Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anurag
Anurag
Uploaded by
Prajjwal ShuklaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anurag
Anurag
Uploaded by
Prajjwal ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD.
BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
The inverse of a function B A f : exists if f is one-one onto i.e., a bijection and is given by x y f y x f = =
) ( ) (
1
.
Consider the sine function with domain R and range [1, 1]. Clearly this function is not a bijection and so it is not invertible.
If we restrict the domain of it in such a way that it becomes oneone, then it would become invertible. If we consider sine as a
function with domain
(
2
,
2
t t
and co-domain [1, 1], then it is a bijection and therefore, invertible. The inverse of sine
function is defined as x x = =
u u sin sin
1
, where
(
2
,
2
t t
u and ] 1 , 1 [ x .
5.1 Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions.
(1) Meaning of inverse function
(i) x = u sin u =
x
1
sin (ii) x = u cos u =
x
1
cos (iii) x = u tan u =
x
1
tan
(iv) x = u cot u =
x
1
cot (v) x = u sec u =
x
1
sec (vi) x = u cosec u =
x
1
cosec
(2) Domain and range of inverse functions
(i) If , sin x y = then , sin
1
x y
= under certain condition.
; 1 sin 1 s s y but x y = sin . 1 1 s s x
Again,
2
1 sin
t
= = y y and
2
1 sin
t
= = y y .
Keeping in mind numerically smallest angles or real numbers.
2 2
t t
s s y
These restrictions on the values of x and y provide us with the domain and range for the function x y
1
sin
= .
i.e., Domain : ] 1 , 1 [ e x
Range:
(
e
2
,
2
t t
y
(ii) Let x y = cos , then x y
1
cos
= , under certain conditions 1 cos 1 s s y
1 1 s s x
t = = y y 1 cos
0 1 cos = = y y
t s s y 0 {as cos x is a decreasing function in [ t , 0 ];
hence 0 cos cos cos s s y t
These restrictions on the values of x and y provide us the domain and range for the function x y
1
cos
= .
i.e. Domain: ] 1 , 1 [ e x
Range : ] , 0 [ t e y
(iii) If x y = tan , then , tan
1
x y
= under certain conditions.
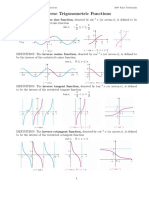
Y
y = cos
1
x
O
(1, t/2)
X
(1, 0)
y
O
x
y = tan
1
x
y =
t/2
y =
t/2
Y
(1, t/2)
y = sin
1
x
O
(1, t/2)
X
1
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
Here, R x R y e e tan ,
2 2
tan
t t
< < < < y y
Thus, Domain R x e ;
Range |
.
|
\
|
e
2
,
2
t t
y
(iv) If , cot x y = then x y
1
cot
=
under certain conditions, ; cot R x R y e e
t < < < < y y 0 cot
These conditions on x and y make the function, x y = cot one-one and onto so that the inverse function exists. i.e.,
x y
1
cot
= is meaningful.
Domain : R x e
Range : ) , 0 ( t e y
(v) If , sec x y = then , sec
1
x y
= where 1 | | > x and
2
, 0
t
t = s s y y
Here, Domain: ) 1 , 1 ( eR x
Range:
)
`
e
2
] , 0 [
t
t y
(vi) If x y = cosec , then x y
1
cosec
=
Where 1 | | > x and 0 ,
2 2
= s s y y
t t
Here, Domain ) 1 , 1 ( eR
Range } 0 {
2
,
2
(
e
t t
Function Domain (D) Range (R)
x
1
sin
1 1 s s x or ] 1 , 1 [
2 2
t
u
t
s s or
(
2
,
2
t t
x
1
cos
1 1 s s x or ] 1 , 1 [ t u s s 0 or ] , 0 [ t
x
1
tan
< < x i.e., R x e or ) , (
2 2
t
u
t
< < or |
.
|
\
|
2
,
2
t t
x
1
cot
< < x i.e., R x e or ) , ( t u < < 0 or ) , 0 ( t
x
y = sec
1
x
y = t/2
(1,t)
O (1,0)
x
y = cosec
1
x
(1, t/2)
y
O (1, t)
y = t
O
x
(0, t/2)
y = cot
1
x
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
x
1
sec
1 , 1 > s x x or ) , 1 [ ] 1 , (
t u
t
u s s = 0 ,
2
or
(
\
|
|
.
|
t
t t
,
2 2
, 0
x
1
cosec
1 , 1 > s x x or ) , 1 [ ] 1 , (
2 2
, 0
t
u
t
u s s = or
(
\
|
|
.
|
2
, 0 0 ,
2
t t
(3) u u =
) (sin sin
1
, Provided that
2 2
t
u
t
s s , u u =
) (cos cos
1
, Provided that t u s s 0
u u =
) (tan tan
1
, Provided that
2 2
t
u
t
< < , u u =
) (cot cot
1
, Provided that t u < < 0
u u =
) (sec sec
1
, Provided that
2
0
t
u < s or t u
t
s <
2
, ) cosec ( cosec
1
u u =
Provided that 0
2
< s u
t
or
2
0
t
u s <
(4) , ) sin(sin
1
x x =
Provided that 1 1 s s x , , ) cos(cos
1
x x =
Provided that 1 1 s s x
tan , ) (tan
1
x x =
Provided that < < x , ) cot(cot
1
x x =
Provided that < < x
, ) sec(sec
1
x x =
Provided that 1 s < x or < s x 1
, ) cosec ( cosec
1
x x = Provided that 1 s < x or < s x 1
(5) x x
1 1
sin ) ( sin
= x x
1 1
cos ) ( cos
= t , x x
1 1
tan ) ( tan
=
x x
1 1
cot ) ( cot
= t x x
1 1
sec ) ( sec
= t x x
1 1
cosec ) ( cosec =
(6)
2
cos sin
1 1
t
= +
x x , for all ] 1 , 1 [ e x
2
cot tan
1 1
t
= +
x x , for all R x e
2
cosec sec
1 - 1
t
= +
x x , for all ) , 1 [ ] 1 , ( e x
Important Tips
Here; x x x
1 1 1
tan , cosec , sin
belong to I and IV Quadrant.
Here; x x x
1 1 1
cot , sec , cos
belong to I and II Quadrant.
I Quadrant is common to all the inverse functions.
III Quadrant is not used in inverse function.
IV Quadrant is used in the clockwise direction i.e., 0
2
s s y
t
(7) Principal values for inverse circular functions
Principal values for 0 > x Principal values for 0 < x
2
sin 0
1
t
s s
x 0 sin
2
1
< s
x
t
2
cos 0
1
t
s s
x t
t
s <
x
1
cos
2
2
tan 0
1
t
< s
x 0 tan
2
1
< <
x
t
I
IV
t/2
t/2
I
0 t
II
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
2
cot 0
1
t
s <
x t
t
< <
x
1
cot
2
2
sec 0
1
t
< s
x t
t
s <
x
1
sec
2
2
cosec 0
1
t
s <
x 0 cosec
2
1
< s
x
t
Thus ,
6 2
1
sin
1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
not
3
2
2
1
cos ;
6
5
1
t t
= |
.
|
\
|
not
3
4t
;
3
) 3 ( tan
1
t
=
not
3
2t
;
4
3
) 1 ( cot
1
t
=
not
4
t
etc.
Note : x x x
1 1 1
tan , cos , sin
are also written as arc x sin , arc x cos and arc x tan respectively.
It should be noted that if not otherwise stated only principal values of inverse circular functions are to be
considered.
(8) Conversion property : Let, y x =
1
sin y x sin = |
.
|
\
|
=
x
y
1
cosec |
.
|
\
|
=
x
y
1
cosec
1
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
x
x
x
x
x
x
x x
1
cosec
1
1
sec
1
cot
1
tan 1 cos sin
1
2
1
2
1
2
1 2 1 1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
2
1
2
1 1
2
1 2 1 1
1
cot
1
1
cosec
1
sec
1
tan 1 sin cos
x
x
x
x x
x
x x
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= + = |
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
x
x
x
x
x x
x
x
2
1 2 1 1
2
1
2
1 1
1
cosec 1 sec
1
cot
1
1
cos
1
sin tan
Note : x
x
1 1
cosec
1
sin
= |
.
|
\
|
, for all ) , 1 [ ] 1 , ( e x
, sec
1
cos
1 1
x
x
= |
.
|
\
|
for all ) , 1 [ ] 1 , ( e x
< +
>
= |
.
|
\
|
0 for , cot
0 for , cot 1
tan
1
1
1
x x
x x
x t
(9) General values of inverse circular functions: We know that if o is the smallest angle whose sine is x, then
all the angles whose sine is x can be written as , ) 1 ( o
n
nx + where ,..... 2 , 1 , 0 = n Therefore, the general value of x
1
sin
can
be taken as o t
n
n ) 1 ( + . The general value of x
1
sin
is denoted by x
1
sin
.
