Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E CM KG Ee A M V E V V MV M R Period T Be Be: Electronic Devices and Circuits
E CM KG Ee A M V E V V MV M R Period T Be Be: Electronic Devices and Circuits
Uploaded by
aamer_shahbaazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E CM KG Ee A M V E V V MV M R Period T Be Be: Electronic Devices and Circuits
E CM KG Ee A M V E V V MV M R Period T Be Be: Electronic Devices and Circuits
Uploaded by
aamer_shahbaazCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
BRIEF NOTES
www.jntuworld.com
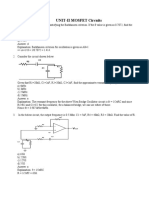
UNIT I :: ELECTRON DYNAMICS: CRO
19 31
1.602 10 , 9.1 10 e C m kg
, F force on electron in uniform electric field E
F=eE; acceleration
eE
a
m
If electron with velocity ' ' v moves in field ' ' E making an angle ' ' can be
resolved to sin , cos v v .
Effect of Magnetic Field B on Electron.
When B & Q are perpendicular path is circular
2
; ' '
mv m
r Period t
Be Be
When slant with ' ' path is # Helical.
EQUATIONS OF CRT
ELECTROSTATIC DEFLECTION SENSITIVITY
2
e
a
lL
S
dV
MAGNETIC DEFLECTION SENSITIVITY
2
m
a
e
S lL
mV
Velocity due to voltage V,
2eV
v
m
When E and B are perpendicular and initial velocity of electron is zero, the path is
Cycloidal in plane perpendicular to B & E. Diameter of Cycloid=2Q, where
u
Q
,
E
u
B
,
Be
m
.
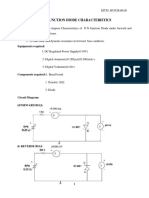
UNIT II :: SEMICONDUCTOR JUNCTION
,
i e
S G
have 4 electrons in covalent bands. Valency of 4. Doping with trivalent
elements makes ' ' p , Pentavalent elements makes ' ' n semiconductor.
Conductivity ( )
n p
e n p +
where
, n p
are concentrations of Dopants.
&
n p
are mobilitys of electron and hole respectively.
- 1 -
Diode equation
1
d
T
V
nV
d s
I I e
_
,
2
; ln
d T A P
d o
d i
V V N N kT
r V
I I q n
_
0 19
0 273; 1.602 10 T C q C
+
Diode drop changes
0
@2.2 / mv C , Leakage current
s
I
doubles on
0
10 C
Diffusion capacitance is
d
dq
c
dv
of forward biased diode it is I
Transition capacitance
T
C
is capacitance of reverse biased diode
n
V
1 1
2 3
n to
RECTIFIERS
COMPARISION
HW FW CT FW BR
DC
V
m
V
2
m
V
2
m
V
rms
V
2
m
V
2
m
V
2
m
V
- 2 -
;
T
kT
V
q
K= Boltzman Constant
Ripple factor
1.21 0.482 0.482
Rectification efficiency
40.6% 81% 81%
PIV
Peak Inverse Voltage
m
V 2
m
V
m
V
UNIT III :: FILTERS
Harmonic Components in FW Output,
0
2 4 1 1
cos 2 cos 4 .....
3 15
m
V
v wt wt
+ +
' ;
- 3 -
Capacitance Input Filter,
Inductor Input Filter,
Critical inductance is that value at which
diode conducts continuously, in or half cycle.
LC FILTER,
2
2
12 LC
or
1.2
, 50 , , . for Hz Lin H Cin F
LC
FILTER,
RC FILTER,
LC LADDER,
1 2
1 2
2
. . .....
3
n
n
c c c
L L L
X X X
X X X
ZENER DIODE
ZENER REGULATOR
;
i z
s i z
s
V V
I V V
R
>>
z
z
z
V
r
I
TUNNEL DIODE
Conducts in ,
f
r
b b
, Quantum mechanical tunneling in region a-0-b-c.
-ve resistance b-c, normal diode c-d.
p
I
= peak current,
v
I = valley current;
p
v
=peak voltage 65 mV,
v
v =valley voltage
0.35 V. Heavy Doping, Narrow Junction , Used for switching & HF oscillators.
VARACTOR DIODE
Used in reverse bias & as tuning variable capacitance.
