Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Tech
Uploaded by
Puneet WaliaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Food Tech
Uploaded by
Puneet WaliaCopyright:
Available Formats
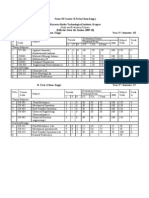
SYLLABI FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) EXAMINATIONS 2011 2012 SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION
Paper
Subject
Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 1 P C 3 3 3 3 3 3
Exam. Sessional Marks Marks
Total Marks
FIRST SEMESTER FT 101 FT 102 FT 103 FT 104 FT 105 FT 106 Mathematics-I Introduction to Bio-Sciences Chemistry (Organic) Introduction to Food Technology Physical Chemistry Engineering Mechanics
50 50 50 50 50 50
50 50 50 50 50 50
100 100 100 100 100 100
Practicals FT 151 FT 152 FT 153 FT 154 Bio-Sciences Lab. Organic Chemistry Lab. Engineering Graphics-1 Lab. Physical Chemistry Lab. Total 18 4 2 2 2 2 8 1 1 1 1 22 25 25 25 25 400 25 25 25 25 400 50 50 50 50 800
L: Lectures/Week T: Tutorials/Week P: Practical Hours/Week C: Number of Credits NC: No Credits
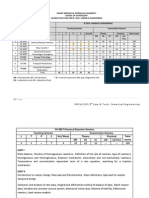
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 3 2 T 1 1 1 1 P C 4 4 4 3 4 NC 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 Qualifying 100 100 100 100 100 Exam. Sessional Marks Marks Total Marks
SECOND SEMESTER FT 201 FT 202 FT 203 FT 204 FT 205 FT 206 Practicals FT 251 FT 252 FT 253 FT 254 FT 255 FT 256 Engineering Graphics-II Lab. Inorganic Chemistry Lab. *Basic workshop Techniques Biochemistry & Nutrition Lab. Physics Lab. Behavioral Sciences and Communication Skills Total Mathematics-II Chemistry (Inorganic) Biochemistry & Nutrition Applied Physics Material and Energy Balances Environmental Studies
17
2 2 2 2 2 2 12
1 1 1 1 1 1 25
25 25 25 25 25 375
25 25 25 25 25 25 400
50 50 50 50 50 25 775
* There will be 4 weeks training in Basic Workshop Techniques during the summer vacations.
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 P C 4 4 4 50 50 50 50 50 50 100 100 100 Exam. Sessional Marks Marks Total Marks
THIRD SEMESTER FT 301 FT 302 FT 303 Food Microbiology Mechanical Operations Fundamentals of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Fluid Flow Engineering Materials Food Chemistry
FT 304 FT 305 FT 306 Practicals FT 351 FT 352 FT 353 FT 354 FT 355
3 3 3
1 1 1
4 4 4
50 50 50
50 50 50
100 100 100
Food Microbiology Lab. Computer Programming Lab. Food Chemistry Lab. Fluid Flow Lab. Electrical & Electronics Engineering Lab. Total
18
2 2 2 2 2 10
1 1 1 1 1 29
25 25 25 25 25 425
25 25 25 25 25 425
50 50 50 50 50 850
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 1 1 P C 4 4 4 4 4 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 100 100 100 100 100 Exam. Sessional Marks Marks Total Marks
FOURTH SEMESTER FT 401 FT 402 FT 403 FT 404 FT 405 Practicals FT 451 FT 452 FT 453 FT 454 Particle Mechanics Lab. Environmental Engineering Lab. Cereals & Pulses Processing Lab.
#
Mathematics-III Environmental Engineering Heat Transfer Material & Energy Balances Processing of Cereals & Pulses
15
2 2 2 6
1 1 1 1 24
25 25 25 25 350
25 25 25 325
50 50 50 25 675
Comprehensive Viva Voce-I Total
The Comprehensive Viva Voce-I Examination (Paper FT 455) will cover the subjects taught during the First, Second, Third and Fourth Semesters.
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 1 1 1 P 100 100 100 100 100 100 50 50 50 50 50 50 150 150 150 150 150 150 Exam. Marks Sessional Marks Total Marks
FIFTH SEMESTER FT 501 FT 502 FT 503 FT 504 FT 505 FT 506 Mathematics-III Processing of Fruits & Vegetables Processing of Milk & Milk Products Processing of Oil seeds, Oils & Fats Mass transfer-I Process Instrumentation
Practicals FT 551 FT 552 FT 553 FT 554 FT 551 Process Plant Design-I Fruits & Vegetables Processing Lab. Milk & Milk Products Processing Lab. Oil & Fats Processing Lab. Heat Transfer Lab. Total 18 6 2 2 2 2 2 10 50 50 50 50 50 850 50 50 50 50 50 550 100 100 100 100 100 1400
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 1 P 100 100 100 100 100 100 50 50 50 50 50 50 150 150 150 150 150 150 Exam. Marks Sessional Marks Total Marks
SIXTH SEMESTER FT 601 FT 602 FT 603 FT 604 FT 605 FT 606 Reaction Engineering Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Confectionary Technology Mass Transfer-II Environmental Engineering Beverage Technology
Practicals FT 651 FT 652 FT 653 FT 654 Mass Transfer Lab. Process Plant Design-II Beverage & Confectionary Processing Lab. Environmental Engineering Lab. Total 18 4 2 2 2 2 8 50 50 50 50 800 50 50 50 50 500 100 100 100 100 1300
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 3 3 T 1 1 1 1 P 100 100 100 100 50 50 50 50 150 150 150 150 Exam. Marks Sessional Marks Total Marks
SEVENTH SEMESTER FT 701 FT 702 FT 703 FT 704 Food Regulation & Quality Control Process Engineering Economics Packaging Technology Biochemical Engineering
Practicals FT 751 FT 752 FT 753 FT 754 FT 851 Food Quality Control & Packaging Lab. Engineering Computation Lab. Literature Survey, Report Writing and Seminar Factory Training & Tour Report Project Work Total 12 4 2 2 2 2 8 50 50 500 50 50 100 100 500 100 100 100 100 1000
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION (2011 2012) Paper Subject Teaching Hrs. per Week L 3 3 T 1 1 P 100 100 50 50 150 150 Exam. Marks Sessional Marks Total Marks
EIGHTH SEMESTER FT 801 FT 802 Industrial Management Process Dynamics & Control
Elective (Any one of following ): FT 803 FT 804 FT 805 Processing of Meat, Fish & Poultry Membrane Separation Processes Food Rheology 3 1 100 50 150
Practicals FT 851 FT 852 FT 853 FT 854 FT 855 Project Work Elective Lab. Process Instrumentation & Control Lab. Process Modeling & Simulation Lab. Viva Voce-II (Comprehensive) Total 9 3 2 2 2 2 8 50 50 50 50 100 600 100 50 50 50 400 150 100 100 100 100 1000
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) FIRST SEMESTER FT 101 MATHEMATICS-I
Convergence and divergence of infinite series and some simple problems, trigonometric and exponential functions of a complex variable, hyperbolic functions, separations into real and imaginary parts, summation of series (C+IS method only). Successive differentiation, expansion of function, applications of maxima and minima of a function of two or more variables, curves in polar co-ordinates, angle between radius vector and tangent line, curvature, partial differentiation, Asymptotes singular and multiple points, curve tracing. Definite integrals and their properties, definite integrals as the limit of a sum of the fundamental theorem of integral calculus, determination of areas and lengths of curves, volumes and surfaces and solids of revolution. Double and triple integrals with their simple applications. Solution of ordinary differential equations of first order and first degree with simple applications of engineering problems. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Prasad, G. Prasad, G. Shanti Narayan Shanti Narayan Grewal, B. S. Kreyszig, Erwin Jain, R. K. & Iyengar, S. : Differential Calculus, 17th Edition, Pothishala Private Ltd. Allahabad. : Integral Calculus, 19th Edition, Pothishala Private Ltd., Allabahad. : Differential Calculus, 14th Edition, S. Chand and Co., New Delhi. : Integral Calculus, 10th Edition, S. Chand And Co., New Delhi. : Higher Engineering Mathematics, 41st Edition, Khanna Pub., New Delhi. : Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 8th Edition, John Wiley and Sons. : Advanced Engg. Mathematics, 2nd Publishing House, New Delhi, 2003. Edition, Narosa
FT 102 INTRODUCTION TO BIO-SCIENCES Introduction to Biology and its branches. Prokaroytic and Eukaryotic cells.
Cells: Animal and Plant cell structures, organelles and their functions. Cell division and cell cycle. Histology : Plant and Animal tissues, Muscles in animals. Photosynthesis of Plants. Digestion of foods in animals. Organisms and their environments Ecosystems. Growth and development in plants and animals. Relevance of Microbiology in preservation of foods. Composition of microbial world. Branches of Microbiology. Microscopes and their application in Microbiology. Morphology and physiology of virus, bacteria, yeast, molds and algae. Growth, nutrition and reproduction. Isolation and identification of microorganisms. Pure cultures and their characteristics. Sterilization. Maintenance of cultures. Culturing techniques: Batch culturing, Continuous culturing, Fed-batch culturing. Factors affecting growth. Generation of energy and its uses in biosynthesis. General principles of bacterial genetics, DNA as genetic material, Mutations and their Chemical basis, recombinant DNA technology. - Strain improvement by mutations, recombinant DNA technology - Application of recombinant DNA technology, recombinant products available in the market, in pipeline and at laboratory scale. - Microorganisms and environment: Microorganisms and environment, Water Microbiology. Management of toxic industrial wastes. - Physical and chemical methods of control of microorganisms. Microbial integrations. Food industry waste as fermentation substrate. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Sherman Sherman Ford & Montroe Nason, A. and : : : Biology (A Human Approach), Oxford University Press, 1998. Living Systems: Canfield Press San Francisco, 1977. A Textbook of Modern Biology, 1976. Cambridge University Press, 1996. Microbiology, 2nd Edition, CBS Publication, New Delhi, 2006. Industrial Microbiology, CBS Publication, New Delhi. Industrial Microbiology, CBS Publication, New Delhi, 1985. Food Microbiology, CBS Publication, New Delhi, 2007.
Green, Stout, : Taylor and Soper Prescott, Klein Casida Frazier Herley, : : : :
Prescott & Dunn
FT 103 CHEMISTRY (ORGANIC) 1. Classification of organic compounds: IUPAC nomenclature, Structural isomerism, Cis-trans isomerism. Shapes and Molecular orbital structures of compounds containing C, N and O. Conformations of alkanes. Structures of dienes, pyridine, pyrrole, aromatic compounds. 2. Delocalisation: Concept of aromaticity, stability of cycloalkanes, resonance concept, inductive and mesomeric effects, directive effects, activating and deactivating groups. Hydrogen-bonding, organic reagents and reaction intermediates. 3. Chemistry of hydrocarbons: House synthesis, halogenation of alkanes, free radical mechanism, cracking, effect of structure on physical properties of compounds. Alkenes, catalytic hydrogenation, dehydration of alcohols, dehydrohalogenation, Saytzeff rule, electrophillic addition reactions, peroxide effect, mechanism of allylic substitution, acidity of 1-alkynes, conjugated dienes, 1,2-and 1,4-additions, free radical and ionic mechanisms of addition polymerisation reactions, ring-opening reactions of cyclopropane and cyclobutane, chemistry of benzene and alkylbenzenes, aromatic electrophillic substitution reactions, Friedel-Crafts reactions. 4. Chemistry of functional groups: Alkyl and aryl halides, nucleophilic substitution, synthetic utility of Grignard reagents and alkyllithiums, mechanism of Grignard reactions of alcohols, benzylalcohol, acidity of phenols epoxy compounds, Anisole nucleophilic addition, benzaldehyde, acetophene, benzophenone, aldol condensation, acidity of acids, alkyl and aryl amines. Synthetic utility of diazonium salts, basicity of amines, multistep synthesis. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Bahl, B. S. & Bahl, Arun Solomons, T. W. G. : : Text-book of Organic Chemistry, 16th Edition, S. Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi. Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1994.
FT 104 INTRODUCTION TO FOOD TECHNOLOGY Definition of food, food science, and food technology. Professional bodies both in India and abroad dealing with food technology. General introduction of food preservation. Historical developments. Contamination of foods by microorganisms from natural sources, spoilage of different foods general principles, causes and spoilage and growth of microorganisms in foods. Food intoxicants, mycotoxins, food poisoning and food infections-investigation of a food borne disease outbreak. Contamination, preservation and spoilage of different foods like milk and milk products, meat and meat products, vegetables and fruits, cereal and cereal products, sugar and sugar products. Water: Water Resources, Storage & Distribution of Water. Reuse & Conservation of Water.
Food containers: rigid and flexible: glass, metal, plastic, packaging system characteristics and advantages. Charactersitics of plant and animal foods. Causes of food spoilage and methods of prevention. Preservation of foods by: pasteurization, sterilization, drying, radiation, refrigeration, freezing, sugar, salt, chemicals, radiation, microorganisms. Intermediate moisture foods. Fortification and enrichment of foods. Recent trends in food processing and preservation: processing, Hurdle technology, Ohmic heating etc. Introduction to high pressure
General principles of food hygiene in food handling, personnels, food processing plants. Impurities in water and its treatment. Sanitation facities and procedures in food processing plants. Application of mathematical techniques to describe food processing operations such as drying, rheology, degradation of nutrients and pigments during processing and storage. Use of semi-log and log-log paper. Books Recommended: 1 2 3 Potter, N.N. Desrosier and Desrosier Frazier : Food Science, CBS publication, New Delhi, 2005. : Technology of Food Preservation CBS publication, New Delhi, 2006. : Food Microbiology, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2007.
