Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distillation Column
Uploaded by
Neeshä RagnathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Distillation Column
Uploaded by
Neeshä RagnathCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 10 1
Distillation Column External Balance
Lecture 10 2
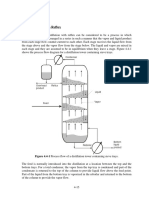
Column Distillation
Typical Specified Variables
Column pressure, P
c
.
Feed flow rate, F.
Feed composition, z.
Feed temperature, T
F
; enthalpy, h
F
; or quality, q = L/F.
Reflux temperature, T
R
; or enthalpy, h
D
.
Reflux ratio, L/D; or distillate composition, x
D
.
Bottoms composition, x
B
.
Lecture 10 3
Column Distillation
Tools for Solution
Equilibrium relationships
Mass balances
Energy balances
Lecture 10 4
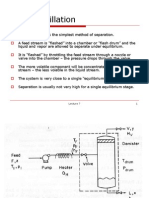
Column Distillation
External Balance
Column
Condenser
Reboiler
Lecture 10 5
Distillation Column External Balance
Lecture 10 6
External Column Balances
Overall
Eq. (4-1)
Component
Eq. (4-2)
Energy
Eq. (4-5)
D B F + =
D B F
Dx Bx Fz + =
B D R C F
Bh Dh Q Q Fh + = + +
Lecture 10 7
Distillate and Bottom Streams
Distillate Stream D
Eq. (4-3)
Bottoms Stream B
Eq. (4-4)
F
x x
x z
D
B D
B F
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
F
x x
z x
D F B
B D
D
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
Lecture 10 8
Condenser Conditions
Partial only part of the incoming vapor stream, V
1
,
is condensed. We have both vapor and liquid streams
at saturated conditions. D is taken as a saturated
vapor and the liquid reflux, L
o
, is returned to the
column as a saturated liquid. Both must be at
saturated conditions since we have equilibrium in
fact the partial condenser is an additional equilibrium
stage. We will look at partial condensers later.
Total all of the incoming vapor stream, V
1
, is
condensed to liquid. We then split the resulting liquid
outlet into the distillate stream, D, and the reflux L
o
,
which is returned to the column. We will consider
only total condensers for now.
Lecture 10 9
Partial Condenser
Lecture 10 10
Distillation Column Total Condenser
Lecture 10 11
Total Condenser Important Note
The important thing to note for a total condenser is
that the mole fraction, y
1
, of the vapor stream from
the top of the column is equal to both the mole
fractions, x
D
and x
o
, of the liquid streams!
y
1
= x
D
= x
o
Eq. (4-7)
The condition of the outlet of the condenser has to be
specified as either a saturated liquid or a subcooled
liquid in order to use the energy balance. The state of
the liquid determines the heat duty of the condenser.
Lecture 10 12
Total Reboiler
Lecture 10 13
Distillation Column Partial Reboiler
Lecture 10 14
Reboiler Conditions
Partial only part of the incoming liquid stream, L, is
vaporized. We have both vapor and liquid streams exiting
the reboiler at saturated conditions. B is taken as a
saturated liquid and the boilup, V
n+1
, is returned to the
column as a saturated vapor. Both streams must be at
saturated conditions since we have equilibrium in the
reboiler in fact the partial reboiler is an additional
equilibrium stage.
Total the incoming liquid stream, L, is split first to obtain
our bottoms stream, B, as a saturated liquid. It has to be a
saturated liquid since it leaves the equilibrium stage at the
bottom of the column. We then reboil all of the remaining
liquid and return it to the column as a vapor stream, V.
Lecture 10 15
Total Reboiler Important Note
The important thing to note for a total reboiler is that
the mole fraction, x
N
, of the liquid stream from the
bottom of the column is equal to the mole fraction, x
B
,
of the bottom liquid stream and that fed to the partial
reboiler!
x
B
= x
N
The condition of the outlet of the reboiler has to be
specified as either a saturated vapor or a superheated
vapor in order to use the energy balance. The state
of the vapor determines the heat duty of the reboiler.