( )
T n
T R
K
C
V V
+
; n=0.3 for diffusion, n=0.5 for alloy junction,
1
o
T n
R
T
C
C
V
V
_
+
,
25
B
C
C
is figure of merit, Self resonance
1
2
o
S T
f
L C
- 4 -
FWD Bias Normal
Diode 0.7 V Drop
Reverse Bias
PHOTO DIODES
Diode used in reverse bias for light detection.
Different materials have individual peak response to a range of wave lengths.
UNIT - IV
BJT, Bipolar Junction Transistor has 2 Junctions: BE, BC
Components of current are
,
nE pE
I I
at EB junction where
nE nE
nE pE E
I I
I I I
+
Emitter efficiency,
* nc
nE
I
I
transportation factor.
/ ; / BE f b BC r b
- 5 -
e b c
I I I +
;
c c
e b
I I
I I
Doping Emitter Highest
Base Lowest
e c b
I I I > >
Leakage currents :
, ,
CBO CEO EBO
I I I
( ) 1
CEO CBO
I I +
3 Configurations are used on BJT, CE, CB & CC
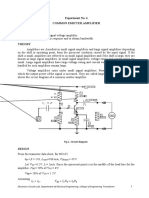
Common Emitter, VI characteristics
0
;
ce BE
i ie e ce
B c
V V
R h r r r
I I
AC Equivalent Circuit
COMMON BASE VI CHARACTERISTICS
- 6 -
Input Characteristics Circuit Output Characteristics
CE
C
V
B
I
I
;
1
C
E
I
I
; ;
V
CB
C cb EB
ib e fb cb
E e c
I V V
h r h r
I I I
UNIT - V
h- parameters originate from equations of amplifier
2 2 0 2
,
i i i r f i
v hi h v i h i h v + +
&
i i
v i are input voltage and current
2 2
& v i are output voltage and current
i
h
input impedance
, ,
ie ib ic
h h h ( ) , , 1
e e e
r r r + 1
]
f
h
current gain
, ,
fe fb fc
h h h
( ) , , 1 + 1
]
r
h
reverse voltage transfer
, ,
re rb rc
h h h
o
h
output admittance
, ,
oe ob oc
h h h
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR, FET is Unipolar Device
- 7 -
COMPARISON
BE BC
SATURATION f/b f/b
ACTIVE f/b r/b
CUT OFF r/b r/b
AMPLIFIER COMPARISON
CB CE CF
i
R
LOW MED HIGH
I
A
I
A 1 +
V
A
High High <1
o
R
High High low
AC Equivalent Circuit
Construction n-Channel p-Channel
S=Source, G=Gate, D=Drain
GS Junction in Reverse Bias Always
gs
V
Controls Gate Width
VI CHARACTERSTICS
Transfer Characteristics Circuit Forward Characteristics
Shockley Equation
2
1
gs
d dss
p
V
I I
V
_
,
,
0
1
gs
m m
p
V
g g
V
_
,
MOSFET: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET, IGFET
Depletion Type Mosfet Symbols Enhancement Mosfet
Depletion Type MOSFET can work width
0
gs
V >
and
0
gs
V <
Transfer Forward
Characteristics Characteristics
- 8 -
MOSFET JPET
High
10
10
i
R
8
10
0
50 R k
1m
Depletion
Enhancement Mode
Depletion
Mode
Delicate Rugged
Enhancement MOSFET operates with,
gs t
V V >
,
t
V Threshold Voltage
Forward Characteristics Transfer Characteristics
UNIT VI :: BIASING in BJT & JFET