FT 105 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 1. Solutions: Ideal and non-ideal solutions, Raoultss law, change of free energy, enthalpy, and entropy on mixing of liquids, distillation of binary solutions. Partially miscible liquids such as Phenol- water, triethylamine- water, and Nicotine- water systems. Henrys law, Nernst distribution law, Colligative properties of dilute solutions. Abnormal molar mass, degree of dissociation and association of solutes. 2. Chemical Kinetics: Rate equation of reactions of various orders, rate mechanism, kinetics of complex reactions. Concept of energy barrier and energy of activation. Theories of reaction rates, measurement of extent of reaction, zero order reactions. Rates of flow systems. Lindemann theory of unimolecular reactions. 3. Surface Phenomena: Adsorption of gases by solids. Types of adsorption, adsorption isotherms, Langmuirs adsorption equation, B.E.T. equation for determination of surface area of adsorbents, applications of adsorption, catalysis, kinetics of surface reactions. Introduction to micelles, emulsions and gels. 4. Photochemistry: Laws of photochemistry, principles of photochemical excitation, quantum efficiency, Kinetics of photochemical reactionsElectrochemistry: Conductance of electrolytic solutions, transference number and its determination, Kohlrauschs law of independent migration of ions, Interionic attraction theory, activity and activity coefficients of strong electrolytes, ionic equilibria. Ionizaton of water, ionization
constants of weak acids and weak bases, hydrolysis, pH, commonion effect, solubility product and salt effect. 5. Electrochemical Cells: Reversible and irreversible cells, e.m.f. and its measurement, cell reactions and e.m.f., thermodynamics of electrode potentials, half- cell potential and its determination, Nernst equation, concentration cells, liquid junction potential, determination of activity co-efficient from cell potential data, potentiometric titrations. Books recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Maron, Samuel H. Prutton, Carl F. Glasstone, Samuel Barrow, M. Gorden Rose, J. Puri, B.R., Sharma, L.R. and Pathania, Madan, S. Negi, A.S. and Anand, S.C. Laidler, Keith J. Moore, W.J. Atkin, P.W. : : : : : : : : : Principles of Physical Chemistry, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi. Textbook of Physical Chemistry, MacMillan and Co. Ltd. London Physical Chemistry, McGraw Hill, N.Y. Dynamics of Physical Chemistry, Lond Pitman Principles of Physical Chemistry, S. Nagin &Co Jalandhar. A Text Book of Physical Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Ltd. New Delhi. Chemical Kinetics, Tata McGraw-Hill Co. Ltd., New Delhi. Basic Physical Chemistry, Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi. A Text Book of Physical Chemistry, Oxford University Press.
FT 106 ENGINEERING MECHANICS 1. Force System: Introduction, force, principle of transmissibility of a force, resultant of a force system, resolution of a force, moment of force about a line. Varigon's theorem, couple, resolution of force into force and a couple, properties of couple and their application to engineering problems. 2. Equipments: Force body diagram, equations of equilibrium and their applications to engineering problems, equilibrium of two forces and three-force member. 3. Structure: Plane truss, perfect and imperfect truss, assumption in the truss analysis, analysis of perfect plane trusses by the method of joints, method of section and graphical method. 4. Friction: State and kinetic friction, laws of dry friction, co-efficient of friction, angle of friction, angle of repose, cone of friction, frictional lock, friction of flat pivot and collered thrust bearings, friction of journal-bearing, friction in screws, derivation of equation n T1/T2 = c A and its application.
5. Distributed Forces: Determination of centre of gravity, centre of mass and centroid by direct integration and by the method of composite bodies, mass moment of inertia and area moment of inertia by direct integration and composite bodies method, radius of gyration, parallel axis theorem, Pappus theorems, polar moment of inertia. 6. Dynamics: Rectilinear motion, plane curvilinear motion-rectangular co-ordinates, normal and tangential coordinates. 7. Kinetics of Particles: Equation of motion, rectilinear motion and curvilinear motion, work energy equation, conservation of energy, impulse and momentum, conservation of momentum, impact of bodies, co-efficient of restitution, loss of energy during impact. 8. Kinematics of Rigid Bodies: Concept of rigid body, types of rigid body motion, absolute motion, introduction to relative velocity, relative acceleration (Coriolis component excluded) and instantaneous centre of zero velocity. Velocity and acceleration polygons for four bar mechanism and single slider mechanism. 9. Kinematics of Rigid Bodies: Equation of motion, translatory motion and fixed axis rotation, application of work energy, principles to rigid bodies conservation of energy. 10. Vibration: Classification, torsional free vibrations-single rotor and two rotar systems. Spring mass system-its damped (linear dash pot) and undamped free vibrations, spring in series and parallel, simple problems. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Meriam, J. L. & Kraige, L. G. Meriam, J. L. & Kraige, L. G. Hidgen, Stiles : : : Statics, 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons. Dynamics, 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons. Statics and Dynamics, Longman
FT 151
BIOSCIENCES LAB
Use of microscopic technique for identification of microorganisms on the basis of cell morphology and specific staining technique. Isolation of pure cultures of bacteria, yeasts, moulds and taxonomic identification on the basis of morphology and physiology. Preparation of nutrient broth and media with agar, gelatin and specific media for culture of microorganisms. Microorganisms are Ubiquitous and concept of aseptic conditions while cooking Grams Staining Dilutions, pour plating, spread plating, streaking Media preparation & strelization. Microbial growth determination by - O.D. and Viable Counting.
Phenol-Coefficient: Concept and Determination of those of germicides available in market. Microbiological assay of water. Enzyme production and assay. Measurement of activity of anti-microbial agents for the control of microorganisms in foods. FT 152 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB 1. Lab Safety 2. Preparation of Benzamide & Aspirin-Purification, determination of melting point and percentage yield. 3. Identification of unknown organic compounds Hydrocarbons, Phenols, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic acids, Amides and Amines. FT 153 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS-1 LAB Introduction to Engineering Graphics, Methods of projections, Theory of orthographic projection. Conventional practices, dimensioning as per BIS SP 46-1988 Pictorial sketching Projection of points, lines and planes on principal planes Projection on auxiliary planes Recommended Books 1. James D. Bethune : AutoCAD, Pearson Publishers 2. R.K. Dhawan : A textbook of engineering Drawing, S. Chand & Co. Ltd. New Delhi 2nd edition. 3. Sham Tickoo : Understanding AutoCAD 2006, Wiley Publication
FT 154 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY LAB 1. Surface tension of liquids using Stalagmometer and calculation of Parachor values. 2. Distribution of Iodine between water and carbon tetrachloride. 3. Kinetics of the hydrolysis of methylacetate in the presence of hydrochloric acid. 4. Adsorption of acetic acid on activated charcoal. 5. Viscosity of liquids and composition of a binary solution. 6. Conductometry
Variation of equivalent conductance and specific conductance on dilution. Dissociation constant of acetic acid. Solubility of sparingly soluble salts. Conductometric titrations of HCl vs NaOH and acetic acid vs NaOH. 7. Potentiometric titration of HCl vs NaOH and acetic acid vs NaOH and determination of dissociation constant of acetic acid. 8. Colorimetry Verification of Lambert-Beer Law. Determination of concentration of solution of KMnO4/K2Cr2O7. Determination of composition of Fe-Salicylic Acid Complex by Jobs Method. Books Recommended: 1. Lavitt, B.P. : Findlays Practical Physical Chemistry, Longman Group Ltd.
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) SECOND SEMESTER
FT 201 MATHEMATICS-II
Relationship between cartesian, cylindrical polar and spherical polar co-ordinate systems: standard forms of equation of sphere, cone, cylinder. Matrices: Rank of matrix, elementary transformation, Eigen-values, Eigen-vectors, Cayley-Hamilton Theorem. Fourier Series: Eulers Formulae, Dirchielets Conditions for Expansion, Change of interval, Odd and Even Functions, Expansion of Odd and Even Periodic Functions, Introduction to Harmonic Analysis. Vectors: Gardient, Divergence, Curl, Statement of Greens Gauss and Stokes Theorem and their simple applications. Linear Differential Equations with constant Coefficients, Homogeneous Linear Equations, method of variation of Parameters, Simultaneous Liner Differential Equations with Constants Coefficients. Books Recommended: 1. Kreyszig Erwin 2. Hilderband, F. B. 3. Sastry, S. S. 4. Grewal, B. S. 5. Bajpai, A. C. 6. Jain, R. K. Iyengar, S. : : : : : & : Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 7th Edition, John Wiley and Sons. Introduction to Numerical Analysis, Tata McGraw Hill. Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall. Higher Engineering Mathematics, 41st Edition, Khanna Publishers, Delhi. Numerical Methods for Engineers and Scientists, 1st Edition, John Wiley. Advanced Engg. Mathematics, 2nd Publishing House, New Delhi, 2003. Edition, Narosa
FT 202 CHEMISTRY (INORGANIC) 1. Quantum theory and atomic structure: Introduction to wave mechanics, the Schrodinger equation, the Schrodinger equation as applied to hydrogen atom, the origin of quantum numbers and shapes of orbitals.
2. Chemical Bonding: Molecular orbital and valence bond theories of bond formation and application of molecular orbital theory to the formation of homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules. 3. The Solid State: A recapitulation of close packing of spheres, structures of NaCl, CsCl, ZnS, CaF2, crystal defects and applications of defect structures (transistors, rectifiers, photovoltaic cells and computer chips). 4. Coordination Compounds: Werners theory, effective atomic number, bonding of transition metal complexes: valence bond theory, crystal field theory, crystal field splitting in tetrahedral, octahedral and distorted octahedral (square planar) crystal fields. Thermodynamic aspects of coordination compounds (crystal field stabilization energies of octahedral and tetrahedral complexes, spectrochemical series). Kinetic aspects of coordination compounds (substitution reactions in complexes with coordination number 4 and 6 and their mechanism - SN1, SN2). Magnetic behaviour of complexes Para magnetism, diamagnetism, ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism and measurement of magnetic susceptibility of complexes by Guoys method. 5. Organometallic Compounds: Nomenclature, types of ligands and bonding in organometallic compounds, use of organometallics in industry. 6. Inorganic polymers: Types of inorganic polymers, polyphosphazenes, polysiloxanes their structures and properties. 7. Role of Metals in Biological Systems: Bio-inorganic Chemistry of Iron Heme proteins & Non-Heme iron proteins; bioinorganic chemistry of cobalt-vitamin B12 and metalloenzymes. 8. Metal toxicology: Toxic effects of heavy metals with special reference to Cd, Pb, Hg and As. 9. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Theory of quantitative inorganic analysis. Books Recommended: Sharpe, A. G. Lee, J. D. Cotton, F. A. & Wilkinson, G. Cotton, F. A. & Wilkinson, G. : : : : Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd Edition, Longman Publishers ELBS, 1992. Concise: Inorganic Chemistry, 5th Edition, Chapman and Hall Publishers, 1996. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd Edition, Wiley Eastern Ltd., 1982. Basic Inorganic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Ltd., 1987. Inorganic Polymer, Prentice Hall, New Jersey Publishers, 1982. Inorganic Reaction Mechanism, 2nd Edition, Wiley Eastern Publishers, 1984. Casarett and Doulls Toxicology, Pergamon Press, New York, 1991.
Mark, J., West, R. & Allcock, : H. Basola, F. & Pearson, R. G. Amdur, Doull & Klaasen (Eds.) : :
8.
William & Burson (Eds.)
Industrial Toxicology: Safety and Health applications in the work place, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1985.
FT 203 BIOCHEMISTRY & NUTRITION Introduction to biochemical science, Enzymes and coenzymes. Introduction, definition, nomenclature, classification, numbering structure and functions of water-soluble enzymes, energy-rich compounds, active sites, mechanism of enzymes action, effect of temperature, pH, enzyme concentration and substrate concentration on the rate of enzyme reaction, specificity of enzymes, enzyme inhibition, kinetics of enzymes action, activation of enzymes, nature and functions of enzymes involved in digestion. Metabolism of Carbohydrates: Respiratory quotient, Embden-Meyerhoff pathway, Cori and Cori Cycle, Kreb's Cycle, electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation. Metabolisms of Lipids: Digestion and absorption of lipids, fatty liver, lipotropic agent, oxidation pathway, methylmalonyl Co- pathway metabolism of ketone bodies, energy balance. Metabolism of Proteins: Digestion and absorption of proteins, amino acids or nitrogen pool, nitrogen balance, general metabolism of proteins and amino acids. Nitrogen fixation. Nucleic Acids and their Components: Bases, nucleotides and nucleotides (cyclic also). Structures of different types of RNA and DNA. Physiochemical properties of DNA and RNA. Nucleoproteins. Replication, Transcription and Translation. Biotechnological Concepts: Vectors used for recombinant DNA technology. Application of cloned DNA, Screening of newly synthesized DNA. Introduction to Human Nutrition: The functions of foods. The need for energy, basal energy metabolism. Energy value of foods. Protein quality, Dietary allowances and standards for different age groups, nutritive value of foods. Dietary interrelationship, techniques for assessment of human nutrition. Physiological functions, deficiency, role in metabolism and daily requirements of Vitamin A, D, E, K, C, B1, B2, niacin, pyridoxin, cyanocobalamine, folic .acid, choline, p-aminobenzoic acid. Minerals as structural and functional constituents in human metabolism, specific role of iron, calcium, phosphorus, iodine, sodium, chlorine, potassium, copper, and magnesium. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lehninger Stryer Conn and Stumpf Zuleay, G.L. Swaminathan : : : : Biochemistry, Mac Millan Publisher. Biochemistry, Freeman Publisher. Outlines of Biochemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1995. Outlines of Biochemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1995. Nutrition.
