Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Designing Recruitment, Selection & Talent Management Model Tailored To Meet UNJSPF's Business Development Needs
Designing Recruitment, Selection & Talent Management Model Tailored To Meet UNJSPF's Business Development Needs
Uploaded by
kimfuentesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Designing Recruitment, Selection & Talent Management Model Tailored To Meet UNJSPF's Business Development Needs
Designing Recruitment, Selection & Talent Management Model Tailored To Meet UNJSPF's Business Development Needs
Uploaded by
kimfuentesCopyright:
Available Formats
Traditionalists, Baby Boomers, Generation X, Generation Y (and Generation Z) Working Together
WHAT MATTERS AND HOW THEY LEARN? how different are they? fact and fiction
Executive Ofce, Talent Management Team United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund New York Secretariat Headquarters
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
Rational for Introducing the Generational Communication Gap into the Workplace
Casey Carlson!& Deloitte & Touche Study !
Fundamental Questions!
Where does your personal view fall in the following generational change spectrum? Level 5: The generation of people in the top boxes is the only one that mattersthe rest just need to grow up or shut up. Level 3: The generational change is an emerging issue within our organization but we havent done much about it. Level 2: We view generational change as an emerging opportunity. Level 1: Were actively changing the work culture to harness! the power of generational change.
Differences in Opinion and Attitude
This generational stuff is just socially acceptable stereotypingpolitically correct rationale offered for immature behavior When is someone going to ask me what I need? Doesnt everyone want the same thing anyway? Even if this generational stuff were true, this is still planet earth and we know how our business needs to be run for it to be a success Can we go back to work now? These kids will either get with the program or theyll leave just like they always have I dont get it! My managers are barely technologically literate yet theyre never open to suggestions on how to improve a process with technology. Whats up with this attitude ? Dont they want the home at night ?! They act as if I should want to work 60-70 hours a week year in and year out. Im not afraid of hard work, but thats not the only thing I want to do with my life. Im older, have more experience and stop asking so many questions. You dont answer my questions either because you dont know the answer why or you wish youd asked the same question when you were my age but didnt have the nerve.! !
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
The Common Trait
Exclusive attitudes and an atmosphere that does not take into consideration differences. WHAT IS THE ORGANIZATIONAL GOAL? Understanding strengths and differences of each generational group. Leveraging the strengths and creating the work environment that values differences. WHAT REALITIES DO WE FACE?! The basic conict arises from trying to t an increasingly nontraditional workforce into a largely traditional workplace. Shrinking talent pool. WHOSE PROBLEM IS THIS? All stakeholders.
The Challenge
Managing multigenerational workforces is an art in itself.! Young workers want to make a quick impact, the middle generation needs to believe in the mission, and older employees dont like ambivalence.! Your move.!
Harvard Business School Working Knowledge Newsletter - April 17, 2006:! Can you manage different generations?
The Four Generations
Understanding differences between the generations is fundamental in building successful multigenerational workplace. For each generation there! are particular experiences that mold specic preferences,! expectations, beliefs and work style. Here is a brief! description of each generation and their socioeconomic experiences and how they! have impacted their work and leadership styles.