Fixing Operating Point Q is biasing
Fixed Bias Emitter Stabilized Feedback Bias
CC B B BE
V I R V +
Fixed Bias ( ) 1
CC C B B B BE
V R I I R V + + +
( ) 1 Re
CC B B BE
V I R V + + +
- 9 -
D
JFET I Table
gs
V
D
I
0
DSS
I
0.3
P
V
2
DSS
I
0.5
P
V
4
DSS
I
P
V
0
COMPARISIONS
BJT FET
Current controlled Voltage controlled
High gain Med gain
Bipolar Unipolar
Temp sensitive Little effect of T
High GBWP Low GBWP
( ) ,
DS GS T
V sat V V
( )
2
( )
ds GS T
I ON K V V
VOLTAGE DIVIDER BIAS EMITTER STABILIZED
FIXED BIAS
STABILITY EQUATIONS
1 0 2 3 c c BE
I S I S V S + +
1 2 3
; ;
C C C
CO BE
I I I
S S S
I V
, STABILITY FACTOR
( ) 1
1
B
C
S
dI
dI
S must be as small as possible, Most ideal value =1
How to do determine stability factor for bias arrangement? Derive
B
C
dI
dI
and
substitute in S
Amplifier formulae:
l
V I
i
Z
A A
Z
,
i
Z
measured with output shorted
0
Z
measured with input shorted
CE amplifier
I
A
fe
h or
;
;
i
Z re
;
T
e
V
r
I
;
L
v
e
R
A
r
CB amplifier
1
A ; ;
L
v i e
e
R
A Z r
r
CC amplifier
( )
I
A 1 ; 1 ;
ie
V
i
h
A
R
+
( )
1
i fe E ie
R h R h + +
H Parameter Model CE
;
1
fe
I
oe l
h
A
h z
+
L
V fe
ie
Z
A h
h
- 10 -
2
1 2
CC
B
V R
V
R R
+
,
;
E
E B BE C
E
V
V V V I
R
( ) ( ) 1 Re
.
Vcc Rc Ib
Ib Rb Vbe
+ +
+ +
CB amplifier
; ; .
L
i ib I fb V fb
ib
R
R h A h A h
h
FET
CS amplifier ( )
0
|| ;
V m d d d
A g R r Z R
Common Gate Amplifier
,
1
s
V m d i
m s
R
A g R Z
g R
+
Common Drain
1
;
1
m s
V o
m s m
g R
A Z
g R g
+
RC Coupled Amplifiers
If cut off frequency
1
1
2
f
RC
,
1
1
1
1
tan ;
1
f
A
f
f
j
f
_
, _
+
,
6 / , 20 / Slope dB octave dB decade
,
f
Octave= 2
2
or f
is beta cut off frequency where
0.707
fe
h falls by
is
cut off frequency where 0.707
t
f
is
1
fe
h
gain bandwidth product.
UNIT VII :: FEED BACK AMPLIFIERS
Amplifier gain stands for any of Voltage amplifier, Current amplifier, Trans resistance
Trans admittance amplifier
Ve feed back amplifier depends on
| 1 | 1 , 1
b b
A ve f ve f + > < +
Feed back reduces noise distortion, gain variation due to parameters, increases BW.
( ) 1 A +
is called de-sensitivity factor.
Feed back amplifiers
Voltage series, voltage shunt; Current series, current shunt
- 11 -
0
0
; ;
1
f
f
i
X
X A
A A
A X X
+
i s f
X X X
for voltage, current series
( ) 1
f
i i
z z A +
1
f
A
A
A
+
, for all
1
f
i
i
z
z
A
+
, for voltage or current shunt
( ) 1
f
o o
z z A +
, for current series, shunt
0
1
f
o
z
z
A
+
, for voltage series and shunt.
UNIT VIII :: OSCILLATORS
Barkausen Criterion for oscillation loop gain =1, =0
0
, 360
0
.
