Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Materials Engineer REVIEWER
Uploaded by
Jomz OlañoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Materials Engineer REVIEWER
Uploaded by
Jomz OlañoCopyright:
Available Formats
Materials Engineer
1. In soil Engineering the term SOIL includes a. clay b. gravel c. sand d. all of the preceding 2. The compressibility of a fine grained soil is a. high b. low c. it depends upon the grain size 3. Sand has a greater load-carrying capacity than clay a. true b. false c. it depends on gradation d. it depends on water content 4. The highest moisture content in the plastic consistency of fine-grained soil is the liquid limit a. plastic limit b. shrinkage limit 5. Compaction increases the strength of soil by a. expelling air from its voids b. forcing soil particles into more intimate contact c. both a and b 6. Indicates a range of moisture content over which soil is plastic a. plastic limit b. shrinkage limit c. plasticity index 7. Water content of an undisturbed soil is called a. optimum moisture content b. hygroscopic moisture content c. natural water content 8. In the performance of Moisture Density Relations Test, the equipment used is a. liquid limit device b. sand-cone apparatus c. rammer and mold d. none of the above 9. Peat and muck are a. fair subgrade soils b. stable soils c. unstable soils d. good subgrade soils
10. The particle size distribution of a soil is determined by a. liquid limit test b. sieve analysis test c. plastic limit test d. any of the preceding 11. To prevent intrustion of soft subgrade material into the aggregate base or subbase a. reinforced earth b. rock buttress c. gabions d. geotextile may be used 12. The CBR value is generally selected at a. 0.10 b. 0.0375 c. 0.05 d. 0.20 penetration 13. One of the methods in improving the properties of a soil to make it suitable for a particular purpose is a. particle rearrangement b. sodding or sprigging c. paving d. none of the preceding 14. A sample of saturated clay has a mass of 102.8 g. After oven drying, the same soil weighs 73.4 g. If the specific gravity is 2.74, its wet density, g/ml is a. 1.829 b. 1.825 c. 1.827 d. 1.830 15. The dry density, g/ml is a. 1.310 b. 1.306 c. 1.300 d. 1.309 16. Blown Asphalt are usually used for paving a. true b. false c. it depends upon its ductility 17. A mixture of asphalt cement and water with emulsifying agent is called a. R. C. cutback b. M. C. cutback c. Asphalt emulsion d. Oxidized asphalt 18. The a) Marshall Stability Test b) Immersion-Compression Test c) Job-Mix formula compares the compressive strength of dry and wet specimens of asphalt mixes. 19. The effective asphalt content is a) lower than b) higher than c) equal to the actual asphalt content.
20. Which of the following percent air voids is most preferable in bituminous mixture a. 0% b. 5% c. 8% 21. a) Viscocity b) solubility c) Flash point d) Extraction test determines the bitumen content of asphalt cement 22. a) Distillation b) Penetration c) Viscocity d) Ductility is the consistency test on solid asphalt. 23. a) Tack coat b) Prime coat c) Seal coat is the bituminous coating applied to an old concrete pavement to be used as base. 24. A Job-mix formula provides for close control of a. asphalt content b. aggregate gradation c. both a and b 25. a) Flexibility b) Durability c) Stability d) Workability is the resistance of an asphalt pavement against weathering. 26. The temperature of hot mixes being delivered should not be less than its a. mixing b. application c. heating d. compaction temperature 27. A Bituminous Seal Coat is usually applied with aggregate a. true b. false c. it depends on the surface application 28. The maximum specific gravity of an asphalt mix containing 6.0% asphalt by weight of mix is 2.6. If the specific gravity of an asphalt is 1.01, the specific gravity of the aggregate is equal to a. 2.65 b. 2.56 c. 2.76 d. 2.70 29. The weight in air of a core specimen taken from asphalt pavement is 4,128 g. If its SSD weight is 4,137 g. and its weight in water is 2,237 g. Therefore, its bulk density is a. 2.42 b. 1.72 c. 2.28 d. 2.69 30. The bulk specific gravity of a sample of bituminous pavement taken from a newly rolled section is 2.244. If the laboratory compacted specific gravity is 2.362 and the minimum compaction requirement is 95%, the pavement is a. satisfactorily rolled b. over compacted c. in need of more rolling
31. Concrete specimen molded in a 6 x 6 x 21 beam mold should be rodded a. 60 b. 61 c. 62 d. 63 times 32. Quality determination of concrete coarse aggregate sample requires a. abrasion test b. sieve analysis c. stability d. both a and b 33. Concrete fine aggregate should be tested for a. compaction b. stripping c. stability d. none of the preceding 34. Admixtures are used to a. improve workability b. increase strength c. retard initial setting d. all of the preceding 35. a) Compressive strength b) Flexural strength c) Bond d) All of the preceding will improve if water cement ratio is lowered. 36. Angular coarse aggregate will require more a. sand b. water c. both a and b d. coarse aggregate per unit volume of concrete. 37. Slump test could be used to detect a. increase in cement content b. increase in water c. increase in volume d. increase in aggregate 38. Greatest net water is required in a concrete mix with a. very coarse b. coarse c. fine d. very fine, fine aggregate 39. If the concrete beam specimen is raptured during test outside the middle third, but within 5% of the span length, the formula to be used in computing the stress is a. R = PL/bd2 b. R = 3Pa/bd2 c. R = Pla/bd2 40. Concrete mix should be in placi a. 100 min b. 90 min
c. 15 min, after the cement is added into the aggregates and water. 41. The fineness modulus is highest for a. coarse b. very coarse c. fine d. very fine, sand. 42. In molding concrete cylinder specimen, each layer should be rodded a. 25 b. 56 c. 60 d. 100 times. 43. Concrete cylinder sample should be molded in a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 equal layers. 44. Maintaining the water-cement ratio, the concrete containing a. 50.0 mm b. 37.5 mm c. 19.0 mm d. 12.5 mm maximum size aggregate will develop the highest strength. 45. Paving concrete will need less a. sand b. water c. coarse aggregate d. both a & b, than that of structural concrete. 46. The maximum percentage of abrasion loss allowed for concrete coarse aggregate is a. 40 b. 45 c. 50 47. For Bituminous Concrete Surface Course, if asphalt cement is used, the percentage based on the weight of aggregate should be a. 3 to 5% b. 5 to 8% c. 6 to 10% 48. An aggregate base course of 21,600 m3 will require a. 14 b. 15 c. 72 quality tests. 49. Coarse aggregate for Crushed Stone Aggregate Surface Course should have not less than a. 40 b. 45 c. 50 d. 60 with at least one fractured face
50. Crushed Gravel Base Course, Grading C, shall be compacted in layers of not more than a. 10 cm b. 15 cm c. 20 cm loose thickness. 51. An embankment to be constructed to a height of 65 cm will have a minimum of a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 layers. 52. To give Bituminous Plant Mix Base Course greater to resistance to water a. to 1% b. 1 to 2% c. 2 3% hydrated lime should be added during mixing. 53. The type of Bituminous Macadam Pavement is a. asphalt cement b. asphalt emulsion c. rock asphalt d. either a or b. 54. Prestressed Concrete Structures use concrete class a. A b. B c. C d. D 55. a) 5 b) 9 c) 3 pipes should be taken as sample to represent 225 reinforced concrete pipes. 56. Before placing the asphalt pavement, the gravel base course should be a. seal coated b. tack coated c. prime coated 57. Concrete used in reinforced concrete culvert pipe should generally have a compressive strength of a a. 16.54 Mpa ( 2400) b. 27.56 Mpa ( 4000) c. 20.67 Mpa ( 3000) d. 34.45 Mpa ( 5000)
58. Concrete railings, pipes, and piles require the use of what class of concrete? a. A b. B c. C d. D 59. Steel bars for concrete reinforcement is tested for its a. tensile b. compression c. bending d. both a and c for properties.
