Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Healthcare Energy WP Tac 9
Healthcare Energy WP Tac 9
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Healthcare Energy WP Tac 9
Healthcare Energy WP Tac 9
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecCopyright:
Available Formats
White Paper
Most important, integrating building management Ongoing services Proactive maintenance Remote monitoring Carbon reporting Long-term energy planning Executive reporting Training Building optimization All of these features and capabilities add up to an integrated solution that enables hospitals to manage several different subsystems as a single cohesive network, including those from thirdparty providers. This smart grid approach can generate comprehensive energy savings across the enterprise. In addition, it is possible to better control and optimize overall savings over time with an intelligent metering and centralized energy monitoring system. with your hospitals IT, security, and building systems, offers greater cost savings and allows facility managers to see real-time energy use trends and building alarms, and avoid costly reactive maintenance. For example, a smart grid enables organizations to link peak energy costs to load shedding and/or the building management system. There are many other significant cost-saving scenarios available to hospitals. For example, by integrating bed-flow management software to patient room control systems, you can set lights to turn off and lower room temperatures automatically for patient rooms that are not in use. Another example: By integrating with the peri-operative management software systems, ventilation systems can be set to operate in a reduced mode when operating theatres are not in use, yet still maintain the minimum required air changes, as well as temperature and humidity requirements.
Energy Efficiency Projects Ensure Healthy Financial Performance for Healthcare Facilities | 9
You might also like
- Unit-5 CCDocument22 pagesUnit-5 CCSonga Sowjanya100% (4)
- RAPIDPoint 500 Operator S Guide - English - Rev C DXDCM 09008b83808b103e-1573180329705Document498 pagesRAPIDPoint 500 Operator S Guide - English - Rev C DXDCM 09008b83808b103e-1573180329705Олександр100% (1)
- Hawker 8TS Battery Charger - Technical Programing HandbookDocument15 pagesHawker 8TS Battery Charger - Technical Programing HandbookDaniel Aguirre100% (4)
- Meter Data Management SystemDocument12 pagesMeter Data Management SystemPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- How To Fix A Broken Heart - Guy WinchDocument2 pagesHow To Fix A Broken Heart - Guy Winchjhonrydc11050% (2)
- Syllabus CHM136 Summer 2020 (Updated)Document8 pagesSyllabus CHM136 Summer 2020 (Updated)georgeNo ratings yet
- CCMS Intelligent Building SystemsDocument7 pagesCCMS Intelligent Building SystemsSneha PeriwalNo ratings yet
- Building Automation OverviewDocument5 pagesBuilding Automation OverviewguhanmNo ratings yet
- Benefits: Building ManagersDocument2 pagesBenefits: Building Managersrasika.ouNo ratings yet
- Power MonitoringDocument2 pagesPower MonitoringKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 145 A Guide To Access Control SustainabilityDocument7 pages145 A Guide To Access Control SustainabilitynmsNo ratings yet
- Energy Management SystemDocument14 pagesEnergy Management SystemAlexis LlarenaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Buildings Vs Automated BuildingsDocument15 pagesIntelligent Buildings Vs Automated Buildingstannu singhNo ratings yet
- BMS-Automation & Energy ManagementDocument7 pagesBMS-Automation & Energy ManagementAtshayaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines - CCMS - EMSDDocument31 pagesGuidelines - CCMS - EMSDPaul KwongNo ratings yet
- ROI and FinanacialsDocument8 pagesROI and FinanacialsEduardo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 75F Smart Buildings EbookDocument22 pages75F Smart Buildings EbookRajiv Ranjan100% (2)
- Energy Management Systems (EMS) : ObjectivesDocument11 pagesEnergy Management Systems (EMS) : ObjectivesmsmgectNo ratings yet
- Intelligent InteriorsDocument9 pagesIntelligent InteriorsMaria IqbalNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Solutions For Manufacturing Industry PDFDocument7 pagesEnergy Management Solutions For Manufacturing Industry PDFco2bin100% (1)
- Building Energy Management SystemsDocument7 pagesBuilding Energy Management SystemsManvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- School of Graduate StudyDocument2 pagesSchool of Graduate StudywswrNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument8 pagesInternet of ThingsMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Energy Management System 11556 E9ey9X5Document13 pagesEnergy Management System 11556 E9ey9X5janhaviNo ratings yet
- Facity Management AssignmentDocument12 pagesFacity Management Assignmentnorah wanzaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Energy WP Tac 8Document1 pageHealthcare Energy WP Tac 8sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Week - 12 NotesDocument53 pagesWeek - 12 Notescharusri74No ratings yet