HARTLEY OSCILLATOR
CRYSTAL OSCILLATORS
Tuned ckt replaced with Crystal
Phase shift oscillator
Wein Bridge Oscillator
- 12 -
1
2
T
f
L C
,
1 2 T
L L L M + t , ;
2
1
L
L
,
COLLPITS OSILLATOR,
1 2
, L L
replaced by
1 2
, C C
,
C replaced by L;
1
2
T
f
LC
1
s
LC
,
1
p
T
LC
FET MODEL
1
2 6
f
RC
, 29 A ,
Minimum RC sections 3
1 2 1 2
1
2
f
R R CC
,
if R1=R2=R, C1=C2=C ,
1
2
f
RC
;
1
3 A
BJT MODEL
1
4
2 6
C
f
R
RC
R
_
+
,
, 29 A ,
Minimum RC sections 3
- 13 -
You might also like
- Tolerances HandbookDocument0 pagesTolerances Handbooksidhesh87No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Manual de Partes Gz150Document66 pagesManual de Partes Gz150panxoskatesk8100% (1)
- Quiz Finance 1Document3 pagesQuiz Finance 1studentNo ratings yet
- APU EMBRAER Training - Compas - Printing VersionNov2018 - Rev01Document141 pagesAPU EMBRAER Training - Compas - Printing VersionNov2018 - Rev01gantuya battulgaNo ratings yet
- Edc Important PointsDocument12 pagesEdc Important Points29viswa12No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Document7 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Telecom Engineering EDC-1 Question Bank For IA-02 A.Y 2021-22Pratik BhalakeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No6Document8 pagesExperiment No6alaaNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationmanjunathgprNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesSemiconductorsGiezel RevisNo ratings yet
- 05 BJT-Amplifiers PDFDocument40 pages05 BJT-Amplifiers PDFMd ArifNo ratings yet
- BJT DC BiasingDocument58 pagesBJT DC BiasingMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits K-NotesDocument42 pagesAnalog Circuits K-NotesNitin TembhurnikarNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationTaufique ZamanNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument30 pagesSmall-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Exp9 s04Document8 pagesExp9 s04SITI HAJAR AzizNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits - Unit - 2 - MCQDocument4 pagesElectronic Circuits - Unit - 2 - MCQShivani AndhaleNo ratings yet
- Devices and Circuits Ii: Lecture GoalsDocument6 pagesDevices and Circuits Ii: Lecture GoalsMạnh Cường TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 Multistage AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLecture21 Multistage AmplifierscitraumariNo ratings yet
- Lab10 2011Document5 pagesLab10 2011Venkat RamananNo ratings yet
- Multistage Amplifiers: Bipolar Junction Transistor: MosfetDocument16 pagesMultistage Amplifiers: Bipolar Junction Transistor: MosfetRomelDianonNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3-BJT Common-Emitter Amplifier Ver3Document41 pagesLECTURE 3-BJT Common-Emitter Amplifier Ver3Sankalp SharmaNo ratings yet
- 9 CE AmplifierDocument5 pages9 CE AmplifierAnsh PratapNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument26 pagesFrequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- BJT Diff AmplifierDocument15 pagesBJT Diff AmplifierAdrià Amézaga SàrriesNo ratings yet
- AE Lab Manual For EeeDocument53 pagesAE Lab Manual For EeeSRUJANA VNo ratings yet
- BEE Small Signl ModelDocument13 pagesBEE Small Signl ModelalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- BJT Basics 1Document69 pagesBJT Basics 1Sarvesh RajbharNo ratings yet
- BJT Basics 1Document69 pagesBJT Basics 1sjbloomsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Multistage AmplifiersDocument43 pagesLecture 8 - Multistage AmplifiersRanjan KarkiNo ratings yet
- Single-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2Document19 pagesSingle-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2karan007_mNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowDocument23 pagesUnit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowAzImmNo ratings yet
- Ec FinalDocument46 pagesEc FinalManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- BJT ModelsDocument6 pagesBJT ModelsArmor BatsNo ratings yet
- EC2257 Lab ManualDocument48 pagesEC2257 Lab Manualmmrr24jesusNo ratings yet
- EC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesEC Lab ManualAshwath NadahalliNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowDocument23 pagesUnit - 6 AMPLIFIERS: Small Signal LowHemant TulsaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Linear Amplifiers BJT-1-1Document31 pagesChapter 13 Linear Amplifiers BJT-1-1doubleagent93No ratings yet
