Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table
Table
Uploaded by
Rohan JindalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table
Table
Uploaded by
Rohan JindalCopyright:
Available Formats
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT GUIDE
PRE-FORMULATION - TABLETS
Introduction Guidelines for the development of a ANDA product for the US market, Note: some tests or procedures may be unnecessary. The order of performing the various stages may change depending on the product under development. These guidelines may be modified for other geographic zones. Development Stage Scope of Product Development
Stage 1
Literature Research FDA - FOI On-line search
Literature Search
USP BP Pharm. Eur, PDR, Martindale, Merck, Florey, Vidal Summary Basis of Approval
computerized Electronic Data Base (articles and publication on test methods, Dissolution synthesis procedures, drug impurities, pharmacokinetics and dynamics) Evaluation of Biostudy parameters, Dissolution methods. FDA CDER Patent evaluation Orange Guide + FDA CDER WWW Patent Consultant
Stage 2
Sourcing for Active Raw Material
Active
Sourcing
International Suppliers US, European, Asian, e.g. (ACIC-Canada) (AllChem-UK) (Lek-Czech), (Esteves; Moehs; Uquifa-Spain); (Biopharma, S.I.M, Midy-Italy) (Chemcaps, Reddy; Tricon-India); (Federa-Brussels) - Review suppliers catalogues & data critically. Request samples and C of A and Specifications Evaluate at least two suppliers fully.
Potential Suppliers List
Stage
Evaluate Actives
Active
Evaluation
Potential Evaluate at least two to three potential active suppliers DMF availability Compliance with USP monograph Impurity profile and stability Potential Polymorphic forms Commitment for physical specifications Statement of non-patent infringement
Stage
Active
Purchasing
Purchase (Potential) Evaluate at least two potential active material suppliers for Active Material approved supplier status
Stage
Active
Testing
Testing of Active Chemical testing by the R&D analytical lab as per Material sample a. Pharmacopoeia monograph (if present) b. Pharmacopoeia Forum (if available) c. In-house method (based on manufacturer) d. Supplier's test methods and specifications
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 15
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
PRE-FORMULATION
Development Stage Scope of Product Development Innovator's Product Purchasing
Stage
DRUG PRODUCT Innovator Samples
Purchase at least 3 different lots in smallest and largest pack size for each product strength
Stage
Innovator's
Product Testing
Innovator Testing
Evaluate physical parameters:tablet shape, tablet color, code for punch embossing, pack sizes containers materials, closure types; cotton and desiccants. Physical testing Weight; Thickness; Hardness; LOD; Friability; Disintegration: Evaluation of tablet punch; size; score; embossing and shape
Innovator Physical Testing
Evaluation of Innovator Summary Formula in PDR; International PDRs (Italian, French, formula ingredients Swiss) and Innovators product's insert (obtain latest FOI -FDA) Perform actual analytical testing on innovator's product. Microscopic observation Particle/crystal information on Particle size Crystal shape, habit, Differentiation on the presence of specific excipients can be verified from microscopic observation. E.g., Cross-linked cellulose's Starch and Avicel have a specific shapes and morphology and maybe easily detected. Review FDA CDER Home page for listing and Biostudy parameters USP monograph and FDA method - (where present) Dissolution; 12 unit Dissolution Profile.
Evaluation of Biostudy parameters Dissolution profile
Stage
Bulk
Active Testing
FIRST BATCH FROM APPROVED SUPPLIER Full Physical characterization
Physical characterization of bulk batch Polymorphism B.E.T. Particle size distribution (& method development) Bulk density; Microscopic observation Chemical characterization Assay Stressed Analysis Degradants (Expected) Impurity profile Optical rotation Enantiomeric purity O.V.I. Testing
FULL CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 16
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
DEVELOPMENT BATCHES
Development Stage
Scope of Product Development Excipients
using DSC methods and stability
Stage
Evaluation of formuExcipient compatibility lation with suitable assessment excipients
Stage
10
Container Closure System
Choice of container-closure-liner system including: material composition, type of thermoplastic resin and resin pigments, manufacturers and suppliers, liners and seals used by closure manufacturer, cotton and desiccants. manufacturer's DMF numbers for all component parts Letters of Access for regulatory authorities to view DMF dossiers
Evaluation of suitable Container-Closure System
Stage
11
Manufacturing Process
Wet granulation (aqueous or non aqueous) high shear mixing / low shear mixing FBD spray procedure), or Dry mixing, dry granulation and/'or Slugging Determination of order of mixing Determination of pre-mixing (in Granulator) Wet Granulation Determination of fluid addition (if relevant) Dry Granulation Determination of granulation time (chopper I & II) Determination of torque end-point value Slugging and Dry Determination of Drying parameters Granulation Determination of LOD limits Determination of testing temperature for checking LOD limits (State machine used e.g. Mettler, Computrac). Flow properties, GRANULATION Density, Physical Properties of Particle-size distribution Granulate Compressibility Compression Weight, Hardness, Physical Properties of Thickness, Friability Compressed Tablets Disintegration Dissolution Final Formula Assessment of Final Master Formula and accelerated 1-3 month Established stability profile. EVALUATION SUITABLE MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
Stage
12
Bulk Active Purchased
Ordering of Active material for Process Qualification (PQ) and Pivotal Batch(es). On approval of final formula, order sufficient material for the PQ (2) and Pivotal Lots (sufficient for all strengths and batch sizes). NB: Never mix batch numbers in PQ and Pivotal Lots.