60. Aggregate Base Course with a volume of 112,000m3 will have a minimum number of a. 74 b. 75 c. 56 d. 374 quality tests. 61. Which plasticity index is most suitable for aggregate base course? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 50 The fraction passing the 0.425 mm (No.40) shall have a liquid limit not greater than 25 and plasticity index not greater than 6. 62. The specified flexural strength for paving concrete is a. 350 b. 400 c. 525 d. 300 63. The sample of 12.5 mm diameter steel bar to be submitted for test should be at least a. 20 cm b. 40 cm c. 100 cm d. none of the above 64. a) Third point loading b) Three-edge bearing test c) Mid-span loading d) none of the above method used in determining the strength of concrete pipes. 65 Prestressed concrete requires the use of Class a. A b. B c. C d. D concrete 66. If an asphalt pavement will be constructed over an old existing concrete pavement a. prime coat b. tack coat c. seal coat d. mortar coat should be applied to the concrete pavement. 67. For bituminous concrete mixes, the asphalt material may either be asphalt cement or asphalt emulsion a. true b. false 68. Coarse Aggregate for Bituminous Macadam Pavement should be a. crushed gravel or stone b. natural gravel c. both a and b d. none of the above 69/70. Tests for coarse aggregate include a. abrasion b. mortar strength is the
c. absorption d. all of the preceding 71/72. Tests for fine aggregate for concrete include a. gradation b. mortar strength c. abrasion d. all of the preceding 73. Unless otherwise specified in the special provision, the type of portland cement used in paving concrete shall be a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III d. Type IV 74. During construction of a road project, if all the materials to be used are tested for quality, inspection is no longer required a. true b. false 75. The degree of compaction of an embankment in our present Specifications is based on a. CBR method b. Unconfined compression test c. AASHTO Designation T-180 d. Bulk Specific Gravity 76/77. Under Excavation for Structure, Item 106, the backfilling operation shall be done in 20 cm loose layer and compacted to at least 95 Percent. 78. Soils are natural aggregates of minerals connected by strong and permanent cohesive forces a. true b. false 79. The boundary between sand and gravel is a. 0.425 mm (#40) b. 4.750 mm (#4) c. 2.00 mm (#10) d. 0.075 mm (#200) 80. A a) sandy clay b) clayey sand c) sand clay d) none of the preceding is a soil which exhibits the properties of a clay but contains an appreciable amount of sand. 81. Plasticity test is done on soils passing a. 0.425 mm (#40) b. 2.00 mm (#10) c. 0.075 mm (#200) sieve. 82. a) Soil compaction b) mechanical analysis c) In-place unit weight d) CBR is the process whereby soil particles are contained more closely together through a reduction in the air voids, generally by mechanical means. 83. Soils containing more than 35% passing 0.075mm (#200) sieve are classified under a. silt-clay materials b. granular materials
c. it depends on the plasticity index 84. a) Surface drainage b) chemical admixtures c) compaction d) subsoil drainage is provided for the purpose of counteracting moisture movement within the structure either by seepage or capillary action. 85. A subgrade soil with a CBR value of a) 5% b) 15% c) 30% d) 3% will require a thicker layer of subbase and base course. 86. a) Particle arrangement b) sodding or sprigging c) paving d) flattening is one of the methods of stabilizing inferior soils. 87. The physical and engineering properties of soils may be improved by a. compaction b. stabilization c. both a and b d. neither a nor b. 88. Water content of soils is generally based on the a. total weight of soil b. total volume of soil c. weight of solids d. none of the preceding 89. The density to which a soil can be compacted is related to a. compactive efforts b. water content c. both a and b d. none of the preceding 90. Disturbed samples may be used for a. sieve test b. liquid limit c. compaction test d. any of the preceding 91. A soil with a Group Index of 5 is stronger than another with a Group Index of 10 a. true b. false c. it depends on the water content 92. a) Water content b) void ratio c) degree of saturation d) porosity determines the relative amount of water in the voids. 93 a) Rock asphalt b) Asphalt emulsion c) asphalt cement d) cutback asphalt is an asphalt formed by natural process of evaporation. 94. Uncrushed aggregates are preferable than crushed aggregates for bituminous mixtures a. true b. false c. it depends on the type of bituminous material 95. The apparatus used in determining the consistency of liquid asphalt is the a. flowmeter