6.
Gopalan, Rama Sastri & Balasubramanium
Nutritive Value of Indian Foods.
FT 204 APPLIED PHYSICS 1. Relativity: Frames of reference, Michelson Morley experiment, Galilean and Lorentz transformation, Lorentz Fitz Gerald contraction, time dilation, postulates of special theory of relativity, variation of mass with velocity, mass energy relation. 2. Mechanics: Surface tension, how to calculate surface tension for a drop, experimental determination of surface tension by Jaegers method. Viscosity: Coefficient of viscosity, critical velocity, Poiseuilles equation for flow of a liquid through a tube, motion in viscous medium, Reynolds number, Bernoulies equation and its applications: venturimeter and pitot tube. 3. Optics: Ultrasonics: production, detection and uses of ultrasonics. Interference: Formations of colours in thin films, Newtons rings, Michelson interferometer. Diffraction: Diffraction at a single slit, double slit diffraction grating, its theory, dispersive power and resolving power. Polarization: Polarization by reflection, scattering, absorption and double refraction. Quarter wave and half wave plates, production and analysis of plane, circular and elliptically polarized light. Fiber optics: Basic principle, step index and graded index fiber, qualitative idea of signal distortion and dispersion, transmission losses, fiber optics sensors and their applications. Laser: Elementary ideas, He-Ne and Ruby laser, uses. Holography: Basis principle, theory. 4. Quantum Physics: Difficulties with classical physics, blackbody radiation, photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Debroglie hypothesis, uncertainty principle, time dependent and independent Schrodingers equation, properties of well behaved wave function. Operators and their expectation value. X-ray diffraction and Braggs law. 5. Physics of Materials: Magnetic materials, classification of materials, ferromagnetism, ferri and anti ferromagnetism, hysteresis. Superconductivity, Meissner effect, thermodynamics of superconducting transitions, qualitative idea of BCS theory. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Halliday, D. & Resnick, R. D. S. Mathur Arthur Beiser : : : Physics, 3rd Edition. Elements of Properties of Matter, 10th Edition. Perspectives of Modern Physics.
4. 5.
Theraja, B. L. M. Ali Omar
: :
Modern Physics for Engineers, 1st Edition. Elementary Solid State Physics, 1st Edition.
FT 205 MATERIAL AND ENGERGY BALANCE 1. Review: Stoichiometric and composition relationship gas laws; Gaseous mixtures, vapor pressure, humidity, etc. 2. Material Balances for Non-reaction systems including balances involving recycle and by-pass streams. 3. Material Balances for Reacting systems including balances involving recycle and purge streams. 4. Combustion Calculations. 5. Energy balances on nonreactive and reactive systems. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bhatt, V. I. & Vora, S. M. Himmelbleau, D. M. Felder, R. M. & Rousseau R.W. Reklaithis, G. V. Lubyben, L.W. & Winzel, L. A. : Stiochiometry, 3rd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 1984. : Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical Engineering, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall, 1977. : Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, 3rd Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 1986. : Introduction of Material and Energy balances, John Wiley, 1983. : Chemical Process Analysis, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1988.
FT 206 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES Unit I Unit II : The Multi-disciplinary nature of Environmental Studies: Definition, scope and importance; need for public awareness. : Ecology and Ecosystems: Definition of ecology: Structure and function of ecosystem; Producers, conserver and decomposers; Energy flow in the ecosystem; Ecological succession; Food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids. Introduction, types, characteristic features, structure and function of the following ecosystems: Forest ecosystem; Grassland ecosystem; Desert ecosystem; Aquatic ecosystem (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries). : Biodiversity and its conservation: Introduction - Definition: Genetic species and ecosystem diversity. Value of biodiversity: Consumptive use, productive use, social, ethical, aesthetic and option values; Biodiversity at global, National and local levels; India as a mega-diversity nation; Hotspots of biodiversity; Threats to biodiversity: Habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, man wildlife conflicts;
Unit III
Unit IV
Unit V
Unit VI
Endangered and endemic species of India; Conservation of biodiversity; In-situ and Ex-situ conservation of biodiversity. : Natural Resources: Natural resources and their conservation: (a) Air Resources: Features, composition, structure; air quality management. (b) Forest Resources: Use and over-exploitation, deforestation, case studies, timber extraction, mining, dams and their effects on forests and tribal people. (c) Water Resources: Use and over utilization of surface and ground water, floods, drought, conflicts over water, dams benefits and problems; water quality management; manager of water resources e.g. rivers, lakes, ground water, etc. Fluorosis and arsenic problems. (d) Mineral Resources: Draw on and exploitation, environmental effects of extracting and using mineral resources, case studies. (e) Food Resources: World food problems, changes caused by agriculture and overgrazing, effects of modem agriculture, fertilizer-pesticide problems, water logging, salinity, case studies. (f) Energy Resources: Growing energy needs, renewable and non-renewable energy sources, use of alternate energy sources. Case studies. (g) Land Resources: Land as a resource, land degradation: Man induced landslides, solid erosion and desertification. Role of an individual in conservation of natural resources and prevention of pollution; Equitable use of resources for sustainable lifestyles; Disaster management: Floods, earthquake, cyclone and landslides. : Environment Pollution: Definition -Air pollution: Definition, causes, effects and control measures: Air Quality Management; Air Pollution Case Studies. Water Pollution: Definition, causes, effects and control measures; Case studies; Water Quality Management: Definition, causes, effects and control measures. Marine pollution. Thermal pollution. Soil pollution: Definition, causes and control measures : Case studies. Noise pollution. Nuclear hazards waste management. Waste management through cleaner technologies: Reuse and recycling of wastes. Solid waste management: Causes, effects and control measures of urban and industrial wastes, hazardous waster; bio-medical waste; Role of an individual in prevention of pollution; Pollution case studies. Disaster Management: Floods, earthquake, cyclone and landslides. : Social issues and the Environment: From Unsustainable to Sustainable development; Urban problems related to energy; Water conservation, rain water harvesting, watershed management; Resettlement and rehabilitation of people: Its problems and concerns. Case studies; Environmental ethics: Environmental value relationships; Environmental ethics and species preservation; Climate change: Global warming, acid rain, ozone layer depletion, nuclear accidents and holocaust. Case studies. Wasteland reclamation; Consumerism and waste products. Legislation to Protect the Environment: Environmental Protection Act; Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act; Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act; Wildlife Protection Act; Forest Conservation Act; Environmental
Unit VII
Impact Assessment (EIA); Environmental Management Systems (EMS); Environmental Information Systems (EIS); P.I.L: Public Hearing and Role of NGO's; ISO 9000 and 14000; Issues involved in enforcement of environmental legislation; Public awareness. Environmental Economics: Environment and standard of living. : Human Population and the Environment: Population growth, variation among nations; Population explosion "Family Welfare Programme"; Environment and human health; Human Rights; Value education; HIV/AIDS; Women and Child Welfare; Role of Information Technology in Environment and human health. Case studies.
FT 251 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS-II LAB Projection of solids, solid modeling Section of solids Elementary development and intersection of solids General introduction to isometric views Applications: Drawing of threaded fasteners and assembly drawing using 1st angle/3rd angle projections. Introduction and application to CAD software.
Recommended Books 1. James D. Bethune : AutoCAD, Pearson Publishers 2. R.K. Dhawan : A textbook of engineering Drawing, S. Chand & Co. Ltd. New Delhi 2nd edition. 3. Sham Tickoo : Understanding AutoCAD 2006, Wiley Publication
FT 252 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY LAB 1. Volumetric Analysis (i) Redox Titrations:Titrations involving (b) KMnO4 (Estimation of C2O4-2) (c) K2Cr2O7 (Estimation of Fe+2/Fe+3)
(d) Iodine [Iodometry & Iodimetry] (Estimation of Cu+2, AsO3-3 and Sb+3) (ii) Complexometric Titrations- Determination of Zn by EDTA titration. 2. Gravimetric Analysis (a) Estimation of Ba+2/SO4-2 as BaSO4 (b) Estimation of Fe+2/Fe+3 as Fe2O3 FT 253 BASIC WORKSHOP TECHNIQUES Carpentry Shop: Introduction to various types of timber and particle, boards defects in timber, seasoning of wood. Description and use of carpenter's tools, i.e. saws, planes, chisels, adze, etc. Different types of timber in common use, making of lap joint, Bridle joint, dovetail joint and Mitre joint. Machine Shop: Classification of fabrication processes, machine tools and materials, introduction to working of lathe, shaper, milling and drilling machines, power hacksaw, shearing machine and grinding wheel. Simple turning, threading, drilling board and knurling operations on a lathe. Welding: Use of arc welding and gas welding in making different types of joints. FT 254 BIOCHEMISTRY & NUTRITION LAB Analytical techniques in Bio-Chemistry, isolation and purification of enzyme, Determination of activity of enzyme, preparation, specificity, inhibition and kinetics of enzymatic reaction. Detection and estimation of amino acid by paper and column chromatography. Assessment of nutritive value of foods. FT 255 PHYSICS LAB Coefficient of viscosity of water, milk, juices, etc by flow through a capillary tube, surface tension of water by Jaegers method. Mechanical equivalent of heat by calendar and Bornes apparatus. Refractive Index of the material of glass prism by spectrometer. Wavelength of sodium light by Newtons rings. Wavelength of sodium light by diffraction grating. Vertical and horizontal distance using sextant. Density of a given wire using sonemet box. Magnetic-meters. Internal resistance of Leclanche Cell by Post Office Box and Voltmeter method. Conversion of a Galvanometer into a Ammeter or a Voltmeter of a given range, comparison of e.m.fs of two cell by (I) Potentiometer (II) Lumsdens Method. Value of H by using Tangent Galvanometer and Copper Voltmeter. Accuracy of a given meter being copper Voltmeter. Total intensity of earths magnetic field using dipcircles. Books Recommended: 1 2 Workshop, B.L., Flint, H.T. Arora, C.L. : : Advance Practical Physics, Metheun & Co., London. B.Sc. Practical Physics, S. Chand & Co.
FT 256 BEHAVIORAL SCIENCES AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS 1. Need and Importance: Need of good communication skills, Presentation skills with and without physical media (Computer and Multimedia Projector), Communication skills in a group Group discussion, communication skills in an employment interview, Communication skills and proper body language, Professional and Social etiquette, Professional meeting skills. 2. Role Playing: Role playing as an event comparer, Role playing as Chairman, Role playing as team leader. The workshop would involve learning of practical skills to develop and perfect communication ability. Students would be required to give presentations both as an individual and in a team. Group discussions would be held to develop the communication skills while in a group. Role playing would require the students to practice the knowledge and expertise gained in communication skills to various situations where they would be required to perform the roles mentioned. The students would be evaluated on the basis of their communication skills, participation in various activities and on the ability to work in a team. Books Recommended: 1. Mohan, K. and Banerji, M. : Developing Communication Skills, Macmillan
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) THIRD SEMESTER FT 301 FOOD MICROBIOLOGY Contamination of foods by microorganisms from natural sources, spoilage of different foods: general principles, causes and spoilage and growth of microorganisms in foods Preservation of foods by different preservation methods, contamination, preservation and spoilage of different food products. Food poisoning and food infections investigation of food borne disease outbreak. Microbiology of individual food products Dairy products, bread. Food from microbes: Fermented foods. Microbial flavour fragrances. Food Allergies. Antimicrobial agents used in foods. Rapid methods for microbiological analysis of foods. Food processing plant, hygiene and sanitation: Importance of hygiene and sanitation. Chemicals and methods used in sanitation of plant and equipments. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Prescott, Herley, Klein Stain Salley Prescott & Dunn Casida Pelczar Frazier : : : : : : : Microbiology, 2nd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill. General Microbiology. Bacteriology, Tata McGraw Hill. Industrial Microbiology, CBS Publishers. Industrial Microbiology, John Wiley. Microbiology, Tata McGraw Hill. Food Microbiology, Tata McGraw Hill, India.
FT 302 MECHANICAL OPERATIONS
1. Size Reduction: Crushers and Grinders: jaw crusher, crushing rolls, Gyratory Crusher Tumbling/revolving mills, hammer Mill and Fluid energy mill. Closed and open circuits grinding. Power requirements. Laws of crushing. 2. Mechanical Separation: Screening: Stationery screens, Grizzlies, Trommel and Vibrating screens. International Standard Screens & Indian Standard Screens. Screening Analysis-differential and cumulative.
Motion of particle through a fluid: Stokes Newtons law. Free and hindered setting. Setting tank and double cone classifiers Batch and continuous thickeners Settling chamber, cyclone, filter bag and electrostatic precipitators. 3. Filtration: Plate and frame filter press, continuous rotary vacuum filter, filter aids, theory of filtration for non-compressible cakes. 4. Centrifugation: Tubular bowl centrifuge, disk centrifuge and batch basket centrifuge. 5. Fluidization: Conditions for fluidization: Aggregate and particulate fluidization. Erguns and Carman-Kozeny equations.
6. Mixing and Agitation: Basic ideas and characteristics of mixing equipment power consumptions scale-up. 7. Conveying: Mechanical and pneumatic conveying systems, storage & handling of materials. Books Recommended: 1. Mc Cabe, Warren L., Smith, Juluain C. and Harroit, Peter Foust, Alan S., Wenseli, Leonard A., Clump, Curtis W., mans, Louis and Anersen, L. Bryce Coulson, J.M. and Richardson, J.F. Gupta, Santosh K. Badger, Walter L. and Banchero, Julius T. Brown, C.G. Chattopadhyay, P. : Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, 5th Edition, Mc Graw Hill Int. ed (Chemical Engineering Series) Mc Graw Hill Book Company, New York, 1993. : Principles of Unit Operations, Wiley International Edition, John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York. : Unit Operations (Volume 2 of Chemical Engineering) New York: Mc Graw Hill Book Co;, Inc. : Momentum Transfer Operations, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi. : Introduction to Chemical Engineering, Mc Graw-Hill, Kogarkusha Ltd., New Delhi. : Unit Operations, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. : Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, Vol. I, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi. OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS
2.
3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
FT 303 FUNDAMENTALS ENGINEERING.
DC Circuits and Single Phase A.C. Fundamentals: General introduction to Electrical Engineering, Kirchoffs Laws,Mesh and Node analysis, Superposition theorem, Thevenin Theorem, Norton Theorem, Maximum power transfer theorem. Generation of alternating
voltages and currents, Equations for AC quantities, cycle, time period, frequency, amplitude, calculation of R.M.S values, Average values for different waveforms, solution and phasor diagram of single phase AC circuit with sinusoidal source of excitation, AC through pure resistance, inductance and capacitance, series and parallel combination of R-L-C circuits, resonance in series and parallel circuits. Three Phase AC Fundamentals: Disadvantages of single phase system, star and delta connection in three phase circuits, relation between line and phasor quantities, power in three phase system, solution of three phase balanced circuits, power and power factor measurement by two wattmeter method. Electrical Machines: Introduction to magnetic circuits, Basic principle and construction of transformers, E.M.F equation, approximate equivalent circuit, phasor diagram, losses, efficiency and condition for maximum efficiency, open circuit and short circuit test on single phase transformers. Operating principle and construction of three phase induction motors, production of rotating field, concept of slip, frequency etc.Operating principle and construction of DC generators, types of DC Generators, E.M.F equations, , Armature reaction, commutation in DC Generators. Principle of DC Motors and their applications. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors: General introduction to Electronics. Concept of stiff Voltage and Current Source. PN Junction, Depletion layer, Barrier Potential, Forward and Reverse Bias, Breakdown voltage, V-I characteristics, Half wave and full wave rectifiers, Zener diode. Introduction to junction transistors, Transistor amplifying action, CB, CE, CC-configuration characteristics, applications of transistor as an amplifier, Operational Amplifiers: Block Diagram, characteristics of an ideal OP-AMP, Application of OP-AMP as an inverting amplifier, Phase Shifter, Scale Changer, Non-Inverting Amplifier, Adder, Differential, Integrating amplifier. Digital Electronics: Binary and Hexadecimal number system, conversion of numbers from one system to other, OR, AND, NOR, NAND, NOT Gates, Universal Gates, Exclusive OR, NOR gates, De-Morgans Theorem, Boolean Relations: Commutative, Associative and Distributive Laws. Concept of flip-flops, RS,D, JK, T types, masterslave flip flops, Shift registers,Concept of synchronous and asynchronous counters. Test and Measuring Instruments :Block diagram, concept of digital electronic voltmeters, ammeter and wattmeter, CRO, Sensors and Transducers and their classification. Working principle of resistive, capacitive, photosensitive and temperature transducers. Books Recommended: 1. Edward Hughes : Electrical and Electronic Technology, Pearson Education Publication, Asia, 2003.
2. Nagsarkar, T.K. and : Basic Electrical Engg., Oxford University Press, 2004. Sukhija M.S. 3. Nagrath, I.J. Kothari, D.P. and : Basic Electrical Engg., TMH, New Delhi.
4. Bhargava 5. Millman, J. 6. Malvino FT 304 FLUID FLOW
: Basic electronics and Linear circuits, Tata McGraw Hill. : Integrated Electronics. : Digital Principles and Applications, Tata McGraw Hill.
Fluid Statics: Normal forces in fluids, Pressure Measurements, Forces on Submerged bodies, Buoyancy and Stability. Fluid Properties: Newtonian and non-Newtonian Fluids, Nature of Turbulence, Eddy Viscosity, Flow in Boundary Layers, Basic Equation of Fluid Flow. Bernoullis Equation. Navier stokes equation: Applications of Dimensional analysis to Fluid Flow. Problems. Flow of Incompressible Fluids: Laminar and Turbulent flow in pipes, Velocity Distribution in Pipes, Frictional Losses in Pipes and Fittings, Fanning equation, Estimation of economic pipe diameter. Derivation of HAGEN-POISEULLI and f=16/Re equations. Flow of compressible fluids: Compressible flow and flow through nozzles. Flow Measurements: Pilot tube, Orifice, Venturi, Rotameter and Notches, wet gas metre etc. Fluid Machinery: Classification and Performance of Pumps, Turbines, Compressors, and Blowers, Selection and Specification, Net positive Suction Head. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Books Recommended: Mc Cabe, W.L. and Smith, J.C. : Unit Operation of Chemical Engineering, McGraw Hill. Coulson, J.M. and Richardson, J.F. : Chemical Engineering, Vol. I, Pergamon. Foust, A.S., Wensel, L.A., Clump, : Principles of Unit Operations, John Wiley. C.W., Maus, L. and Anderson, L. Badger, W.L. and Banchero, J.T. Fox, R.W. and McDonald, A.T. Chattopadhya, P. : Introduction to Chemical Engineering, McGraw Hill Pub. Co. Ltd., 1997. Tata
: Introduction of Fluid Mechanics (SI Version), 4th Ed., John Wiley and Sons, 1996. : Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, Vol. I, Khanna Publishers, Delhi, 1997.
FT 305 ENGINEERING MATERIALS 1. Atomic Structure: Review of bonding in solids, structure property-processing Relationships 2. Crystal Structure : Space lattice,crystal systems, Miller indices, effect of radius ratio on co-ordination, structures of common metallic, polymeric, ceramic, amorphous and partly crystalline materials.
3. Imperfections in atomic arrangement: various defects in atomic arrangement, diffusion phenomenon in solids, Ficks first and second law of diffusion, solid solution, slip systems, various methods of strengthening materials, Schmids law. 4. Phase Diagrams and phase transformation: binary phase diagrams Fe-Fe3C, Cu-Ni, Pb-Sn. microstructure development, TTT diagrams, heat treatment processes-hot and cold working, hardening and softening processes. 5. Materials: Standards and specifications, unified alloy numbering system, ferrous metals and alloys, non-ferrous metals and alloys; overview of ceramic, polymeric and composite materials; Mechanical tests: standard test procedures for mechanical property determination-strength, toughness, fracture toughness, hardness, deformation, fatigue, creep etc. 6. Corrosion: Types and mechanism of corrosion, factors influencing corrosion, combating corrosion, selection of materials of construction for handling different chemicals. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Askelland, Donald R. Shackleford, J.F. Van-Vlack, L.H. Raghavan, V. Callister Jr. William D. : : : : : The Science & Engineering of Materials, PWSKENT. Introduction to Material Science for Engineers, Mc Millan. Elements of Material Science & Engineering, Addison Wesley Material Science & Engineering, Prentice Hall of India Materials Science and Engineering- An Introduction, Wiley
FT 306 FOOD CHEMISTRY Moisture in foods : Hydrogen bonding, bound water, water activity. Carbohydrates: Definition, classification and nomenclature. General properties (physical and chemical) of sugar. Reducing and non-reducing sugars. Common mono-saccharides, di-saccharides and poly-saccharides. Chemistry of starch, cellulose, gums and mucilage. Crude fibre. Protein: Classification. Amino acid sequence in proteins, pleated sheet and helix structure of proteins. Molecular weight of proteins and ultra-centrifuge separation and purification of proteins. Physical and chemical properties of amino acids. Chromatographic separation of amino acids. Food proteins and their characteristics. Protein denaturation. Lipids : Classification. Occurance in foods and composition, identification of natural fats and oils in foods. Physical (melting point, softening point, slipping point, short melting point, specific gravity, refractive index, smoke-flash and fire point, turbidity point) and chemical properties. Flavor changes in fats and oils. Natural pigments and Flavouring Agents: Chlorophylls, carotenoids, anthocyanins, anthoxanthins, flavonoids, tannins and natural flavour constituents. Saponins, Alkaloids. Pectic substances-Protopectin, pectin gels, Importance of Pectin in food products.
Vitamins: Occurance and chemistry of various vitamins: A, B, C, D, E, K. ,Losses during processing and storage. Food Additives: Types; Methods for safety levelanalysis, color additives legislation. Recommended Books. 1 Food Chemistry: L.H. Meyer, C.B.S. Publishers, Delhi, 1987. 2 Food chemistry: Fenamma 3 Food Chemistry: de Man
FT 351 FOOD MICROBIOLOGY LAB Bacteriological examination of foods: General protocol taking the examples of different foods. Presumptive coliform test of milk, butter, cream, ice-cream and dahi. Standard plate count for pasteurized milk and ice-cream. Yeast and mold count for butter, dahi and bread. To access bacteriological quality of milk by methylene blue reduction test and resazurin reduction test.
FT 352 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LAB C++ fundamentals C++ Programming Basics: C++ Program Structure, Variables, Input /Output statements, Arithmetic Operators, Assignment and Increment Operators. Control statements Loops and Decisions: Relation operators, Iterations: While Loop, for Loop, do Loop, Decisions: if statement, if else statement, nested if else statement, switch statement. Logical operators, other control statements: break statement, continue statement and go to statement. Programming and Compiling, Exercises Functions Books Recommended: 1. 2. Lafore, R. Kanetkar,Y. : Object Oriented Programming in Turbo C++, Galgotia Publications. : Let Us C++, BPB Publications.
FT 353 FOOD CHEMISTRY LAB Preparation of samples for analyses. Determination of moisture content (wet basis and dry basis). Ash: total, acid soluble, alkali soluble and water soluble. Lipids, protein, crude fibre, reducing and non-reducing sugar. Estimation of ascorbic acid, vitamin-A, chlorophyll, carotenoids etc. Estimation of iron, copper, lead, tin etc.
FT 354 FLUID FLOW LAB 1. General study of pipe fittings, valves and other equipments in the unit operations laboratory. 2. Pressure drop for flow through pipelines, valves & fittings. 3. Characteristics of pumps. 4. Flow measurement by the use of orificemeter, venturimeter, rotameter & pitot tube. 5. Flow over weirs and notches. 6. Flow measurement of compressible fluids.
FT 355 ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB. 1. Overview of the equipments, instruments and procedure to be used, safety precautions and report writing. 2. To study resonance in R-L-C series and parallel circuit. 3. Measurement of power and power factor by three voltmeter method. 4. Measurement of power and power factor by three ammeter method. 5. To measure power and power factor using a single wattmeter in a single phase circuit. 6. Measurement of power and power factor of three phase balanced load by two wattmeter method. 7. To perform open circuit test and short circuit test on a single phase transformer and draw equivalent circuit. 8. To obtain magnetization characteristics of DC Machine 9. Study the forward and reverse biased diode characterstics. 10. Study the CB, CE, CC transistor characterstics. 11. To obtain the waveforms of half wave rectifier circuit on CRO
. 12. To obtain the waveforms of full wave rectifier circuit on CRO . 13. To study the OP-AMP as an Inverting amplifier , Phase Shifter, Integrator , Differentiator. 14. Verification of basic and universal gates.
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) FOURTH SEMESTER
FT 401 MATHEMATICS-III Fourier Series: Eulers Formulae, Dirchiels Conditions for Expansion, Change of interval, Odd and Even Functions, Expansion of Odd and Even Periodic Functions, Introduction to Harmonic Analysis. Vectors: Gardient, Divergence, Curl, Statement of Greens Gauss and Stokes Theorem and their simple applications. Linear Differential Equations with constant Coefficients, Homogeneous Linear Equations, method of variation of Parameters, Simultaneous Liner Differential Equations with Constants Coefficients. Laplace transform: Definition, Transforms of Elementary functions, Properties of Transforms, Inverse Transforms, Transform of Derivative Unit. Unit Step Function, Dirac Della Function & Unit Impulse function. Period Functions, Application of Transform to the solution of ordinary Differential equations. Function of complex variable, analytic functions, Cauchys theorem, Cauchys integral formula, introduction to Taylers series and Laurents series, Residues, theorem and its simple applications. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Kreyszig, Erwin Grewal, B.S. Jain, R. K. and Iyengar, S. : Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 7th Edition, John Wiley & Sons. : Higher Engineering Mathematics, 41st Edition, Khanna Publishers, Delhi. : Advanced Engg. Mathematics, 2nd Edition, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, 2003.