Active material Bulk purchase
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 17
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
FULL LABORATORY EVALUATION
Development Scope of Product Development Analytical Evaluation
of Dissolution - in USP medium (Multipoint profiles) and other relevant media versus Innovator's product U of C-for low active concentrations. Refer to USP requirements for uniformity of content vs. uniformity of dosage units. Validation of analytical package i.e. Assay; Dissolution ; Content Uniformity completed prior to Process Qualification
Stage
13
Analytical testing tablets/Caplets
PROCESS OPTIMIZATION
Development Scope of Product Development Process Optimization
Stage
14
GRANULATION OPTIMIZATION
Effect of granulation parameters Granulation time Speed of choppers (I & II) or mixer blades Solvent addition rate and overall amount Ratio of intra-granulate Disintegrant and binders agents Screen size for milling (e.g. 0.6 or 0.8mm) Adjusting mill screen size up or down to fine tune hardness Evaluation of optimized granulate and tablet attributes FB Drying temperature versus target LOD and range limits and the effect on granulate and tablet properties (flow, capping, sticking).
DRYING
BLENDING
Blending times Lubricant Split into two parts (pre-blending and final blending) The effect on Content Uniformity, Granule lubrication and Dissolution profile. Evaluation of unit dose sampling vs. Content Uniformity
COMPRESSION
Effect of hardness on tablet properties (aging, dissolution, friability). Evaluation of Hardness Range Limits Evaluation of stability results of optimized mfg. process Prepare PO Report. This Process Optimization Report forms part of the product Development Report
PROCESS OPTIMIZATION
REPORT
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 18
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
ESTABLISHING AND INVITRO INVIVO CORRELATION
Development Scope of Product Development Analytical Evaluation
Dissolution - in USP medium (Multipoint profiles) and other relevant media versus Innovator's product. Perform IVIV Bioavailability Study (where relevant) Establish a Level A or C correlation without adjusting dissolution parameters and time scale Adjust the dissolution parameters or time scale to achieve a Level A or C correlation (adjust only if necessary)
Stage
15
IVIV Correlation
SCALE
UP
Scope of Product Development
Development
Stage
Scale-up
16
SCALE
UP
Scale-up batch may be
Scale-up lot prepared if larger batch size scale up problems anticipated. Process Qualification batch and evaluated as a single batch.
Scale-up Report
The preparation of a Scale-up Report. The Scale-up report forms part of the overall Development Report
PROCESS QUALIFICATION
Development Stage Scope of Product Development Process Qualification
Stage
17
The process qualification batch is manufactured in order to detect any problems that may arise during the manufacture of production size batches, allowing a solution prior the manufacture of the pivotal demonstration batch. Scale-up to the pivotal batch size or 70% of the pivotal batch may be combined with qualifying the manufacturing process At this stage full manufacturing documentation is prepared alone standard procedures.
PRODUCTION FACILITIES
Process Qualification batch should be compressed in a production (or production type with same principle and operation) tabletting machine Size of pivotal and marketing batch confirmed (NLT 100 000 net/ packed at target parameters or 10% of proposed market batch).
BATCH DOCUMENTATION
Preparation of Master Formula and Processing Instructions Discussion of formula, manufacturing process and control parameters with production personnel and QA Staff
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 19
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
PROCESS QUALIFICATION
Development Stage Scope of Product Development Process Qualification
Stage
17 (Cont)
FINAL REVIEW and Review of proposed formula, manufacturing process and control AUTHORIZATION parameters with production personnel and QA Staff with authorization signatures (RD; QA-QC; RA; and Production) PROTOCOL KEY STEPS OPERATING CONDITIONS P.Q. REPORT PQ. protocol prepared Critical manufacturing steps designated and sampling and testing parameters specified. Presence of production and control personnel during PQ manufacture Upon completion prepare Process Qualification Report. This P-Q report forms part of the overall Development Report
PIVOTAL BATCH
Development Scope of Product Development Pivotal Production
Pivotal batch MUST be compressed in a production tabletting machine (or production type with same principle and operation) Preparation of FINAL Master Formula and Processing Instructions Review of FINAL formula, manufacturing process and control parameters with production personnel and QA Staff. Pivotal authorization signatures (RD; QA-QC; RA; and Production) attached. Operation of production and control personnel during Pivotal manufacture, aided by development team. The preparation of a Pivotal Report. This pivotal report forms part of the overall Development Report.