b. viscometer c. penetrometer d. pycnometer 96. a) Solid b) liquid c) Blown d) hot asphalt is preferable for bituminous prime coat. 97. a) Distillation b) Extraction c) Penetration d) Solubility is the test used in determining amount of asphalt cement in a liquid asphalt. 98. a) Asphalt cement b) cut-back asphalt c) asphalt mixes d) asphalt emulsion are usually tested for extraction. 99. Extraction test is the procedure used for separating a. the asphalt from water in emulsified asphalt b. asphalt from mineral aggregates c. asphalt from kerosene solvent d. asphalt from gasoline solvent 100. The optimum asphalt content obtained in a Marshall Stability test is the average of the asphalt content of the Maximum Stability, Maximum density and a. Maximum flow b. Maximum air voids c. 4% air voids d. 4% flow 101. a) VMA b) Air voids c) Permeable voids are intergranular void spaces between aggregate particles. 102. The main difference between a bulk measured specific gravity of a bituminous mixtures and its maximum measured specific gravity is the a. weight of the voids b. weight of the asphalt c. volume of the voids d. volume of the aggregates 103. a) Asphalt cement b) emulsified asphalt c) Rapid curing d) medium curing cut-back is the best type of asphalt to be used for hot mixes. 104. A bituminous coating applied in an existing road prior to laying of a bituminous surface overlay is a. prime coat b tack coat d. seal coat 105. The distance traveled by a standard penetration needle on a prepared sample of asphalt under conditions for normal penetration is 8.6 mm. The material is a. 40 50 b. 85 100 c. 120 150 d. 200 300 penetration grade 106. The maximum specific gravity of an asphalt mix containing 6.0% asphalt by weight of mix is 2.5. if the specific gravity of the asphalt is 1.01, the specific gravity of the aggregate is equal to a. 2.65 b. 2.56 c. 2.76 d. 2.70
107. A job-mix formula provides for close control of a. aggregate gradation b. asphalt content c. both of them d. neither of them 108. The desired property of fresh concrete is a. strength b. durability c. workability d. water tightness 109. The sieve used in the separation of aggregates after the abrasion test is a. 1.70mm ( No. 12 ) b. 0.425mm ( No. 40 ) c. 4.75mm ( No. 4 ) d. 0.075mm ( No. 200 ) 110. Normally, concrete mix with a) 0.75 b) 0.35 c) 0.50 d) 0.45 water-cement ratio will develop the lowest strength. 111. a. b. c. d. 112. a. b. c. d. 113. a. b. c. d. 114. a. b. c. d. 115. a. b. c. d. The most important single factor which affects the quality of concrete is cement content aggregate gradation water-cement ratio aggregate quality Paving concrete will need less sand water coarse aggregate both a and b than that of structure concrete. Concrete specimen molded in a 6x6x21 beam should be rodded 60 61 62 63 Quality determination of concrete coarse aggregate sample requires abrasion test sieve analysis stability both a and b Concrete mix should be in place 100 minute 120 15 90 after the cement is added into the aggregate and water.
116. a. b. c. d. 117. a. b. c. d. 118. a. b. c. d. 119. a. b. c. d.
Concrete beam specimens for paving concrete are molded in 2 equal layers 3 equal layers 4 equal layers any of the preceding A minimum cement factor of 7.5 8.5 9.5 10.0 bags/cubic meter of concrete is required for paving concrete (Based on the 94 lbs. Bag of cement) The volume of the concrete cement air all of the preceding can be calculated by performing the unit weight test on the fresh concrete. The used of manufactured fine aggregate will generally require more mixing water fine aggregate coarse aggregate both a and b.
120. The two (2) major components of concrete are a. paste and mineral aggregates b. cement and water c. water and coarse aggregates 121. The coarser the fine aggregate, the higher the fineness modulus a. yes b. no c. depends on grading test 122. The more the concrete is exposed, the greater the range of movement is a. true b. false c. it depends upon the type of cement 123. The samples of RSB to be submitted for test should be at least a. 20 cm b. 40 cm c. 100 cm 124. The efficient compaction, the embankment material should at the time of rolling be a. dry b. wet c. at optimum moisture content 125. a) 15,000 kg b) 10,000 kg c) 5,000kg of 12.5mm diameter steel bar for concrete reinforcement is the maximum quantity that a sample can represent.
126
a) Rock asphalt b) asphalt emulsion c) Asphalt cement d) Cut-back asphalt is an asphalt formed by natural process of evaporation.
127. Uncrushed aggregates are preferable than crushed aggregates for bituminous mixtures a. true b. false c. it depends on the type of bituminous material. 128. The apparatus used in determining the consistency of liquid asphalt is the a. flowmeter b. viscometer c. penetrometer d. pycnometer 129. a) Solid b) liquid c) blown d) hot asphalt is preferable for bituminous prime coat. 130. a) Distillation b) Extraction c) Penetration d) solubility is the test used in determining the amount of asphalt cement in a liquid asphalt. 131 . a) Asphalt cement b) Cut-back asphalt c)Asphalt mixes d) Asphalt emulsion are usually tested for extraction.
132. Extraction test is the procedure used for separating a. the asphalt from water in emulsified asphalt b. asphalt from mineral aggregates c. asphalt from gasoline solvent d. asphalt from kerosene solvent. 133. a) Distillation b) Viscosity c) Flash point d) Softening point indicated the safe working temperature of the asphalt. 134. The optimum asphalt content obtained in a Marshall Stability Test is the average of the asphalt content of the Maximum stability, maximum density and a. maximum flow b. maximum air voids c. 4% air voids d. 45 flow 135. a) VMA b) Air voids c) Permeable voids are intergranular void spaces between aggregate particles. 136 . a) Asphalt cement b) Emulsified asphalt c) rapid curing cut-back d) medium curing cutback is the best type of asphalt to be used for hot mixes.
137. The field density of a bituminous pavement shall not be less than a. 92 % b. 95 % c. 98 % of the specific gravity of the laboratory compacted specimen. 138. For ITEM 311 PCC pavement, coarse aggregate shall have a mass percent of wear not exceding a. 50 % b. 40 % c. 45 % d. 60 % when tested by AASHTO T- 96.