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
Traditionalist Born 1925 - 1945
Baby Boomers Born 1946-1964
GenX Born 1965-1980
GenY Millennial Born 1981 and after (Gen Z-Nexters-born after 2000)
TEAM PLAYERS INDIRECT IN COMMUNICATING LOYAL TO THE ORGANIZATION RESPECT THE AUTHORITY DEDICATION AND SACRIFICE DUTY BEFORE PLEASURE OBEDIENCE RESPOND WELL TO DIRECTIVE LEADERSHIP SENIORITY AND AGE CORRELATED ADHERENCE TO RULES
BIG PICTURE/SYSTEMS IN PLACE BRING FRESH PERSPECTIVE DO NOT RESPECT THE TITLES DISAPPROVE ABSOLUTES AND STRUCTURE OPTIMISM TEAM ORIENTATION
POSITIVE ATTITUDE IMPATIENCE GOAL ORIENTATED MULTI-TASKING THINKING GLOBALLY SELF-RELIANCE FLEXIBLE HOURSE, INFORMAL WORK ENVIRONMENT JUST A JOB TECHNO-LITERAL INFORMAL - BALANCE GIVE THEM A LOT TO DO AND FREEDOM TO DO THEIR WAY QUESTION THE AUTHORITY
CONFIDENCE SOCIABILITY MORALITY STREET SMARTS DIVERSITY COLLECTIVE ACTION HEROIC SPIRIT TENACITY TECHNOLOGICAL SAVY LACK OF SKILLS FOR DEALING WITH DIFFICULT PEOPLE MULTITASKING NEED FLEXIBILITY
UNCOMFORTABLE WITH CONFLICT PERSONAL GROWTH SENSITIVE TO FEEDBACK HEALTH AND WELLNESS PERSONAL GRATIFICATION
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
Traditionalist Attire Formal
Baby Boomers Business - casual (high end) Long hours - ofce only
Generation X Business - casual (low end) Ofce, home, desires exible schedule
Generation Y/Z Whatever feels comfortable Ofce, home desires exible schedule Maintain personal life Constant feedback needed
Work Ofce only Environment
Motivators
Self - worth
Salary
Security
Mentoring
Not necessary
Does not handle well negative feedback
Not necessary to receive feedback
Retention
Loyalty
Salary
Security/Salary
Personal relationship E-mail/IM/Text
Client Orientation Technology
Personal contact
Telephone
Dictates documents, e-mail only in the ofce, use of library instead of web, limited phone use
Documents prepared by the Associates, e-mail primarily in the ofce, web use to google
Creates own documents, uses mobile and laptop, uses web to research, review etc., e-mail/mobile 24/7 Build a transferable career, variety of skills and experiences
Creates own documents, creates databases, uses web to research and network, use of email/IM/text 24/7 Build several parallel careers, have a several jobs simultaneously
Career Goals
Build a legacy, a life-time career with one company
Build a perfect career, excel
The! Traditionalists (Veteran Generation) The Veteran! Generation, born between 1925 and 1945, were brought up in a more! challenging time with life experiences that included WW II. The economic and political uncertainty that they experienced led them! to be hard working, nancially conservative, and cautious.! Organizational loyalty is of an essence and they have advanced with the premiss that the seniority is important to advance in one's career.! They do not like the change, they are not very! risk tolerant, have a respect for authority and hard work.!This! tends to lead to a command and control style of leadership. This!generation set and obey the rules.
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund 5
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
The! Baby Boomers The Boomers, born between 1946! and 1964, were brought up in an abundant, healthy post-war economy,! becoming an egocentric generation. They saw the world! revolving around them. Nuclear families! were the norm. More than anything, work has been! a dening part of both, their self worth and their evaluation of others.! Their life style revolves around the fact that they live to work.! Balance is a quaint idea but not really a possibility. As such, they!see the workday at least!8 a.m. to!5 p.m.! This is a signicant! tension point between them and the newer generations, as they expect! others to have the same work ethic and work the same hours. The earlier! part of this generation followed the bent rules set by the traditionalists. Generation! X The generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, was the rst generation raised on to do lists and grew up with high rate of blended families.! They were also brought up in the shadow of the inuential boomer! generation. They witnessed their parents sacrice greatly for their companies. As a consequence, they! developed behaviors (not values) of independence, resilience and! adaptability more strongly than previous generations.! In opposition to the hard driving Boomers who live to work, they work! to live and view the world with a little cynicism and distrust. Generation! Y The Y generation, born! between 1981 and 2000, has been portrayed as the next big generation, an!enormously powerful group that has the sheer numbers to transform every life stage it enters.!!They were brought up during the empowerment years where everyone won!and everyone got a medal. Raised by parents who nurtured! and structured their lives, they were drawn to their families for! safety and security. They were also encouraged to make their own! choices and taught to question authority. This group was also raised in! a consumer economy, and as
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund 6
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
such, expects to inuence the terms and! conditions of their job. As a result, they expect employers to! accommodate their consumer expectations in this regard.! This is the basis for the expecting more style that characterizes this! generation. They dont necessarily see that they should get more, but! that an employer should give more to their employees. They were brought up with an empowered parenting style and therefore they are not afraid to! express it their opinion. Generation Y (as well as X, to a lesser degree) is also the rst to! grow up with computers and the Internet as a signicant part of their! lives. Constant experience in the networked world has had a profound! impact on their style in approaching problem-solving situations. This! generation of worker is coming into the workforce with networking,! multiprocessing, and global-minded skills that the traditionalists and baby boomers could not have imagined. The advent of interactive media such as instant messaging, text! messaging, blogs, and especially multi player games have generated new! skills and styles of collaborating in the generation X and the generation Y to such degree that it has made them different. This always on or always connected mind-set is!at the heart of some of the friction that exists between the! generations. The x and y generation is challenged by the! rigidity of the eight to ve workdays.