- 1 Understanding Energy A Requirements Analysis For Cost Effective Energy Metering System in Commercial Buildings PDFDocument1 page1 Understanding Energy A Requirements Analysis For Cost Effective Energy Metering System in Commercial Buildings PDFzaheeruddin_mohdNo ratings yet
- Smart BuildingDocument2 pagesSmart BuildingKrisman SinagaNo ratings yet
- A Brief About Building Management System?Document4 pagesA Brief About Building Management System?mahmoudramadan007No ratings yet
- Healthcare Energy WP Tac 6Document1 pageHealthcare Energy WP Tac 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Building Automated SystemsDocument10 pagesBuilding Automated SystemsSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Reliable, Sustainable, and Efficient: TÜV-certified Power Monitoring System in Accordance With ISO 50001Document10 pagesReliable, Sustainable, and Efficient: TÜV-certified Power Monitoring System in Accordance With ISO 50001cc_bauNo ratings yet
- Role of Energy Manager in Manufacturing IndustryDocument2 pagesRole of Energy Manager in Manufacturing IndustryBalu Pakhare100% (2)
- IEMTCModule7 FinalDocument34 pagesIEMTCModule7 FinaljokishNo ratings yet
- Building AutomationDocument19 pagesBuilding AutomationvandniNo ratings yet
- Abb Data CenterDocument13 pagesAbb Data CenterIhechiluru AnyaharaNo ratings yet
- ASMA BuildingDocument5 pagesASMA BuildingmicrefeeNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Synopsis 1 - CEngDocument4 pagesTechnical Report Synopsis 1 - CEngMerhan Fouda100% (1)
- Order Costing Systems Are Vital For Analysis and Control of PlantDocument1 pageOrder Costing Systems Are Vital For Analysis and Control of Plantكريم محمدNo ratings yet
- Making Your Energy Productive: Plantstruxure Energy Management SolutionsDocument16 pagesMaking Your Energy Productive: Plantstruxure Energy Management SolutionsmsohaibkhalidNo ratings yet
- Innovative Power Distribution For Hospitals PDFDocument26 pagesInnovative Power Distribution For Hospitals PDFQuophi Click LyfttedNo ratings yet
- Energy Management System: Software For EMSDocument5 pagesEnergy Management System: Software For EMSRicha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Truly Smart MetersDocument5 pagesTruly Smart MetersNico DishanthNo ratings yet
- Tips Energy Audit Operation & MaintenanceDocument17 pagesTips Energy Audit Operation & MaintenancePradip LayekNo ratings yet
- Smart Power Management Reduces Cost and Increases FlexibilityDocument4 pagesSmart Power Management Reduces Cost and Increases FlexibilityEmanuele EgidioNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving Opportunities: - Remote Monitoring and Control Improve Data Availability and Accessibility, WhilstDocument11 pagesEnergy Saving Opportunities: - Remote Monitoring and Control Improve Data Availability and Accessibility, Whilstأحمد صابرNo ratings yet
- Energy System EconomizationDocument17 pagesEnergy System EconomizationmsaadullahNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit and ManagementDocument10 pagesEnergy Audit and ManagementVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Power Usage BenefitsDocument2 pagesPower Usage BenefitsTendai KapantengaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument67 pagesUntitledRonn ManaloNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance Monitoring PDFDocument6 pagesEnergy Performance Monitoring PDFVirnia PatziNo ratings yet
- WP155002EN Optimizing Rack LRDocument4 pagesWP155002EN Optimizing Rack LRgbaludbNo ratings yet
- Network Management Software For A Small Health Institution: Student NameDocument16 pagesNetwork Management Software For A Small Health Institution: Student NameNaveed Akhtar BalochNo ratings yet
- PowerOn Fusion PDFDocument16 pagesPowerOn Fusion PDFJagan VanamaNo ratings yet
- Ee Computer Application: EecompDocument13 pagesEe Computer Application: EecompJas PayaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Energy Management SystemDocument3 pagesBenefits of Energy Management SystemHaidar Ali ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Brochure Meet New Standard BMS Colleges UniversitiesDocument8 pagesBrochure Meet New Standard BMS Colleges UniversitiesCarlos FerreiraNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document73 pagesCH 5Universal EmailNo ratings yet
- PROJECTDocument12 pagesPROJECTpraneethNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Building Automation SystemsDocument18 pagesIntelligent Building Automation Systemsnandu shahNo ratings yet
- Building Analytics BrochureDocument8 pagesBuilding Analytics BrochureVinzoKei100% (1)
- SMART GRID Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSMART GRID Seminar ReportSalil Kumar Gautam56% (9)