Stage
18
PRODUCTION FACILITIES BATCH DOCUMENTATION REVIEW and AUTHORIZATION
OPERATING CONDITIONS REPORT
BIOEQUIVALENT STUDY
Stage Scope of Product Development
Stage 19
BIOSTUDY Fasted BIOSTUDY [Food Effect] HIGHEST DOSAGE One or two studies WAIVER CONDITIONS SIMILARITY TESTING
BIOSTUDY Evaluation
Perform Fasted / Food Effect Biostudy on Pivotal Lot Samples Perform Food Effect Biostudy on Pivotal Lot Samples (See food effect guidelines, where appropriate) Biostudy generally performed on highest strength of product Fasted AND Food Effect Study may be required For multiple strength products Invitro dissolution testing conducted in three different pH media on lower dosage forms Perform Similarity Test [F2 Test] on dissolution results.
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 20
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
PRE-SUBMISSION AUDITING
Development Stage Scope of Product Development ANDA Pre-Submission Auditing
Audit all raw data supporting Development Report Audit Plant and Laboratory Documentation as per ANDA Review SOP System and Update level Review cGMP of Manufacturing Processes Evaluate and develop a IVIV correlation (Level A where possible.) Product Process Validation Protocol complete and signed
Stage 20
Development Report ANDA Regulatory File SOPs cGMP Biostudy Report Validation Protocol
ANDA SUBMISSION
Development Stage Scope of Product Development ANDA Submission
Submit ANDA structured as Part Two of this Handbook (9 Copies -as per Color system) (1 Field Copy)
Stage
21
ANDA Submission
VALIDATION BATCHES
Development Stage Scope of Product Development Process Validation
Process Validation Protocol for 3 consecutive marketing lots Process Validation of 3 consecutive marketing lots Process Validation Report Show intra-batch similarity Show inter-batch similarity between Biobatch (Pivotal) and the Commercial Validation Lots
Stage
Protocol
22
Execute validation Report Similarity Bio-Validation Similarity
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 21
Generic Development
ORAL TABLETS
DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 2
COMMERCIAL RE-VALIDATION
DUE TO MAJOR CHANGE
Development Stage Scope of Product Development Process Re-validation
Revalidate procedure with new formula process or equipment with a different operating principle
Stage
23
Formula Change Process Change Equipment Change Minor change
Follow SUPAC Rules Level I II or III
IMPORTANT NOTE ON DEVELOPMENT
Developers are encouraged to develop IVIVC for IR dosage forms, where applicable
to the BCS, (Biopharmaceutical Classification System) in the expectation that the information will be useful in establishing appropriate dissolution specifications and thus permit certain post approval formulation and manufacturing changes to be effected, - without additional bioequivalence studies.
The
objective of developing an IVIVC is to establish a predictive mathematical model describing the relationship between invitro dissolution settings and the actual invivo drug-plasma parameters found, (such as AUC, Cmax, Tmax).
The
invitro dissolution settings are adjusted (via media, pH agitation) until a I : I correlation is achieved (Level A) or a single dissolution point and a plasma parameter is shown to correlate (Level C). When more than one point correlates a multiple Level C is obtained - which may possibly be upgraded to a Level A with additional development work.
This
matching of dissolution settings with plasma levels, that are derived from a specific IR formula and its corresponding manufacturing process, is in fact simply an arbitrary set of values that establish the so called 'predictive mathematical model'.