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
How to motivate Generation X
How to effectively train Generation X
How to motivate Generation Y
How to effectively train Generation Y They thrive in multimedia environment They can learn any time anywhere They need exibility Multi-tasking Enable internet reliance (Webinars, IM, Blogs, Podcasts, Avatars, YouTube) Enable social internet (My Space, Friendster) Provide with simulations Provide with the structured learning regardless of the form Connect me with everything True team players
They tend to avoid corporate politics They are generally not very interested in traditional perks They are motivated by the prospects of independence, the lack of corporate structure and lack of rigidity They are motivated by the possibility of the latest technological advances They need to be made clear what you are looking for Allow them to question the experts and the authority
Web-based training They love a challenge Allow them to ask questions and challenge the concepts Keep the training materials brief and easy to read Offer multi-media learning opportunities Ensure access to simple, logically organized knowledge database Sensitive to design and graphics This group maintains short attention span They function well as team members They want to be heroes They want to be surrounded by bright, creative people They want it right now
They are looking for networking through the empowerment
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
The Disconnect While there are different formative experiences that inuence each! generation, the popular media and many generation gurus have taken! these differences between the generations too far in describing them as!a clash of values. The! Way Forward Most of the workplaces today loaded with stress. The need for results, time! pressure and opportunities are contributing factors in the biggest migration of workers. GenX and GenY is making today the most signicant impact in the workplace. They are empowered, consumer oriented,! technologically savvy and they are not afraid to speak up for change in! their workplace. GenX and GenYs are advocating for a more uid use of time in their! workday. They think, why not work from morning till noon, take off part! of the afternoon and then restart again at 5 p.m. and continue to! midnight? In their minds and in their always on world, they see this! arrangement as perfectly legitimate as long as they get their work done! and meet customer expectations. For the Boomers, who are either afraid! of new technology or just simply do not understand it, the impact is! that the new generations do not seem fully committed. There is still the perception in a workplace that if the employees are not seen, they cannot be working. There is a perception by the older generations that the new generations do! have an entitlement mentality, that they are presumptuous and want to be accommodated with their demands. They expect more and express! differently.! Driven by their formative experiences, they are simply! not afraid to expect more from their employers and they are certainly!not afraid to ask for more. Such attitude can be viewed by Traditionalists and Boomers as rude and presumptuous. The biggest danger might be the impact that emotionally! unintelligent managers are having on the younger generations as a! result of their reactions and judgments. GenX and
" Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund 9
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
GenY employees leave managers and not organizations and managers inability to deal with the frustration that comes with managing the younger generation result in lost productivity, conict in the workplace and increased turnover. Avoiding the trap of understanding generational differences cannot be overstated. It is critical for to KNOW the new generation, connect with their preferred style and expectations. Entering into the conversation or situation,! understanding expectations and what emotion is driving their behavior is far more productive as oppose to jumping to a judgement based on a stereotype and style differences. It is important to take time and build the trusting relationship where each generation brings ahead their potentials and works towards the common goal. Summary With the upcoming demographic shift, the organizations trained to bridge the gap between traditionalists/boomers and GenX and GenY, mindful of their different values, will be able to succeed, attract, retain and engage the GenX and GenY, this talented generation of employees.