FT 402 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Ambient air and water standards. Principal sources of pollution. Inter-relationship between energy and environment pollution. Prevention of environmental pollution through conservation, raw material substitutions, process and equipment modifications. A case study on the concept of zero discharge. Air Pollution: Principal air pollutants and their usual sources. Effect of air pollutants on human health, animals, vegetation and materials.
Atmospheric dispersion of air pollutants, temperature inversions, Estimation of pollutants by Gaussian plume model. Process and equipments used for the control of particulate pollutants. Types of water pollutants, their sources and effects. BOD and COD Waste water treatment techniques and equipments, flocculation, skimming, floatation, etc. Primary Treatment-through settling. Secondary Treatment-Aerobic and anaerobic digestion, activated sludge process, trickle filter and oxidation ponds
Water Pollution: -
Solid wastes: Control and disposal, sanitary landfill, incineration, pyrolysis gasification and recycling. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Perkins, H.C. Rao, C.S. Williamson, S.J. Numerow, N.L. Sincero, A.P. and Sincero, G.A. Hammer, M.J. and Jr. Hammer, M.J. Mahajan, S.P. Metcalf and Eddy : Air Pollution, McGraw Hill, N.Y. : Environmental Pollution Control Engineering, 2nd Edition, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., 2006. : Fundamental of Air Pollution, Addison Wesley Co. N.Y. : Liquid Wastes of Industry, Addison Wesley Co., N.Y. Environmental Engineering, Prentice-Hall of India, 1999. : : Water and Wastewater Technology, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India, 2008. : Pollution Control of Process Industries, Tata McGraw Hill. : Waste-Water Engineering, 4th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007.
FT 403 HEAT TRANSFER Conduction: Steady state conduction in one dimensional system, general conduction equation, effect of variable thermal conductivity, steady state conduction involving internal heat generation, lagging on pipes, the critical thickness of insulation on pipes, extended surfaces of uniform thickness and fin effectiveness, fin efficiency. Convection: Free and forced convection, concept of heat transfer co-efficient, dimensionless numbers in free and forced convection, Dimensional analysis,
Determination of Heat transfer coefficient using heat and momentum transfer analogies, experimental determination of heat transfer coefficient and common working correlations. Condensation and Boiling: Condensation heat transfer phenomenon, film condensation on vertical plates and cylinders as well as on horizontal cylinders. Effects of noncondensable gases and vapor velocity on condensation, pool boiling, forced convection boiling, working correlations for pool boiling. Evaporation: Types of Evaporators, single and multiple effects, single and multiple effects calculations, evaporator capacity, economy, effect of liquid head and boiling point elevation, methods of feeding. Heat Exchangers: Various types of heat exchangers, overall heat transfer coefficients, heat exchanger mean temperature differences, heat exchanger effectiveness and the number of transfer units. Radiation Heat Transfer: Black Body radiation, and grey body radiation, physical mechanism, radiation properties and shape factor, heat exchange between non-black bodies, radiation shields pyrometry and effect of radiation on temperature measurement. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mc Cabe, W.L., Smith, J.C. Holman, J.P. Mc Adams, W.H. Chapmann, A.J. Kern, D.Q. Kreith, F. Geankoplis, C.J. : Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering McGraw Hill. : Heat Transfer, McGraw Hill Book Co. : Heat Transmission, McGraw Hill Book Co. : Heat Transfer, Mc Millan Publishing Co. : Process heat Transfer, McGraw Hill Book Co. : Principles of Heat Transfer, Harper & Row Pub., London. : Transport Processes and Unit Operations, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., 3rd Edition, 1999.
FT 404 MATERIAL & ENERGY BALANCE 1. Review: Stoichiometric and composition relationship gas laws; Gaseous mixtures, vapor pressure, humidity, etc. 2. Material Balances for Non-reaction systems including balances involving recycle and by-pass streams. 3. Material Balances for Reacting systems including balances involving recycle and purge streams. 4. Combustion Calculations. 5. Energy balances on nonreactive and reactive systems.
Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bhatt, V. I. & Vora, S. M. Himmelbleau, D. M. Felder, R. M. & Rousseau R.W. Reklaithis, G. V. Lubyben, L.W. & Winzel, L. A. : Stiochiometry, 3rd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 1984. : Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical Engineering, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall, 1977. : Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, 3rd Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 1986. : Introduction of Material and Energy balances, John Wiley, 1983. : Chemical Process Analysis, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1988.
FT 405 PROCESSING OF CEREALS & PULSES Composition, structure and quality, characteristics of cereal grains and pulses. Paddy Milling: Principles of milling of paddy. Traditional and modem methods of paddy milling. Parboiling of paddy, Paddy milling machinery. Processed foods from rice, byproducts of paddy milling and their uses. Milling of Wheat: Criteria of wheat and flour quality, flour milling, wheat milling machinery. Rheology and Chemistry of dough, Physical dough testing instruments. Technology of baking bread, biscuit, cookies, cakes. Durum wheat and pasta products like macaroni, noodles and spaghetti. Cereal based infant foods. Corn Milling: Dry and wet milling of corn, corn based ready to eat breakfast cereals. Corn oil- processing and utilization, Corn starch modification and uses, Corn sweeteners such as glucose syrup, high fructose corn syrups, dextrose, maltodextrin. Milling of Pulses: Different methods of pulse milling. Pulse milling machinery. Application of enzymes in processing of cereals and pulses processing. Sanitation in the processing plant. Design of equipment used in milling of wheat, rice, corn and pulses. Plant layout. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Kent, N.L. Pomeranz, Y. Tanley A. Watson & Paul E. Ramstad Julliano, B.O. Pandey, P.H. : : : : : Technology of Cereals, CBS Publisher. Wheat Chemistry and Technology, CHIPS Book, USA. Corn Chemistry and Technology, ADCC, USA. Rice Chemistry and Technology, AACC, USA. Post Harvest Technology.
FT 451 PARTICLES MECHANICS LAB 1. Pressure drop and two phase flow characteristics in packed and fluidized beds. 2. Measurement of drag force. 3. Batch settling of slurries. 4. Constant pressure filtration. 5. Mixing, crushing, grinding, screening and particle size analysis. FT 452 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING LAB 1. To find BOD of water sample. 2. To find COD of waste sample. 3. To find the total dissolved solids (TDS) and its volatile and non-volatile components. 4. To find the total suspended solids (TSS) and its volatile and non-volatile components. 5. To do the chromium separation by different techniques from electroplating wastes. 6. To find the phenol content of water sample and evolution of parameters. 7. To operate the electrodialysis apparatus. 8. To find the biodegradation constant (K) and the effect of timing on it. 9. To use the membrane separation techniques for salt brine and reverse osmosis process for sugar. 10. To use stack monitoring kit to find: (a) Efficiency of a cyclone. (b) Dust sampling. Note: Any six of the above mentioned experiments are to be conducted.
FT 453 CEREALS & PULSES PROCESSING LAB. (PRACTICALS) Milling of wheat. Evaluation of properties of wheat and milled products - Physical, chemical and rheological. Baking of bread, biscuit, cake, pastries. Evaluation of baked bread. Evaluation of properties of rice (physical and chemical). Cooking quality of rice.
Experiment on parboiling, evaluation of quality. Milling of rice, assessment of degree of polishing. Milling of pulses. Visit to flour mill, rice mill and pulse mill industries.
FT 454 COMPREHENSIVE VIVA-VOCE-I The viva-voce examination will be comprehensive and covering mainly subjects covered during the first four semesters.
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) FIFTH SEMESTER FT 501 MATHEMATICS III Solution of differential equations in series with reference to Bessel and Legendre equations, elementary properties of Bessel and Legendre functions. Solution of differential equations by numerical methods, Picards method, Eulers method, Runge-Kutta method, Milnes method. Solution of difference equation with constant coefficients. Formation and classification of partial differential equations, first order linear equations, standard forms of non linear equations, Charpits method, homogeneous linear equations with constant coefficients. Different methods for parabolic equations, hyperbolic equations and elliptic equations. Solution of partial differential equations of engineering interest by method of separation of variables. Z-transforms: Introduction, standard Z transforms, properties of z-transforms, initial value and final value theorems, Inverse Z-transforms, Inverse Z-transforms by power series method, partial fractions method and integral method, application to difference equations. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Kreyszig, Erwin Grewal, B.S. Jain, R. K. & Iyengar, S. Jain, R.K. : Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 8th Edition, Wiley-Eastern, New Delhi, 2002. : Higher Engineering Mathematics, 40th Edition Khanna Publishers, Delhi, 2008. : Advanced Engg. Mathematics, 2nd Edition, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, 2003. : Numerical Solutions of Differential Equations, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1987.
FT 502 PROCESSING OF FRUITS & VEGETABLES Physiology of ripening. Effect of physical and chemical treatments on post harvest life of fruits and vegetables. Role of plant growth regulators in post harvest storage, Storage and handling of fresh fruits and vegetables. Preservation of fruits and vegetables by heat treatment, Canning Processing and preservation of fruits and vegetable juices. Preparation of jams, jelly, marmalade, preserves, pickles and vegetable products. Fermented fruit and vegetable products. Freezing and dehydration of fruits and vegetables. Concentration of fruits and vegetable juice. Effects of processing on the nutritive value of fruits and vegetables. Food additives, Fermented foods, pickling and
curing of food. Intermediate moisture foods, by product and their utilization. Application of enzymes in processing of fruit and vegetable juices. Design of cleaning, cutting, blanching, and thermal processing equipments. Plant layout. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Giridhari Lal Ranganna Luh & Woodroof Woodroof & Luh : Preservation of Fruits & Vegetables, ICAR Publication, India. : Analysis of Fruits land Vegetables, Tata MacGraw Hill, India. : Commercial Vegetable Processing, AVI Publishing, USA. : Commercial Fruit Processing, AVI Publishing, USA
FT 503 PROCESSING OF MILK & MILK PRODUCTS Chemical composition, nutritive value and physical characteristics of milk and milk products. Production, processing, distribution and storage of liquid milk. Technology of manufacture of cream, butter, ghee and ice-cream. Technology of manufacture of evaporated milk and condensed milk. Technology of manufacture of cheese and other fermented milk products. Fortification of milk products with nutrients, quality standards. Production of infant milk food. Utilization of dairy byproducts such as whey, butter-milk etc. Quality control in milk and milk products including various analytical techniques of determination of milk quality. Milk plant hygiene, sanitation Design of storage tank, pasteurizer, cream separator, milk evaporator, ice-cream mixer and freezer. Plant layout. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. De, S. Ahmed, T. Eckles : : : Outlines of Dairy Technology, OUP, India.. Dairy Industry Plant Layout. Chemistry & Technology of Milk, CBS Publisher, India.
FT 504 PROCESSING OF OIL SEEDS, OILS & FATS Status of oils & fats and Indian economy. General chemistry. Analytical methods for characterization. Quality standards of edible oils & fats in diet, nutrition & disease. Detection of adulteration.
Oil milling methods: Ghani, mechanical expeller, hydraulic press, solvent extraction. Refining of edible oils & fats. Classification of vegetable oil. Modifications of the properties of oils & fats including chemical and biotechnological processes. Confectionary plastic fats. Preparation of various products including different shortenings, margarine, salad dressing & mayonnaise, imitation of dairy products low calorie spreads. Animal fat, oil derivatives. Technology of oilseed protein isolate. Utilization of byproducts from the oil milling industry. Design of oil milling equipments and plant layout. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Bailey Williars, P.N. & Devine, J. : Fats and Oil, Wiley, USA. : The Chemistry & Technology of Edible Oils & Fats.
FT 505 MASS TRANSFER-I Mass transfer operations, classification of mass transfer operations, choice of separation methods, methods of conducting mass transfer operations, design principles. Introduction to mass transfer and diffusion, molecular diffusion in gases and liquids, diffusion coefficients for gases and liquids, diffusion in solids, types of solid diffusion. Mass transfer coefficients, types of mass transfer coefficients, mass transfer coefficients in laminar flow, theories of mass transfer. Interphase mass transfer, concept of overall mass transfer coefficient. Working principle, construction and industrial applications of various gas liquid contacting equipments like sparged vessels, mechanically agitated vessels, tray towers, packed towers, spray chambers, venturi scrubbers. Humidification operations, psychometric chart, adiabatic saturation temperatures, wet bulb temperature, adiabatic operations, types of cooling towers. Principle of drying, batch drying, drying curve, constructional details and working of different dryers. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Treybal, Robert E. : Mass Transfer Operations, 3rd Edition. McGraw-Hill, 1981.
Sherwood, T.K., Pifford, Robert : Mass Transfer, McGraw-Hill. L. and Wilke, Charles R. Sharma, K.R. McCabe, Warren L., : Principles of Mass Transfer, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., 2007. Smith : Unit Operations of Chemical Engg., 7th Edition,
Juliam C. and Harriott, Peter 5. Coulson & Richardson
McGraw-Hill, 2005. : Chemical Engineering, Vol.I (6th Edition, 2009) and Vol. II. (5th Edition, 2006).
FT 506 PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION General Concept: Need and classification of measurements and instruments, Basic and auxiliary functional elements of a measurement system Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Instruments: Static Characteristics: Range and span, accuracy and static error, reproducibility and drift, sensitivity and dead zone. Dynamic Characteristics: Speed of response and lag, fidelity and dynamic error, dead time. Temperature measurement: Thermal expansion methods bimetallic thermometers, liquid-in-glass thermometer and filled-in-system thermometers. Thermocouples, metal resistance thermometers and thermistors, optical and radiation pyrometers, radiation receiving elements. Pressure measurement: Use of manometers, Bourdon gauge, bellows type gauge. Vacuum measurementMcleod gauge, thermoionic type ionization gauge, pirani vacuum gauge. Measurement of pressure in corrosive fluids: Diaphragm seal, liquid seal and purge system. Liquid level measurement: Direct measurement of liquid level Float & tape liquid level gauge, float and shaft liquid level unit, hydraulic remote transmission of liquid level. Level measurement in open vessels: Bubbler system, diaphragm box system, air trap system. Level measurement in pressure vessels Differential pressure manometer, use of liquid seals with a manometer, displacement float liquid level gauge. Measurement of viscosity, conductivity, humidity and pH. Density measurement liquid level method, displacement meter and hydrometer. Measurement of weight spring scale, pneumatic force meter and hydrostatic force meter. Process InstrumentationRecording instruments, indicating and signaling instruments, control centre, transmission of instrument reading, instrumentation diagrams. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Eckman, Donald P. Singh, S.K. Considine, D.N. : Industrial Instrumentation, CBS Publisher and Distributors, Indian Reprint 2004. : Industrial Instrumentation and Control, 2nd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007. : Process Instruments and Controls Handbook 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill, 1974.
4. 5.
Fribance, A.E. Patranabis, D.
: Industrial Instrumentation Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd., 1962. : Principles of Industrial Instrumentation, 2nd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd., 1999.
FT 551 PROCESS PLANT DESIGN -I 1. Design of piping & piping networks. 2. Selection, specification & power requirements of process pumps, fans and blowers. 3. Design of settling equipment like Dor thickners, dust chambers, cyclone separator & centrifuges. 4. Design of agitated vessels using various types of impellers. 5. Design of conveyor system for solids. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Luding, E.E. Perry, J.H. Joshi, M.V. Peters, M.S. and Timmerhaus, K.D. : Applied Process Design in Chemical in Petrochemical Plants, Gulf Publishing Company. : Chemical Engineering Handbook, McGraw Hill. : Process Equipment Design, Macmillan Indian. : Plant Design and Economics for chemical Engineers, McGrawHill.
FT 552 FRUITS & VEGETABLES PROCESSING LAB 1. Blanching of fruits and vegetables: Effect of temperature, time and selected compounds on blanching. 2. Preparation of fruit juices. Squashes, R- T -S, nectar. 3. Preparation of jam, marmalade preserve, candy. 4. Preparation of fruit juice concentrate and powder. 5. Preparation of tomato products. 6. Preparation of pickles, chutneys, sauces. 7. Drying of fruits & vegetables. 8. Freezing of fruits & vegetables. 9. Quality control of processed products. 10. Can seaming operation and canning of fruits and vegetables. 11. Visit to a fruit and vegetable processing plant.
FT 553 MILK & MILK PRODUCTS PROCESSING LAB 1. Physical and chemical analysis of milk & milk products. 2. Testing the adulteration in milk & milk products. 3. Preparation of cream, butter, ghee, ice-cream, milk powder and condensed milk. 4. Quality evaluation of milk products. 5. Visit to a milk processing plant. FT 554 OILS & FATS PROCESSING LAB 1. Determination of oil content of foods by Soxhlet method. 2. Determination of specific gravity of oils and fats. 3. Determination of refractive index of oils and fats by Abbes Refractometer. 4. Determination of free fatty acids and acid value of fats and oils. 5. Determination of peroxide value of fats and oils. 6. Determination of iodine value of fats and oils. 7. Determination of melting point and smoke point of fats and oils. 8. Determination of saponification value of fats and oils. 9. Determination of adulteration in fats and oils. 10. Determination of Reichert Neisl number and Polenske value of fats and oils. 11. Determination of oil absorption during deep-oil frying of foods FT 555 HEAT TRANSFER LAB 1. Determination of heat transfer coefficient for different types of heat transfer equipment. Wilson plots. 2. Unsteady state heat transfer in jacketed vessels. (Open pan evaporator) 3. Correlation of instantaneous heat transfer coefficients with time study deposition of scale on a heating surface. 4. Determination of heat losses for insulated pipes 5. Study of double pipe heat exchanger and to determine overall heat transfer coefficient 6. Study the performance characteristics of a 1,2 - shell and tube heat exchanger 7. Study and operation of long tube, forced circulation and multiple effect evaporators. 8. Duhring plot for solutions involving nonvolatile solutes.
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) SIXTH SEMESTER FT 601 REACTION ENGINEERING Introduction and a brief review of the kinetics of homogeneous reactions. Interpretation of rate data from constant volume and constant pressure systems. Single Ideal reactors. Design for single reactions. Design for multiple reactions. Thermal characteristics of reactors: temperature and pressure effects. Non-ideality in reactors and its effects on chemical conversion. One parameter models to represent the behaviour of chemical reactors. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Levenspiel, O. Smith, J.M. Dinbigh, K. & Turner, K.G. Scott Fogler, H. : Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2004. : Chemical Engineering, Kinetics, 3rd Edition, and McGraw Hill, 1981. : Chemical Reactor Theory An Introduction, Cambridge Univ. Press. : Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2007.
FT 602 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Brief review of the terms: state functions, types of systems, internal energy, heat and work and reversible and irreversible processes. First Law of Thermodynamics and its Engineering Applications i.e. constant volume processes, constant pressure processes, isothermal and adiabatic processes, pumps, turbines, compressors, nozzles, heat exchangers, pitot tube, venturimeter and orifice meter. Throttling Processes, JouleThomson Coefficient, liquefication of gases, thermochemistry includes a brief review of heat capacities and their measurement, standard heat of reaction, standard heat of formation, standard heat of combustion, flame temperature, H-x diagrams, heat of solution, partial, molar enthalpies, enthalpy for phase change etc. Equation of state for real gases and their mixtures. Principle of corresponding states and generalized compressibility factor. Review of Second law of thermodynamics, entropy concept, Entropy and lost work calculations. Microscopic interpretation of entropy. Third Law of thermodynamics and its applications. Free energy functions and their significance in phase and chemical
equilibria, Clapeyrons equation and some important correlations for estimating vapor pressures. Estimation of thermodynamic properties by using graphs and tables. Phase Equilibria: Partial molar properties, partial molar Gibbs free energy, Chemical potential and its dependence on temperature and pressure Ideal solutions (Lewis-Randel Rule). Fugacity and its calculations. Dependence of fugacity of temperatures and pressure Solution behaviour of real liquids and solids. Activity and activity coefficients. Variation of activity co-efficient with temperature and composition. Activity coefficients of electrolytes standard states. Properties of mixing. Excess Properties, Gibbs-Duhem equation and its application to vapour-liquid equilibria. Chemical Equilibria: Equilibrium constant in terms of measurable properties variations of equilibrium constant with temperature and pressure. Adiabatic reactions, Gibbs phase rule, equilibria in heterogeneous reactions. Books Recommended: 1. Smith, J.M., Van Ness, H.C. and Abbott, M.M. Elliott, J.R and Lira, C.T. Rao, Y.V.C. Dodge, B.F. : Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 7th Edition, McGraw Hill Professional, 2005. Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamic, Prentice Hall PTR, 1999. Chemical Engg. Blackswan, 1997. Thermodynamics, Orient
2. 3. 4.
: : :
Chemical Engg. Thermodynamics, McGraw Hill, 1944, Original from the University of Michigan, 2007. A Textbook of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 2004.
5.
Narayanan, K.V.
FT 603 CONFECTIONARY TECHNOLOGY 1. 2. 3. 4. Types of confectionary goods. Characteristics and processing of raw materials. Technology of manufacture of toffee, chocolate, fruit drops, hard-boiled candies, bars, chewing gums, bubble gums and special confectionary goods. Color, flavor and texture of confectionery. Standards and regulations.
5. 6. 1. 2.
Economics and marketing of confectionery goods. Design of equipments used in confectionary. Plant layout. Books Recommended: Beckette Marie : Industrial Chocolate Manufacture: 3rd Edition, CBS Publication, New Delhi, 2000. : Handbook of Sweeteners, CBS Publication, New Delhi, 2000.
FT 604 MASS TRANSFER-II Absorption: Equilibria for absorption systems use of Raoults law, Henrys law for solubility predictions, Selection of absorbent, limiting liquid gas ratios, absorption factor use in design of plate absorbers. Kremser equation for ideal plates and translation of ideal plates to real plates using various efficiencies. Concept of transfer units for the design of packed absorbers. Distillation: Limitations and applications, prediction of VLE using thermodynamic & experimental techniques. Dew point & bubble point estimations for binary & multicomponent mixtures. Distillation methods flash distillation, differential distillation for binary systems, steam distillation, optimum reflux ratio. Fractionation of binary mixtures using McCabe Thiele method and enthalpy concentration method (Ponchon and Savarit method). Packed distillation columns. Azeotropic & extractive distillation preliminaries and molecular distillation. Liquid-Liquid Extraction: Ternary Equilibria and its representation on various plots. Selection criteria for solvent, Multistage extraction using partially miscible & immiscible solvents. Stagewise contact for countercurrent and crosscurrent extraction. Constructional details of equipment like mixer-settler, packed columns, pulsed extractor, sieve-tray extractor and centrifugal extractor. Leaching: Preparation of solid, countercurrent and crosscurrent multistage contact Shanks system. Constructional details of equipment like Rotocel extractor, Hildebrandt extractor, Bollman extractor, Kennedy Extractor & Beet-Sugar Diffusion battery extractor. Adsorption: Types of adsorption, nature of adsorbents, equilibria for adsorption systems. Brief manufacture and commercial applications and characteristics for common adsorbents. Stagewise & continuous contacting of fluid and solid phase. Description of contact filtration adsorption system. Hypersorber Ion-exchange system. Crystallization: Growth and properties of crystals saturation, nucleation, growth of crystals, effect of impurities on crystal formation, effect of temperature on solubility, fractional crystallization, yield of crystals, crystal purity, yield calculation using phase diagram, energy requirements using enthalpy-concentration diagram. Methods of creating super saturation-Meirs supersolubility curve. Mechanism and methods for nucleation. Derivation for ideal growth of crystals and discussion of actual growth. Swanson-Walker and various vacuum crystallizers.
Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Treybal, Robert E. : Mass Transfer Operations, 3rd Edition, McGraw-Hill, 1981. Sherwood,T.K., Pigford, : Mass Transfer, McGraw-Hill, Chemical Engineering Series, R.L & Wilke,C.R. 1975. Skelland, A.H.P. McCabe, Warren L., Smith Julian C. and Harriot, H.P. King, C.J. Geankoplis, C.J. : Diffusion Mass Transfer, John Wiley & Sons., New York, 1974. : Unit-Operations of Chemical Engg., 7th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2005. Separation Processes, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd., : New Delhi , 1982. : Transport Process and Separation Processes, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall Inc., New Delhi, 2003.
5. 6.
FT 605 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Ambient air and water standards. Principal sources of pollution. Inter-relationship between energy and environment pollution. Prevention of environmental pollution through conservation, raw material substitutions, process and equipment modifications. A case study on the concept of zero discharge. Air Pollution: Principal air pollutants and their usual sources. Effect of air pollutants on human health, animals, vegetation and materials. Atmospheric dispersion of air pollutants, temperature inversions, Estimation of pollutants by Gaussian plume model. Process and equipments used for the control of particulate pollutants. Types of water pollutants, their sources and effects. BOD and COD Waste water treatment techniques and equipments, flocculation, skimming, floatation, etc. Primary Treatment-through settling. Secondary Treatment-Aerobic and anaerobic digestion, activated sludge process, trickle filter and oxidation ponds.
Water Pollution: -
Solid wastes: Control and disposal, sanitary landfill, incineration, pyrolysis gasification and recycling.
Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Perkins, H.C. Rao, C.S. Williamson, S.J. Numerow, N.L. Sincero, A.P. and Sincero, G.A. Hammer, M.J. and Jr. Hammer, M.J. Mahajan, S.P. Metcalf and Eddy Rao and Rao : Air Pollution, McGraw Hill, N.Y. : Environmental Pollution Control Engineering, 2nd Edition, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., 2006. : Fundamental of Air Pollution, Addison Wesley Co. N.Y. : Liquid Wastes of Industry, Addison Wesley Co., N.Y. Environmental Engineering, Prentice-Hall of India, 1999. : : Water and Wastewater Technology, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India, 2008. : Pollution Control of Process Industries, Tata McGraw Hill : Waste-Water Engineering, 4th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007. : Air Pollution, Tata McGraw Hill.