An
IVIVC should be evaluated to demonstrate that predictability of the invivo performance of the drug product (i.e. derived from the plasma parameters) from its in vitro dissolution characteristics (e.g. equipment settings / and manufacturing changes) is maintained over the product's dissolution profile
Handbook of Pharmaceutical
Sect:2 2 . 22
Generic Development
You might also like
- Aka GMP Audit FormDocument8 pagesAka GMP Audit FormAlpian BosixNo ratings yet
- Hold Time Study Protocol OF Cleaned Manufacturing Equipment Awaiting For UseDocument11 pagesHold Time Study Protocol OF Cleaned Manufacturing Equipment Awaiting For UseMarwa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Report Approval Sheet: Modi Sugar Mills, ModinagarDocument7 pagesReport Approval Sheet: Modi Sugar Mills, Modinagar9889187549100% (2)
- Cream & Ointment Process ValidationDocument3 pagesCream & Ointment Process Validationtajmir haqueNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Industry - PQR - 201312 PDFDocument9 pagesGuidance For Industry - PQR - 201312 PDFAshok LenkaNo ratings yet
- Sr. Formulation ScientistDocument2 pagesSr. Formulation Scientistapi-77624700No ratings yet
- Compliance Program Program: Chapter 56: Drug Quality AssuranceDocument29 pagesCompliance Program Program: Chapter 56: Drug Quality AssuranceMin Thura OoNo ratings yet
- Critical Quality Attributes Critical Process ParametersDocument40 pagesCritical Quality Attributes Critical Process ParametersSergiu LungNo ratings yet
- ASEAN Guideline Process OnDocument7 pagesASEAN Guideline Process OnVipin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Put Your Continued Process VerificationDocument9 pagesPut Your Continued Process VerificationMinh LeNo ratings yet
- Inspection ProformaDocument91 pagesInspection ProformaTejaswini BaingNo ratings yet
- Systems-Based Inspections For Cleaning Validation: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesSystems-Based Inspections For Cleaning Validation: ObjectivesPrashansa Shrestha100% (1)
- 2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFDocument4 pages2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFVishal SomaniNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Annual Product Quality ReviewDocument2 pagesProcedure For Annual Product Quality ReviewMARY JOY PAMBIDNo ratings yet
- PQR Overview 2016Document24 pagesPQR Overview 2016ike mayaNo ratings yet
- Tem-300 Product Transfer ProtocolDocument15 pagesTem-300 Product Transfer Protocolthien Doan100% (1)
- Critical Materrial Attributes in QBD TIPADocument47 pagesCritical Materrial Attributes in QBD TIPAsurapolNo ratings yet
- Alconox Detergent Cleaning ValidationDocument12 pagesAlconox Detergent Cleaning ValidationstanlesNo ratings yet
- IPQC Solid D FDocument32 pagesIPQC Solid D FmajumdarshivNo ratings yet
- Raw MaterialDocument23 pagesRaw MaterialGantisAlfidasariNo ratings yet
- Pure & Cure Healthcare Pvt. LTD: Restricted CirculationDocument4 pagesPure & Cure Healthcare Pvt. LTD: Restricted CirculationDarlenis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Final Version of Annex 15 To The EU Guide To GMP 2-8!4!15 - V4AN15Document11 pagesFinal Version of Annex 15 To The EU Guide To GMP 2-8!4!15 - V4AN15gustavoesanchezNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Training On Good Manufacturing Practices - WHODocument18 pagesSupplementary Training On Good Manufacturing Practices - WHOPESH SAP HCMNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine and Celecoxib Tablets PDFDocument38 pagesAmlodipine and Celecoxib Tablets PDFNarongchai PongpanNo ratings yet
- 1-7 Manufacturing BasicsDocument29 pages1-7 Manufacturing Basicssadiq455No ratings yet
- STP Montelukast Sa.Document6 pagesSTP Montelukast Sa.ShagorShagor100% (1)
- Vijay Kashinath Ghadge Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesVijay Kashinath Ghadge Career ObjectiveLarry RossNo ratings yet
- FAQ of Blister Packaging Machine-Jornen Machinery - Blister Machine, Blister Packaging Machine, Blister Packing Machine, Cartoner, Cartoning Machine For Pharmaceutical PackagingDocument3 pagesFAQ of Blister Packaging Machine-Jornen Machinery - Blister Machine, Blister Packaging Machine, Blister Packing Machine, Cartoner, Cartoning Machine For Pharmaceutical PackagingAshish MittalNo ratings yet
- 2 4 15 199Document10 pages2 4 15 199nsk79in@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure: L L M L L MDocument9 pagesOrganization Structure: L L M L L MNasef Mohd0% (1)
- Company Name Label Control Record: Sop # Section I: Work Order InformationDocument1 pageCompany Name Label Control Record: Sop # Section I: Work Order Informationg3medNo ratings yet
- Equipment Cleaning Validation Protocol FOR Aceclofenac /etodolac TabletsDocument25 pagesEquipment Cleaning Validation Protocol FOR Aceclofenac /etodolac TabletsQA PROTECH100% (1)