Thus, we have
2 2
and sin if 1, 1 , 1) ( sin
1
x x n x
n
s s = s s + =
Similarly, general values of other inverse circular functions are given as follows:
x
1
\1 x
2
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
1 1 , 2 cos
1
s s =
x n x o t ; If x = o cos , t o s s 0
, tan
1
o t + =
n x R x e ; If , tan x = o
2 2
t
o
t
< <
, cot
1
o t + =
n x R x e ; If x = o cot , t o < < 0
o t =
n x 2 sec
1
, 1 > x or 1 s x ; If
2
and 0 , sec
t
t o o = s s = x
1 , ) 1 ( cosec
1
> + =
x n x
n
o t or 1 s x ; If 0 and
2 2
, cosec = s s = x x
t
o
t
o
Example: 1 The principal value of
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
3
sin
1
is [Roorkee 1992]
(a)
3
2t
(b)
3
t
(c)
3
4t
(d)
8
5t
Solution: (b)
3 3
sin sin
1
t t
=
(
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
< <
2
sin
2
1
t t
x
Example: 2 =
)] 30 [sec( sec
1 o
[MP PET 1992]
(a)
o
60 (b)
o
30 (c)
o
30 (d)
o
150
Solution: (c)
o o o
30 ) 30 (sec sec )] 30 [sec( sec
1 1
= =
.
Example: 3 The principal value of |
.
|
\
|
3
5
sin sin
1
t
is [MP PET 1996]
(a)
3
5t
(b)
3
5t
(c)
3
t
(d)
3
4t
Solution: (c)
3 2
3
sin
3
5
sin sin
1 1
t t
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
= |
.
|
\
|
.
Example: 4 The principal value of
(
|
.
|
\
|
3
2
sin sin
1
t
is [IIT 1986]
(a)
3
2t
(b)
3
2t
(c)
3
4t
(d) None of these
Solution: (d) The principal vlaue of )]
3
2
[sin( sin
1
t
t
=
3 3
sin sin
1
t t
= |
.
|
\
|
.
Example: 5 Considering only the principal values, if
(
|
.
|
\
|
=
2
1
cot sin ) tan(cos
1 1
x , then x is equal to [IIT 1991; AMU 2001]
(a)
5
1
(b)
5
2
(c)
5
3
(d)
3
5
Solution: (d) Put
2
1
cot
2
1
cot
1
= = |
.
|
\
|
u u
.
5
2
sin = u Put | =
x
1
cos then | cos = x
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
Also
3
5
cos ,
5
2
tan = = = | | x .
Example: 6 If )] 600 ( [sin sin
1
=
u , then one of the possible value of u is [Kerala (Engg.) 2002]
(a)
3
t
(b)
2
t
(c)
3
2t
(d)
3
2t
Solution: (a) )] 600 [sin( sin
1 o
=
u = )] 240 360 sin( [ sin
1
+
] 240 sin [ sin
1 o
=
u )] 60 180 sin( [ sin
1 o o
+ =
o
60 sin sin
1
= u
3 3
sin sin
1
t t
=
(
|
.
|
\
|
=
.
Example: 7 Value of |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
3
5
sin sin
3
5
cos cos
1 1
t t
is [Roorkee 2000]
(a) 0 (b)
2
t
(c)
3
2t
(d)
3
10t
Solution: (a) |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
3
5
sin sin
3
5
cos cos
1 1
t t
(
|
.
|
\
|
+
(
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
2 sin sin
3
2 cos cos
1 1
t
t
t
t 0
3 3
= =
t t
.
Example: 8 The equation
6
11
sin cos 2
1 1
t
= +
x x has [AMU 1999]
(a) No solution (b) Only one solution (c) Two solutions (d) Three solutions
Solution: (a) Given equation is
6
11
sin cos 2
1 1
t
= +
x x
6
11
) sin (cos cos
1 1 1
t
= + +
x x x
2 6
11
cos
1
t t
=
x
3
4
cos
1
t
=
x , which is not possible as | | e
t , 0 cos
1
x .
Example: 9 If ,
3
2
sin sin
1 1
t
= +
y x then = +
y x
1 1
cos cos [EAMCET 1994]
(a)
3
2t
(b)
3
t
(c)
6
t
(d) t
Solution: (b)
3
2
sin sin
1 1
t
= +
y x
3
2
cos
2
cos
2
1 1
t t t
= +
y x
3
cos cos
1 1
t
= +
y x .
Example: 10 If , tan cos sin
1 1 1
x x x
+ = u 0 > x then the smallest interval in which u lies is [Orissa JEE 2003]
(a)
4
3
2
t
u
t
s s (b)
4
0
t
u s s (c) 0
4
s s u
t
(d)
2 4
t
u
t
s s
Solution: (b) x x x x
1 1 1 1
tan
2
tan cos sin
= + =
t
u
We know
2
tan
2
1
t t
< <
x
4
tan
2
0
2
tan
2
1 1
t t t t
< < > >
x x .
Example: 11 If
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
...
4 2
sin
3 2
1
x x
x
2
...
4 2
cos
6 4
2 1
t
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
x x
x for , 2 | | 0 < < x then x equals [IIT Screening 2001]
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
(a)
2
1
(b) 1 (c)
2
1
(d) 1
Solution: (b) We know that 1 | | ,
2
cos sin
1 1
s = +
y y y
t
According to question, ... ..........
4 2
..........
4 2
6 4
2
3 2
+ = +
x x
x
x x
x
2 | | 0 ( ,
2
1
2
1
2
2
< <
+
=
+
x
x
x
x
x
)
2
2
2 2 x
x
x
x
+
=
+
3 2 3
2 2 x x x x + = +
2
x x =
0 0 ) 1 ( 0
2
= = = x x x x x and x = 1, but . 0 = x So, 1 = x .
Example: 12 If ,
2 2
1
cot sin
1 1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
+
x then x is [Karnataka 1999; Roorkee 1999]
(a) 0 (b)
5
1
(c)
5
2
(d)
2
3
Solution: (b)
2 2
cot sin
1 1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
+
x
x
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
5
1
cos
2
1
cot
1 1
2
5
1
cos sin
1 1
t
= +
x ; Clearly,
5
1
= x .
Example: 13 The value of ) sin(cot
1
x
is [MP PET 2001; UPSEAT 1987]
(a)
2 / 3 2
) 1 ( x + (b)
2 / 3 2
) 1 (
+ x (c)
2 / 1 2
) 1 ( x + (d)
2 / 1 2
) 1 (
+ x
Solution: (d) ) sin(cot
1
x
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
2
1
1
1
sin sin
x
=
2
1
1
x +
.
Example: 14 The number of real solutions of
2
1 sin ) 1 ( tan
2 1 1
t
= + + + +
x x x x is [IIT Screening1999]
(a) Zero (b) One (c) Two (d) Infinite
Solution: (c)
2
1 sin ) 1 ( tan
2 1 1
t
= + + + +
x x x x
) 1 ( tan
1
+
x x is defined, when 0 ) 1 ( > + x x ........(i)
1 sin
2 1
+ +
x x is defined, when 1 1 ) 1 ( 0 s + + s x x or 0 ) 1 ( 0 s + s x x ........(ii)
From (i) and (ii), 0 ) 1 ( = + x x or 0 = x and 1.
Hence, number of solutions is 2.
5.2 Formulae for Sum and Difference of Inverse Trigonometric Function.
(1)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= +
xy
y x
y x
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
; If 0 , 0 > > y x and 1 < xy
(2)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ = +
xy
y x
y x
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t ; If 0 , 0 > > y x and 1 > xy
1
2
\5
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
(3)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ = +
xy
y x
y x
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t ; If 0 , 0 < < y x and 1 > xy
(4)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
xy
y x
y x
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
; If 1 > xy
(5)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ =
xy
y x
y
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t ; If 0 , 0 < > y x and 1 < xy
(6)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ =
xy
y x
y x
1
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t ; If 0 , 0 > < y x and 1 < xy
(7)
(
+ +
= + +
zx yz xy
xyz z y x
z y x
1
tan tan tan tan
1 1 1 1
(8)
(
+ +
+
= + + +
........ 1
. ..........
tan tan .......... tan tan
6 4 2
5 3 1 1 1
2
1
1
1
S S S
S S S
x x x
n
,
where
k
S denotes the sum of the products of
n
x x x ,........, ,
2 1
taken k at a time.
(9)
x y
xy
y x
+
= +
1
cot cot cot
1 1 1
(10)
x y
xy
y x
+
=
1
cot cot cot
1 1 1
(11) } 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x + = +
;
If 1 , 1 s s y x and 1
2 2
s + y x or if 0 < xy and 1
2 2
> + y x
(12) }, 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x + = +
t If x < 0 , 1 s y and 1
2 2
> + y x
(13) }, 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x + = +
t If 0 ; 1 < s y x and 1
2 2
> + y x
(14) }, 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x =
If 1 ; 1 s s y x and 1
2 2
s + y x if or 0 > xy and 1
2 2
> + y x .
(15) }, 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x =
t If 0 1 , 1 0 < s s < y x and 1
2 2
> + y x .
(16) }, 1 1 { sin sin sin
2 2 1 1 1
x y y x y x =
t If 1 0 , 0 1 s < < s y x and 1
2 2
> + y x .
(17) } 1 . 1 { cos cos cos
2 2 1 1 1
y x xy y x = +
, If 1 , 1 s s y x and 0 > + y x .
(18) } 1 1 { cos 2 cos cos
2 2 1 1 1
y x xy y x = +
t , If 1 , 1 s s y x and 0 s + y x
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
(19) }, 1 1 { cos cos cos
2 2 1 1 1
y x xy y x + =
If , 1 , 1 s s y x and y x s .
(20) }, 1 1 { cos cos cos
2 2 1 1 1
y x xy y x =
If , 0 1 s s y 1 0 s < x and y x > .
Important Tips
If ,
2
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t
= + +
z y x then 1 = + + zx yz xy .
If , tan tan tan
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then xyz z y x = + + .
If ,
2
sin sin sin
1 1 1
t
= + +
z y x then 1 2
2 2 2
= + + + xyz z y x .
If , sin sin sin
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then xyz z z y y x x 2 1 1 1
2 2 2
= + + .
If , 3 cos cos cos
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then 3 = + + zx yz xy .
If , cos cos cos
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then 1 2
2 2 2
= + + + xyz z y x .
If ,
2
3
sin sin sin
1 1 1
t
= + +
z y x then 3 = + + zx yz xy .
If , sin sin
1 1
u = +
y x then u t = +
y x
1 1
cos cos .
If , cos cos
1 1
u = +
y x then u t = +
y x
1 1
sin sin .
If ,
2
tan tan
1 1
t
= +
y x then 1 = xy .
If ,
2
cot cot
1 1
t
= +
y x then 1 = xy .
If , cos cos
1 1
u = +
b
y
a
x
then u u
2
2
2
2
2
sin cos
2
= +
b
y
ab
xy
a
x
.
Example: 15 The value of
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
13
3
cos
5
3
sin tan
1 1
is [AMU 2001]
(a)
17
6
(b)
13
6
(c)
5
13
(d)
6
17
Solution: (d)
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
13
3
cos
5
3
sin tan
1 1
= |
.
|
\
|
+
3
2
tan
4
3
tan tan
1 1
=
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
3
2
.
4
3
1
3
2
4
3
tan tan
1
=
(
6
12
12
17
tan tan
1
=
6
17
.
Example: 16 = +
3
1
tan
2
1
tan
1 1
[MP PET 1997, 2003; UPSEAT 2003; Karnataka CET 2001]
(a) 0 (b)
4
t
(c)
2
t
(d) t
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
Solution: (b)
4
1 tan
3
1
.
2
1
1
3
1
2
1
tan
3
1
tan
2
1
tan
1 1 1 1
t
= =
+
= +
.
Example: 17 If , sin
3
2
sin
3
1
sin
1 1 1
x
= + then x is equal to [Roorkee 1995]
(a) 0 (b)
9
2 4 5
(c)
9
2 4 5 +
(d)
2
t
Solution: (c)
(
(
+
=
(
(
+ = +
9
2 4 5
sin
9
1
1
3
2
9
4
1
3
1
sin
3
2
sin
3
1
sin
1 1 1 1
Therefore,
9
2 4 5 +
= x .
Example: 18 3 cot
5
1
sin
1 1
+ is equal to [MP PET 1993; Karnataka CET 1995]
(a)
6
t
(b)
4
t
(c)
3
t
(d)
2
t
Solution: (b) 3 cot
5
1
5
1
1
cot 3 cot
5
1
sin
1 1 1 1
+
|
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
= + =
4
) 1 ( cot
2 3
1 3 2
cot ) 3 ( cot ) 2 ( cot
1 1 1 1
t
= = |
.
|
\
|
+
= +
.
Example: 19 If , sin
13
12
cos
5
3
sin
1 1 1
C
= |
.
|
\
|
+ then = C [Pb. CET 1999]
(a)
56
65
(b)
65
24
(c)
65
16
(d)
65
56
Solution: (d) Given,
13
12
cos
5
3
sin sin
1 1 1
+ = C
13
5
sin
5
3
sin sin
1 1 1
+ = C
+ =
25
9
1
13
5
169
25
1
5
3
sin
1
65
56
65
56
sin
1
= |
.
|
\
|
=
C .
Example: 20 If , 3 3
2
1
2
cos cos ) (
2 1 1
)
`
+ + =
x
x
x x f then
(a)
3 3
2 t
= |
.
|
\
|
f (b)
3 3
2
cos 2
3
2
1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
f (c)
3 3
1 t
= |
.
|
\
|
f (d)
3 3
1
cos 2
3
1
1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
f
Soltuion: (a,d)
+ + =
2 1 1
1 .
2
3
2
1
cos cos ) ( x x x x f
= ) cos
2
1
(cos cos
1 1 1
x x
, according as >
2
1
cos
1
or x
1
cos
<
=
2
1
cos
1
if , cos
2
1
cos
1 1
x
> which holds for
3
2
= x
=
2
1
cos cos 2
1 1
x if , cos
2
1
cos
1 1
x
< which holds for
3
1
= x .
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Example: 21 = + +
16
63
tan
5
4
cos
13
12
sin
1 1 1
(a) 0 (b)
2
t
(c) t (d)
2
3t
Solution: (c)
16
63
tan
4
3
tan
5
12
tan
1 1 1
+ + =
16
63
tan
36 20
15 48
tan
1 1
+
+
+ t ( 1 > xy ) = t t = +
16
63
tan
16
63
tan
1 1
.
Example: 22 If
3
1
sin
5
4
sin
1 1
+ = o and
3
1
cos
5
4
cos
1 1
+ = | , then
(a) | o < (b) | o = (c) | o > (d) None of these
Solution: (a)
(
(
+ =
25
16
1
3
1
9
1
1
5
4
sin
1
o =
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
(
(
+
15
3 2 8
sin
15
3
15
2 8
sin
1 1
Since
2
, 1
15
3 2 8 t
o < <
+
2
) (
3
1
sin
2 5
4
sin
2
1 1
t
o t
t t
| > = |
.
|
\
|
+ =
| o < .
Example: 23 If ,
3
cos
2
cos
1 1
u = +
y x
then = +
2 2
4 cos 12 9 y xy x u
(a) u
2
sin 36 (b) u
2
cos 36 (c) u
2
tan 36 (d) None of these
Solution: (a) u = +
3
cos
2
cos
1 1
y x
u cos
9
1
4
1
3
.
2
2 2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
y x y x
) 9 )( 4 ( ) cos 6 (
2 2 2
y x xy = u u u u
2 2 2 2
sin 36 ) cos 1 ( 36 4 cos 12 9 = = + y xy x .
Example: 24 The number of solutions of
3
2 sin sin
1 1
t
= +
x x is
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) Infinitie
Solution: (b) x x
1 1 1
sin
2
3
sin 2 sin
=
(
(
=
4
3
1 1 .
2
3
sin
2 1
x x
2
1
2
3
2
2
x
x x =
) 1 (
4
3
2
5
2
2
x
x
= |
.
|
\
|
or 3 28
2
= x
7
3
2
1
28
3
= = x , (not
7
3
2
1
) .
Example: 25 If o = |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
b
y
a
x
1 1
cos cos , then = +
2
2
2
2
cos
2
b
y
ab
xy
a
x
o [UPSEAT 1999; MP PET 1995]
(a) o
2
sin (b) o
2
cos (c) o
2
tan (d) o
2
cot
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
Solution: (a) We have o =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
2
2
2
1
1 1 . cos
b
y
a
x
b
y
a
x
o cos 1 1
2
2
2
2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
b
y
a
x
ab
xy
2 2
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
1 cos
b a
y x
b
y
a
x
ab
xy
+ = |
.
|
\
|
o
2 2
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
2 2
2 2
1 cos
2
cos
b a
y x
b
y
a
x
ab
xy
b a
y x
+ = + o o o o o
2 2
2
2
2
2
sin cos 1 cos
2
= = +
b
y
ab
xy
a
x
.
Example: 26 If a, b, c be positive real numbers and the value of
ca
c b a b
bc
c b a a ) (
tan
) (
tan
1 1
+ +
+
+ +
=
u
ab
c b a c ) (
tan
1
+ +
+
, then
u tan is [IIT 1981]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) c b a + + (d) None of these
Solution: (a)
ab
c b a c
ca
c b a b
bc
c b a a ) (
tan
) (
tan
) (
tan
1 1 1
+ +
+
+ +
+
+ +
=
u
Let
abc
c b a
s
+ +
=
2
2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 1
tan tan tan s c s b s a
+ + = u
) ( tan ) ( tan ) ( tan
1 1 1
cs bs as
+ + = u
(
(
+ +
=
2 2 2
3
1
1
tan
cas bcs abs
abcs cs bs as
u
0
) ( 1
) (
tan
2
2
=
(
(
+ +
+ +
=
s ca bc ab
abcs c b a
s u )] ( [
2
c b a abcs + + =
Trick : Since it is an identity so it will be true for any value of a,b,c. Let 1 = = = c b a then
, 3 tan 3 tan 3 tan
1 1 1
t u = + + =
0 tan = u .