TALENT MANAGEMENT How to Train Across Multigenerational Workplace? Approximately 10% of all learning takes place in formal training.! Approximately 20% of learning comes from materials and access to IT systems such as books, manuals, procedures, systems, and embedded methodologies.! The employees learn by doing and reading using the information provided in both structured (ie. a website) and unstructured form.! 70% of learning occurs on the job.! Most of such learning occurs by talking with their managers, talking with peers, nding experts, and by doing mistakes. This is the traditional structure of learning outlined primarily by the older generations. The question is how to provide the GenX and GenYs with more learning opportunities in formal
" 10 Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
training and on-demand training through series of structured web-enabled job related modules, creating virtual mentors? The question is also how to create the desired shift from learning on the job and mentoring to effective self-training? The Performance and Capacity There is not noticeable deterioration in performance in workers across generations. The single factor that impacts the level of performance is training. Employers Attitudes to Training Older Workers There is an assumption about the older workers that they are less adaptable and less able to grasp new ideas or technologies. The older workers are often excluded from the training opportunities as employer normally calculates the return on investment. The invested training has to offset against the likely gains from the improved skills over the time. The similar concern may surround the younger workers who may be perceived as being early on in their career and more likely to change jobs in the near future. How to Design the Effective Training Policy Implementing a training policy framework serves as a facilitator of the training practices. It is essential to engage managers throughout the organization in this exercise. The basis for successful implementation of training programs is the training policy that emphasizes an equal access to training across multigenerational groups based on the organizational needs as skills development requirements. The rst step is outlining the mandatory training requirements at the organizational level (Security in the Field, Sexual Harassment Training, HIV Training, Diversity in a Workplace training). The well structured training will outline the training requirements for each job category and link it to the PAS work-plan. The existence of the precise matrix outlining skills needed for each job category will clearly identify employees training needs. Managers play an essential role in empowering the employees to design the training plan that would be reection of the gap analysis between existing and required skills for the job, keeping in mind career progression opportunities and cross training. This approach is of an utmost importance to GenX and GenY.
" 11 Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
Developing staff to train others The benets from in house Mentoring Program are far reaching. By working with Managers, the Talent Management group will identify and train Mentors in each business unit as well as develop the system to keep track of measurable impact of such program. This program would relate directly to job function and trainee would be provided with one on one consultative style coaching related directly to the job function. This approach would ensure the high performance and high level of engagement of the new employee, especially throughout the On-Boarding phase. The target group for these roles would be older workers which will add to their job satisfaction and engagement with the company. Designing knowledge database and Multimedia Learning Opportunities Designing the E-Learning programs E-Learning has rapidly taken stake in the global workforce for all industry sectors. An effective e-Learning strategy requires three main components: relevant and engaging course content, an effective platform for the delivery of courses, and an ability to manage employee learning. The e-Learning will be most benecial and cost effective in the area of mandatory training and skills building. Even though it takes time to design and develop, it is proved to be highly cost effective solution to standardize training procedures across an organization and drill down specic skill sets. It is well received by GenX and GenY and would be highly It would highly benecial in PECSS. Identify the agencies and outside learning centers There are number of highly specialized organizations that can provide high level of expertise for virtually any learning area. An effective Training policy will identify such areas of expertise that are not covered by in house training capacities. Webinars/Webcasts/Podcasts Talent Management Team will create a portal with various web-sites and advertise on a weekly basis web-cast series designed and targeted towards specic client group. For example, IMS would be offered series of lectures related to their job. TMT would also offer programs that would facilitate maintenance of license requirements. Social Networking In addition to promoting traditional Networking events, GenX and GenY have been drown to cyber networking groups such as Linkden, MySpace, FaceBook etc.
" 12 Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
Overcoming Generational Gap in the Workplace
Make it Interactive As different generations have different learning styles, it is important to design the training policy and training program that would foster interactive learning experience and use combination of variety of styles.
Learning and Career Development Across Generations
Traditionalist General Expectation s of Career Planning I am happy to be where I am. Baby Boomers My dedication and service have to be rewarded. Generation X It is about time to promote me! Generation Y/Z What do you mean I cannot be promoted yet. I have delivered the results I was asked to deliver.