- Aer 534 QCDocument48 pagesAer 534 QCsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Industrial and Logistics Light GuideDocument14 pagesIndustrial and Logistics Light Guidesunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case StudyDocument4 pagesLED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case Studysunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 5Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 5sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- NOWA Price ListDocument2 pagesNOWA Price Listsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Stylus Plus Pricelist 2012-13Document2 pagesStylus Plus Pricelist 2012-13sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- H 3-Phase Online Ups Technical SpecificationDocument9 pagesH 3-Phase Online Ups Technical Specificationsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 11Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 11sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
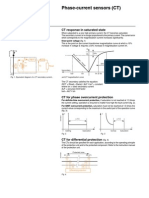
- Phase-Current Sensors (CT)Document1 pagePhase-Current Sensors (CT)sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
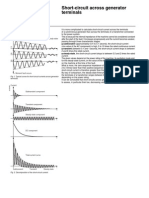
- Short-Circuit Across Generator TerminalsDocument1 pageShort-Circuit Across Generator Terminalssunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 24Document1 pageCg0021en 24sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 19Document1 pageCg0021en 19sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 18Document1 pageCg0021en 18sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- ICOT - Brochure 2022Document32 pagesICOT - Brochure 2022Robson CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Thself Activity 12BDocument1 pageThself Activity 12BPrincess Mae QuezonNo ratings yet
- Resume of Basic Cost - Management ConceptDocument4 pagesResume of Basic Cost - Management ConceptismailkunNo ratings yet
- Viona Rosalita Research ProposalDocument17 pagesViona Rosalita Research ProposalRenaldi Dwi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-03 Organization of Maintenance ForceDocument34 pagesLecture-03 Organization of Maintenance ForceMohammad ShafiNo ratings yet
- Mettrack Users ManualDocument50 pagesMettrack Users ManualNANDO7695No ratings yet
- KWM - Specsheet-1 KWM9612+Document2 pagesKWM - Specsheet-1 KWM9612+mr. adamNo ratings yet
- Atos - Modular Relief Valve - HMP HM KMDocument4 pagesAtos - Modular Relief Valve - HMP HM KMClaudecir PereiraNo ratings yet
- (Yves Meyer, Ronald Coifman) Wavelets Calderón-ZDocument335 pages(Yves Meyer, Ronald Coifman) Wavelets Calderón-Zcharlyshaka1No ratings yet
- From Research To Revenue: Module 3: Preparation of Patent Search & Analysis ReportDocument34 pagesFrom Research To Revenue: Module 3: Preparation of Patent Search & Analysis ReportBanty MehtaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3 TPKDocument2 pagesKelompok 3 TPKMia YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Dhaka University of Engineering and Technology (DUET), Gazipur Department of Textile EngineeringDocument48 pagesDhaka University of Engineering and Technology (DUET), Gazipur Department of Textile EngineeringAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- cNT1ZwHyTOid5IhGX3dU - Orica - WebGen 4pp-A4-Brochure - WEBDocument4 pagescNT1ZwHyTOid5IhGX3dU - Orica - WebGen 4pp-A4-Brochure - WEBJuan MedinaNo ratings yet
- WITHOUT SYLLABUS (Updated)Document5 pagesWITHOUT SYLLABUS (Updated)Shiela FalculanNo ratings yet
- Heliocentric AstrologyDocument10 pagesHeliocentric AstrologyMichael ErlewineNo ratings yet
- Edition 13 Electric Power Distribution in Data Centres Using L-PDUsDocument14 pagesEdition 13 Electric Power Distribution in Data Centres Using L-PDUscesarchiletNo ratings yet
- Resume DST Ritunesh KumarDocument2 pagesResume DST Ritunesh KumarRitunesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit: Diagram Showing Configuration and Approximate LengthsDocument6 pagesPacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit: Diagram Showing Configuration and Approximate LengthsedosviracNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Solutions: Smart Office - Energy Management - LED Lighting Solution - Infrastructure ManagementDocument9 pagesEnterprise Solutions: Smart Office - Energy Management - LED Lighting Solution - Infrastructure ManagementpradeeshNo ratings yet
- How Batteries WorkDocument8 pagesHow Batteries WorkJagdeep S.0% (1)
- WT.025.055.000.IE - ps.0714 Evoqua ChlorinatorDocument8 pagesWT.025.055.000.IE - ps.0714 Evoqua ChlorinatorNguyễn Đăng QuýNo ratings yet
- Counting Ones, Tens and Hundreds: Mathematics Week 2, Day 1Document61 pagesCounting Ones, Tens and Hundreds: Mathematics Week 2, Day 1Jester MabutiNo ratings yet
- 11 Inlis-II (5sag)Document93 pages11 Inlis-II (5sag)Serdar KurbanovNo ratings yet
- Perfecting Your Pitch: The Garage Ten Slide DeckDocument8 pagesPerfecting Your Pitch: The Garage Ten Slide DeckYamil Sejas SuarezNo ratings yet
- Doppler/GPS Navigation Set: AN/ASN-128B/CDocument2 pagesDoppler/GPS Navigation Set: AN/ASN-128B/CTenshiJibrilNo ratings yet
- Midterm PrepDocument2 pagesMidterm PrepSAKHAWAT HOSSAIN KHAN MDNo ratings yet