Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gap Test
Uploaded by
shijinbgopalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gap Test
Uploaded by
shijinbgopalCopyright:
Available Formats
next up previous Next: Poker Test Up: Tests for Random Numbers Previous: Tests for Auto-correlation
Gap Test
The gap test is used to determine the significance of the interval between recurrence of the same digit. A gap of length x occurs between the recurrence of some digit. See the example on page 313 where the digit 3 is underlined. There are a total of eighteen 3's in the list. Thus only 17 gaps can occur. The probability of a particular gap length can be determined by a Bernoulli trail.
If we are only concerned with digits between 0 and 9, then
The theoretical frequency distribution for randomly ordered digits is given by
Steps involved in the test. Step 1. Specify the cdf for the theoretical frequency distribution given by Equation (8.14) based on the selected class interval width (See Table 8.6 for an example). Step 2. Arrange the observed sample of gaps in a cumulative distribution with these same classes. Step 3. Find D, the maximum deviation between F(x) and Step 4. Determine the critical value, . as in Equation 8.3 (on page 299).
, from Table A.8 for the specified value of
and the sample size
Step 5. If the calculated value of D is greater than the tabulated value of independence is rejected. See the Example 8.13 on page 314 next up previous
, the null hypothesis of
Next: Poker Test Up: Tests for Random Numbers Previous: Tests for Auto-correlation Meng Xiannong 2002-10-18
You might also like
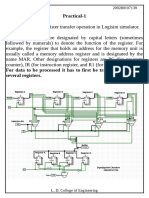
- Practical-1 AIM: Implement Register Transfer Operation in Logisim SimulatorDocument23 pagesPractical-1 AIM: Implement Register Transfer Operation in Logisim SimulatorDigvijay Sinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exam Question Paper and Answer Booklet InstructionsDocument17 pagesExam Question Paper and Answer Booklet InstructionsMay JingNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Management SystemDocument25 pagesBlood Bank Management Systemshijinbgopal56% (9)
- AVL Tree Program in CDocument7 pagesAVL Tree Program in CshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- ADC Dynamic ErrorsDocument34 pagesADC Dynamic ErrorsPranavateja ChilukuriNo ratings yet
- Automatic Parallel Parking System ReportDocument23 pagesAutomatic Parallel Parking System ReportFrances Ekenedilichukwu Awachie50% (2)
- Chapter Three Searching and Sorting AlgorithmDocument47 pagesChapter Three Searching and Sorting AlgorithmAbeya Taye100% (1)
- Traffic Light Simulator Using 8086 Assembly LanguageDocument14 pagesTraffic Light Simulator Using 8086 Assembly Languagedihosid99No ratings yet
- Final Full DocumentDocument72 pagesFinal Full DocumentMussie DDKNo ratings yet
- Clearance Management System UpdatedDocument25 pagesClearance Management System UpdatedMilkiyas Mosisa100% (1)
- Railway Reservation SystemDocument3 pagesRailway Reservation SystemArun RangrejNo ratings yet
- "Bus Ticketing System": A Project Report OnDocument56 pages"Bus Ticketing System": A Project Report OnDasmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Exam Scheduling System ProPosal.Document4 pagesExam Scheduling System ProPosal.amare abraham gendoNo ratings yet
- DS Placement Linked List 2018Document6 pagesDS Placement Linked List 2018vinay harshaNo ratings yet
- KINGPAKDocument59 pagesKINGPAKUmakant GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Cultural Heritage Information Management System For Gondar Culture and Tourisim BureauDocument87 pagesCultural Heritage Information Management System For Gondar Culture and Tourisim BureauTinsaye GetanehNo ratings yet
- Report a Crime Online with E-CopsDocument43 pagesReport a Crime Online with E-CopsMonira Mohamed YousufNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Notice AppDocument70 pagesAmbo University Notice Appmhfdgd0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Scan ConversionDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Scan ConversionHimanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- MC (SampleDocument11 pagesMC (SampleCabdi XuseenNo ratings yet