Traditionalist Mix up different learning styles Informational learning style Traditional classroom setting utilizing predominantly lectures Excellent Mentors Excellent source of institutional knowledge and experience Receptive to one on one coaching Task specic
Baby Boomers Transformational learning style Traditional classroom learning extended to learning through participation, critical reection, reection and feedback
Generation X Self-Directed or Self-Paced Highly receptive to e-learning series of structured lectures Requires integration of technology and media in learning. Make it easy to access the information and industry procedures
Generation Y/Z Informal, incidental learning. Short attention span Requires integration of technology and media in learning (webinars, social networking sites, Avatars) Personalized learning through customized environment
" 13
Talent Management Team - Executive Ofce - United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund
You might also like
- Psychological Safety: The key to happy, high-performing people and teamsFrom EverandPsychological Safety: The key to happy, high-performing people and teamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Oxford Handbook of Modern German History (Helmut Walser Smith) (Z-Library)Document971 pagesThe Oxford Handbook of Modern German History (Helmut Walser Smith) (Z-Library)Sonico50% (2)
- Conversations With God, Book 3Document7 pagesConversations With God, Book 3Brisaiguy100% (3)
- MANAGING MILLENIALS - NV UploadDocument23 pagesMANAGING MILLENIALS - NV UploadNovianingtyastutiNo ratings yet
- IIM Ranchi - The Think TankDocument10 pagesIIM Ranchi - The Think TankKritibandhu SwainNo ratings yet
- Peran Strategis Kemampuan Belajar Mandiri Dalam Pengembangan SiswaDocument87 pagesPeran Strategis Kemampuan Belajar Mandiri Dalam Pengembangan SiswaMichaelHo100% (1)
- Lia Carney Knowdell Career ValuesDocument1 pageLia Carney Knowdell Career ValuesLia CarneyNo ratings yet
- Generations at Work: Motivating and Managing Today's WorkforceDocument16 pagesGenerations at Work: Motivating and Managing Today's WorkforcePam BeckermanNo ratings yet
- Navigating Change by Gy 2017Document37 pagesNavigating Change by Gy 2017illidanstormrage32No ratings yet
- Speaker: Dr. Nay Zin Latt Chairman: Business Group Hotel GroupDocument32 pagesSpeaker: Dr. Nay Zin Latt Chairman: Business Group Hotel GroupThe Vimokkha Online JournalNo ratings yet
- Indian Grassroots OrganizationsDocument13 pagesIndian Grassroots OrganizationsTanju RoyNo ratings yet
- Managing Multigen WorkforceDocument12 pagesManaging Multigen Workforceamirhabibpak9No ratings yet
- Intro To Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneurial BehaviorDocument24 pagesIntro To Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneurial Behaviormobile legendsNo ratings yet
- Personality & Values: Group 6Document10 pagesPersonality & Values: Group 6nishan01234No ratings yet
- Part 1 Understanding A Misunderstood Generation NEW EDITIONDocument28 pagesPart 1 Understanding A Misunderstood Generation NEW EDITIONVera GrigorieNo ratings yet
- Managing MillenialsDocument37 pagesManaging MillenialsElisa Maya SelfianaNo ratings yet
- BUSI271 Global Strategy: Analysis and Practice: Individual ReportDocument8 pagesBUSI271 Global Strategy: Analysis and Practice: Individual ReportPsixeya PNo ratings yet
- Kursus Ketua Polis Daerah Dec 3,2007Document89 pagesKursus Ketua Polis Daerah Dec 3,2007bakaipkkedahNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument18 pages1 - IntroductionEmily PhilipNo ratings yet
- Generations WorkplaceDocument32 pagesGenerations WorkplaceRanny Fitriani RosadiNo ratings yet
- 485 B 63 C 61954 CDocument36 pages485 B 63 C 61954 CAbong'o ChachaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalization On Organizational BehaviorDocument28 pagesImpact of Globalization On Organizational BehaviorRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Entrepreneurial ArchitectureDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - Entrepreneurial ArchitectureNabil MustaqimNo ratings yet
- Triangle of SuccessDocument45 pagesTriangle of SuccessAbdul AzisNo ratings yet
- Change ModelDocument16 pagesChange ModelDidi KurniadiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Culture: Culture Refers To The Symbolic or Expressive Side of Human LifeDocument13 pagesOrganizational Culture: Culture Refers To The Symbolic or Expressive Side of Human LifeRahul SanghviNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - Social EntrepreneurshipDocument56 pagesClass 3 - Social EntrepreneurshipSelina Sofie ArnelundNo ratings yet
- Opportunity AnalysisDocument35 pagesOpportunity Analysisdocziau86100% (1)
- New-Age Practices For Millennials and Post-MillennialsDocument6 pagesNew-Age Practices For Millennials and Post-Millennialsmanmeet kaurNo ratings yet
- Teaching The Millenials and The Z GenerationDocument38 pagesTeaching The Millenials and The Z GenerationIKA HASANAHNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Change Management: By: M KamranDocument42 pagesInnovation and Change Management: By: M Kamranjisanus5salehinNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 The Evolution of LeadershipDocument20 pagesLECTURE 2 The Evolution of LeadershipNeovi TeogangcoNo ratings yet
- OB Culture 18Document21 pagesOB Culture 18Sushreeta PalNo ratings yet
- Global Workplace: The Coming FutureDocument16 pagesGlobal Workplace: The Coming FutureabigailNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries: NB. There'S No User Manual !Document46 pagesPreliminaries: NB. There'S No User Manual !Swapnil JainNo ratings yet
- People Skills (Profed10) Mo.6Document15 pagesPeople Skills (Profed10) Mo.6Maria ElaNo ratings yet
- 1 Human Relations - Nature of The PeopleDocument26 pages1 Human Relations - Nature of The Peopleრაქსშ საჰაNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument15 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of NeedsAlban Williams JeromeNo ratings yet
- Behaviour at Work Case StudyDocument13 pagesBehaviour at Work Case StudyainNo ratings yet
- Adapted and Development by DR Dallas L. Holmes, Extension Specialist Diversity and Civil RightsDocument30 pagesAdapted and Development by DR Dallas L. Holmes, Extension Specialist Diversity and Civil Rightsrajeshraj0112No ratings yet
- Gerenciando La Diversidad CulturalDocument48 pagesGerenciando La Diversidad CulturalFreeLatinBirdNo ratings yet
- Birkman - How Generational Differences Impact Organizations & TeamsDocument15 pagesBirkman - How Generational Differences Impact Organizations & TeamsCansu ÇördükNo ratings yet
- BA-Human Behavior: Open Systems View of OrganizationDocument21 pagesBA-Human Behavior: Open Systems View of OrganizationAngelie JalandoniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Family Business Midterm CoverageDocument83 pagesUnderstanding Family Business Midterm CoverageJoebet Balbin BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Generation Differences and HRMDocument8 pagesGeneration Differences and HRMAmira Abdulshikur JemalNo ratings yet
- Managing A Multi-Generational WorkforceDocument8 pagesManaging A Multi-Generational WorkforceTota Simatupang100% (1)
- 6 Dimensions ExplanationDocument10 pages6 Dimensions ExplanationGaurav KherodiaNo ratings yet
- Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Understanding Different CountriesDocument10 pagesHofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Understanding Different CountriesAyesha HaroonNo ratings yet
- Biological Characteristic Environmental Factors Org. & Individual FactorsDocument18 pagesBiological Characteristic Environmental Factors Org. & Individual FactorsSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- WT Big Reset 22 10 Sprint 7 Culture and Organizational Performance ReportDocument31 pagesWT Big Reset 22 10 Sprint 7 Culture and Organizational Performance ReportKholoudNo ratings yet
- The Basic Functions of Organizational CultureDocument25 pagesThe Basic Functions of Organizational CulturesanhaaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Renewal CycleDocument24 pagesOrganizational Renewal CycleDea Lyn Bacula100% (2)
- Chapter 1 The Entrepreneurial MindsetDocument50 pagesChapter 1 The Entrepreneurial MindsetFranklin Anak Ejam H21A2052No ratings yet
- Adam's Equity Theory of MotivationDocument8 pagesAdam's Equity Theory of MotivationJnanusNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument189 pagesOrganizational BehaviorManish ShawNo ratings yet
- Group Behaviour: Human Relations at Work: Social DimensionsDocument41 pagesGroup Behaviour: Human Relations at Work: Social DimensionshunterboyrajNo ratings yet
- Leaping The Generational GapDocument42 pagesLeaping The Generational Gappadmajakarri1234No ratings yet
- T2 - The Entrepreneurial MindsetDocument50 pagesT2 - The Entrepreneurial Mindseta23a1665No ratings yet
- Hofstede'S Six Dimensions of Culture: PDI Characteristics TipsDocument8 pagesHofstede'S Six Dimensions of Culture: PDI Characteristics TipsJemilyn Cervantes-SegundoNo ratings yet
- Organization Theory & BehaviorDocument35 pagesOrganization Theory & Behaviorasad siddiqui71% (7)