139. Plasticity Index for Aggregate Surface Course is a. not greater than 6 b. not greater than 25 c. 4 to 9 d. 12. 140. At least one (1) set of 3 concrete cylinder samples shall be taken from a. 50 b. 75 c. 100 d. 150 cubic meter of each class of concrete or fraction thereof, placed each day. 141. Fine aggregates used in concrete pavement shall contain not more than a. 1.5 b. 3 c. 4 d. 1 percent of material passing the 0.075mm sieve by washing. 142. The degree of compaction required for embankment is at least a. 100 b. 90 c. 95 d. 85 percent of the maximum density as determined by AASHTO T-90 Method. 143. Requirement of PCCP Construction a. opening to traffic after 14 days the concrete was placed b. opening to traffic after 28 days the concrete was placed c. a compressive strength of 25.08 Mpa or more d. none of the above. 144. Roadway embankment in earth material shall be placed and compacted in horizontal layers not exceding a. 150 mm b. 200 mm c. 100 mm d. 250 mm loose requirement, before the next layer is placed. 145. Steel bars for concrete reinforced is tested for its a. tensile b. compressive c. yield d. both a and c. 146. To give Bituminous Concrete Surface Course greater resistance to water a. 2 - 3 % b. 1 - 2 % c. - 1 % d. 4 5 % hydrated lime should be added. 147. In Aggregate Subbase Course, the degree of compaction of each layer shall continue until a field density of at least a. 100
b. 95 c. 90 percent of the maximum dry density determined in accordance with AASHTO T-180, Method D has been attained. 148. The maximum percentage wear allowed for Aggregate Subbase Course in a coarse portion retained on a 2.00mm (No. 10) sieve is a. 45 b. 50 c. 40 d. 55 percent by Los Angeles Abrasion Test determined by AASHTO T-96. 149. In manufacture of culvert pipes, the class of concrete used is a. Class C b. Class B c. Class A d. Class P 150. For Bituminous Concrete Surface Course, if Asphalt cement is used, the percentage based on the weight of aggregate should be a. 3 to 5 % b. 5 to 8 % c. 6 to 10 % d. 4.5 to 8 % 151. Coarse aggregate for Crushed stone Aggregate Surface Course should have a mass percent of not more than a. 40 % b. 45 % c. 60 % d. 50 % of the particle retained on the 4.75mm (No.4) sieve and shall have at least one (1) fractured face. 152. Before placing the asphalt pavement, the gravel base course should be a. seal coated b. tack coated c. prime coated 153. Prestressed Concrete structures uses concrete of class a. A b. B c. C d. P 154. An aggregate base course of 21,600m3 will require a. 14 b. 25 c. 72 ? d. 40 155. An embankment to be constructed to a height of 600mm will have a minimum number of a. 4 b. 5 c. 3 d. 6 layers.
156. Aggregate base course with a volume of 112,000 m3 will have a minimum number of a. 74 b. 75 c. 56 d. 62 quality tests. 157. A portland cement concrete pavement, 6.5m wide and 23 cm. thick will be constructed for a total paved area of 165,000 m3. Angular coarse aggregate will be used. If pavement will be opened to traffic 14 days. a. how many bags of cement will be required for Class A concrete? b. How many quality tests are required for the cement? c. How many quality and grading tests each are required for the coarse and fine aggregates? d. How many sets of concrete beam samples will be required? Vconcrete = 165000 x 0.23 = 37,950 m3 a. cement = 37950 x 9.1 = 345,345 bags b QT of cement = 345,345/2000 = 173 c. VFA = 37950 x 0.54 = 20493 ; QFA = 20493/1500 = 14 ; GFA = 20493/75 = 274 VCA = 37950 x .68 = 25,886 ; QCA = 25806/1500 = 18 ; GCA = 25806/75 = 345 d. 37950/75 = 506 sets 158. Per our present Specifications for Highways and Bridges, including amendments, it is mandatiry to open PCCP to traffic not later than a. 14 days after pouring b. 21 days after pouring c. 7 days after pouring d. 28 days after pouring 159. For 850 m3 of concrete paved in one day a. 3 b. 2 c. 1 sets of concrete beam samples should be taken and tested for strength (thickness of pavement = 0.23 m). 160. For 4050 m3 concrete coarse aggregate a. 6 b. 5 c. 3 d. 4 samples should be submitted for quality tests. 161. The coarse aggregate of Item 201, Aggregate Base Course shall have a percentage of wear of not more than a. 40 % b. 45 % c. 50 % d. 60 % as determined by Los Angeles Rattler Test. 162. The rate of application of emulsified asphalt used as bituminous prime coat is a. 0.5 to 1.0 liter b. 1.0 to 1.5 liter c. 1.5 to 2.0 liter per square meter.
163. Steel bars for concrete reinforcement is tested for its a. tensile b. compression c. bending d. both a and c properties. 164. For 250 gallons of Red Lead Paint a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 samples should be submitted for quality test. 165. The number of samples of structural steel (reduced section) required for 38,000 kg. Is a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 166. a.) Third - point loading b.) mid span loading c.) three edge bearing is the method used in determining the strength of concrete pipes. 167. An aggregate base course of 23750 m3 will require a. 50 b. 20 c. 16 quality tests. 168. The Plasticity Index of aggregate base course should not be greater than a. 12 b. 6 c. 10 d. 8 169. Concrete Hollow Blocks are tested for its a. compression b. absorption and dimension c. tensile d. both a and b. 170. Item 306 is called a. Bituminous Surface Treatment b. Bituminous Road Mix Surface Course c. Bituminous Plant Mix (Stockpile Maintenance mixture) d. Bituminous Penetration Macadam Pavement 171. In the preparation of an asphalt design mix intended for Item 310, the proportion of bituminous material (asphalt cement) on the basis of total dry aggregates shall be from: a. 4 to 8 % b. 3 to 5 % c. 5 to 7 % d. 5 to 8 % 172. Item -------- includes general requirements that are applicable to all types of bituminous plant mix surface courses irrespective of gradation of aggregates or kind and amount of bituminous material. a. Item 306
b. Item 307 c. Item 308 d. Item 310 173. ---------- is the result of asphalt layer instability or granular base or subgrade weakness. The pavement usually twist out of shape. a. disintegration b. upheaval c. distortion d. bleeding 174. ---------- the localized upward displacement if a pavement due to swelling of the subgrade or some portion of the pavement structure. a. upheaval b. edge cracking c. raveling d. depression 175 Item ---------- consist of furnishing and placing one or more courses of graded aggregates and one or more application of bituminous material followed by a seal coat with cover aggregates constructed in a prepare base is: a. 303 b. 304 c. 305 d. 306 An asphalt cement submitted in the laboratory for quality test should always have a corresponding Job mix formula Test report Sample card Minimum testing requirements If an asphalt pavement will be constructed over an old existing concrete pavement, ---------should be applied to the pavement. tack coat prime coat seal coat mortar coat The amount of emulsified asphalt to be added in a Bituminous Plant-Mix Surface Course, Cold Laid (Item 308) shall be ------------ mass percent, total dry aggregate basis: 4 to 8 5 to 10 NOTE: If MC is used the proportion of bituminous material on the basis of 6 to 10 total dry aggregate shall be from 4.5 to 7.0 %. 7 to 12 ------------ test is measure by the distance to which it will elongate before breaking when two (2) ends of a briquet with specimen are pulled apart at a specified speed and temperature. penetration solubility ductility viscosity
176. a. b. c. d. 177. a. b. c. d. 178. a. b. c. d. 179. a. b. c. d.
180. Another name for hot asphalt is ----------a. bituminous asphalt
b. asphalt cement c. emulsified asphalt d. blown asphalt 181. a. b. c. d. 182. a. b. c. d. 183. a. b. c. d. In cutback asphalt, medium curing type is a combination of the following asphalt cement and road oils asphalt cement and kerosene asphalt cement and gasoline asphalt cement and emulsifier ------------ test determines the amount of asphalt present in a bituminous mix distillation extraction solubility compression The softness and hardness of an asphaltic material can be determined by -------- test. softening point loss on heating penetration distillation
184. The temperature of bituminous hot mix delivered in the project site should not be less than its ------temperature. a. mixing b. compaction c. molding d. spreading 184. a. b. c. d. 185. a. b. c. d. 186. a. b. c. d. 187. a. b. c. d. Resistance to deformation of bituminous mixture is measured by ----------flow index index of retained strength ductility test extraction test The apparatus used in determining the grade of asphalt cement is: hydrometer penetromanometer petronmeter penetrometer In an Immersion-Compression test, molding of specimen is done into ------- layer/s. 1 2 3 NOTE: In Marshall Stability, molding of specimen is done into 4 one (1) layer. The actual cementing power in asphalt is called the -----------petrolene asphaltene bitumen resin
188. a. b. c. d. 189. a. b. c. d. 190. a. b. c. d. 191. a. b. c. d. 192. a. b. c. d. 193. a. b. c. d. 194. a. b. c. d. 195. a. b. c. d.
------------- test indicates the temperature in which an asphalt cement may be heated without the danger of catching fire. It is used as criterion in eliminating fire hazards. softening point flash point laser point heating point An asphalt pavement needs sufficient -------- to avoid flushing or bleeding. compaction air voids binder mineral filler A job mix formula provides for close control of: asphalt content aggregate gradation temperature of asphalt, aggregate and mix all of the above The thinnest and most fluid grade of medium curing cutback asphalt is: MC 800 MC 250 MC 70 NOTE: For MC, the higher the grade the thicker MC 30 The amount of asphalt in a typical asphalt emulsion is: 40 % 50 % NOTE: After distillation the amount of asphalt (residual) retained should 60 % at least 60 %. 70 % Another name for joint filler is: asphalt cement cutback asphalt mineral filler blown asphalt The type of asphaltic material that is usually classified by its viscosity is: liquid asphalt blown asphalt rock asphalt lake asphalt Item 310, Bituminous Surface Course, Hot Laid provides an air voids between: 35% 57% 58% 8 10 %
196. Emulsified asphalt that has a positive charge particle is usually classified: a. anionic
b. cationic c. pozzolanic d. ultrasonic 197. a. b. c. d. 198. a. b. c. d. 199. a. b. c. d. 200. The characteristics of a bituminous mix that indicates resistance to disintegration is called: stability flexibility durability integrity The coarse aggregates used in bituminous mix are those retained at sieve No. 8 10 30 200 ---------- test compares the compressive strength of dry and wet specimen of bituminous mix marshall stability immersion-compression extraction bulk specific gravity
In item 310, bituminous Surface Course, Hot laid requires 70% minimum index of retained strength (IRS). In the immersion-compression test, the dry stability is about 900 psi. Based on the data, the wet stability should be at least ------- psi a. 270 b. 630 Wet stability c. 1286 NOTE: IRS = ----------------- X 100 d. 1500 Dry stability 201. a. b. c. d. 202. a. b. c. d. 203. a. b. c. d. 204. a. b. c. d. A compacted bituminous pavement shall have a minimum density of equal to or greater than -85 % 90 % NOTE: The compacted pavement shall have a density equal to, or greater than 95 95 % mass percent of the density of a laboratory specimen. 100 % The rate of application of emulsified asphalt used as tack coat, should be within the range of 0.2 0.5 liter/ m2 0.2 0.7 NOTE: The rate of application of either the Rapid Curing or the 0.15 0.7 Emulsified asphalt shall be within the range of 0.2 to 0.7 1.0 2.0 liter/m2, the exact rate as determined by the Engineer. The type of asphaltic material that is being referred to by penetration grade is: emulsified asphalt cutback asphalt asphalt cement mastic asphalt The optimum asphalt content obtained in a marshall stability test is the average of the asphalt content of maximum stability, maximum density and minimum flow index maximum VMA 4 % or designed air voids maximum VFA
205. a. b. c. d. 206. a. b. c. d. 207. a. b. c. d. 208.
The service performance of an asphalt pavement is greatly influenced by: grade of asphalt quantity of asphalt a and b none of the above In bituminous mixture, aggregates account for 92 % to 95 % of the weight of the mixture, while asphalt ( the binder of the aggregates ) accounts for --------------35% 58% NOTE: The proportion of bituminous material on the basis of total 5 10 % dry aggregate, shall be from 5.0 to 8.0 mass percent. 7 10 % In asphalt pavement, prior to acceptance, a sample of full depth, 150mm x 150mm or 100mm diameter shall be taken by a saw or core drill for -------- test thickness determination density stability a and b In an asphalt pavement construction, after spreading bituminous mix, compaction will follow where rolling shall begin at the sides and proceed longitudinally parallel toward the road centerline, each trip overlapping ------- of the roller width, gradually progressing to the crown of the road 1 1 2.0 The control of temperature during the mixing and compaction is of great significance in the ---of the resulting pavement strength skid resistance flexibility all of the above based on the minimum testing requirements for Item 309, Bituminous Plant Mix, General, one quality test for asphaltic material requires for every ------ tonnes or fraction thereof. 40 50 60 70 The test in emulsified asphalt which determines the resistance of the emulsion to break when mixed with mineral aggregates solubility sieve test cement mixing storage stability
a. b. c. d. 209. a. b. c. d. 210. a. b. c. d. 211. a. b. c. d.