FT 606 BEVERAGE TECHNOLOGY 1. Status of the beverage industry in India. Its future prospects. 2. Technology of manufacture of mineral water. 3. Technology of manufacture of non-alcoholic beverages: fruits & vegetable juices, soft drinks, dairy beverages, etc. 4. Technology of manufacture of alcoholic beverages: Beer, wine, whiskey, rum etc. 5. Technology of manufacture of tea and coffee drinks. 6. Design of equipments used in manufacturing of beverages. Plant layout. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Woordroof & Phillips Wangham, D.A. Ranganna : Beverages, AVI Publication, USA. : Coffee & Tea, Interscience Publication, USA. : Handbook of Analysis of Fruit and Vegetable Products.
FT 651 MASS TRANSFER LAB 1. Determination of mass transfer coefficients for naphthalene-air system. 2. To determine drying rate curves for different wet solids in a batch drier under constant drying conditions 3. Fractional approach to equilibrium for liquid-liquid extraction from single drop. 4. Verification of Rayleighs equation for differential distillation.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Determination of flooding velocities in packed columns. Determination of HETP for packed distillation columns. Study and operation of a pilot sized distillation column under total reflux. Study of different mass transfer equipments.
FT 652 PROCESS PLANT DESIGN II 1. Process design and specifications of double pipe heat exchanger, shell and tube heat exchanger, plate type heat exchanger, condenser and reboiler. 2. Equilibrium procurement techniques experimental and use of thermodynamics for its evaluation and then use in design height of distillation column. Calculations using McCabe Thiele, Plate-to-Plate calculation methods for fractionators, design of batch fractionating columns, design of fractionators internals for sieve-tray. 3. Absorber/Stripper design of stage-wise and continuous contact equipment (packed column), height of column and diameter calculation, design of various internals of absorber/stripper. 4. Process flow sheets, material and energy balance flow sheeting analysis. Books Recommended: 1. Coulson, Richardson & Sinnott, R.K. Ludwig, E.E. Perry, J.H. Kern, D.Q. Joshi , M.V. Shell and Tube Type Heat Exchangers, Indian Standards. Peters, M.S. and Timmerhaus, K.D. : Chemical Engineering, Volume 6 An Introduction to Chemical Engineering Design, 4th Edition, Pergamon Press, 2007. : Applied Process Design in Chemical and Petrochemical Plants, 2nd Edition, 1977. : Chemical Engineers Handbook, 8th Edition, McGraw Hill, 2007. : Process Heat Transfer, McGraw Hill, 1965. : Process Equipment Design, 3rd Edition, Macmillan India, 2007. : Instt., IS: 43-197. : Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers, 5th Edition, McGraw Hill, 2004.
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
FT 653 BEVERAGE & CONFECTIONARY PROCESSING LAB 1. Water hardness, acidity, basicity, chlorination, total dissolved solids, chlorides, iron, phosphorus in water. 2. Determination of alcoholic content in beer and wine using the distillation method.
3. Sulphur dioxide content in juices, squash, wine etc. 4. Acidity and total soluble solids determination in different beverages. 5. Manufacture of whey. 6. Estimation of caffeine in tea and coffee. 7. Determination of extract in tea leaves. 8. Sensory evaluation techniques and their uses. 9. Manufacture of milk based beverages (fermented and un-fermented). 10. Experiments on preparation of confectionary goods.
FT 654 ENVIRONMENT ENGINEERING LAB 1. To find BOD of water sample. 2. To find COD of waste sample. 3. To find the total dissolved solids (TDS) and its volatile and non-volatile components. 4. To find the total suspended solids (TSS) and its volatile and non-volatile components. 5. To do the chromium separation by different techniques from electroplating wastes. 6. To find the phenol content of water sample and evolution of parameters. 7. To operate the electrodialysis apparatus. 8. To find the biodegradation constant (K) and the effect of timing on it. 9. To use the membrane separation techniques for salt brine and reverse osmosis process for sugar. 10. To use stack monitoring kit to find: 11. Efficiency of a cyclone. 12. Dust sampling. Note: Any six of the above mentioned experiments are to be conducted.
13. SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) SEVENTH SEMESTER FT 701 FOOD REGULATION & QUALITY CONTROL General Principles of Quality Control, Quality Attributes: Colour, gloss, viscosity and consistency, size, shape and texture, flavour, taste, sensory evaluation techniques. Microbiological methods of quality evaluation. Government and trade standards for quality. Food Laws and Regulations: PFA, FPO, BIS, AGMARK, ISO, etc. Quality of Different Food Products: Cereals, fruits, vegetables, milk, egg, meat, fish etc. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Krammar and Twigg Herschdoerfar, S.N. Ranganna : Quality Control for Food Industry, AVI Publishing, 1979. : Quality Control in Food Industry, Academic Press, U.K. : Handbook of Analysis of Fruit and Vegetable Products, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 1986.
FT 702 PROCESS ENGINEERING ECONOMICS Cost estimation: Factors affecting Investment and production costs. Capital investments, fixed investments and working capital. Cost indices. Estimating equipment costs by scaling 6/10 factor rule. Methods for estimating capital investment. Estimation of total product cost. Different costs involved in the total product costs. Different cost involved in the total product for a typical chemical process plant. Interest and Investment Costs: Simple and compound interest. Nominal and effective rates of interest. Continuous interest ordinary annuity. Perpetuities and capitalized costs. Taxes and Insurance: Types of taxes and tax returns, Types of insurance and legal responsibility. Depreciation: Types of depreciation. Service life salvage value, present value and methods of determining depreciation, single unit and group depreciation. Profitability: Alternative Investments and Replacements: Mathematical methods of profitability evaluation. Cash flow diagrams. Determination of acceptable investments. Alternatives when an investment must be made and analysis with small increment investment, replacement. Breakeven analysis. Balance sheet and income statement. Optimum Design: Procedure with one variable, optimum reflux ratio in distillation and other examples.
Preliminary Steps in Plant Design: Plant design factors. Project organisation, plant location, preliminary data collection, process engineering. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Peters, M.S. & Timmerhaus, K.D. Ulrich, G.D. Guthrie, K.M. Jelen, F.C. Holland, F.A. & Wastson, F.A. Bassel, W.D. : : : : : Plant Design and Economic of Chemical Engineers, 4th Edition, Mc Graw Hill, New York, 1991. A Guide to Chemical Engineering Process Design and Economics John Wiley, 1984. Process Plant Estimating, Evaluation and Control, Craftsman Solano Beach; Calif, 1947. Cost and Optimisation Engineering, McGraw Hill, New York, 1970. Introduction to Process Economics, 2nd Edition, Wiley, 1983. Preliminary Chemical Engineering Plant Design, Elsevier, New York, 1976.
FT 703 PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY Basic concepts, function of food package, packaging materials, cellulosic, glass, metal, polymeric composite, rigid, semi-rigid and flexible package forms, adhesive, band and closure, coatings and labels, packaging, product characteristics and packaging requirements, selection of material, form, machinery and method of packaging, package printing, standards and regulations. Special problems in packaging of foodstuffs. Biodegradable packaging. Design of packaging equipments. Evaluation of packaging materials for different food products and package performance. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pines, F.A. : Fundamentals of Packaging, Cornhill Publication, London. Aseptic Processing and Packaging & Food, CRC Press. Food Packaging, AVI Publishing, Westport, Conn. Flexible Packaging of Foods, CRC Cleveland, Ohio Press. Principle of Food Packaging, An International Guide United Nations Food & Agricultural Organization, Rome, Italy, 1970. David, J.R. & David, : D.R.D. Sacharow & Griffin Brody, A.L. Heiss, R. : : :
FT 704 BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING Isolation and Utilization of Enzymes: Purification, immobilization, application of enzyme technology.
Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions: The substrate, enzyme kinetics, factors affecting enzymatic activity and enzymatic reactions in heterogeneous reactions. Metabolic Pathways and Energetics of the Cell: The concept of energy coupling, aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, photosynthesis and biosynthesis, transport across cell membranes. Cellular Genetics and Control: Growth and reproduction of a single cell, alteration of cellular DNA, commercial applications. Kinetics of Substrate Utilization. Product Yield and Biomass Production: Growth cycle for batch cultivation and its mathematical modeling, products synthesis kinetics, thermal death kinetics of cells and spores. Transport Phenomena in Microbial Systems: Gas-liquid mass transfer, determination of oxygen transfer rates, mass transfer, surface-area correlations for mechanically agitated vessels, scaling of mass transfer equipment, particulate mass transfer, heat transfer. Design and Analysis of Biological Reactors: The ideal continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor (CSTR), residence time distribution, different types of reactors, relationship between batch and continuous biological reactors. Fermentation technology, product manufacture by fermentation, reactors for biomass production.
Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Balley & Ollis Aiba Humphrey & Millis Whitaker Stanbury Whitaker, Hall : Biochemical Engineering Fundamentals, McGraw Hill Book Co., 1986. : Biochemical Engineering, Academic Press, 1973. & : Principles of Fermentation Technology, Adita Books, New Delhi, 1997.
FT 751 FOOD QUALITY CONTROL & PACKAGING LAB Quality Control: Estimation of product quality with respect to the color, size, shape. Viscosity, texture, flavour, taste, sensor evaluation, market testing of products. Evaluation of food standards. Packaging: 1. Strength properties of packaging materials. 2. Water vapour and gas transmission rates of flexible packaging materials. 3. Identification of plastic films. 4. Pre-packaging of vegetables. 5. Shrink packaging of poultry.
6. Estimation of shelf life of packaged foods. 7. Vacuum and gauge packaging. 8. Performance evaluation of transport packaging. FT 752 ENGINEERING COMPUTATION LAB Errors analysis, solution of linear and non-linear algebric equations. Numerical differential & integration. Interpolation. Least squares approximation. Ordinary and partial differential equations. Development of computer programs based on the above topics using Matlab and their applications in chemical process computations. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Grewal, B.S. Sastry, S.S. : : Numerical Methods in Engineering and Science, Khanna Publishers, N. Delhi, 2001. Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis, Prentice Hall of India.
FT 753 LITERATURE SURVEY, REPORT WRITING AND SEMINAR Selection of topic for the seminar related to food processing. Preparation of technical report on an assigned topic after survey of scientific, technical and commercial literature, using journals, popular articles and other information retrieval methods. Use of computer softwares for report writing. Presentation of the seminar.
FT 754 FACTORY TRAINING & TOUR REPORTS Each student will be required to submit a report after each factory visit/training programme throughout the entire course. The reports will be assessed by teachers in charge of the programme.
FT 851 PROJECT WORK Each student is required to submit a project report on the design of a food processing plant, selecting the best process with optimum equipment size and operating conditions. The object is to test the ability of the student to apply his entire knowledge of food
processing technology principles to conceptualize, analyze and solve the problems. To judge his knowledge and originality and capacity for application of laboratory data in designing food processing plants and to determine the level of his proficiency at the end of the course.
SYLLABUS FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (FOOD TECHNOLOGY) EIGHTH SEMESTER FT 801 INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT Process of decision making, elements in decision making nature and framework of planning short and long range planning policy formulation organisation structure and behaviour, decentralisation and delegation. line-staff relationship motivation and morale, communication, inter-personal and group behaviour, coordination and direction. Purpose, processes and areas of control; control standards, control reports, budget as control device. Economic planning and policy in India, industrial policy, industrial development in India. Position and problems of chemical industries in India. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Koontz & ODonnel Newman & Summer Terry, George, R. Davar, R.S. Rathermund, Dietimar : : : : : Essentials of Management, New York, McGraw Hill Publishing Company, 1990. Process of Management. Principles of Management Homewood Richards, D. Irwin INC, 1990 The Management Process, Bombay, Progressive Corporation, 1980. An Economic History of India from precolonical Times to 1986, Manohar Press, New Delhi, 1988.
FT 802 PROCESS DYNAMICS & CONTROL Incentives for chemical process control, design aspects of a process control system. Difference between feedback and feed forward control configuration. Hardware elements of a control system, Block Diagrams. Laplace transform and transfer functions. Difference between lumped and distributed parameter systems, Dynamic behaviour of first and higher order systems, interacting and non-interacting systems, dead time. Different modes of control actions and their basic characteristics, controllers and their characteristics, control valve. Closed-loop transfer functions, transient response of simple control systems, Routh stability criterion, Root Locus. Introduction to frequency response: Bode diagrams, control system design by frequency response: Ziegler-Nichols controller settings, stability using frequency response, gain margin and phase margin.
Introduction to advanced control techniques such as cascade control, feed forward control, ratio control, inferential control. Books Recommended 1. Coughanowr, D.R. : Process Systems Analysis and Control, 2nd Edition. Mc Graw Hill, 1991. 2. Stephanopolous G. : Chemical Process Control -An Introduction to Theory and Practice, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2008. 3. Luyben W. L. and Luyben M.L.: Essentials of Process control, Mc Graw Hill International Editions, 1997. 4. Ogata K.: System Dynamics, 4th Edition, Pearson Education, 2004. 5. Harriott, P. : Process Control, TMH Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd., New Delhi, 1972. FT 803 PROCESSING OF MEAT, FISH & POULTRY Development of meat and poultry industry in India. Ante-mortem examination of animals and poultry birds. Slaughter and dressing, post mortem examination. postmortem changes, factors affecting them and their effect on shelf life of meat. Nutritive value of meat. Poultry dressing, wholesale and retail cuts. Communicated meat products. Canning of meat and meat products. Curing and smoking of meat. Meat tenderization. Disposal and utilization of meat industry by-products. MFPO. Sanitation of abattoir and meat processing. Modified atmospheric packaging of meats. Structure, composition and nutritive value of poultry eggs. Quality of eggs and its preservation. Egg Spoilage. Spray dried and frozen egg products. Fish structure and composition, cold storage, freezing preservation and canning of fish. Pickling of fish, fish protein concentrates, fish meal and by-products of fish processing industry. Sanitation in meat, fish, egg and poultry processing plants. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Henricksons, R.L Levie, Albert : : Meat, Poultry and Sea Food Technology, Prentice Hall. Meat Hand Book, 4th Edition, AVI Publishing, Connecticut, 1984. Poultry Products Technology, 3rd Edition, Food Products Press, 1995. Fish as Food (Vol. i, ii, iii, iv), Academic Press, New York, 1963. Fish Technology.
Mountney, G.J. and : Poukhurst, C.R. Borgstrom, George Roberts, R.J. : :
Practicals: (a) Fish & Meat: Cutting and handling. (b) Dressing of poultry. (c) Evaluation of quality of meat, fish & poultry. (d) Canning, freezing, dehydration & curing of meat & fish. (e) Quality of egg & egg powder, egg preservation. (f) Preparation of pettie, emulsion etc. (g) Visit to meat, fish & poultry processing industries. FT 804 MEMBRANE SEPARATION PROCESSES Fundamental, mechanism of membrane transport, gaseous diffusion, separation in liquid phase, dialysis, reverse osmosis, ultra filtration, liquid membrane. Electromembrane processes, transfer coefficient and its determination, engineering aspects of membrane separation and industrial application. Practicals: (a) Preparation of membranes. (b) Study of separation characteristics of membranes. (c) Study of the effective life of membranes. (d) Liquid membranes (i) emulsion type (ii) supported liquid membrane. (e) Emulsion membrane: Design of liquid surfactant membrane system to treat industrial effluent. (f) Concentration of liquid foods such as milk, juices using membranes. FT 805 FOOD RHEOLOGY Food Rheology Basic Concepts of Stress and Strain, Elastic Solids: Hookean and Non-Hookean Behavior Classification of Fluid Behavior: Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluids - Shear Dependence, Time Dependence, Mechanical Models, Determination of Flow Properties, Laminar Flow of Fluids, Circular Ducts, Between Parallel plates Modeling Rheological Behavior, Yield Stress Phenomena, Concepts of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses, Viscoelastic Fluids, Measurement Methods: Extensional Flow; Empirical Measurement Methods and Texture Profile Analysis; Farinograph; Mixograph; Cone Penetrometer; Warner-Bratzler Shear; Kramer Shear Cell; Melt Flow Indexer Pipeline Design Calculations for Non-Newtonian Fluids, Fanning Friction Factors: Power Law and Bingham Plastic Fluids, Laminar and Turbulent Friction Losses in Valves and Fittings, Velocity Profiles in Laminar and Turbulent Flows
Rheology as structural analysis tool for a) Solid food materials b) Fluid and semi-solid food materials Description and measurement of solid food rheology: Dough, cheese, fruits and vegetables, extrudates Classification, description and measurement of fluid and semi-solid food rheology Rheology of food hydrocolloids dispersions, food suspensions, pastes, gels, emulsion Books Recommended: Steffe, J.F., Daubert, J.F. (2006) Bioprocessing Pipelines: Rheology and Analysis, East Lansing, MI, Freeman Press Steffe, J.F. (1996) Rheological Methods in Food Process Engineering, Second Edition, East Lansing, MI, Freeman Press Rao, M.A., Steffe, J.F. (1992) Viscoelastic Properties of Food, New York, Elsevier Applied Science FT 851 PROJECT WORK Each student is required to submit a project report on the design of a food processing plant, selecting the best process with optimum equipment size and operating conditions. The object is to test the ability of the student to apply his entire knowledge of food processing technology principles to conceptualize, analyze and solve the problems. To judge his knowledge and originality and capacity for application of laboratory data in designing food processing plants and to determine the level of his proficiency at the end of the course. FT 852 ELECTIVE LAB. Based on theory. FT 853 PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL LAB Calibration of temperature, pressure, flow and composition measuring instruments. Study of process characteristics. Investigation of the operation of pneumatic and electronic controller with proportional integral, derivative action. To determine the best setting of a controller with controlling as actual process. To solve first order or higher order differential equations with the help of an analog computer and to study control problems by analog simulation. Selected experiments on isothermal, homogeneous batch and continuous reactors, stirred tank and tubular reactors. Residence time distribution. FT 854 PROCESS MODELLING & SIMULATION LAB Functional design, property estimate as inputs for design. System concepts for computer aided design, computer aided flow sheet design. Process analysis . Process variables selection, equipment design through the selection of free parameters subject to constraints and other parameters, Modular design. Simulation optimality . Dynamic design including control stability.
Typical equipments to be considered heat exchanges, distillations factor and process equipments. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Luyben, W.L. Franks, R.G. E. Mischke, C. : : : Process Modeling, simulation and control, Mc Graw-Hill Book Co. Modeling and Simulation in Chemical Engineering, Wiley Interscience. Computer Aided Design, Prentice Hall.
FT 855 VIVA-VOCE-II (COMPREHENSIVE) The viva-voice examination will be comprehensive and covering mainly food technology subjects covered during all the semesters including the Eighth Semester.
You might also like
- BL1002 Schedule 2015-2016-MasterDocument8 pagesBL1002 Schedule 2015-2016-MasterLucy ByrneNo ratings yet
- B.E. CHEMICAL 2011-12 SYLLABI AND SCHEMEDocument65 pagesB.E. CHEMICAL 2011-12 SYLLABI AND SCHEMERajat MittalNo ratings yet
- Syllabi For Bachelor of Engineering (Chemical) EXAMINATIONS 2010 - 2011 Scheme of Teaching and ExaminationDocument66 pagesSyllabi For Bachelor of Engineering (Chemical) EXAMINATIONS 2010 - 2011 Scheme of Teaching and ExaminationSandeep SandyNo ratings yet
- SYLLABI FOR FIVE YEAR INTEGRATED BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (CHEMICAL WITH M.B.ADocument67 pagesSYLLABI FOR FIVE YEAR INTEGRATED BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (CHEMICAL WITH M.B.ATanveer AbbottNo ratings yet
- B.E. - Chemical - 2011 2012Document64 pagesB.E. - Chemical - 2011 2012Sandeep SandyNo ratings yet
- Dept. of Chem Eng. Pg-Biochemical EnggDocument57 pagesDept. of Chem Eng. Pg-Biochemical EnggH.J.PrabhuNo ratings yet
- ChE SyllabusDocument30 pagesChE SyllabusSubodh DwivediNo ratings yet
- ChE SyllabusDocument30 pagesChE SyllabusRavindra Kumar NiranjanNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology JUJ Pahang 2012Document463 pagesSPM Biology JUJ Pahang 2012reachmya100% (1)
- MSc Biotechnology Scheme of Studies & Exams 2012-13Document39 pagesMSc Biotechnology Scheme of Studies & Exams 2012-13DeepakNo ratings yet
- Ench4rt Outline 2012Document5 pagesEnch4rt Outline 2012thirushkaNo ratings yet
- 2005 Mar BT 3 8 Curi&syllDocument58 pages2005 Mar BT 3 8 Curi&syllJaga SelvanNo ratings yet
- BT - 2004 SyllabusDocument95 pagesBT - 2004 SyllabusMohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- 20130704150210-Bemba Chem 2013-14Document80 pages20130704150210-Bemba Chem 2013-14Mohit MangalNo ratings yet
- Btech BiotechnologyDocument58 pagesBtech BiotechnologyKumar UditNo ratings yet
- G.B. Technical University, Lucknow: SyllabusDocument58 pagesG.B. Technical University, Lucknow: SyllabusNitish Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus BSC Food NutritionDocument41 pagesDetailed Syllabus BSC Food NutritionChandan Kumar BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3361.002.11f Taught by Mehmet Candas (Candas, hjn091000)Document9 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3361.002.11f Taught by Mehmet Candas (Candas, hjn091000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Engineering Syallabus Kuk Univ.Document131 pagesComputer Science Engineering Syallabus Kuk Univ.Er Saurabh Sharma100% (1)
- Food Technology SyllabusDocument45 pagesFood Technology Syllabusb.duttaNo ratings yet
- Industrial BiotechDocument50 pagesIndustrial BiotechlmnmpnsNo ratings yet
- Cse All SemDocument131 pagesCse All Semarpankruze007No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Document67 pagesBachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Devesh Garg0% (1)
- M SC Bangalore University SyllabusDocument95 pagesM SC Bangalore University Syllabusche911No ratings yet
- B.Sc. TY Biotechnology PDFDocument26 pagesB.Sc. TY Biotechnology PDFHanumant Suryawanshi0% (1)
- B.TECH. (Engineering Physics) 2009-2013: Delhi Technological UniversityDocument64 pagesB.TECH. (Engineering Physics) 2009-2013: Delhi Technological UniversityAkshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- University of Calicut (Abstract) : Contd ..2Document44 pagesUniversity of Calicut (Abstract) : Contd ..2Nbisht25No ratings yet
- Etc 5THDocument29 pagesEtc 5THHIMANSU SEKHAR SAHUNo ratings yet
- H. B. Technological Institute, Kanpur-02 (U.P.)Document8 pagesH. B. Technological Institute, Kanpur-02 (U.P.)Christina JamesNo ratings yet
- B.sc. Industrial ChemistryDocument79 pagesB.sc. Industrial ChemistryOmar Abd Elsalam0% (1)
- Syllabus Ag Final 040808Document24 pagesSyllabus Ag Final 040808Hargovind_GujjarNo ratings yet
- auB.E. (Electronics and Communication) - 4 Year Degree Course SyllabusDocument89 pagesauB.E. (Electronics and Communication) - 4 Year Degree Course Syllabusanjaiah_19945No ratings yet
- Pdpu/Sot/5 Sem.B. Tech. Chemical EngineeringDocument11 pagesPdpu/Sot/5 Sem.B. Tech. Chemical EngineeringMeetNo ratings yet
- Projek Jawab Untuk Jaya 2010 BiologyDocument207 pagesProjek Jawab Untuk Jaya 2010 BiologywhywhyqNo ratings yet
- B (1) .Tech Curriculam FinalDocument57 pagesB (1) .Tech Curriculam FinalBrahadeesh ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Syllabus OldDocument31 pagesBiotechnology Syllabus OldJuan Antonio DiazNo ratings yet
- Food Tech - Curri&SyllabiV To VIIIDocument58 pagesFood Tech - Curri&SyllabiV To VIIIsmartsriNo ratings yet
- Ceramah&Bengkel Menjawab Soalan Science Process SkillsDocument131 pagesCeramah&Bengkel Menjawab Soalan Science Process SkillsFarah AzilahNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology 1 2 3 4 Year 2010-11Document58 pagesBiotechnology 1 2 3 4 Year 2010-11smsmbaNo ratings yet
- 2 B.tech Biotechnology 27 38Document38 pages2 B.tech Biotechnology 27 38Anju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, LudhianaDocument17 pagesGuru Nanak Dev Engineering College, LudhianaAravind KnNo ratings yet
- B - Tech CHEMICAL 2010 2011 2012Document63 pagesB - Tech CHEMICAL 2010 2011 2012Ssheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- CSU Environmental Engineering Unit OperationsDocument4 pagesCSU Environmental Engineering Unit OperationsJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- UPTU SyllabusDocument44 pagesUPTU SyllabusRoshan MishraNo ratings yet
- ECE Andhra University SyllabusDocument91 pagesECE Andhra University Syllabush9emanth4No ratings yet
- AU College Electronics Engineering Curriculum Scheme OverviewDocument98 pagesAU College Electronics Engineering Curriculum Scheme OverviewkorumillichanduNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Vishwakarma Institute of TechnologyDocument211 pagesSyllabus - Vishwakarma Institute of TechnologyAditya PophaleNo ratings yet
- RTU MECHENGG Curriculum SheetDocument4 pagesRTU MECHENGG Curriculum SheetjoennelmayariNo ratings yet
- 1st and 2nd Semester Syllabus 28082011Document44 pages1st and 2nd Semester Syllabus 28082011Gurdeep ChahalNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Engineering of Plastics: Technology, Economy and EnvironmentFrom EverandLife Cycle Engineering of Plastics: Technology, Economy and EnvironmentL. LundquistNo ratings yet
- Advancing Theory for Kinetics and Dynamics of Complex, Many-Dimensional Systems: Clusters and ProteinsFrom EverandAdvancing Theory for Kinetics and Dynamics of Complex, Many-Dimensional Systems: Clusters and ProteinsTamiki KomatsuzakiRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Forecast Verification: A Practitioner's Guide in Atmospheric ScienceFrom EverandForecast Verification: A Practitioner's Guide in Atmospheric ScienceNo ratings yet
- Data Mining and Learning Analytics: Applications in Educational ResearchFrom EverandData Mining and Learning Analytics: Applications in Educational ResearchSamira ElAtiaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- WEEE Recycling: Research, Development, and PoliciesFrom EverandWEEE Recycling: Research, Development, and PoliciesAlexandre ChagnesNo ratings yet