Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cg0021en 19
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cg0021en 19
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecCopyright:
Available Formats
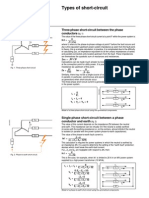
Types of short-circuit
DE57221EN
Zsc
U
Zsc
Ik2
Zsc
ZN
E
I 1 = ----------------------------Z1 + Z2 + Z
Fig. 1. Two-phase short-circuit clear of earth.
Two-phase short-circuit between phase conductors (fig.1)
The value of the two-phase short-circuit current at a point within the power system is:
U
Ik2 = -----------------Z1 + Z2
In a power system supplied by a transformer (fault far from the sources), the value of
the two-phase short-circuit current at a point within the power system is:
U
Ik2 = -------------------2 Zsc
The two-phase short-circuit current is weaker than three-phase short-circuit current,
by a ratio of 3/2, i.e. approximately 87%.
If the fault occurs close to a generator (Z2 Z1), the current can be higher
than in a three-phase fault.
E
I 2 = ----------------------------Z1 + Z2 + Z
DE55224EN
Short-circuit currents
V1
Z1
V2
Z2
I0 = 0
E ( Z2 + Z )
V 1 = ---------------------------Z1 + Z2 + Z
V0
Z0
E Z2
V 2 = ---------------------------Z1 + Z2 + Z
I1
I2
I0
V0 = 0
Zsc
Two-phase short-circuit between two phase
conductors and earth (fig. 2)
Zsc
For a solid short-circuit (fault far from the sources), the value of the two-phaseto-earth short-circuit is:
3U
IkE2E = --------------------------( Z 1 + 2Z 0 )
U
Ik2E
Zsc
IkE2E
ZN
Fig. 2. Two-phase-to-earth short-circuit.
E ( Z 2 + Z 0 + 3Z )
I 1 = -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Z 1 Z 2 + ( 3Z + Z 0 ) ( Z 1 + Z 2 )
DE55225EN
DE57222EN
Model of a two-phase short-circuit using the symmetrical components.
V1
Z1
E ( Z 0 + 3Z )
I 2 = -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Z 1 Z 2 + ( 3Z + Z 0 ) ( Z 1 + Z 2 )
V2
Z2
E Z2
I 0 = -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Z 1 Z 2 + ( 3Z + Z 0 ) ( Z 1 + Z 2 )
V0
Z0
I1
I2
3Z
I0
Model of a two-phase-to-earth short-circuit using the symmetrical components.
15
You might also like
- Cg0021en 18Document1 pageCg0021en 18sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Electro Risk 2 MaiDocument7 pagesElectro Risk 2 MaiKarthikNo ratings yet
- PTC Ee Epse 2.2 ND MP - MCDXDocument10 pagesPTC Ee Epse 2.2 ND MP - MCDXAbhay ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- IV - Passive Filters (Full Ans)Document25 pagesIV - Passive Filters (Full Ans)rraaaNo ratings yet
- Problem 20.28: Acc 2 AccDocument1 pageProblem 20.28: Acc 2 Accarnabrc123No ratings yet
- Microwave Circuit Design: ECE 5250/4250 Lecture Notes Fall 2009Document62 pagesMicrowave Circuit Design: ECE 5250/4250 Lecture Notes Fall 2009Badai TimurNo ratings yet
- Zig Zag Transf - 1Document24 pagesZig Zag Transf - 1Razvan Mares100% (2)
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 28, 159-172, 2012Document14 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 28, 159-172, 2012puriaNo ratings yet
- R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov "RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications" 2 Edition Figures For Chapter 2Document38 pagesR. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov "RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications" 2 Edition Figures For Chapter 2ECEOCETNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document30 pagesChapter 13Girish KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Passive Devices: (3 Port Network)Document39 pagesPassive Devices: (3 Port Network)AzaharuddinMohdNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Wire Dipole AntennaDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Wire Dipole AntennaIncorrigible Procrastinator AbhishekNo ratings yet
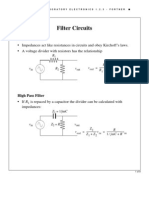
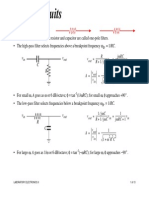
- Filter CircuitsDocument8 pagesFilter CircuitsAmartuvshin_854No ratings yet
- Dynamic Modelling & Controller Design For Z-Source DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesDynamic Modelling & Controller Design For Z-Source DC-DC ConverterEditor IJSETNo ratings yet
- System and ControlsDocument8 pagesSystem and ControlsMak Wai YongNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Single-Stub Matching: - Matching Using TL - Open or Shorted Stub (TL)Document21 pages5.2 Single-Stub Matching: - Matching Using TL - Open or Shorted Stub (TL)Eduardo pfNo ratings yet
- Passive Devices: (3 Port Network)Document39 pagesPassive Devices: (3 Port Network)Sandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin SultanaDocument13 pagesElectrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin SultanaWarishaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Parameters of Two Parallel Wires: Appendix DDocument4 pagesTransmission Line Parameters of Two Parallel Wires: Appendix DAnjireddy ThatiparthyNo ratings yet
- EC303Document37 pagesEC303api-3853441No ratings yet