212. a. b. c. d. 213. a. b. c. d. 214. a. b. c. d. 215. a. b. c. d. 216. a. b. c. d. 217. a. b. c. d. 218. a. b. c. d.
What Item in the DPWH standards and specification is Bituminous Tack Coat? 301 302 303 304 In identifying project location intended for asphalt pavement, which of the following criteria is not appropriate to recommend? drainage facilities is well-maintained location is not a typhoon belt area existing base course is stable flood-prone section An asphalt cement can be a good bituminous binder material for Item: 301 302 308 310 Which of the following bituminous material is best recommended for sealing weakened plane and construction joints of the PCCP. asphalt cement emulsified asphalt cutback asphalt joint filler asphalt The primary quality control mechanism for the production of asphalt mixtures which will have a high degree of uniformity that will satisfy job requirements is called: marshall stability test job mix formula immersion compression stability test a and b When a completed asphalt pavement exhibits too much voids, it is usually caused by the following except of: rolling the mixture below the temperature requirements too much coarse aggregates too little binder too much fine aggregates Test results from specimen taken from a recently rolled asphalt pavement showed that its total asphalt content is 5.45 % by weight of mix. If the asphalt absorbed by the aggregate is 0.95 %, the effective asphalt content by weight of mix is: 4.8 % Pba 4.552 % NOTE: Pbe = ----- x Ps 5.10 % 100 5.50 %
Where: Pbe = effective asphalt content, percent by total weight of mixture Pba = absorbed asphalt, percent by weight of aggregate Pb = asphalt content, percent by total weight of mixture Ps = aggregate content, percent by total weight of mixture 219. An asphalt mix prepared in the laboratory used 30 %, 50 %, 20 % by weight of coarse aggregate (CA), fine aggregate (FA) and mineral filler (MF), respectively. If the specific gravity of CA,
a. b. c. d. 220. a. b. c. d. 221.
FA, and MF are 2.50, 2.65 and 2.50, respectively, the overall specific gravity of composite aggregates is: 2.58 30 + 50 + 20 2.45 SG oa = --------------------------------2.66 30/2.5 + 50/2.65 + 20/2.5 2.77 If 95 % of the aggregates in question no. 45 is mixed with 5 % asphalt by weight of mix, the specific gravity of the mix (if it is voidless) is: specific gravity of asphalt is 1.01. 2.45 2.23 100 2.39 Gmm = Gmb = ------------------------2.18 ( voidless) 95/2.58 + 5/1.01
If the bituminous mix in No.46 has a 5 % air voids, the bulk specific gravity (Gmb) can be computed as: a. 2.51 Gmm - Gmb b. 2.27 % Air Voids = ----------------- x 100 c. 2.39 Gmm d. 2.41 2.39 - Gmb 5/100 = -----------------2.39 222. a. b. c. d. 223. a. b. c. d. 224. a. b. c. d. If the dry stability of a bituminous mix is 3,950 lbs. And its wet stability is 2,830 lbs., the Index of Retained Strength (IRS) is: 50.20 % 71.60 % Wet Stability 73.20 % IRS = ----------------- x 100 61.10 % Dry Stability The voids in the mineral aggregate (VMA) is: the sum of the air voids and the volume of the mix the difference between the volume of the mix and the volume of aggregate the sum of the air voids and volume of aggregate the difference between the volume of mix and volume of asphalt The distance travelled by a standard penetration needle on a prepared sample of asphalt cement under condition for normal penetration is 9.0 mm ( the penetration scale has 1/10 mm calibration). Asphalt cement is classified as --------- penetration grade. 60 70 85 100 120 150 200 - 300
You might also like
- Consulting Proposal Template 06Document20 pagesConsulting Proposal Template 06rekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-10 GuidelinesDocument55 pagesASCE 7-10 GuidelinesMe MeNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology 100 Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesConcrete Technology 100 Objective Questionsanbumani100% (1)
- Materials Exam ReviewerDocument88 pagesMaterials Exam ReviewerRod PasionNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument15 pagesAnswerMARK ARQUE LACANARIANo ratings yet
- Materials ReviewerDocument31 pagesMaterials Reviewerrekcah eht100% (12)
- Materials Engineer ReviewerDocument32 pagesMaterials Engineer ReviewerMark Angelo España Suril100% (12)
- Questions - Materials TestingDocument43 pagesQuestions - Materials TestingMaria Iza BelleNo ratings yet
- Material Engineer Test Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesMaterial Engineer Test Reviewer PDF-adrian Cruz-100% (1)
- DPWH MATERIALS ENGINEERING EXAM REVIEWER FOR ITEM 300 WITH NOTES FROM A MATERIALS ENGINEER LLDocument76 pagesDPWH MATERIALS ENGINEERING EXAM REVIEWER FOR ITEM 300 WITH NOTES FROM A MATERIALS ENGINEER LLWillard Apeng97% (38)
- Qcs 2010 Section 5 Part 6 Property RequirementsDocument30 pagesQcs 2010 Section 5 Part 6 Property Requirementsbryanpastor106100% (5)
- Pavement Design - (Rigid Flexible) DPWHDocument25 pagesPavement Design - (Rigid Flexible) DPWHrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- MQCHD Test QuestionDocument94 pagesMQCHD Test Questionanon_728940158No ratings yet
- Construction Materials and Testing-Final ExaminationDocument4 pagesConstruction Materials and Testing-Final ExaminationAdrian Rigos PrenicolasNo ratings yet
- NSCP 2015 TutorialDocument32 pagesNSCP 2015 Tutorialmakmak makmakNo ratings yet
- Summary of DPWH Standard Specs and Min Test RequirmentDocument35 pagesSummary of DPWH Standard Specs and Min Test RequirmentWynna Segundo86% (14)
