LabDocument73 pagesMba Iii - T N Rao - LabmehulNo ratings yet
- Fin 103 - Final Notes Recovery of Credit GrantedDocument10 pagesFin 103 - Final Notes Recovery of Credit GrantedDianara PagarNo ratings yet
- Modes of Charging SecuritiesDocument11 pagesModes of Charging SecuritiesKopal Agarwal50% (4)
- Credit Transactions GuideDocument12 pagesCredit Transactions GuidermelizagaNo ratings yet
- Special ContractDocument22 pagesSpecial Contractbas 2minNo ratings yet
- BAM 242 Credit TransactionsDocument18 pagesBAM 242 Credit TransactionsAndrea GarinNo ratings yet
- Hypothecation and PledgeDocument13 pagesHypothecation and PledgeSanjit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Banker and CustomerDocument10 pagesRelationship Between Banker and Customerswagat098No ratings yet
- Types of Mortgages in India DefinedDocument6 pagesTypes of Mortgages in India Definedravi1214No ratings yet
- Types of SecuritiesDocument8 pagesTypes of SecuritiesA U R U M MDNo ratings yet
- Bailment and PledgeDocument25 pagesBailment and PledgeSalman AnsariNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions by Pineda PDFDocument12 pagesCredit Transactions by Pineda PDFNyl John Caesar GenobiagonNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Types GuideDocument5 pagesMortgage Types GuideSaurabh AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document79 pagesChapter 4Aliza NazarNo ratings yet
- 9236 - Pledge and Mortgage NotesDocument5 pages9236 - Pledge and Mortgage NotesmozoljayNo ratings yet
- L9.Slides.Security(1)Document6 pagesL9.Slides.Security(1)aakintunde07No ratings yet
- Void and Voidable ContractDocument10 pagesVoid and Voidable ContractSupriya BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Credit Trans - NotesDocument18 pagesCredit Trans - NotesCath VillarinNo ratings yet
- Borrowed To Complete A Certain Project) Calculator Mo Nang Hindi Nagpapaalam at Hinayaan Mo Lang)Document2 pagesBorrowed To Complete A Certain Project) Calculator Mo Nang Hindi Nagpapaalam at Hinayaan Mo Lang)Moises A. AlmendaresNo ratings yet
- Special Contracts: 1. Delivery of Goods - It MayDocument8 pagesSpecial Contracts: 1. Delivery of Goods - It MayHarsh Gupta100% (1)
- All Other Law Nov 2019 PDFDocument148 pagesAll Other Law Nov 2019 PDFGaurav Patel100% (2)
- Commercial TransactionsDocument5 pagesCommercial TransactionsElizabeth ChilufyaNo ratings yet
- REY ALMON T. ALIBUYOG CREDIT TRANSACTIONSDocument4 pagesREY ALMON T. ALIBUYOG CREDIT TRANSACTIONSRey Almon Tolentino AlibuyogNo ratings yet
- Law On Sales, Agency and Credit Transactions Part 4Document60 pagesLaw On Sales, Agency and Credit Transactions Part 4PierreNo ratings yet
- Unit II Contract of BailmentDocument34 pagesUnit II Contract of BailmentHemanta PahariNo ratings yet
- Business Regulations-notesDocument22 pagesBusiness Regulations-notesallentyler858No ratings yet
- Concept of Security in Banking SectorDocument9 pagesConcept of Security in Banking SectorSNo ratings yet
- Law of Contracts II Module 1: Rights of IndemnityDocument83 pagesLaw of Contracts II Module 1: Rights of Indemnityskkaviya sethilrajakirthikaNo ratings yet
- Indemnity and GuaranteeDocument42 pagesIndemnity and GuaranteeAbhyudaya GargNo ratings yet
- Study Credit TransactionsDocument9 pagesStudy Credit TransactionsMojiNo ratings yet
- Credit Transaction Premid HONGDocument87 pagesCredit Transaction Premid HONGJetJuárezNo ratings yet
- LOANSDocument7 pagesLOANSJulia San JoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Credit NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 16 - Credit NotesEthan WongNo ratings yet
- Article 1933-1940Document4 pagesArticle 1933-1940Maricon AsidoNo ratings yet
- Isaac SpeechDocument1 pageIsaac SpeechCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Supreme Court ManilaDocument10 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Supreme Court ManilaDanilo Dela ReaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Bar Bulletin No. 1Document3 pages2013 Bar Bulletin No. 1Eli Benjamin Nava TaclinoNo ratings yet
- Requirements For The Bar Examinations For RepeatersDocument1 pageRequirements For The Bar Examinations For RepeatersCoolbuster.Net100% (1)
- Science AssignDocument2 pagesScience AssignCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Credit Card OverchargingDocument2 pagesCredit Card OverchargingCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE II & III Phil. ConstitutionDocument3 pagesARTICLE II & III Phil. ConstitutionCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Other Bar MattersDocument5 pagesOther Bar MattersCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- RA 7890 - Amending Art. 286, Sec. 3, Chapter 2, Title 9 of RA 315 As Amended (Revised Penal Code)Document2 pagesRA 7890 - Amending Art. 286, Sec. 3, Chapter 2, Title 9 of RA 315 As Amended (Revised Penal Code)Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- RA 8177-Designating Death by Lethal Infection For Capital Punishment Etc...Document2 pagesRA 8177-Designating Death by Lethal Infection For Capital Punishment Etc...Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Repeal of Anti-Subversion Act RA 1700Document1 pageRepeal of Anti-Subversion Act RA 1700Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Rules 1 71Document8 pagesRules 1 71Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- PD 38-Amending Articles 135, 136, 137, 138, 140, 142, 177, 178 and 179 of The Revised Penal CodeDocument3 pagesPD 38-Amending Articles 135, 136, 137, 138, 140, 142, 177, 178 and 179 of The Revised Penal CodeCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- TITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersDocument11 pagesTITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- RA 8249: Amends PD 1606 expanding Sandiganbayan jurisdiction over graft casesDocument6 pagesRA 8249: Amends PD 1606 expanding Sandiganbayan jurisdiction over graft casesCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethics MCQDocument21 pagesLegal Ethics MCQCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- TITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersDocument11 pagesTITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Promisory NoteDocument1 pagePromisory NoteCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- TITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersDocument11 pagesTITLE VII of RPC - Crimes Committed by Public OfficersCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Executive Order 12 - Creating The Presidential Anti-Graft Commission EtcDocument14 pagesExecutive Order 12 - Creating The Presidential Anti-Graft Commission EtcCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Book One - Articles 1-113Document51 pagesBook One - Articles 1-113Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Land Titles and DeedsDocument253 pagesLand Titles and DeedsCrislene Cruz100% (3)
- Proof of ServiceDocument1 pageProof of ServiceCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Title of A Pleading(s)Document1 pageTitle of A Pleading(s)Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Signature of CounselDocument1 pageSignature of CounselCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Value Added TaxDocument10 pagesValue Added TaxCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- The New Rules of Procedure of NLRC (As Amended Series 2002)Document26 pagesThe New Rules of Procedure of NLRC (As Amended Series 2002)Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Verification: DefinitionDocument1 pageVerification: DefinitionCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument1 pageSpecial Power of AttorneyCrislene CruzNo ratings yet