- QBD For ANDA An Example For Modified-Release Dosage Forms-2012 PDFDocument161 pagesQBD For ANDA An Example For Modified-Release Dosage Forms-2012 PDFJuanCarlosPossuCuadrosNo ratings yet
- 01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Document2 pages01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Ravi YadavNo ratings yet
- Temperature Excursion Management - A Novel Approac PDFDocument8 pagesTemperature Excursion Management - A Novel Approac PDFPharmacist100% (1)
- VMP Proses Rev.13 2018Document19 pagesVMP Proses Rev.13 2018fajarRS69No ratings yet
- CPV ProtocolDocument26 pagesCPV ProtocolPatricia Joyce Malabanan SunglaoNo ratings yet
- TEM 300 Product Transfer Protocol Template SampleDocument7 pagesTEM 300 Product Transfer Protocol Template SampleamebadhaNo ratings yet
- Sanfuliq PVP RegistrasiDocument25 pagesSanfuliq PVP RegistrasiFajarRachmadiNo ratings yet
- QMS InspectionDocument41 pagesQMS InspectionJulienne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- APIC Cleaning Validation 2014Document55 pagesAPIC Cleaning Validation 2014Alfons Gata CaminsNo ratings yet
- Turkey Qualification ValidationDocument28 pagesTurkey Qualification ValidationBalesh NidhankarNo ratings yet
- Prevalidation Study of A Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machine - Pharmaceutical & Medical Packaging NewsDocument3 pagesPrevalidation Study of A Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machine - Pharmaceutical & Medical Packaging NewsJanna Hendrix BabsonNo ratings yet
- 2.Pv Semisolid FDADocument37 pages2.Pv Semisolid FDARahayu Maulida RNo ratings yet
- Basic Aspects of Process Validation of Solid Oral Dosage FormsDocument33 pagesBasic Aspects of Process Validation of Solid Oral Dosage FormsMahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- CHECKLIST Q3-2 2013b PDFDocument13 pagesCHECKLIST Q3-2 2013b PDFJoe Luis Villa MedinaNo ratings yet
- Sandiip CVDocument2 pagesSandiip CVMunir ShmaitNo ratings yet
- SOP For HPLC Shimadzu LabSolutionsDocument6 pagesSOP For HPLC Shimadzu LabSolutionsfawaz khalilNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation ProcessDocument11 pagesCleaning Validation Processsamia khanNo ratings yet
- THAI COATER Spec PDFDocument4 pagesTHAI COATER Spec PDFConfundo Paa DuroNo ratings yet
- SOP For Yield Range For TV Batches With CommentsDocument5 pagesSOP For Yield Range For TV Batches With CommentsPurushothaman SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Generic Drug Product Development IntroductionDocument19 pagesGeneric Drug Product Development IntroductionAbhijit kanavajeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Preformulation and FormulationDocument10 pagesPharmaceutical Preformulation and FormulationPrashansa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Errors With The Batch Release ProcessDocument11 pagesAvoiding Errors With The Batch Release ProcessAnthony CollierNo ratings yet
- For Re-Classification of Sample Only Differential Test To Be PerformedDocument4 pagesFor Re-Classification of Sample Only Differential Test To Be PerformedGlobela2 QCNo ratings yet
- Process Validation Interim / Final Report: (Enter Product Title, Number & Strength) Product CodeDocument4 pagesProcess Validation Interim / Final Report: (Enter Product Title, Number & Strength) Product CodevanessaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandQuality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- Good Distribution Practice A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandGood Distribution Practice A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Preformulation Studies For Development of A Generic Capsule Formulation of Celecoxib Comparable To The Branded (Reference) ProductDocument14 pagesPreformulation Studies For Development of A Generic Capsule Formulation of Celecoxib Comparable To The Branded (Reference) Productsskkale100% (2)
- Pharmacognosy (5 Exp) (0807)Document53 pagesPharmacognosy (5 Exp) (0807)Krunal Chorey71% (7)
- Trndes in Prid DevelompmetnDocument3 pagesTrndes in Prid DevelompmetnsskkaleNo ratings yet
- A Classification of Prescription ErrorsDocument3 pagesA Classification of Prescription ErrorssskkaleNo ratings yet
- Cold Cream FormDocument2 pagesCold Cream FormsskkaleNo ratings yet
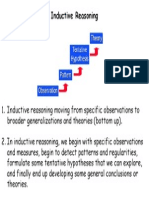
- InductiveDocument1 pageInductivesskkaleNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument12 pagesLatent HeatsskkaleNo ratings yet
- Semester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemDocument41 pagesSemester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemAmit KhairnarNo ratings yet
- EPISD ProposalDocument1 pageEPISD ProposalsskkaleNo ratings yet