- Materials Engineer Reviewer Min Req - 2Document88 pagesMaterials Engineer Reviewer Min Req - 2Zner NivlekNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument18 pagesExamMark MamaradloNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineering Exam Reviewer-DPWH-Bureau of Research and Standards Part 1 ME AccreditationDocument46 pagesMaterials Engineering Exam Reviewer-DPWH-Bureau of Research and Standards Part 1 ME AccreditationWillard Apeng81% (27)
- Material Engineer Exam Flow Chart DPWHDocument1 pageMaterial Engineer Exam Flow Chart DPWHKiyoshi Jin100% (7)
- Cylinder Strength Versus Cube StrengthDocument26 pagesCylinder Strength Versus Cube Strengthfsirfan100% (2)
- Endura MRL: Low-Rise ElevatorDocument24 pagesEndura MRL: Low-Rise ElevatorMohd Abu AjajNo ratings yet
- DPWH Minimum Test Requirements PDFDocument30 pagesDPWH Minimum Test Requirements PDFWilliam100% (4)
- DPWH Standard Specifications On Prime Coat, TackDocument8 pagesDPWH Standard Specifications On Prime Coat, TackChesterMercado100% (2)
- Rock Wool Glass WoolDocument3 pagesRock Wool Glass WoolPrasanna IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineer Test ReviewerDocument40 pagesMaterials Engineer Test Reviewersheenamae2013100% (4)
- Pre ExamDocument12 pagesPre Examneal bryan v. recamaraNo ratings yet
- DPWH ReviewerDocument597 pagesDPWH Reviewercharles sedigoNo ratings yet
- ME Exam Reviewer1Document17 pagesME Exam Reviewer1Kayes MNo ratings yet
- GROUTING INSTALLATION MANUAL - 1 For Post Tension PDFDocument374 pagesGROUTING INSTALLATION MANUAL - 1 For Post Tension PDFrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineer Test ReviewerDocument37 pagesMaterials Engineer Test ReviewerRam Gacot100% (3)
- DPWH Material EngineeringDocument11 pagesDPWH Material EngineeringDonald Pereyra33% (3)
- M.E ReviewerDocument14 pagesM.E ReviewerAlvin TusiNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineer ReviewerDocument40 pagesMaterials Engineer ReviewerMark Angelo España Suril95% (21)
- MATERIALS ENGINEER REVIEWER - III (Asphalt Technology)Document28 pagesMATERIALS ENGINEER REVIEWER - III (Asphalt Technology)pablojab100% (1)
- Materials Engineer Examination No.5Document14 pagesMaterials Engineer Examination No.5Kulyt G. Bolanio67% (6)
- Materials Engineer Reviewer 1 With Answer KeyDocument22 pagesMaterials Engineer Reviewer 1 With Answer KeymcpayodNo ratings yet
- Materials Reviewer PDFDocument24 pagesMaterials Reviewer PDFFritz Eustace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Wall Panel SystemDocument6 pagesWall Panel SystemDaryl AguilarNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineer Test Reviewer-1Document47 pagesMaterials Engineer Test Reviewer-1Rodrigo Castillo Cacho93% (27)
- Test Questions For Materials EngineerDocument94 pagesTest Questions For Materials EngineerCharles AdoNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineer Accreditation Examination Reviewer 3Document11 pagesMaterials Engineer Accreditation Examination Reviewer 3ibs87100% (1)
- Day 2 Materials Engineer Test ReviewerDocument5 pagesDay 2 Materials Engineer Test Reviewerwe are the gamersNo ratings yet
- Matls - Engr. Accr. ReviewDocument352 pagesMatls - Engr. Accr. ReviewJun Kho100% (1)
- Shotcrete Tunneling Presentation - BarChip - Jan 2014Document45 pagesShotcrete Tunneling Presentation - BarChip - Jan 2014rekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire-40 SlidesDocument40 pagesQuestionnaire-40 Slideskimberly dacurroNo ratings yet
- PE Reviewer 1Document15 pagesPE Reviewer 1Bienmark Domingo Idorita CE0% (1)
- Manual of Concrete InspectionDocument233 pagesManual of Concrete Inspectionrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Singapore Building Code 2013 Chapter 6 Fire Fighting SystemsDocument24 pagesSingapore Building Code 2013 Chapter 6 Fire Fighting SystemsyokeleetanNo ratings yet
- Astm D4643Document4 pagesAstm D4643rekcah eht100% (1)
- Astm D 4944Document4 pagesAstm D 4944Au C. GacotNo ratings yet
- Materials EngineerDocument31 pagesMaterials EngineerMarvin Perez MacatunoNo ratings yet
- Materials EngineersDocument14 pagesMaterials EngineersBebierose Otto CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Materials ReviewerDocument10 pagesMaterials ReviewerMilray AutidaNo ratings yet
- MQHD Test QuestionsDocument60 pagesMQHD Test QuestionsKaren Mae Samoy PerachoNo ratings yet
- MATERIALS Engineer Examination No. 5Document3 pagesMATERIALS Engineer Examination No. 5Bebierose Otto CarmonaNo ratings yet
- ME1Document29 pagesME1Karen Mae Samoy PerachoNo ratings yet
- 2015 SeptemberDocument15 pages2015 Septembercimpstaz100% (1)
- Accreditation Exam-2Document14 pagesAccreditation Exam-2Gin GineerNo ratings yet
- ME ReviewerDocument16 pagesME ReviewerNil DGNo ratings yet
- Material Engineer Test ReviewerDocument7 pagesMaterial Engineer Test ReviewerAntonette Marie ElgarioNo ratings yet
- 1st Sat. July 31, 2010 Assessment Examination For ME With AnswerDocument13 pages1st Sat. July 31, 2010 Assessment Examination For ME With AnswerEljay VinsonNo ratings yet
- 2014 MarchDocument10 pages2014 MarchPatricia FloresNo ratings yet
- 2016 SeptemberDocument15 pages2016 SeptembercimpstazNo ratings yet
- Materials Reviewer PDFDocument25 pagesMaterials Reviewer PDFMarlatif SakandalNo ratings yet
- For Core Specimens How Many Cores Will Be Taken From Each SegmentDocument7 pagesFor Core Specimens How Many Cores Will Be Taken From Each SegmentGerard VelicariaNo ratings yet
- ME Exam 2015 - MarchDocument8 pagesME Exam 2015 - MarchPatricia FloresNo ratings yet
- Soil Questionnaire WITH ANSWERS August 2021Document7 pagesSoil Questionnaire WITH ANSWERS August 2021Queenie Aparente BaloNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Materials-Engineer-Test-ReviewerDocument5 pagesDay 6 - Materials-Engineer-Test-Reviewerwe are the gamersNo ratings yet
