Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypertension
Uploaded by
Allyne GavinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypertension
Uploaded by
Allyne GavinoCopyright:
Available Formats
Aguilera Demata Gavino Generalao
Luna Padua Ruda Torralba
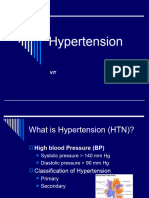
Hypertension CONTENT High blood pressure (HBP) or hypertension means high pressure (tension) in the arteries. Arteries are vessels that carry blood from the pumping heart to all the tissues and organs of the body. Blood Pressure the product of cardiac output multiplied by peripheral resistance. Cardiac output the product of the heart rate multiplied by stroke volume 2 measurements: systole (contracting heart muscle), diastole (relaxation between beats) Classifications: Primary no underlying medical cause Secondary caused by other conditions Stages: Prehypertension = 120 139mmhg(systole) over 80 - 89mmhg (diastole) Stage 1 = 140 150 (systole) over 90 99mmhg (diastole) Stage 2 = 160 (sytole) over 100 (diastole) Viewed in 3 ways : (1) a sign, (2) risk for atherosclerosis and (3) a disease Factors leading to HBP Age Sodium (salt) sensitivity Race (African american) Alcohol use Heredity Lack of exercise Gender medications obesity Signs and symptoms A portion of people with HBP reports: headache tinnitus lightheadedness altered vision / fainting episodes vertigo Complications: stroke heart failure heart attack eye problems aneurysm embolism kidney failure Treatments: Medications: diuretics combined alpha and beta blockers aldosterone receptor blocker vasodilators beta blockers ace inhibitors alpha blockers angiotensin II receptors calcium channel blockers Nsg. Interventions: monitor BP suggest to reduce activity pulse quality (central&peripheral) help perform self-care activities as needed auscultation of heart & breath sounds back & neck massage skin color, moisture, temp and capillary refill relaxation techniques observe gen. edema give fluid restriction and sodium diet as indicated provide quiet and calm environment Prevention in 6 steps i. follow healthy eating habit ii. reduce salt in your diet iii. maintain healthy weight iv. being physically active v. limit alcohol intake vi. quit smoking
You might also like
- HTNDocument54 pagesHTNapi-232466940No ratings yet
- Heart Failure Signs and Symptoms:: It Is Inability of The Heart To Pump Enough Blood To The Body TissuesDocument4 pagesHeart Failure Signs and Symptoms:: It Is Inability of The Heart To Pump Enough Blood To The Body Tissuesمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi: DR M. Arman Nasution SPPDDocument101 pagesHipertensi: DR M. Arman Nasution SPPDDian PuspaNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi PBLDocument41 pagesHipertensi PBLkholilgantengNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi: Maimun SyukriDocument41 pagesHipertensi: Maimun Syukriandreva8No ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapgfhbgfhgf71% (7)
- HYPERTENSIONDocument10 pagesHYPERTENSIONChelsea Faith SarandiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Prepared By: Eden Marie D. Francisco Lorraine Nicolne B. CortejoDocument27 pagesHypertension: Prepared By: Eden Marie D. Francisco Lorraine Nicolne B. CortejoAlecNo ratings yet
- Hypertension LectureDocument10 pagesHypertension LectureHarold CapidosNo ratings yet
- Hyper TentionDocument19 pagesHyper TentionAnthony MarkNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Detection, Evaluation and Non-Pharmacologic InterventionDocument42 pagesHypertension: Detection, Evaluation and Non-Pharmacologic InterventionLullaby HunterNo ratings yet
- Return To Top: Alternative NamesDocument7 pagesReturn To Top: Alternative NamesDewi SNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument55 pagesHYPERTENSIONviennns100% (4)
- Congestive Heart Failure ReportDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure ReportSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (1)
- Hypertension: High Blood PressureDocument6 pagesHypertension: High Blood PressureAnne BattulayanNo ratings yet
- 5 Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument74 pages5 Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular Diseaseskarinablanca adranedaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: by Krikor Jabourian Nakhleh Nehmeh Yara YounesDocument33 pagesHypertension: by Krikor Jabourian Nakhleh Nehmeh Yara YounesHamza DibNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Medlineplus TopicsDocument31 pagesHypertension: Medlineplus TopicsMcNover Catlin OsamNo ratings yet
- Hypertension 101028172250 Phpapp01Document16 pagesHypertension 101028172250 Phpapp01DianAyuNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mita HipertensiDocument12 pagesTugas Mita HipertensiPutu MitaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Is Another Name For High Blood PressureDocument91 pagesHypertension Is Another Name For High Blood PressureMd. Sohanul IslamNo ratings yet
- HIPERTENSIDocument57 pagesHIPERTENSIWenny KalamiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument43 pagesNutrition Therapy For Cardiovascular DiseasesChelo Jan GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Hipertensi KMB1 2018Document43 pagesKuliah Hipertensi KMB1 2018Ainu RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study For HypertensionDocument9 pagesCase Study For HypertensionGabbii Cinco100% (1)
- HIPERTENSI Dan Penyakit KardiovaskularDocument39 pagesHIPERTENSI Dan Penyakit KardiovaskulardhestiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension FinalDocument30 pagesHypertension FinalDr Saad ShahNo ratings yet