- Ec2257 LM 1Document48 pagesEc2257 LM 1dr.abdulkareem.abdullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Common Emitter Amplifier AIM: Fig 1. Circuit DiagramDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4 Common Emitter Amplifier AIM: Fig 1. Circuit Diagrampandiyarajan142611No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - RL RS EffectDocument35 pagesLesson 4 - RL RS EffectditmemayNo ratings yet
- EC1256-Lab ManualDocument67 pagesEC1256-Lab Manualjeyaganesh86% (7)
- EC &LD-Lab ManualDocument50 pagesEC &LD-Lab Manualdevirpasad100% (1)
- 1 RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1 RC CircuitsMohmed Al NajarNo ratings yet
- FET Basics 1Document63 pagesFET Basics 1Juno Hera Magallanes HuyanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Common Emitter AmplifierDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 Common Emitter AmplifierVelan PrintersNo ratings yet
- Single Stage Limitations Multi-Stage Amplifiers FeedbackDocument17 pagesSingle Stage Limitations Multi-Stage Amplifiers FeedbackJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Exp 02Document5 pagesExp 02Captain Jack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureDocument128 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureJustin ValdezNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document6 pagesLab 3Saurabh BhiseNo ratings yet
- FET Basics 1Document47 pagesFET Basics 1padmavathy2kNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Posi Stop Plus Troubleshooting GuideDocument32 pagesPosi Stop Plus Troubleshooting GuideJesus AristizabalNo ratings yet
- IT 1 - Introduction To ExcelDocument34 pagesIT 1 - Introduction To ExcelEllah MaeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Aaug-Dec 2019 MVDocument5 pagesAssignment 1Aaug-Dec 2019 MVkamalNo ratings yet
- LogDocument25 pagesLogClariss BahasaNo ratings yet
- Name Synopsis DescriptionDocument2 pagesName Synopsis DescriptionNicolas Fernando Schiappacasse VegaNo ratings yet
- 1SFC151003C0201 79Document1 page1SFC151003C0201 79psatyasrinivasNo ratings yet
- Kenwood KDC-W237, W3037, W311, W3537, W4037Y PDFDocument42 pagesKenwood KDC-W237, W3037, W311, W3537, W4037Y PDFgeenmaNo ratings yet
- Phase Rule: Ternary Liquid System: Save The Titrated MixturesDocument4 pagesPhase Rule: Ternary Liquid System: Save The Titrated MixturesMarthy DayagNo ratings yet
- Connections and SymbolsDocument253 pagesConnections and SymbolsMarko CetrovivcNo ratings yet
- F StringDocument4 pagesF StringhrishipisalNo ratings yet
- Temperature of Freshly Mixed Hydraulic-Cement Concrete: Standard Method of Test ForDocument2 pagesTemperature of Freshly Mixed Hydraulic-Cement Concrete: Standard Method of Test ForLydiaNo ratings yet
- 4180 UpdatedDocument2 pages4180 UpdatedddfbhghNo ratings yet
- Flotronic System Manager: Application GuideDocument89 pagesFlotronic System Manager: Application GuideHafiani HichamNo ratings yet
- Multisim Basics Schematic Capture and SiDocument103 pagesMultisim Basics Schematic Capture and SiVikrant1No ratings yet
- Assembly Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesAssembly Midterm ExamKhaled Sharif0% (1)
- Discrete Math 2 Exam NotesDocument3 pagesDiscrete Math 2 Exam Notesembers poggerNo ratings yet
- OP 1017 RKT FuzesDocument95 pagesOP 1017 RKT Fuzesjbart252No ratings yet
- SURPAC BrochureDocument22 pagesSURPAC BrochureOumar LoNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument3 pagesOverviewNischay MahamanaNo ratings yet
- 5.yagi Uda and Log Periodic Antennas 1Document24 pages5.yagi Uda and Log Periodic Antennas 1Medisetty Devika Sree100% (1)
- Andres Anal Chem CalibrationDocument5 pagesAndres Anal Chem CalibrationAndres, Andrea Lyn M.No ratings yet
- Pepin Primality TestDocument2 pagesPepin Primality Testprajay thulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F3 - End of May 2021 TestDocument2 pagesChemistry F3 - End of May 2021 TestOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- QTDA Su Kien - Chapter 6Document9 pagesQTDA Su Kien - Chapter 6Nguyên TrươngNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Modeling of 270 Ksi Low-Relaxation Prestressing StrandsDocument7 pagesStress-Strain Modeling of 270 Ksi Low-Relaxation Prestressing StrandsDian Jaka PraharaNo ratings yet
- Micro Ass.Document4 pagesMicro Ass.Mohammed O'AfifiNo ratings yet