- Decision TableDocument6 pagesDecision TableHide Meh100% (1)
- Keys stored in chained hash table questionsDocument11 pagesKeys stored in chained hash table questionsHarshit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems Lab ProgramsDocument23 pagesDistributed Systems Lab Programsgoodsp_007No ratings yet
- Hospital Management System: University of South Asia LahoreDocument49 pagesHospital Management System: University of South Asia LahoreCorina PruteanuNo ratings yet
- Blood Managment SystemDocument76 pagesBlood Managment SystemIbsa GemechuNo ratings yet
- BCSL 058 Computer Oriented Numerical Techniques Lab Solved Assignment 2019 20Document17 pagesBCSL 058 Computer Oriented Numerical Techniques Lab Solved Assignment 2019 20mahesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Online Bus Ticketing and Reservation System (OBTRS) : Submitted byDocument35 pagesOnline Bus Ticketing and Reservation System (OBTRS) : Submitted byAhsan RazaNo ratings yet
- Railway ReservationDocument33 pagesRailway ReservationvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Bcs - 051 Software Engineering (IGNOU) (Important Questions) (Previos Year Qestions)Document4 pagesBcs - 051 Software Engineering (IGNOU) (Important Questions) (Previos Year Qestions)viiiNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design ProjectDocument18 pagesSystem Analysis and Design ProjectEyob Desta0% (1)
- Feedback System and AutopilotDocument3 pagesFeedback System and AutopilotKoshal ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Railway Reservation SysytemDocument63 pagesRailway Reservation SysytemParag Waghmare0% (1)
- Tic Tac Toe GameDocument3 pagesTic Tac Toe GameMaduka NadeeshaniNo ratings yet
- An Interactive RFID-Based Bracelet For Airport Luggage Tracking SystemDocument5 pagesAn Interactive RFID-Based Bracelet For Airport Luggage Tracking SystemNaveed BeighNo ratings yet
- Path Visualizer: Gaurav Rana 01 Abhishek Kumar Singh 17 Adarsh Singh 18 Mentor-Mrs. Huda KhanDocument18 pagesPath Visualizer: Gaurav Rana 01 Abhishek Kumar Singh 17 Adarsh Singh 18 Mentor-Mrs. Huda KhanNEWNo ratings yet
- AmiDocument17 pagesAmisuryanshNo ratings yet
- Bus ReservationDocument18 pagesBus ReservationDheeraj Babu100% (3)
- Online Shopping DFDDocument5 pagesOnline Shopping DFDanand_gsoft3603No ratings yet
- Airline Reservation SystemDocument38 pagesAirline Reservation SystemSimar Randhava100% (1)
- Solution Assignment 2Document15 pagesSolution Assignment 2Sania ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Online Police Station Criminal Management System: Name of StudentDocument56 pagesOnline Police Station Criminal Management System: Name of StudentDagim Fekadu AmenuNo ratings yet
- Online Blood Donation Management System ABSTRACTDocument2 pagesOnline Blood Donation Management System ABSTRACTLOGIC SYSTEMSNo ratings yet
- Output PrimitivesDocument20 pagesOutput Primitivesvijay_dhawaleNo ratings yet
- Dbms Project On Bus Reservation System Last ReportdocxDocument13 pagesDbms Project On Bus Reservation System Last ReportdocxUrja DhabardeNo ratings yet
- Lec #4 (System of Linear Equations)Document21 pagesLec #4 (System of Linear Equations)Hamna YounisNo ratings yet
- Design of Intelligent Traffic Light Controller Using GSMDocument8 pagesDesign of Intelligent Traffic Light Controller Using GSMapi-2781938430% (1)
- Tic Tac ToeDocument10 pagesTic Tac ToeAbeerHassanNo ratings yet
- 434 HW 3 SolDocument5 pages434 HW 3 SolSweet AliaNo ratings yet
- Online Railway ResevationDocument13 pagesOnline Railway ResevationAlok Singh0% (1)
- Deep Learning Algorithms Report PDFDocument11 pagesDeep Learning Algorithms Report PDFrohillaanshul12No ratings yet
- Doctor's Hub: Telemedicine App for BangladeshDocument30 pagesDoctor's Hub: Telemedicine App for BangladeshMd. Rashedul Islam 1511108042No ratings yet
- Inter Office Communication File Managment SystemDocument87 pagesInter Office Communication File Managment SystemGudata GechoNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QuestionsDocument6 pagesCompiler Design QuestionsNaman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Streams and File IODocument44 pagesChapter 4 Streams and File IOGalatom Yadeta100% (1)
- Railway Reservation System Software RequirementsDocument19 pagesRailway Reservation System Software RequirementssarthakNo ratings yet
- Online Locker Management SystemDocument21 pagesOnline Locker Management Systemnidhi singhNo ratings yet
- 00 Lab NotesDocument8 pages00 Lab Notesreddykavya2111No ratings yet
- Wilcoxon 1945Document5 pagesWilcoxon 1945Daniel MoránNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representations and Frequency Distribution TablesDocument12 pagesGraphical Representations and Frequency Distribution TableshkaqlqNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSDocument22 pagesModule 3 - DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSTherese SibayanNo ratings yet
- 1998 Material Ease 5Document4 pages1998 Material Ease 5Anonymous T02GVGzBNo ratings yet
- احصاء محاضرة 4 PDFDocument12 pagesاحصاء محاضرة 4 PDFفاضل حمزه فاضلNo ratings yet
- Dms 2007discrete Mathematical Structures Nov 2012 NovDocument2 pagesDms 2007discrete Mathematical Structures Nov 2012 NovshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematical Structures Nov 2012Document2 pagesDiscrete Mathematical Structures Nov 2012shijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Sdet ExperiencedDocument2 pagesSdet ExperiencedshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Merging C ProgramDocument4 pagesMerging C ProgramshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Programming in C Question PaperDocument1 pageProgramming in C Question PapershijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics - ClippingDocument4 pagesComputer Graphics - ClippingshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Graphical Password CuedDocument17 pagesGraphical Password CuedshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- BacktrackingDocument8 pagesBacktrackingshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Fil Error Handling - CDocument2 pagesFil Error Handling - CshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Ruby TutorialDocument42 pagesRuby TutorialRadu PavelcoNo ratings yet
- KeywordDocument1 pageKeywordshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Tele-Immersion Seminar AbstractDocument1 pageTele-Immersion Seminar AbstractshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Cycle StealingDocument1 pageCycle StealingshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Combinational & Seqential CircutsDocument1 pageCombinational & Seqential CircutsshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Intel FeaturesDocument1 pageIntel FeaturesshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Symbolic ConstantDocument1 pageSymbolic ConstantshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Symbolic ConstantDocument1 pageSymbolic ConstantshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Tele ImmersionDocument20 pagesTele Immersionapi-3827000100% (8)
- Line Input & Output in CDocument1 pageLine Input & Output in CshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Free Space OpticsDocument1 pageFree Space OpticsshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Self-Referential Data Structures Explained with Linked List ExampleDocument2 pagesSelf-Referential Data Structures Explained with Linked List ExampleshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Android AdaptersDocument45 pagesAndroid AdaptersshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Bit Field-CDocument1 pageBit Field-CshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Double PointerDocument1 pageDouble PointershijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Android Data Storage, Retrieval & SharingDocument12 pagesAndroid Data Storage, Retrieval & Sharingshijinbgopal100% (1)
- Basic File Handling in CDocument33 pagesBasic File Handling in CUbaid_Ullah_Fa_1194No ratings yet
- Android Widget Toolbox & ViewsDocument6 pagesAndroid Widget Toolbox & ViewsshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Android DatabaseDocument22 pagesAndroid DatabaseshijinbgopalNo ratings yet