Example: 27 All possible values of p and q for which
4
3
1 cos 1 cos cos
1 1 1
t
= + +
q p p holds, is [Karnataka CET 2002]
(a)
2
1
, 1 = = q p (b)
2
1
, 1 = > p q (c)
2
1
, 1 0 = s s q p (d) None of these
Solution: (c) q p p = +
1 cos
4
3
1 cos cos
1 1 1
t
q p p
|
|
.
|
\
|
= +
1 cos
2
1
cos 1 cos cos
1 1 1 1
(
(
= q q p p p p .
2
1
1 .
2
1
1 1 q q = 1 0
2
1
= q .
5.3 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles.
(1) ) 1 2 ( sin sin 2
2 1 1
x x x =
, If
2
1
2
1
s s x (2) ), 1 2 ( sin sin 2
2 1 1
x x x =
t If 1
2
1
s s x
(3) ) 1 2 ( sin sin 2
2 1 1
x x x =
t , If
2
1
1
s s x (4) ), 4 3 ( sin sin 3
3 1 1
x x x =
If
2
1
2
1
s s
x
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
(5) ) 4 3 ( sin sin 3
3 1 1
x x x =
t , If 1
2
1
s < x (6) ), 4 3 ( sin sin 3
3 1 1
x x x =
t If
2
1
1 < s x
(7) ) 1 2 ( cos cos 2
2 1 1
=
x x , If 1 0 s s x (8) ) 1 2 ( cos 2 cos 2
2 1 1
=
x x t , if 0 1 s s x
(9) ) 3 4 ( cos cos 3
3 1 1
x x x =
If 1
2
1
s s x (10) ) 3 4 ( cos 2 cos 3
3 1 1
x x x =
t , If
2
1
2
1
s s x
(11) ) 3 4 ( cos 2 cos 3
3 1 1
x x x + =
t , If
2
1
1 s s x (12) |
.
|
\
|
=
2
1 1
1
2
tan tan 2
x
x
x , if 1 1 s < x
(13) |
.
|
\
|
+ =
2
1 1
1
2
tan tan 2
x
x
x t , If 1 > x (14) |
.
|
\
|
+ =
2
1 1
1
2
tan tan 2
x
x
x t , If 1 < x
(15) |
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2
x
x
x , If 1 1 s s x (16) |
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2
x
x
x t , If 1 > x
(17) |
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2
x
x
x t , If 1 < x (18)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
2
1 1
1
1
cos tan 2
x
x
x , If < s x 0
(19)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
2
2
1 1
1
1
cos tan 2
x
x
x , If 0 s < x (20)
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
2
3
1 1
3 1
3
tan tan 3
x
x x
x , If
3
1
3
1
< <
x
(21)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2
3
1 1
3 1
3
tan tan 3
x
x x
x t , If
3
1
> x (22)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2
3
1 1
3 1
3
tan tan 3
x
x x
x t , If
3
1
< x
(23)
a
x
x a
x
1
2 2
1
sin tan
=
(
(
(24)
a
x
x a a
x x a
1
2 2
3 2
1
tan 3
) 3 (
3
tan
=
(
(25)
2 1
2 2
2 2
1
cos
2
1
4
1 1
1 1
tan x
x x
x x
+ =
(
(
+
+ + t
(26) x
x
x
1 1
cos
2
1
1
1
tan
=
+
Example: 28 ), cosec ( tan ) (cos tan 2
2 1 1
x x
= then x = [UPSEAT 2002]
(a)
2
t
(b) t (c)
6
t
(d)
3
t
Solution: (d) ) (cos tan 2
1
x
) ec (cos tan
2 1
x
=
x x
x
x x
x
2 2 2
1
2
1
sin
1
sin
cos 2
sin
1
tan
cos 1
cos 2
tan = |
.
|
\
|
= |
.
|
\
|
3
1 cos 2
t
= = x x .
Example: 29 The solution set of the equation x x
1 1
tan 2 sin
= is [AMU 2002]
(a) {1, 2} (b) } 2 , 1 { (c) } 0 , 1 , 1 { (d) } 0 ,
2
1
, 1 {
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
Soltuion: (c) x x
1 1
tan 2 sin
=
2
1 1
1
2
sin sin
x
x
x
+
=
x
x
x
=
+
2
1
2
0
3
= x x } 0 , 1 , 1 { 0 ) 1 )( 1 ( = = + x x x x .
Exmaple: 30
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
cos
2
1
tan sin
x
x
x
x
is equal to [Kurukshetra CEE 2001]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d)
2
1
Solution: (b)
)
`
+ |
.
|
\
|
x x
1 1
tan 2 tan 2
2
sin
t
=
2
sin
t
= 1.
Example: 31 If ,
1
2
tan
1
1
cos
1
2
sin
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
x
x
b
b
a
a
=
+
+
then = x [EAMCET 1989]
(a) a (b) b (c)
ab
b a
+
1
(d)
ab
b a
+
1
Solution: (d) Put | u tan , tan = = b a and , tan = x then reduced form is
) 2 (tan tan ) 2 (cos cos ) 2 (sin sin
1 1 1
| u
= | u | u = = 2 2 2
Taking tan on both sides, we get ) tan( | u = tan
| u
| u
tan
tan . tan 1
tan tan
=
+
Substituting these values, we get x
ab
b a
=
+
1
Example: 32 =
(
|
.
|
\
|
4 5
1
tan 2 tan
1
t
[IIT 1984]
(a)
7
17
(b)
7
17
(c)
17
7
(d)
17
7
Solution: (d)
(
(
(
(
=
(
|
.
|
\
|
) 1 ( tan
25
1
1
5
2
tan tan
4 5
1
tan 2 tan
1 1 1
t
=
17
7
12
5
1
1
12
5
tan . tan ) 1 ( tan
12
5
tan tan
1 1 1
=
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
(
.
Example: 33 = +
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
5
1
tan 4
1 1 1
[Roorkee 1981]
(a)
2
t
(b)
3
t
(c)
4
t
(d) None of these
Solution: (c)
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
5
1
tan 4
1 1 1
+ =
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
25
1
1
5
2
tan 2
1 1 1
+
(
(
(
(
=
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
12
5
tan 2
1 1 1
+ |
.
|
\
|
=
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
144
25
1
6
5
tan
1 1 1
+
(
(
(
(
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
=
99
1
tan
70
1
tan
119
120
tan
1 1 1
+ |
.
|
\
|
=
(
(
(
(
+
70
1
.
99
1
1
70
1
99
1
tan
119
120
tan
1 1
= |
.
|
\
|
+
6931
29
tan
119
120
tan
1 1
=
239
1
tan
119
120
tan
6931
29
tan
119
120
tan
1 1 1 1
= =
4
) 1 ( tan
239
1
119
120
1
239
1
119
120
tan
1 1
t
= =
(
(
(
(
.
Example: 34 The value of = +
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
) 2 2 (tan cos
3
1
tan 2 sin
1 1
[AMU 1999]
(a)
15
16
(b)
15
14
(c)
15
12
(d)
15
11
Solution: (b) )] 2 2 ( [tan cos
3
1
tan 2 sin
1 1
+
(
|
.
|
\
|
= )] 2 2 ( [tan cos
9
1
1
3
2
tan sin
1 1
+
(
(
(
(
] 2 2 cos[tan
4
3
tan sin
1 1
+
(
= =
15
14
3
1
5
3
3
1
cos cos
5
3
sin sin
1 1
= + =
(
+
(
.
Example: 35
(
+
(
+
b
a
b
a
1 1
cos
2
1
4
tan cos
2
1
4
tan
t t
equal to [MP PET 1999]
(a)
b
a 2
(b)
a
b 2
(c)
b
a
(d)
a
b
Solution: (b) Let
b
a
b
a
= =
u u cos cos
1
(
+
(
+
b
a
b
a
1 1
cos
2
1
4
tan cos
2
1
4
tan
t t
=
t
t
t
t
+
+
1
1
1
1
, where
2
tan
u
= t
a
b
t
t 2
cos
2
1
) 1 (
2
2
2
= =
+
=
u
.
Example: 36
239
1
tan
5
1
tan 4
1 1
is equal to [UPSEAT 1995]
(a) t (b)
2
t
(c)
3
t
(d)
4
t
Solution: (d) Since,
2
1 1
1
2
tan tan 2
x
x
x
=
25
1
1
5
2
tan 2
5
1
tan 2 2
5
1
tan 4
1 1 1
=
(
=
576
100
1
24
20
tan
24
10
tan 2
1 1
= =
119
120
tan
1
=
So,
239
1
tan
119
120
tan
239
1
tan
5
1
tan 4
1 1 1 1
=
239
1
.
119
120
1
239
1
119
120
tan
1
+
=
120 ) 239 119 (
119 ) 239 120 (
tan
1
+
=
4
1 tan
1
t
= =
.
Example: 37 The formula x
x
x
1
2
2
1
tan 2
1
1
cos
=
+
holds only for
(a) R x e (b) 1 | | s x (c) ] 1 , 1 ( e x (d) ) , 1 [ + e x
Solution: (d) If , 1 = x LHS = ,
2
t
RHS = |
.
|
\
|
2
2
t
. So, the fomula does not hold.
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
If , 1 < x the angle on the LHS is in the second quadrant while the angle on the RHS is 2 (angle in the fourth quadrant), which
cannot be equal.
If , 1 > x the angle on the LHS is in the second quadrant while the angle on the RHS is 2 (angle in the first quadrant) and these two
may be equal.
If 0 1 < < x , the angle on the LHS is positive and that on the RHS is negative and the two cannot be equal.
Example: 38
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2
x
x
x
+
+
is independent of x , then
(a) ) , 1 [ + e x (b) ] 1 , 1 [ e x (c) 1 , ( e x ] (d) None of these
Solution: (a) Let u tan = x . Then ) 2 (sin sin
tan 1
tan 2
sin
1
2
sin
1
2
1
2
1
u
u
u
=
+
=
+ x
x
) 2 (sin sin 2
1
2
sin tan 2
1
2
1 1
u u
+ =
+
+
x
x
x
If
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2 ,
2
2
2 x
x
x
+
+ s s
t
u
t
= = = +
x
1
tan 4 2 2 u u independent of x.
If
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan 2 ,
2
2
2 x
x
x
+
+ s s
t
u t
t
= u t u u t u 2 2 )] 2 [sin( sin 2
1
+ = +
= t = independent of x.
(
e
4
,
4
t t
u but
(
e
4
3
,
4
t t
u and from the principal value of x
1
tan
.
|
.
|
\
|
e
2
,
2
t t
u . Hence, |
.
|
\
|
e
2
,
4
t t
u
|
.
|
\
|
e
2
,
4
t t
u t =
+
+
2
1 1
1
2
sin tan
x
x
x .
Also at t
t t t t
u = + = + =
+
+ =
2 2
1 sin
4
. 2
1
2
sin tan 2 ,
4
1
2
1 1
x
x
x .
The given function = t = constant if |
.
|
e
2
,
4
t t
u . i.e., ) , 1 [ + e x .
Example: 39 The number of positive integral solutions of the equation
10
3
sin
1
cos tan
1
2
1 1
=
+
+
y
y
x or 3 tan cot tan
1 1 1
= + y x
is [Roorkee 1993]
(a) One (b) Two (c) Zero (d) None of these
Solution: (b) 3 tan
1
tan tan
1 1 1
= +
y
x or
y
1
tan
1
= x
1 1
tan 3 tan
or
x
x
y 3 1
3
tan
1
tan
1 1
+
=
x
x
y
+
=
3
3 1
As , x y are positive integers, 1 = x , 2 and corresponding , 2 = y 7
Solutions are ) 7 , 2 ( ), 2 , 1 ( ) , ( = y x .
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
1. The domain of x
1
sin
is [Roorkee Screening 1993]
(a) ) , ( t t (b) [ 1, 1] (c) ) 2 , 0 ( t (d) ) , (
2. The range of x
1
tan
is [DCE 2002]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
2
,
t
t (b) |
.
|
\
|
2
,
2
t t
(c) ) , ( t t (d) ) , 0 ( t
3. x x
1 1
cos sin
+ is equal to [Pb. CET 1997; DCE 2002]
(a)
4
t
(b)
2
t
(c) 1 (d) 1
4. =
)
`
+
2
1
cos
2
1
sin sin
1 1
[EAMCET 1985]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 1
5. The value of |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
3
5
cos sin
3
5
cos cos
1 1
t t
is [UPSEAT 2003]
(a)
2
t
(b)
3
5t
(c)
3
10t
(d) 0
6. =
(
|
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
7
1
sin
7
1
cos cos
1 1
[EAMCET 2003]
(a)
3
1
(b) 0 (c)
3
1
(d)
9
4
7. The value of x x
1 1
cot 2 tan
+ is [Kurukshetra CEE 1998]
(a)
3
t
(b)
6
t
(c)
3
2t
(d) t 2
8. If ,
3
2
cot 2 tan
1 1
t
= +
x x then = x [Karnataka CET 1999]
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 3 (d)
1 3
1 3
+
9. If , cos sin 4
1 1
t = +
x x then x is equal to [UPSEAT 2001]
(a) 0 (b)
2
1
(c)
2
3
(d)
2
1
10. =
(
+
5
1
sin
5
1
cos 2 cos
1 1
[IIT 1981]
(a)
5
6 2
(b)
5
6 2
(c)
5
1
(d)
5
1
B Ba as si ic c L Le ev ve el l
Properties of Inverse Trigonometrical Function
141
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
11. The value of |
.
|
\
|
5
33
cos sin
1
t
is
(a)
5
3t
(b)
5
7t
(c)
10
t
(d)
10
t
12. If , ) 1 ( sin 2
1
sec
1 1
t = + |
.
|
\
|
x
then x equals [AMU 1988]
(a)
2
1
(b) 1 (c)
2
t
(d) None of these
13. The value of |
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
1
sin
2
3
sin
1 1
is [MP PET 2003]
(a)
o
45 (b)
o
90 (c)
o
15 (d)
o
30
14. The value of )) 2 (tan cos(tan
1
is [AMU 2002]
(a)
5
1
(b)
5
1
(c) 2 cos (d) 2 cos
15. The value of x which satisfies the equation
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
10
3
sin tan
1 1
x is [Pb. CET 1999]
(a) 3 (b) 3 (c)
3
1
(d)
3
1
16. If , cosec sec
1 1
y x =
then = +
y x
1
cos
1
cos
1 1
[Orissa JEE 2002]
(a) t (b)
4
t
(c)
2
t
(d)
2
t
17. If ,
1
cos
1
u = |
.
|
\
|
x
then = u tan [MNR 1978; MP PET 1989]
(a)
1
1
2
x
(b) 1
2
+ x (c)
2
1 x (d) 1
2
x
18. If
5
sin
1
t
=
x for some ), 1 , 1 ( e x then the value of x
1
cos
is [DCE 1997; Karnataka CET 1996; IIT 1992]
(a)
10
3t
(b)
10
5t
(c)
10
7t
(d)
10
9t
19. ) cosec ( sec
1
x
is equal to [Kurukshetra CEE 2001]
(a) ) (sec cosec
1
x
(b) x cot (c) t (d) None of these
20. ) (cos tan
1
x
is equal to [IIT 1993]
(a)
x
x
2
1
(b)
2
1 x
x
+
(c)
x
x
2
1 +
(d)
2
1 x
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
21. =
) sin(cot
1
x [MNR 1987; MP PET 2001; DCE 2002]
(a)
2
1 x + (b) x (c)
2 / 3 2
) 1 (
+ x (d)
2
1
2
) 1 (
+ x
22. =
) cos(tan
1
x [MP PET 1988; MNR 1981]
(a)
2
1 x + (b)
2
1
1
x +
(c)
2
1 x + (d) None of these
23. =
(
|
.
|
\
|
25
7
cos cot
1
[Karnataka CET 1994]
(a)
24
25
(b)
7
25
(c)
25
24
(d) None of these
24. The value of x
1 1
cos tan cot sin
is equal to [Bihar CEE 1974]
(a) x (b)
2
t
(c) 1 (d) None of these
25. =
(
|
.
|
\
|
2
1
4
3
tan sin [EAMCET 1983]
(a)
5
3
(b)
3
5
(c)
25
9
(d)
9
25
26. = +
) 3 (cot osec ) 2 (tan sec
1 2 1 2
c [EAMCET 2001]
(a) 5 (b) 13 (c) 15 (d) 6
27. If , sin cos
1 1
x x
> then
(a) 0 < x (b) 0 1 < < x (c)
2
1
0 < s x (d)
2
1
1 < s x
28. If , 0 ) (sin ) (cos
2 1 2 1
>
x x then
(a)
2
1
< x (b) 2 1 < < x (c)
2
1
0 < s x (d)
2
1
1 < s x
29. The greatest and the least values of
3 1 3 1
) (cos ) (sin x x
+ are
(a)
2
,
2
t t
(b)
8
,
8
3 3
t t
(c)
8
7
,
32
3 3
t t
(d) None of these
30. If x satisfies the equation , 0 2
2
> t t then there exists a value for
(a) x
1
sin
(b) x
1
cos
(c) x
1
sec
(d) None of these
31. If , tan sec ) (
1 1
x x x f
+ = then ) (x f is real for
A Ad dv va an nc ce e L Le ev ve el l
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
(a) ] 1 , 1 [ e x (b) R x e (c) ) , 1 [ ] 1 , ( + e x (d) None of these
32. If
=
n
r
r
n x
2
1
1
, sin t then
=
=
n
r
r
x
2
1
(a) n (b) 2n (c)
2
) 1 ( + n n
(d) None of these
33.
5
2t
is the principal value of
(a) )
5
7
(cos cos
1
t
(b) )
5
7
(sin sin
1
t
(c) )
5
7
(sec sec
1
t
(d) None of these
34. The number of real solutions of ) , ( y x ; where t t 2 2 ), (cos cos , sin | |
1
s s = =
x x y x y is
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) 4
35. The set of values of k for which 0 ) 4 (sin sin
1 2
> +
kx x for all real x is
(a) | (b) ) 2 , 2 ( (c) R (d) None of these
36. x
x x
x x
1 1
2
2 2 1
cos
2
cos
4
1 . 1
2
1
cos
=
+ holds for
(a) 1 | | s x (b) R x e (c) 1 0 s s x (d) 0 1 s s x
37. If , 3 cos cos cos
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then = + + zx yz xy [Karnataka CET 2003]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) 3
38. The value of |
.
|
\
|
3
1
tan
2
1
tan tan
1 1
is [AMU 2001]
(a)
6
5
(b)
6
7
(c)
6
1
(d)
7
1
39. = |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
12
2
tan
11
1
tan
1 1
[DCE 1999]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
132
33
tan
1
(b) |
.
|
\
|
2
1
tan
1
(c) |
.
|
\
|
33
132
tan
1
(d) None of these
40. If , sin sin sin
1 1 1
t = + +
c b a then the value of ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 1 (
2 2 2
c c b b a a + + will be [UPSEAT 1999]
(a) abc 2 (b) abc (c) abc
2
1
(d) abc
3
1
41. If , tan tan tan
1 1 1
A y x
= then = A [MP PET 1988]
B Ba as si ic c L Le ev ve el l
Sum and Difference of Inverse Trigonometrical Function
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
(a) y x (b) y x + (c)
xy
y x
+
1
(d)
xy
y x
+
1
42. If
4
3 tan 2 tan
1 1
t
= +
x x then x = [Roorkee 1978, 1980; MNR 1986; Karnataka CET 2002]
(a) 1 (b)
6
1
(c)
6
1
, 1 (d) None of these
43. If , cos
5
4
sin
5
3
cos
1 1 1
x
= then = x [AMU 1978]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) 2
44. If , cot cot cot
1 1 1
x
= + | o then = x [MP PET 1992]
(a) | o + (b) | o (c)
| o
o|
+
+ 1
(d)
| o
o|
+
1
45. = +
19
8
tan
5
3
tan
4
3
tan
1 1 1
[AMU 1976, 1977]
(a)
4
t
(b)
3
t
(c)
6
t
(d) None of these
46. =
(
+
2
1
tan
3
1
tan cos
1 1
[MP PET 1991; MNR 1990]
(a)
2
1
(b)
2
3
(c)
2
1
(d)
4
t
47. =
+
y x
y x
y
x
1 1
tan tan (where 0 > > y x ) [EAMCET 1992]
(a)
4
t
(b)
4
t
(c)
4
3t
(d) None of these
48.
(
+
3
2
tan
5
4
cos tan
1 1
= [IIT 1983; EAMCET 1988; MP PET 1990; MNR 1992]
(a)
17
6
(b)
6
17
(c)
16
7
(d)
7
16
49. |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
9
2
tan
4
1
tan
1 1
= [EAMCET 1994]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
5
3
cos
2
1
1
(b) |
.
|
\
|
5
3
sin
2
1
1
(c) |
.
|
\
|
2
1
tan
1
(d) Both (a) and (c)
50. 3 cot
5
1
sin
1 1
+ is equal to [Karnataka CET 1995; MP PET 1993]
(a)
6
t
(b)
4
t
(c)
3
t
(d)
2
t
51. If 1 cos
5
1
sin sin
1 1
= |
.
|
\
|
+
x , then x = [UPSEAT 1994]
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
(a) 1 (b) 0 (c)
5
4
(d)
5
1
52. A solution of the equation
2
) 1 ( tan ) 1 ( tan
1 1
t
= + +
x x is [Karnataka CET 1993]
(a) x = 1 (b) x = 1 (c) x = 0 (d) t = x
53. If ,
36
23
tan
1 2
1 2
tan
1
1
tan
1 1 1
=
+
+
+
x
x
x
x
then x = [ISM Dhanbad 1973]
(a)
8
3
,
4
3
(b)
8
3
,
4
3
(c)
8
3
,
3
4
(d) None of these
54. If ,
2 4
5
sec
5
sin
1 1
t
= |
.
|
\
|
+
co
x
then = x [EAMCET 1983]
(a) 4 (b) 5 (c) 1 (d 3
55. = |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
7
1
tan
5
3
sin
1 1
[Karnataka CET 1994]
(a)
4
t
(b)
2
t
(c) |
.
|
\
|
5
4
cos
1
(d) t
56. If 3 tan , 2 tan
1 1
are two angles of a triangle, then the third angle is
(a)
4
t
(b)
4
3t
(c)
4
t
(d) None of these
57. If = + +
z y x
1 1 1
cos cos cos t then [Roorkee 1994]
(a) 0
2 2 2
= + + + xyz z y x (b) xyz z y x 2
2 2 2
+ + + =0 (c) 1
2 2 2
= + + + xyz z y x (d) 1 2
2 2 2
= + + + xyz z y x
58. If ,
2
tan tan tan
1 1 1
t
= + +
z y x then [Karnataka CET 1996]
(a) 0 = + + xyz z y x (b) 0 = + + + xyz z y x (c) 0 1 = + + + zx yz xy (d) 0 1 = + + zx yz xy
59. If , tan tan tan
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then
zx yz xy
1 1 1
+ + = [MP PET 1991]
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c)
xyz
1
(d) xyz
60. If we consider only the principal values of the inverse trigonometric functions, then the value of
|
|
.
|
\
|
) 17 (
4
sin
2 5
1
cos tan
1 1
is
[IIT 1994]
(a)
3
29
(b)
3
29
(c)
29
3
(d)
29
3
A Ad dv va an nc ce e L Le ev ve el l
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
61. The sum of first 10 terms of the series ....... 21 cot 13 cot 7 cot 3 cot
1 1 1 1
+ + + +
is [Karnataka CET 1996]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
6
5
tan
1
(b) ) 100 ( tan
1
(c) |
.
|
\
|
5
6
tan
1
(d) |
.
|
\
|
100
1
tan
1
62. Sum of infinite terms of the series +
(
+ +
(
+ +
(
+
4
3
3 cot
4
3
2 cot
4
3
1 cot
2 1 2 1 2 1
.is
(a)
4
t
(b) 2 tan
1
(c) 3 tan
1
(d) None of these
63. .......
1
1
tan .........
18
1
tan
7
1
tan
3
1
tan
2
1 1 1 1
+ |
.
|
\
|
+ +
+ + + +
n n
to is equal [Karnataka CET 2000]
(a)
2
t
(b)
4
t
(c)
3
2t
(d) 0
64. If , sin sin sin
1 1 1
t = + +
z y x then ), ( 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 4
x z z y y x K z y x z y x + + = + + + where K = [UPSEAT 1997]
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) None of these
65. The sum of the infinite series
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ +
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
) 1 (
1
sin .... ..........
12
2 3
sin
6
1 2
sin
2
1
sin
1 1 1 1
n n
n n
is
(a)
4
t
(b)
3
t
(c)
2
t
(d) t
66. If sum of the infinite series ..... ) 2 . 2 cot( ) 2 . 2 ( cot ) 2 . 2 ( cot ) 1 . 2 ( cot
4 3 1 2 1 2 1
+ + + +
is equal to
(a)
5
t
(b)
4
t
(c)
3
t
(d)
2
t
67. If ,
2
3
sin sin sin
1 1 1
t
= + +
z y x then the value of
101 101 101
100 100 100
9
z y x
z y x
+ +
+ + is equal to
(a) 0 (b) 3 (c) 3 (d) 9
68. If
4 3 2 1
, , , x x x x are roots of the equation , 0 sin cos 2 cos 2 sin
2 3 4
= + | | | | x x x x
then = + + +
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
1
tan tan tan tan x x x x
(a) | (b) |
t
2
(c) | t (d) |
69. If
n
a a a a ........, , , ,
3 2 1
is an A.P. with common difference d, then =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ +
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
n n
a a
d
a a
d
a a
d
1
1
3 2
1
2 1
1
1
tan ..........