- June 2019Document16 pagesJune 2019Eljoy AgsamosamNo ratings yet
- 2019 ExamDocument16 pages2019 ExamcimpstazNo ratings yet
- MQC Practice ExamDocument9 pagesMQC Practice ExamStephen RayosoNo ratings yet
- Set-2 AnswerDocument8 pagesSet-2 AnswerMARK ARQUE LACANARIANo ratings yet
- Seminar On Bridge Management - Maintenance - Repair - RehabilitationDocument19 pagesSeminar On Bridge Management - Maintenance - Repair - Rehabilitationrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing RIL Verification (Stack Foundation)Document18 pagesIsolated Footing RIL Verification (Stack Foundation)rekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Presentation2 Design of RC - GirderDocument18 pagesPresentation2 Design of RC - Girderrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- DESIGN SHEET - SPREAD FOOTING For BridgeDocument7 pagesDESIGN SHEET - SPREAD FOOTING For Bridgerekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Masonry SpecsDocument40 pagesMasonry Specsrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- SPeCTRAL CURVEDocument9 pagesSPeCTRAL CURVErekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Four Story BuildingDocument47 pagesDynamic Analysis of Four Story Buildingrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Screed Bases and In-Situ FlooringsDocument28 pagesScreed Bases and In-Situ Flooringsrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Connection DesignDocument17 pagesConnection Designrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- YANA Consulting Project Proposal:) and Any Comments in The Space BelowDocument1 pageYANA Consulting Project Proposal:) and Any Comments in The Space Belowrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- TIP 11 - Testing Concrete CoresDocument1 pageTIP 11 - Testing Concrete Coresrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Sika® ViscoCrete®-TS 100-2Document3 pagesSika® ViscoCrete®-TS 100-2rekcah eht0% (1)
- Chloride Ion Migration/diffusion Through Concrete and Test MethodsDocument30 pagesChloride Ion Migration/diffusion Through Concrete and Test Methodsrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Core and Cube Compressive Strength of Hardened ConcreteDocument5 pagesComparison of Core and Cube Compressive Strength of Hardened ConcreteRajmonda RamaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete-Analysis & DesignDocument556 pagesReinforced Concrete-Analysis & Designrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Designing Floor Slabs On GradeDocument281 pagesDesigning Floor Slabs On Graderekcah eht100% (10)
- 2424 Ijet IjensDocument8 pages2424 Ijet Ijensrekcah ehtNo ratings yet
- Memoria Kaira Looro InglesDocument3 pagesMemoria Kaira Looro InglesVictoriaGoldaracenaNo ratings yet
- Ce 506 Prestressed Concrete Design: M R M M MDocument2 pagesCe 506 Prestressed Concrete Design: M R M M Mbadr amNo ratings yet
- Shop Drawing LogDocument9 pagesShop Drawing LogMo ajNo ratings yet
- Bottom Up and Top BottomDocument7 pagesBottom Up and Top BottomJonah Dave VegaNo ratings yet
- Korea Fire Safety KFS 411-2019 StandardsDocument38 pagesKorea Fire Safety KFS 411-2019 Standardsyoonchankim0911No ratings yet
- Appron Ref 1Document1 pageAppron Ref 1Jay PardesiNo ratings yet
- Brgy - Pow 150KDocument35 pagesBrgy - Pow 150KRvin Jay Cabontocan MarianoNo ratings yet
- Study of Light Weight Fibre Reinforced Concrete by Partial Replacement of Coarse Aggregate With Pumice StoneDocument10 pagesStudy of Light Weight Fibre Reinforced Concrete by Partial Replacement of Coarse Aggregate With Pumice StoneMohammed Sohel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Structural Audit Report of Bombay GymkhanaDocument91 pagesStructural Audit Report of Bombay Gymkhanapalajay36No ratings yet
- FA00010S-T0101 GENERAL ARCHITECTURE DESCRIPTION (Rev.1)Document26 pagesFA00010S-T0101 GENERAL ARCHITECTURE DESCRIPTION (Rev.1)arief fardy yuskaNo ratings yet
- Renovation of Kaluthara Water Reservoir at Alwis PlaceDocument1 pageRenovation of Kaluthara Water Reservoir at Alwis PlacedamithrathnayakaNo ratings yet
- Cottesloe Brochure PlansDocument6 pagesCottesloe Brochure PlansindyanexpressNo ratings yet
- Grouting MaterialDocument2 pagesGrouting MaterialAjinkya Uprikar100% (1)
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) : Technical Data Sheet (ASTM)Document1 pageABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) : Technical Data Sheet (ASTM)DiegoTierradentroNo ratings yet
- Philips Compact Metal Halide Lamps Bulletin 7-92Document2 pagesPhilips Compact Metal Halide Lamps Bulletin 7-92Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Seismic Isolation Project For Mitchell HallDocument122 pagesSeismic Isolation Project For Mitchell HallVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Doors:: Slab DoorDocument14 pagesTypes of Doors:: Slab DoorJacqueline Gregorio RamosNo ratings yet
- Minimum Depth and CoverDocument1 pageMinimum Depth and CovershafiullahNo ratings yet
- En York Hvac Catalogue 2016 PDFDocument190 pagesEn York Hvac Catalogue 2016 PDFDaniel MilosevskiNo ratings yet
- Schoeck Isokorb Type CPA Technical Manual USADocument16 pagesSchoeck Isokorb Type CPA Technical Manual USAMikeNo ratings yet
- 10 Working Days 1: Time Required For Examination Standard No - Product Name S - Cement Products and Tile UnitDocument7 pages10 Working Days 1: Time Required For Examination Standard No - Product Name S - Cement Products and Tile UnitIrfan chaudharyNo ratings yet
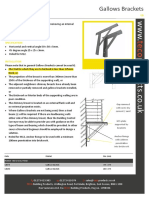
- Gallows Brackets TecoDocument1 pageGallows Brackets TecoAdil MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Pre Cast StructureDocument7 pagesPre Cast StructureRohit TangriNo ratings yet