- Start with the Answer: And Other Wisdom for Aspiring LeadersFrom EverandStart with the Answer: And Other Wisdom for Aspiring LeadersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pilar Company Bank Reconciliation Statement SEPTEMBER 30, 2020 Balance Per Bank Statement Add: Deposit in Transit Receipts Not Yet Deposited Total: P139,314.20 Deduct: Outstanding ChecksDocument16 pagesPilar Company Bank Reconciliation Statement SEPTEMBER 30, 2020 Balance Per Bank Statement Add: Deposit in Transit Receipts Not Yet Deposited Total: P139,314.20 Deduct: Outstanding ChecksStudent Core GroupNo ratings yet
- QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct Bank and Manholes PDFDocument7 pagesQCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct Bank and Manholes PDFbryanpastor106100% (1)
- Presentation For Research ProposalDocument22 pagesPresentation For Research ProposalchocieyNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1016 - b978-012374473-9.00026-6) Houde, E.D. - Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences - Fish LarvaeDocument11 pages(Doi 10.1016 - b978-012374473-9.00026-6) Houde, E.D. - Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences - Fish LarvaeAnkeet KumarNo ratings yet
- M3u@watchtv - Best 453Document6 pagesM3u@watchtv - Best 453alexandreavila2015No ratings yet
- Introduction To Damped ExperimentDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Damped ExperimentLeon TetemuNo ratings yet
- PDF Cellular and Molecular Basis of Mitochondrial Inheritance Mitochondrial Disease and Fitness Peter Sutovsky Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Cellular and Molecular Basis of Mitochondrial Inheritance Mitochondrial Disease and Fitness Peter Sutovsky Ebook Full Chaptergeoffrey.radsky250100% (2)
- Theory II-lecture 1Document28 pagesTheory II-lecture 1Lowie Torres TonioNo ratings yet
- Introducing Cultural Historical Theory: Main Concepts and Principles of Genetic Research MethodologyDocument41 pagesIntroducing Cultural Historical Theory: Main Concepts and Principles of Genetic Research MethodologyNikolai VeresovNo ratings yet
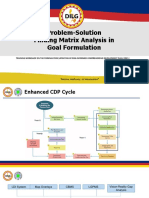
- 2 PSFM Goal FormulationDocument13 pages2 PSFM Goal FormulationKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- PSM TutorialDocument13 pagesPSM TutorialAyu Nawang AsriNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological Universityvifaket581No ratings yet
- Resilience in Parents of Children With IDocument25 pagesResilience in Parents of Children With IVrittee ParikhNo ratings yet
- Joydeep Saha: Summary of QualitiesDocument3 pagesJoydeep Saha: Summary of QualitiesjoydeepsahaNo ratings yet
- Toxic Relationships: EnmeshmentDocument1 pageToxic Relationships: EnmeshmentIrene Fernandez PiñeiroNo ratings yet
- Hittite Vocabulary BookDocument272 pagesHittite Vocabulary BookCodyBeatonNo ratings yet
- How To Enjoy Art by Street, BenDocument160 pagesHow To Enjoy Art by Street, BenJocaAnaNo ratings yet
- RTS - B.Tech (IT) - 202301 - 015 - S05 - S07 - 00 - 01Document17 pagesRTS - B.Tech (IT) - 202301 - 015 - S05 - S07 - 00 - 01Vijay Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- KooBits - Digital Media Projects Win $14m FundingDocument2 pagesKooBits - Digital Media Projects Win $14m FundingKooBits_Edu_3137No ratings yet
- Mega Datasheet Mega Enterprise Architecture enDocument12 pagesMega Datasheet Mega Enterprise Architecture enBunpot ThanaboonsombutNo ratings yet
- Answer: B: Selected/modified From Brown Et Al: Chemistry The Central Science, 10e, 12e, 13e TestbanksDocument6 pagesAnswer: B: Selected/modified From Brown Et Al: Chemistry The Central Science, 10e, 12e, 13e Testbanksفاطمة كليبNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing:: Reading and Thoughtfully CorrespondingDocument34 pagesLetter Writing:: Reading and Thoughtfully CorrespondingsyedmuzammilaliNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument27 pagesDX DiagAlkithyar AdithyargioNo ratings yet
- 15 4 Example Field Level Monitoring ChecklistDocument3 pages15 4 Example Field Level Monitoring ChecklistAbi RajanNo ratings yet
- HPE 3PAR StoreServ 8000 Storage Drive Support Reference-C04895558Document24 pagesHPE 3PAR StoreServ 8000 Storage Drive Support Reference-C04895558Diego ChameNo ratings yet
- Altercasting Theory Long ExplainationDocument12 pagesAltercasting Theory Long ExplainationDorepe IconNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Nozzle - Test: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument6 pagesFuel Injection Nozzle - Test: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- MOS FOR Plaster MetitoDocument7 pagesMOS FOR Plaster Metitoeng mohamad husamNo ratings yet