1
tan
1
tan tan
(a)
n
a a
d n
+
1
) 1 (
(b)
n
a a
d n
1
1
) 1 (
+
(c)
n
a a
nd
1
1 +
(d)
1
1
a a
a a
n
n
+
B Ba as si ic c L Le ev ve el l
Inverse Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
70. a
1
tan 3
is equal to [MP PET 1993]
(a)
2
3
1
3 1
3
tan
a
a a
+
+
(b)
2
3
1
3 1
3
tan
a
a a
+
(c)
2
3
1
3 1
3
tan
a
a a
(d)
2
3
1
3 1
3
tan
a
a a
71. If , tan
1
x A
= then = A 2 sin [MNR 1988; UPSEAT 2000]
(a)
2
1
2
x
x
(b)
2
1
2
x
x
(c)
2
1
2
x
x
+
(d) None of these
72. =
) 8 . 0 sin 2 sin(
1
[MNR 1980]
(a) 0.96 (b) 0.48 (c) 0.64 (d) None of these
73. If ,
9
1
) sin 2 cos(
1
=
x then = x [Roorkee 1975] [MNR 1980]
(a) Only
3
2
(b) Only
3
2
(c)
3
2
,
3
2
(d) Neither
3
2
nor
3
2
74. = |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
5
1
tan 2
17
15
cos
1 1
[EAMCET 1981]
(a)
2
t
(b) |
.
|
\
|
221
171
cos
1
(c)
4
t
(d) None of these
75. = |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
7
1
tan
3
1
tan 2
1 1
[EAMCET 1983]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
29
49
tan
1
(b)
2
t
(c) 0 (d)
4
t
76. = +
3
1
tan 2
5
4
sin
1 1
[Dhanbad Engg. 1971]
(a)
2
t
(b)
3
t
(c)
4
t
(d) None of these
77. If x
b
b
a
a
1
2
1
2
1
tan 2
1
2
sin
1
2
sin
=
+
+
+
, then x = [MNR 1984]
(a)
ab
b a
+
1
(b)
ab
b
+ 1
(c)
ab
b
1
(d)
ab
b a
+
1
78. If ,
3
1
tan
1
tan
3 2
1
tan 3
1 1 1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
x
then x equals [Pb. CET 2001; AMU 1992]
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 3
79.
(
(
+
+ +
x x
x x
sin 1 sin 1
sin 1 sin 1
cot
1
= [UPSEAT 1986]
(a) x t (b) x t 2 (c)
2
t
(d)
2
x
t
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
80. = |
.
|
\
|
5
4
cos
2
1
sin
1
[Karnataka CET 2003]
(a)
10
1
(b)
10
1
(c)
10
1
(d)
10
1
81. =
(
(
2
tan tan 2
1
u
b a
b a
[ISM Dhanbad 1976]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
+
+
u
u
cos
cos
cos
1
b a
b a
(b) |
.
|
\
|
+
+
b a
b a
u
u
cos
cos
cos
1
(c) |
.
|
\
|
+
u
u
cos
cos
cos
1
b a
a
(d) |
.
|
\
|
+
b a
b
u
u
cos
cos
cos
1
82. If x =
] ) [(cos tan ] ) [(cos cot
2 / 1 1 2 / 1 1
o o . Then = x sin [AIEEE 2002]
(a) |
.
|
\
|
2
tan
2
o
(b) |
.
|
\
|
2
cot
2
o
(c) o tan (d) |
.
|
\
|
2
cot
o
83. The value of
+
|
.
|
\
|
kx k x
x
kx k x
x
2 2
1
2 2
1
6
cos cos
3
sin sin
t t
, |
.
|
\
|
> < < 0 , 2
2
where k k x
k
is
(a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
2 2
2 2
1
2
2
tan
k xk x
k xk x
(b)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
2 2
2 2
1
2
2
tan
k xk x
k xk x
(c)
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
2 2
2 2
1
2 2 2
2 2
tan
k xk x
k xk x
(d) None of these
84. Solution of equation 0 )}] tan 2 {cot( cos 2 sin[
1 1
=
x is [UPSEAT 1998; Roorkee 1992]
(a) 1 = x only (b) 2 1 = x only (c) ) 2 1 ( = x only (d) All of these
85. The greater of the two angles ) 1 2 2 ( tan 2
1
=
A and |
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
=
5
3
sin
3
1
sin 3
1 1
B is [IIT 1992]
(a) B (b) A (c) C (d) None of these
86. =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
3
5
cos
2
1
tan
1
[Roorkee 1986]
(a)
2
5 3
(b)
2
5 3 +
(c)
5 3
2
(d)
5 3
2
+
***
A Ad dv va an nc ce e L Le ev ve el l
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC) 10C-82,VASUNDHRA, GHAZIABAD. BRANCH: SAHIBABAD
CALL US @ 09818777-622 www.anuragtyagiclasses.com www.facebook.com/anuragtyagisir
Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
b b b d a b c c b b d b d c a d d a a a
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
d b d a c c d d c c c b b c a c c d d a
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
c b b d a a b b d b d c d d a b d d b d
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
a b b b c b a b b d c a c d d a d b d a
81 82 83 84 85 86
a a c d b d
150
Assignment (Basic & Advance Level) Inverse Trigonometrical Functions
You might also like
- C4 Isi 2013 PDFDocument32 pagesC4 Isi 2013 PDFAnh Bien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Legendre Polynomials PDFDocument19 pagesLegendre Polynomials PDFBappy K M BNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Selected ProblemsDocument13 pagesSolutions To Selected ProblemsAalap JoeNo ratings yet
- Waves & ThermodynamicsDocument71 pagesWaves & ThermodynamicsSindhi Madhuri75% (4)
- Fourier Series' & Its Application': Guided By: - Prof. K.K.PokarDocument32 pagesFourier Series' & Its Application': Guided By: - Prof. K.K.PokarNikunj JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Lebesgue IntegralsDocument30 pagesChapter 14 Lebesgue Integralsankit bansalNo ratings yet
- 2012f Lebesgue Integrals Lecture NoteDocument69 pages2012f Lebesgue Integrals Lecture NoteKelvin JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 PDFDocument65 pagesChapter4 PDFHương HươngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document117 pagesChapter 5Phan Mạnh TườngNo ratings yet
- Orbital Aspects of Satellite CommunicationsDocument20 pagesOrbital Aspects of Satellite CommunicationsLee Robine100% (1)
- Fir FiltersDocument43 pagesFir FiltersAmeerulla ShaikNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing First Reading Assignments: This LectureDocument9 pagesSignal Processing First Reading Assignments: This LecturePVC743No ratings yet
- Riesz Sequence Lebesgue Integral 120106Document71 pagesRiesz Sequence Lebesgue Integral 120106keynote76No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - dsp1 - Co Thuc - Full, dsp1, Co Thuc, Xu Li Tin Hieu, BKDN, DSPDocument120 pagesChapter 5 - dsp1 - Co Thuc - Full, dsp1, Co Thuc, Xu Li Tin Hieu, BKDN, DSPXP2009No ratings yet
- Problems On Abstract Algebra (Group Theory, Rings, Fields, and Galois Theory)Document39 pagesProblems On Abstract Algebra (Group Theory, Rings, Fields, and Galois Theory)Andrew NelsonNo ratings yet
- Ch10 LT Instructor SolutionDocument80 pagesCh10 LT Instructor SolutionPaulo FidelisNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument42 pages1 IntroductionJustine CabuayNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument45 pagesNuclear PhysicsPrasad RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Introductory Mathematical Analysis For Quantitative Finance: Daniele Ritelli and Giulia SpalettaDocument237 pagesIntroductory Mathematical Analysis For Quantitative Finance: Daniele Ritelli and Giulia SpalettaFrancescoNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: - Digital SignaturesDocument21 pagesCryptography: - Digital SignaturessravnumasNo ratings yet
- Análisis Complejo (Notas)Document137 pagesAnálisis Complejo (Notas)Arima YakumoNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Compression TechniquesDocument16 pagesImage Processing Compression TechniquesSurendran JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Classical Dynamics An Intermediate Level Course PDFDocument315 pagesAnalytical Classical Dynamics An Intermediate Level Course PDFNhellCernaNo ratings yet
- 2.orbital Aspects of Satellite CommunicationsDocument65 pages2.orbital Aspects of Satellite Communicationsمحمود عبدالرحمن ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics L1 & L2Document45 pagesOptoelectronics L1 & L2Mustafa AlobaidiNo ratings yet
- Phy 1103Document133 pagesPhy 1103Zhu Ghe LiangNo ratings yet
- Week4 Soluciones ArnoldDocument6 pagesWeek4 Soluciones ArnoldDiana UrizaNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems 4Th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions ManualDocument1,397 pagesCommunication Systems 4Th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions ManualTayyab Naseer100% (3)
- Nuclear Engineering 2Document35 pagesNuclear Engineering 2rajeshNo ratings yet
- Time Invariant SystemsDocument10 pagesTime Invariant SystemsCarl MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- L53 Microwave SystemsDocument16 pagesL53 Microwave SystemsAmeya KadamNo ratings yet
- Ap3114 InformationDocument15 pagesAp3114 InformationGuoXuanChanNo ratings yet
- (L3) - Radioactivity - 1st Dec PDFDocument54 pages(L3) - Radioactivity - 1st Dec PDFArpan ShingalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Lie Groups: Vladimir G. Ivancevic Tijana T. IvancevicDocument74 pagesLecture Notes in Lie Groups: Vladimir G. Ivancevic Tijana T. IvancevicjavamanprimeNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationsDocument72 pagesDigital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationslhslhinNo ratings yet
- Fourier Analysis On PolytopesDocument250 pagesFourier Analysis On PolytopesmenloparkNo ratings yet
- Libro Trench PDFDocument806 pagesLibro Trench PDFJavulicraftNo ratings yet
- Nuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Working PrincipleDocument15 pagesNuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Working PrincipleTamilselvan PNo ratings yet
- Lec. 7 DSPDocument23 pagesLec. 7 DSPlovelearnNo ratings yet
- Computer Integerated Apparel Manufacturing: Fault Analysis Using Image Processing TechniqueDocument28 pagesComputer Integerated Apparel Manufacturing: Fault Analysis Using Image Processing TechniqueMadhu MathiNo ratings yet
- The Fast Fourier Transform: (And DCT Too )Document36 pagesThe Fast Fourier Transform: (And DCT Too )Sri NivasNo ratings yet
- Lec. 10 DSPDocument15 pagesLec. 10 DSPlovelearn100% (1)
- 4b FeherKosToth MathAnExII PDFDocument211 pages4b FeherKosToth MathAnExII PDFIrving JoséNo ratings yet
- Transform Definition: - Definition 2.1 Given The Causal Sequence Then Its Z-Transform Is Defined AsDocument15 pagesTransform Definition: - Definition 2.1 Given The Causal Sequence Then Its Z-Transform Is Defined Asaravishankar23No ratings yet
- Lec. 5 DSPDocument40 pagesLec. 5 DSPlovelearnNo ratings yet
- Theory of LPC VaidhyanathanDocument198 pagesTheory of LPC VaidhyanathanArthi SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- ECE 4316: Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Hany M. ZamelDocument23 pagesECE 4316: Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Hany M. ZamellovelearnNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics by Dr. M. O. Aku PDFDocument62 pagesClassical Mechanics by Dr. M. O. Aku PDFLOUI_GR100% (1)
- Thermal Physics KPN MurthyDocument151 pagesThermal Physics KPN MurthyRithish BarathNo ratings yet
- SS Notes PDFDocument113 pagesSS Notes PDFKhurram RehmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Theory of Linear Partial Differential EquationsFrom EverandIntroduction to the Theory of Linear Partial Differential EquationsNo ratings yet
- Relativity: The Theory and Its Philosophy: Foundations & Philosophy of Science & TechnologyFrom EverandRelativity: The Theory and Its Philosophy: Foundations & Philosophy of Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Systems Method for Solving Nonlinear Operator EquationsFrom EverandDynamical Systems Method for Solving Nonlinear Operator EquationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gravitation and Relativity: International Series in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandGravitation and Relativity: International Series in Natural PhilosophyRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: (Vi) Definition of Cosec XDocument9 pagesWWW - Thinkiit.in: (Vi) Definition of Cosec XthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument10 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions PDFJiung WeiNo ratings yet
- Senior Class FormulaeDocument8 pagesSenior Class FormulaeOP GuptaNo ratings yet
- EGM6341 Sol HW 01Document22 pagesEGM6341 Sol HW 01Redmond R. ShamshiriNo ratings yet
- Resolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2Document11 pagesResolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2ChevronelleNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesSome Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaBlazingStudiosNo ratings yet
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii: Mit Opencoursewaresanskarid94No ratings yet
- JEE-MAIN 2013: Leader & Enthusiast CourseDocument4 pagesJEE-MAIN 2013: Leader & Enthusiast Coursesanskarid94No ratings yet
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit Opencoursewaresanskarid94No ratings yet
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareDocument5 pages5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit Opencoursewaresanskarid94No ratings yet
- 10.00 AM (IST) On 18.12.11 (Sunday) To 09.00 PM (IST) On 28.04.12 (Saturday)Document2 pages10.00 AM (IST) On 18.12.11 (Sunday) To 09.00 PM (IST) On 28.04.12 (Saturday)sanskarid94No ratings yet
- Brilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012Document11 pagesBrilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012sanskarid94No ratings yet
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareDocument8 pages5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit Opencoursewaresanskarid94No ratings yet
- Optional Geography 3 Climatology PDFDocument17 pagesOptional Geography 3 Climatology PDFsandeepgunjiNo ratings yet
- B.MAT Full-Syllabus Tests Schedule For IIT-JEE 2012Document1 pageB.MAT Full-Syllabus Tests Schedule For IIT-JEE 2012sanskarid94No ratings yet
- Iit-Jee 2012 Fst1 p1 SolnsDocument18 pagesIit-Jee 2012 Fst1 p1 Solnssanskarid94No ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsDocument25 pagesIIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsShivamGoyalNo ratings yet
- AP Chem NotesDocument45 pagesAP Chem NotesSajiveSivalingamNo ratings yet
- DimensionsDocument7 pagesDimensionssanskarid94No ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Revision Class ScheduleDocument1 pageJee Advanced Revision Class Schedulesanskarid94No ratings yet
- Askiitians Chemistry Test207 (5) AaassssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssddddddddddddddddddaDocument8 pagesAskiitians Chemistry Test207 (5) AaassssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssddddddddddddddddddaAshok L JoshiNo ratings yet
- Determinant DPPDocument11 pagesDeterminant DPPsanskarid94No ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument18 pagesSample PaperSoham SanyalNo ratings yet
- 09 IGV SystemDocument5 pages09 IGV Systemnabil160874100% (1)
- GreaseDocument3 pagesGreaseWac GunarathnaNo ratings yet
- OG204-TDS Tooke Paint Inspection Gage 201409Document3 pagesOG204-TDS Tooke Paint Inspection Gage 201409lorenzordzrmzNo ratings yet
- Dresser 10C25 Meter IOM Manual CompressedDocument74 pagesDresser 10C25 Meter IOM Manual Compressedangel017No ratings yet
- HAIER - HSU-09 12HC Service ManDocument109 pagesHAIER - HSU-09 12HC Service ManaircoolplusNo ratings yet
- FTH BrochureDocument144 pagesFTH BrochureRebecca StaggNo ratings yet
- Warning: US PATENT NO. 8,316,788 Other Patents PendingDocument16 pagesWarning: US PATENT NO. 8,316,788 Other Patents PendingAntonio RiujanoNo ratings yet
- Estimating Drift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDocument31 pagesEstimating Drift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsPastor PachecoNo ratings yet
- Recombinant TherapeuticsDocument18 pagesRecombinant Therapeuticssachin kumarNo ratings yet
- College of Arts and Sciences Department of Mathematics and PhysicsDocument4 pagesCollege of Arts and Sciences Department of Mathematics and PhysicsBethel Divine JuanNo ratings yet
- Lostgears Fargo July 302008Document3 pagesLostgears Fargo July 302008lostgearsNo ratings yet
- Cosmotic Surgical Center Business PlanDocument37 pagesCosmotic Surgical Center Business PlanRamchandra Cv100% (1)
- UK Bone FortifyDocument1 pageUK Bone FortifyDagoberto Rincon TorresNo ratings yet
- Autonics PR PRW DC 2wire Series ManualDocument1 pageAutonics PR PRW DC 2wire Series ManualKaller Nicolas Ruiz pedrazaNo ratings yet
- MN10 - Midnight - Steel and Shadow (Warriors) PDFDocument70 pagesMN10 - Midnight - Steel and Shadow (Warriors) PDFSteampunkObrimos100% (4)
- Maternal Medical Disorders: SBA QuestionsDocument11 pagesMaternal Medical Disorders: SBA QuestionsBernardo Daniel Lawrencius100% (2)
- Dog Food RecipesDocument284 pagesDog Food RecipesBusyNo ratings yet
- Rights of Husband and Wife Prescribed in Islam and Current SocietyDocument27 pagesRights of Husband and Wife Prescribed in Islam and Current Societydua maqsoodNo ratings yet
- USEM 2speed Amps ModelsDocument2 pagesUSEM 2speed Amps Modelspetronila66No ratings yet
- Case Presented By: Group 1Document6 pagesCase Presented By: Group 1Manav LakhinaNo ratings yet
- Flexray - Physical Layer Conformance Test Specification V1.0Document816 pagesFlexray - Physical Layer Conformance Test Specification V1.0macorcheroNo ratings yet
- UKAS LAB-36 Condisiones AmbientalesDocument5 pagesUKAS LAB-36 Condisiones AmbientalescdokepNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For PDE in C++Document38 pagesNumerical Methods For PDE in C++Anonymous 9rJe2lOskxNo ratings yet
- Rumil Johri Palak Mehta Agrima Chaturvedi Anooj Kapoor Rakesh Gotheria Jeetendra SinghDocument14 pagesRumil Johri Palak Mehta Agrima Chaturvedi Anooj Kapoor Rakesh Gotheria Jeetendra SinghAshima NagpalNo ratings yet
- Giant Omphalocele With OEIS Complex - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesGiant Omphalocele With OEIS Complex - A Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Example DWOP AgendaDocument1 pageExample DWOP Agendagman_g2000100% (1)
- Saudi Arabian Alfalfa Hay Market - Riyadh - Saudi Arabia - 2-22-2017Document4 pagesSaudi Arabian Alfalfa Hay Market - Riyadh - Saudi Arabia - 2-22-2017Amir SaifNo ratings yet
- Fiber Technology For Fiber-Reinforced Composites. © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesFiber Technology For Fiber-Reinforced Composites. © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All Rights ReservedPao FrancavillaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheDocument61 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheHairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Geography - Industries-The Pitch LakeDocument6 pagesGeography - Industries-The Pitch LakeShannen NaraceNo ratings yet