- C-POWER ACB For DC ApplicationDocument4 pagesC-POWER ACB For DC ApplicationAnkan PalNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: X A X AADocument14 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: X A X AAGauravArjariaNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesDocument25 pagesMagnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesKarthik Thirumala100% (1)
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesDocument25 pagesMagnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesNitin MarwahNo ratings yet
- Inverter 2002Document54 pagesInverter 2002Sandro MoreroNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Simulation of LLC Resonant DC-DC Converter For Photovoltaic ApplicationsDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Simulation of LLC Resonant DC-DC Converter For Photovoltaic ApplicationsГеорги ТерзийскиNo ratings yet
- Power Systems PDFDocument21 pagesPower Systems PDFPankajSinghBhati100% (1)
- Magnetically Coupled Networks: Learning GoalsDocument26 pagesMagnetically Coupled Networks: Learning GoalsTegar Ari Satria KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DC To AC Conversion (INVERTER)Document46 pagesChapter 4 DC To AC Conversion (INVERTER)xuanbac198467% (3)
- AC CircuitsmoduleDocument22 pagesAC Circuitsmodulejtapesana1850No ratings yet
- LNA Design ProjectDocument18 pagesLNA Design ProjectCrystal ChenNo ratings yet
- Electrical CouplingDocument23 pagesElectrical CouplingDrezz BobyanNo ratings yet
- EC303Document34 pagesEC303api-3853441No ratings yet
- Filter CircuitDocument13 pagesFilter CircuitNguyen TranNo ratings yet
- Zs CalculationDocument3 pagesZs CalculationRaj KumaranNo ratings yet
- Abrahams Lab9Document7 pagesAbrahams Lab9api-274724891No ratings yet
- 3 Current SRCDocument10 pages3 Current SRCmelwyn_thomasNo ratings yet
- Eecs 2020 59Document37 pagesEecs 2020 59Liviu BadeaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper of Engineering Service Examination 2010 Electrical Engineering Paper-IDocument22 pagesQuestion Paper of Engineering Service Examination 2010 Electrical Engineering Paper-ISantosh SandyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical ModellingDocument84 pagesChapter 2 - Mathematical ModellingDyrul SyaznanNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument21 pagesPower Systemssamg27100% (1)
- PG 000159Document9 pagesPG 000159voNo ratings yet
- Longs Negative WattsDocument17 pagesLongs Negative Wattswalterpereiro100% (1)
- 6-An Unequal Dual-Frequency Wilkinson Power Divider WithDocument19 pages6-An Unequal Dual-Frequency Wilkinson Power Divider WithpuriaNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor PDFDocument26 pagesInduction Motor PDFishak789100% (1)
- Quasi Z-Source Based Voltage Control in Distributed Power GenerationDocument6 pagesQuasi Z-Source Based Voltage Control in Distributed Power GenerationA'Platinum EngNo ratings yet
- Critical Slip and Characteristics of Induction Motor For Borehole Investigating DevicesDocument4 pagesCritical Slip and Characteristics of Induction Motor For Borehole Investigating DevicesAbdullah BokhariNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross Baldicka_r_vijayanand6550No ratings yet
- Ch-2 MCQ'SDocument11 pagesCh-2 MCQ'SKeval DudakiyaNo ratings yet
- Frequecny Response of Lag NetworkDocument4 pagesFrequecny Response of Lag NetworkAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsVishavjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case StudyDocument4 pagesLED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case Studysunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Approved Plan 406173Document1 pageApproved Plan 406173sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Aer 534 QCDocument48 pagesAer 534 QCsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 10Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 10sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Ene BG 4Document14 pagesEne BG 4sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Industrial and Logistics Light GuideDocument14 pagesIndustrial and Logistics Light Guidesunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 8Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 8sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 6Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 4Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 4sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 7Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 7sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 5Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 5sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 6Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 2Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 3Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 3sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 2Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 7Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 7sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4sunny_nsecNo ratings yet