Lecture 10 16
Total-Condenser Mass Balance
Total
Eq. (4-8)
Component
D L V
o 1
+ =
D o o 1 1
Dx x L y V + =
Lecture 10 17
Total Condenser Mass Balance
Lecture 10 18
Reflux Ratio L
o
/D
External reflux ratio
Eq. (4-9)
D
D
L
1 D D
D
L
V
o o
1
|
.
|
\
|
+ = +
|
.
|
\
|
=
Lecture 10 19
Total-Condenser Energy Balance
Eq. (4-10)
Eq. (4-14)
o o D C 1 1
h L Dh Q H V + = +
) H D(h
D
L
1 Q
1 D
o
C
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
) H F(h
x - x
x - z
D
L
1 Q
1 D
B D
B F o
C
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
Lecture 10 20
Partial-Reboiler Energy Balance
Eq. (4-15a)
Eq. (4-15b)
Eq. (4-16)
C F B D R
Q Fh Bh Dh Q + =
) h D(H
D
L
1 Fh Bh Dh Q
D 1
o
F B D R
|
.
|
\
|
+ + + =
) h D(H
D
L
1 Fh Fh
x x
z x
Fh
x x
x z
Q
D 1
o
F B
B D
F D
D
B D
B F
R
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
You might also like
- Plate Contactors & Distillation Tower PresentationDocument61 pagesPlate Contactors & Distillation Tower PresentationAli AmjadNo ratings yet
- MC CabeDocument18 pagesMC CabeSata AjjamNo ratings yet
- Vle & Diff DistDocument14 pagesVle & Diff DistChintan ModiNo ratings yet
- Mc-Cabe Thiele MethodDocument23 pagesMc-Cabe Thiele MethodSyauqi Subri100% (2)
- Types DistillationDocument81 pagesTypes Distillationhet sevakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Reflux Ratio and Column DesignDocument13 pagesLecture 4 Reflux Ratio and Column DesignMohammedTalib100% (1)
- Lecture 07Document20 pagesLecture 07Nagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Two Marks CH 6603 Mass TransferDocument17 pagesTwo Marks CH 6603 Mass Transfersampathkumar100% (1)
- Chap4 4 PDFDocument8 pagesChap4 4 PDFroxetteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg Mass TransferDocument9 pagesChemical Engg Mass TransferSudeshna SahaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument40 pagesTutorialShamsMohd100% (1)
- Flash Distillation GuideDocument29 pagesFlash Distillation GuideAnnanda AdhiPutra MNo ratings yet
- Distillation, Ponchon Savarit, ShahzadDocument30 pagesDistillation, Ponchon Savarit, ShahzadMahad ZahidNo ratings yet
- DistillatnDocument149 pagesDistillatnVinayak ThalangeNo ratings yet
- McCabe-Thiele Method 1Document37 pagesMcCabe-Thiele Method 1HariKrishnaBushi100% (2)
- PartialDocument2 pagesPartialNova RachmadonaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument59 pagesLab ManualmarkNo ratings yet
- Ponchon Savarit MethodDocument34 pagesPonchon Savarit Methodppga410100% (7)
- Distillation Continued: V Moles Per HourDocument12 pagesDistillation Continued: V Moles Per HourronaldNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Separation Process: Distillation ColumnDocument28 pagesOptimization of Separation Process: Distillation ColumnAnonymous rIu5j3yNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Relationship Between P: A OA ADocument19 pagesEquilibrium Relationship Between P: A OA ATarek ChawafNo ratings yet
- Distillation DesignDocument30 pagesDistillation DesignAlonso Flores BelloNo ratings yet
- Multi Component DistillationDocument71 pagesMulti Component DistillationManu Jain83% (6)
- The Intersection of Operating Lines in Fractional DistillationDocument29 pagesThe Intersection of Operating Lines in Fractional DistillationJulian FajariantoNo ratings yet
- Distillation L5Document25 pagesDistillation L5Shiavm PatelNo ratings yet
- 07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolDocument118 pages07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolTakeshi Tanohuye TanohuyeNo ratings yet
- A-Cold Liquid Feed B - Saturated Liquid Feed C - Partially Vaporized Feed D - Saturated Vapor Feed e - Superheated Vapor FeedDocument16 pagesA-Cold Liquid Feed B - Saturated Liquid Feed C - Partially Vaporized Feed D - Saturated Vapor Feed e - Superheated Vapor FeedAmr HassanNo ratings yet