- 11 Anti Hypertensive 17-08-2023Document21 pages11 Anti Hypertensive 17-08-2023ashwin kNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument7 pagesScriptAllen DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Gerontik "Hypertension"Document11 pagesNursing Care of Gerontik "Hypertension"Pradhevi Angelita WijayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 HypertensionDocument3 pagesChapter 31 HypertensionVen SemillaNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi - Interna - Dr. MuzakkirDocument43 pagesHipertensi - Interna - Dr. MuzakkirFarnida JamhalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideDocument9 pagesNursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Prof - Dr.Medhat Ashmawy Professor of Cardiology, Tanta UniversityDocument104 pagesProf - Dr.Medhat Ashmawy Professor of Cardiology, Tanta UniversityIvana LmsNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION DR - Ridwan SPJPDocument43 pagesHYPERTENSION DR - Ridwan SPJPAmanda PutraNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs Lecture-1Document94 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs Lecture-1onyeukwudaniel12No ratings yet
- Adult 1 - Week 7 (Chapter 32)Document5 pagesAdult 1 - Week 7 (Chapter 32)Sydney SmallNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Maimun SyukriDocument55 pagesHypertension: Maimun SyukriLingga Yudistira AbralNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi PBLDocument56 pagesHipertensi PBLVandra PrinosaNo ratings yet
- Gerontic Nursing: Elderly With Hypertension: Arranged Group 11: Suci Aulia (1714201042)Document15 pagesGerontic Nursing: Elderly With Hypertension: Arranged Group 11: Suci Aulia (1714201042)anisaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension FinalDocument54 pagesHypertension FinalPatrick CommettantNo ratings yet
- Hypertension HSE Presentation HSE FormatsDocument18 pagesHypertension HSE Presentation HSE FormatsasepNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With HypertensionDocument13 pagesNursing Care of Patients With HypertensionDon Chiaw Manongdo100% (1)
- What Causes Hypertension?: Vomiting Hypertensive CrisisDocument11 pagesWhat Causes Hypertension?: Vomiting Hypertensive CrisisSabrina Agnes WawaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument39 pagesHypertensionMa. Jewon LAGGUINo ratings yet
- Presented by Asmaa Abdelhameed AhmedDocument24 pagesPresented by Asmaa Abdelhameed AhmedSoma Al-mutairiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Mini Case StudyDocument5 pagesHypertension Mini Case Studymaeca101100% (1)
- CA ReviewerDocument16 pagesCA ReviewerJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Rafey MA, May 2013Document19 pagesHypertension: Rafey MA, May 2013dwi mentariNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument6 pagesHypertensionMatthew Michael100% (1)
- Hypertension Final PDFDocument48 pagesHypertension Final PDFakshayshinde24995No ratings yet
- Chap 7 High Blood PressureDocument3 pagesChap 7 High Blood PressureSabina MoolyeNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument55 pagesHYPERTENSIONCut Putri RiskaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Medical Management and Nutritional ApproachesDocument65 pagesHypertension: Medical Management and Nutritional ApproachesWelki VernandoNo ratings yet
- Case Study HypertensionDocument6 pagesCase Study HypertensionLalaine MontesclarosNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Written ReportDocument5 pagesHypertension Written ReportKate Felongco CambelNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument44 pagesHypertensionasadcabdi613No ratings yet
- Hypertension Group 9Document19 pagesHypertension Group 9Putri AuliaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Uranus MeansDocument1 pageUranus MeansAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The World How The World Was Created Indrapatra at Sulayman Ibalon Samal Genesis The Centipede The Mats The Bread of SaltDocument1 pageThe Origin of The World How The World Was Created Indrapatra at Sulayman Ibalon Samal Genesis The Centipede The Mats The Bread of SaltAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Choose A Topic. The Topic of Apersuasive Essay MustDocument5 pagesChoose A Topic. The Topic of Apersuasive Essay MustAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Choose A Topic. The Topic of Apersuasive Essay MustDocument5 pagesChoose A Topic. The Topic of Apersuasive Essay MustAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- FriendlyDocument19 pagesFriendlyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument5 pagesStudent NurseAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Info DriveDocument10 pagesInfo DriveAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy MondayDocument5 pagesDrugstudy MondayAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Newborn Screening SyllabusDocument2 pagesNewborn Screening SyllabusAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Cookng DmoDocument2 pagesCookng DmoAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Letters XmasDocument23 pagesLetters XmasAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Mission VisionDocument4 pagesMission VisionAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- CommodityDocument2 pagesCommodityAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Jannah R, ManualDocument6 pagesJannah R, ManualAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Gavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Document4 pagesGavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Allyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Report - Copy of Grpm8sDocument1 pageReport - Copy of Grpm8sAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Syl Lab Us Good EnoughDocument2 pagesSyl Lab Us Good EnoughAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet