Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Charge and Electric Field: 5. Principle of Superposition
Uploaded by
rajstudybriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Charge and Electric Field: 5. Principle of Superposition
Uploaded by
rajstudybriCopyright:
Available Formats
Principle of superposition and electric field
7/21/2013
P h y s c is C a t a y ls t c . o m
HOME STUDY MA TERIA L TEST SERIES PA CKA GES OLP FORUM A RTICLES DOWNLOA DS
'Welcome to the world of Physics!'
Login A bout Us
Electric Charge and Electric Field
Sponsored Links
5. Principle Of Superposition
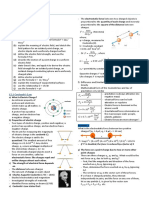
Coulomb's law gives the electric force acting between two electric charges. Principle of superposition gives the method to find force on a charge when system consists of large number of charges. According to this principle when a number of charges are interacting the total force on a given charge is vector sum of forces exerted on it by all other charges. This principle makes use of the fact that the forces with which two charges attract or repel one another are not affected by the presence of other charges.
Find us on Facebook
PhysicsCatalyst
Like 1,795
PhysicsCatalyst Since the car is turning on a curve acceleration is centripetal accelera There are three cases with turnin 1) Unbanked curve. Subscribe
If a system of charges has n number of charges say q1, q2, ...................., qn, then total force on charge q1 according Email: to principle of superposition is F = F12 + F13 + .................................. F1n Where F12 is force on q1 due to q2 and F13 is force on q1 due to q3 and so on. subscribe
Subm it your em ail address and receive free newsletter every m onth. Your em ail is safe with us
F12, F13, .................. F1n can be calculated from Coulomb's law i. e. to, kq1q2r12 kq1q2r1n The total force F1 on the charge q1 due to all other charges is the vector sum of the F12= forces F12, F13, ................................. F1n. 40(r12)2F1n= 40(r1n)2F1 = F12 + F13 + ..................................
ExponentEducation.com/IITJEE-Videos Ask Doubt,Problems & Get Video Sol. Download 30 Min Video Lecture Free!
The vector sum is obtained by parellogram law of addition of vector. Similarly force on any other charge due to remaining charges say on q2, q3 etc. can be found by adopting this method.
6. Electric Field
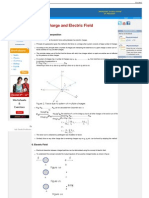
Electrical interaction between charged particles can be reformulated using the concept of electric field. To understand the concept consider the mutual repulsion of two positive charged bodies as shown in fig (a)
Now if remove the body B and label its position as point P as shown in fig (b), the charged body A is said to produce an electric field at that point (and at all other points in its vicinity)
http://physicscatalyst.com/elec/charge_1.php
1/2
Principle of superposition and electric field
7/21/2013
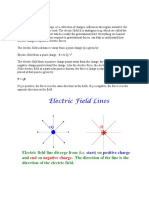
When a body B is placed at point P and experiences force F, we explain it by a point of view that force is exerted on B by the field not by body A itself. The body A sets up an electric field and the force on body B is exerted by the field due to A. An electric field is said to exists at a point if a force of electric origin is exerted on a stationary charged (test charge) placed at that point. If F is the force acting on test charge q placed at a point in an electric field then electric field at that point is E = F/q or F = qE Electric field is a vector quantity and since F = qE the direction of E is the direction of F. Unit of electric field is (N.C-1) Q. Find the dimensions of electric field Ans. [MLT-3A-1]
7. Calculation of Electric Field
In previous section we studied a method of measuring electric field in which we place a small test charge at the point, measure a force on it and take the ratio of force to the test charge. Electric field at any point can be calculated using Coulomb's law if both magnitude and positions of all charges contributing to the field are known. To find the magnitude of electric field at a point P, at a distance r from the point charge q, we imagine a test charge q'to be placed at P. Now we find force on charge q' due to q through Coulomb's law. electric field at P is The direction of the field is away from the charge q if it is positive
qq'
F=
40r2
E=
40r2
Electric field for either a positive or negative charge in terms of unit vector r directed along line from charge q to point P is r = distance from charge q to point P.
qr
E=
When q is negative , direction of E is towards q, opposite to r.
40r2Electric Field Due To Multiple Charges
Consider the number of point charges q1, q2,........... which are at distance r1P, r2P,................... from point P as shown in fig
The resultant electric field is the vector sum of individual electric fields as E = E1P + E2P + .....................
This is also a direct result of principle of superposition discussed earlier in case of electric force on a single charge due to system of multiple charges. E is a vector quantity that varies from one point in space to another point and is determined from the position of square charges.
BACK
Strain Gauge Substitute
NEXT
www.Tekscan.com/Strain-G Measure Force with our Ultra-Thin, Flexible, &
HOME | ABOUT US | ADVERTISE WITH US | CONTACT US | SITE MAP Copyright-2009 Kwality E-Solutions
http://physicscatalyst.com/elec/charge_1.php
2/2
You might also like
- Columbs LawDocument6 pagesColumbs Lawasadaliawanatd1No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument186 pagesPhysicsArunbijuNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple NotesDocument68 pagesClass 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple Noteslplc791No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDocument12 pagesElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedVinod MN50% (2)
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDocument180 pagesElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedGahan Gowda SNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Intensity FormulaDocument6 pagesElectric Field Intensity FormulaRbai praveenNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction of ChargesDocument13 pagesAddition and Subtraction of ChargesSahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Chapter 12Document11 pagesPhysics STPM Chapter 12Chloyee LkyNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields - Chapter1Document11 pagesElectric Charges and Fields - Chapter1TheerthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Coulombs Law)Document5 pagesLecture 2 (Coulombs Law)ayesha khalidNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument12 pagesElectric Charges and FieldscelesteddivaNo ratings yet
- Force per Charge Ratio: Understanding Electric Field StrengthDocument2 pagesForce per Charge Ratio: Understanding Electric Field StrengthLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Tuhin Shubra Manna - Ec501Document7 pagesTuhin Shubra Manna - Ec501amit BeraNo ratings yet
- Electric Field IntensityDocument11 pagesElectric Field IntensityDeeNo ratings yet
- Electric Magnetic Speed of Light C Electric Permittivity Magnetic PermeabilityDocument11 pagesElectric Magnetic Speed of Light C Electric Permittivity Magnetic Permeabilityjonzmy_angelfin29No ratings yet
- 771.lecture Notes 1Document49 pages771.lecture Notes 1fortuneNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument82 pagesElectrostaticsmeritutorNo ratings yet
- Electric Field StrengthDocument13 pagesElectric Field Strengthaidilbackup08No ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS (Page 7 - 13)Document5 pagesELECTROSTATICS (Page 7 - 13)fireNo ratings yet
- 01 (T) - Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument13 pages01 (T) - Electric Charge and Electric Fieldshabbir_ghadialiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields (ELTE 207) : Faculty of EngineeringDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Fields (ELTE 207) : Faculty of EngineeringRyiadh Al-AreibiNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Forces: AP Physics BDocument17 pagesElectric Fields and Forces: AP Physics BBNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument42 pagesElectric FieldMuhammad Kashif IshaqueNo ratings yet
- ElectricfldDocument3 pagesElectricfldAnonymous QvdxO5XTRNo ratings yet
- II PUC Physics Full Book (First Ed.)Document421 pagesII PUC Physics Full Book (First Ed.)Dilini WijesinghNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Electric Fields: Chapter ADocument10 pagesElectric Charges and Electric Fields: Chapter Asiddhartha2862No ratings yet
- Electric Charges FieldsDocument19 pagesElectric Charges FieldsSridevi KamapantulaNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Electrostats PDFDocument29 pagesKvpy Electrostats PDFstudysteps.inNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument25 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceRomil GargNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument63 pagesElectrostaticsSarwar Hosen SimonNo ratings yet
- AP Lec#03Document60 pagesAP Lec#03omerNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics Wk2-2,3Document4 pagesMastering Physics Wk2-2,3Livardy WufiantoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 NotesDocument6 pagesElectric Charges and Fields Class 12 NotesRadhikaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields - Roald K Wangness - Coulombs LawDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Fields - Roald K Wangness - Coulombs LawndaruadyonoNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Summary NotesDocument11 pagesElectric Field Summary NotesVoyce Xavier PehNo ratings yet
- HSSRptr_Splash +2 Physics 2022 FinalDocument52 pagesHSSRptr_Splash +2 Physics 2022 Finalbijijiju8129No ratings yet
- Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering: Potential and Electric Potential EnergyDocument36 pagesAdvanced Electromagnetic Engineering: Potential and Electric Potential EnergyBasir UsmanNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandDocument20 pagesWelcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandDimitris ToubisNo ratings yet
- Gauss's Law and DivergenceDocument11 pagesGauss's Law and DivergenceErxDNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldsDocument19 pagesElectric Fieldsmostafa_m_ibrahim2444No ratings yet
- Electricity Interaction Between Charges: Visual Physics OnlineDocument18 pagesElectricity Interaction Between Charges: Visual Physics OnlineVishal AndaniNo ratings yet
- Electricity Interaction Between Charges: Visual Physics OnlineDocument18 pagesElectricity Interaction Between Charges: Visual Physics OnlineMHLS68No ratings yet
- MST Physics 24 Document Announcements and HomeworkDocument44 pagesMST Physics 24 Document Announcements and HomeworkParanivel KannappanNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential, Potential Energy, Dipole Notes 3Document2 pagesElectric Potential, Potential Energy, Dipole Notes 3plutouecNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic I EELE 3331: Electrostatic FieldsDocument84 pagesElectromagnetic I EELE 3331: Electrostatic Fieldsmae100% (1)
- Group 5 Reporting Physics 1Document39 pagesGroup 5 Reporting Physics 1chloekritzkasilag100% (1)
- Electromagnetics: Varying Electric and Magnetic Fields Are Coupled, Resulting in AnDocument19 pagesElectromagnetics: Varying Electric and Magnetic Fields Are Coupled, Resulting in Anpadmavathy2kNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document54 pagesWeek 2Lyca GunayNo ratings yet
- Ece III Field Theory (10es36) NotesDocument215 pagesEce III Field Theory (10es36) Notesmanjunathitachi50% (2)
- Chapter 12 NotesDocument53 pagesChapter 12 NotesCikgu SyedNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Notes Chapter 1Document9 pagesElectric Charges and Fields Class 12 Notes Chapter 1Sri DharshanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledArnab DasNo ratings yet
- Resonance Class X Vistaar ExpertDocument102 pagesResonance Class X Vistaar ExpertAdarsh Krishnan60% (5)
- XII Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveDocument16 pagesXII Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveKanishk Yadav100% (1)
- 478 - PHS 102 General Physics Pak HabibDocument22 pages478 - PHS 102 General Physics Pak HabibAverus ZamanNo ratings yet
- FullxtDocument22 pagesFullxtashutosh paridaNo ratings yet
- WT EemDocument111 pagesWT Eemrajni kotyalNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge, Additivity of Charges, Conservation and QuDocument2 pagesElectric Charge, Additivity of Charges, Conservation and Qurajstudybri0% (1)
- Electric Charge and Electric Field: 5. Principle of SuperpositionDocument2 pagesElectric Charge and Electric Field: 5. Principle of SuperpositionrajstudybriNo ratings yet
- 5gdfgdffd FFDocument3 pages5gdfgdffd FFrajstudybriNo ratings yet
- Partial FractiovhhnsDocument6 pagesPartial FractiovhhnsrajstudybriNo ratings yet
- Partial FractiovhhnsDocument6 pagesPartial FractiovhhnsrajstudybriNo ratings yet