- Total Reflux. in Design Problems, The Desired Separation Is Specified and A Column IsDocument8 pagesTotal Reflux. in Design Problems, The Desired Separation Is Specified and A Column IsmantascitaNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 4 Del Wankat. SolucionarioDocument21 pagesCapitulo 4 Del Wankat. SolucionarioZadky Rios100% (1)
- Distilasi Flash 1Document28 pagesDistilasi Flash 1astriNo ratings yet
- McCabe-Thiele Graphical Method Binary RectificationDocument12 pagesMcCabe-Thiele Graphical Method Binary RectificationSem FilioNo ratings yet
- Distillation: By: In. Nurul Hasyimah Mohd AminDocument60 pagesDistillation: By: In. Nurul Hasyimah Mohd Aminmsa_adonNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationDocument21 pages01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationtimNo ratings yet
- 13.5.5 Column Configuration: Q V D (R +1) Q D R+1) (13.21)Document4 pages13.5.5 Column Configuration: Q V D (R +1) Q D R+1) (13.21)Flor Valera CáceresNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures Volatility Unit Operation Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesSeparating Mixtures Volatility Unit Operation Chemical ReactionmalavurNo ratings yet
- Distillation Problem 4: Fig. 1: Flow Sheet For Distillation ColumnDocument2 pagesDistillation Problem 4: Fig. 1: Flow Sheet For Distillation Columnshan02140% (1)
- Murphy DisDocument19 pagesMurphy DisMurphy MofeNo ratings yet
- Distillation 2Document20 pagesDistillation 2arslanadeelNo ratings yet
- Mass and Energy Balances - Stripping Section and Partial ReboilerDocument45 pagesMass and Energy Balances - Stripping Section and Partial ReboilerShamsMohd100% (1)
- Distillation: Unit Operations (Che 347/ 251)Document27 pagesDistillation: Unit Operations (Che 347/ 251)Amira KormainNo ratings yet
- Flash Distillation: All Rights Reserved. Armando B. Corripio, PHD, Pe. 2013Document29 pagesFlash Distillation: All Rights Reserved. Armando B. Corripio, PHD, Pe. 2013beshoy naseefNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Feed: The Q-LineDocument8 pagesIntroduction of Feed: The Q-LineQuang Huy BùiNo ratings yet
- Experiment: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment: Objectivevikas jainNo ratings yet
- 327083875-Lab-manual-docxDocument58 pages327083875-Lab-manual-docxAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Flash Drum Theory ExplainedDocument6 pagesFlash Drum Theory ExplainedPrasenjit NathNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Design (External Balances-Binary Mixtures)Document4 pagesDistillation Column Design (External Balances-Binary Mixtures)Sata AjjamNo ratings yet
- L IJIIIDocument8 pagesL IJIIIBambang RiantoNo ratings yet
- Pap (Design of Distillation Column)Document26 pagesPap (Design of Distillation Column)MambaulkNo ratings yet
- 221 06Document25 pages221 06Fransiscus Leo ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit Operation Ii: Operations, Prentice Hall, 1993Document40 pagesUnit Operation Ii: Operations, Prentice Hall, 1993esiri aluyaNo ratings yet
- Steam Tables: DR - Khaled S. Al-ZahraniDocument13 pagesSteam Tables: DR - Khaled S. Al-ZahraniAli RaufNo ratings yet
- Fractionating Column Heat and Mass BalancesDocument5 pagesFractionating Column Heat and Mass BalancesDaniel ObasNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada: III Year B. Tech. Petrochemical Engineering II SemDocument37 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada: III Year B. Tech. Petrochemical Engineering II SemHashmi AshmalNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument124 pagesDistillationasharab70100% (1)
- Distillation ColumnDocument4 pagesDistillation ColumnSyeda Khaliqa HamidNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Plates Calculation by McCabe-Thiele MethodDocument4 pagesTheoretical Plates Calculation by McCabe-Thiele Methodmohammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)