Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditions of The Large Intestine
Uploaded by
Lheidaniel MMM.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditions of The Large Intestine
Uploaded by
Lheidaniel MMM.Copyright:
Available Formats
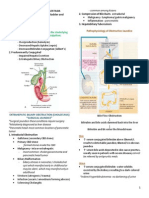
CONDITIONS OF THE LARGE INTESTINE
Ulcerative Colitis - Recurrent ulcerative and inflammatory condition of the mucosal and submucosal layers of the colon and rectum - The colon becomes edematous and develops bleeding ulcerations - Scarring develops overtime with impaired water absorption and loss of elasticity Clinical Manifestations SEVERE diarrhea (10-20 liquid stools/day) with Rectal bleeding 1. Weight loss 2. Fever 3. Anorexia 4. Anemia and Hypocalcemia 5. Dehydration 6. LLQ Abdominal pain and cramping 7. Tenesmus Assessment and Diagnostic Findings - assess for tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension, fever and pallor, level of hydration and nutritional status - stool exam- (+) for blood - hematocrit and hemoglobin and albumin - WBC - Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy - Barium enema - MRI and CT scan Complications - toxic megacolon, perforation, bleeding, osteoporotic fracture
Nursing Interventions For Cd And Uc 1. Maintain NPO during the active phase 2. Monitor for complications like severe bleeding, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance 3. Monitor bowel sounds, stool and blood studies 4. Restrict activities= rest and comfort 5. Administer IVF, electrolytes and TPN if prescribed Monitor complications of diarrhea 6. Instruct the patient to AVOID gas-forming foods, MILK products and foods such as whole grains, nuts, RAW fruits and vegetables especially SPINACH, pepper, alcohol and caffeine 7. Diet progression- clear liquid LOW residue, high protein diet 8. Administer drugs- anti-inflammatory, antibiotics, steroids, bulk-forming agents and vitamin/iron supplements
Appendicitis - Inflammation of the vermiform appendix
Etiology: usually fecalith, lymphoid hyperplasia, foreign body and helminthic obstruction Pathophysiology - Obstruction of lumen increased pressure decreased blood supply bacterial proliferation and mucosal inflammation ischemia necrosis rupture Assessment Findings 1. Abdominal pain: begins in the umbilicus then localizes in the RLQ (Mc Burneys point) 2. Anorexia 3. Nausea and Vomiting 4. Fever 5. Rebound tenderness and abdominal rigidity (if perforated) 6. Constipation or diarrhea
You might also like
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Patho CardsDocument195 pagesNursing Patho Cardsgiogmail100% (1)
- DR A S KumarDocument41 pagesDR A S KumardrmkumarNo ratings yet
- Gastric Cancer: Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesGastric Cancer: Surgical ManagementMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic DiarrhoeaDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic DiarrhoeaVipul Nagnesia100% (2)
- Urology NotesDocument8 pagesUrology NotesCzarinah Bacuado67% (3)
- Disorders of The Renal System - SASAN FINAL - OTL SDocument47 pagesDisorders of The Renal System - SASAN FINAL - OTL SJAN KRISTIAN JIMENEA TULIBASNo ratings yet
- Additional HandoutsDocument10 pagesAdditional HandoutsMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System: BY Pranjal Kulkarni Neha ManeDocument85 pagesHepatobiliary System: BY Pranjal Kulkarni Neha ManeGurneetNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study GuideNataraj LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Urinary System Urinary CalculiDocument5 pagesDisorders of Urinary System Urinary CalculiFreeNursingNotes100% (3)
- Acute Abdomen: Part I: Intestinal Obstruction/Bowel Infarction/ Constipation (And How To Assess and Initiate Management)Document63 pagesAcute Abdomen: Part I: Intestinal Obstruction/Bowel Infarction/ Constipation (And How To Assess and Initiate Management)Rumana IslamNo ratings yet
- CirrhoisDocument6 pagesCirrhoisAslimah RakimNo ratings yet
- Responsesm To Metabolic Gi and Liver AlterationsDocument62 pagesResponsesm To Metabolic Gi and Liver AlterationsEdelen GaleNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Janice Nicklay Catalan M.DDocument27 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis: Janice Nicklay Catalan M.DrianurjanahNo ratings yet
- Nursing MGT of PT With Lower Git DisordersDocument65 pagesNursing MGT of PT With Lower Git DisordersCarlos LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Sheep and Goat Internal DiseasesDocument5 pagesSheep and Goat Internal DiseasesJessica Elizabeth JosephNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Reproduction System 2010Document39 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis: Reproduction System 2010Anonymous Af24L7No ratings yet
- Osces For Medical Students, Volume 2 Second EditionDocument41 pagesOsces For Medical Students, Volume 2 Second EditionNaeem Khan100% (3)
- Surgical Ho Guide PDFDocument76 pagesSurgical Ho Guide PDFMardiana KamalNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology UPDATEDDocument21 pagesGastroenterology UPDATEDmuradkhanNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument22 pagesCirrhosis of LiverKrini Tandel50% (2)
- Extrahepatic CholestasisDocument9 pagesExtrahepatic CholestasisMatet MonjeNo ratings yet
- PP PancreatitisDocument25 pagesPP PancreatitisBrahmayda Wiji LestariNo ratings yet
- Bile, Bile Duct and Pancreatic DiseaseDocument82 pagesBile, Bile Duct and Pancreatic Diseaseshahrul rahmanNo ratings yet
- Pead 3 - Abdominal Pain and VommitingDocument22 pagesPead 3 - Abdominal Pain and Vommitingbbyes100% (1)
- It 2 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersDocument54 pagesIt 2 - Signs and Symptoms of Git Disorderspikaanisa100% (9)
- Urinary Tract DisordersDocument54 pagesUrinary Tract Disorderssharon ocharaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis - Gallbladder Inflammation, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument6 pagesCholecystitis - Gallbladder Inflammation, Symptoms, TreatmentJubitta JobyNo ratings yet
- 01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersDocument51 pages01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersRere AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Renal NursingDocument11 pagesRenal NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (10)
- Cirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesDocument72 pagesCirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutNo ratings yet
- With Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Document72 pagesWith Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Ainun JaariahNo ratings yet
- Gastroduodenal Disorders: Suazo, Trisha Mae S. 3BSN-ADocument12 pagesGastroduodenal Disorders: Suazo, Trisha Mae S. 3BSN-AKenneth OpinaNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument8 pagesLiver CirrhosisgoyaNo ratings yet
- Renal Colic: Prepared By: Regine Anne B. PanganibanDocument19 pagesRenal Colic: Prepared By: Regine Anne B. PanganibanRej PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument25 pagesAcute Abdomenoandy2012No ratings yet
- 6 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+With+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionDocument4 pages6 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+With+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- GI Stressors II StudentDocument67 pagesGI Stressors II StudentBiji Thomas GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 4oral-Fecal DsesDocument153 pages4oral-Fecal Dsesyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary DiseaseDocument60 pagesHepatobiliary DiseaseFirdaus AslamNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Dr. Ali A. Ramadhan M.B.CH.B., Fibms, Fkbms (G & H)Document27 pagesDiarrhea: Dr. Ali A. Ramadhan M.B.CH.B., Fibms, Fkbms (G & H)Ahmed NazarNo ratings yet
- GIT DisordersDocument171 pagesGIT DisordersKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- 4 Care of Clients With Ibs Malabsorp Ulcerative Colitis Crohns FinalDocument35 pages4 Care of Clients With Ibs Malabsorp Ulcerative Colitis Crohns Finalevren yilmazNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing9 (Gastrointestinal Disorder)Document52 pagesPediatric Nursing9 (Gastrointestinal Disorder)Avril GumpalNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument35 pagesAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction2Document26 pagesIntestinal Obstruction2TwinkleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of DiarrheaDocument30 pagesNursing Care of DiarrheayustiNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument3 pagesOral RevalidaJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Pediatric GI DisturbancesDocument59 pagesWeek 7 - Pediatric GI DisturbancesLeyla GalyanoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The StomachDocument26 pagesDisorders of The StomachAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis - Crohn's DiseaseDocument68 pagesUlcerative Colitis - Crohn's DiseaseZulfan RizkyNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDocument35 pagesGenitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDarell M. BookNo ratings yet
- PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedDocument43 pagesPEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedJumbe MohamedNo ratings yet
- Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsDocument3 pagesSalmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsKelvin BolusanNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaDocument38 pagesNeonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaAlex100% (1)
- 01 14 2021 GERD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Irritable Bowel Syndrome ALLENDocument66 pages01 14 2021 GERD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Irritable Bowel Syndrome ALLENMikey ZhitnitskyNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandUlcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Angels We Have Heard On HighDocument3 pagesAngels We Have Heard On HighLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Silent NightDocument1 pageSilent NightLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Abegail BautistaDocument1 pageAbegail BautistaLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Chords Church All EliaDocument1 pageChords Church All EliaLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- ChordschurchalleliaDocument1 pageChordschurchalleliaLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- ALLELUIADocument1 pageALLELUIALheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- CM DB BBM Eb AbDocument2 pagesCM DB BBM Eb AbLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- AlleluiaDocument1 pageAlleluiaLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- ALLELUIADocument1 pageALLELUIALheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Purpose Dea SCH C-IiDocument1 pageGeneric Name Brand Name Purpose Dea SCH C-IiLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Eb Gm7 Ab BBDocument2 pagesEb Gm7 Ab BBLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument4 pagesNursing ManagementLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- 4th Tranche ArmmcDocument2 pages4th Tranche ArmmcLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Repeat Chorus 2xDocument2 pagesRepeat Chorus 2xLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- ChorusDocument3 pagesChorusLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- As High As The HeavensDocument2 pagesAs High As The HeavensLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Professional Adjustment and Nursing JurisprudenceDocument8 pagesProfessional Adjustment and Nursing JurisprudenceLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Jake 2 TooolsDocument8 pagesJake 2 TooolsLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- ALWAYS BE MY BABY CHORDS (Ver 2) by David Cook at Ultimate-GuitarDocument2 pagesALWAYS BE MY BABY CHORDS (Ver 2) by David Cook at Ultimate-GuitarLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet