Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiet Inspiration
Quiet Inspiration
Uploaded by
Michael LewisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiet Inspiration
Quiet Inspiration
Uploaded by
Michael LewisCopyright:
Available Formats
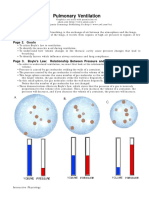
QUIET INSPIRATION Diaphragm.
External intercostals, parasternal intercartileganous muscles contract chest walls expands thoracic volume increases intrathoracic pressure becomes more negative alveolar transmural pressure gradient increases alveoli expand alveolar pressure falls below atmospheric pressure air flows into the alveoli
FORCED INSPIRATION Diaphragm. External intercostals, parasternal intercartileganous, scalaneous anterior and medius, and sternocleidomastoid muscles contract chest walls expands thoracic volume increases intrathoracic pressure becomes MORE negative alveolar transmural pressure gradient increases alveoli expand alveolar pressure falls below atmos. pressure air flows into the alveoli FORCED EXPIRATION Inspiratory muscles relax and intercostal muscles and quadratus lumborum contract thoracic vol. decreases intrathoracic pressure becomes positive alveolar transmural pressure gradient decreases alveoli recoil alveolar pressure rises above atmos. Pressure air flows out of the lungs
QUIET EXPIRATION Inspiratory muscles relax thoracic vol. decreases intrathoracic pressure becomes less negative alveolar transmural pressure gradient decreases alveoli recoil alveolar pressure rises above atmos. Pressure air flows out of the lungs
You might also like
- Chest Tubes: From Indication To RemovalDocument49 pagesChest Tubes: From Indication To Removaldara octavianiNo ratings yet
- End of Respiration, Beginning of Reproduction TranscriptionDocument7 pagesEnd of Respiration, Beginning of Reproduction TranscriptionmarthafaragNo ratings yet
- Breathing During Singing PDFDocument9 pagesBreathing During Singing PDFPaulaRiveroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument79 pagesRespiratory AssessmentKarlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Your 12 Week Guide to the Gym: From Your Armchair to a Complete Body Workout in 12 WeeksFrom EverandYour 12 Week Guide to the Gym: From Your Armchair to a Complete Body Workout in 12 WeeksNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Lung and ChestDocument50 pagesAssessment of Lung and ChestAbdurehman Ayele100% (1)
- Mechanical VentilationDocument262 pagesMechanical VentilationShalini Garg0% (1)
- 1.anatomy & Physiology of AirwayDocument54 pages1.anatomy & Physiology of Airwayqwerty hrNo ratings yet
- Diaphragmatic BreathDocument10 pagesDiaphragmatic BreathPhooi Yee LauNo ratings yet
- 2-Respiratory OrderDocument31 pages2-Respiratory OrderCumar TimirNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Part IbDocument40 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Part IbKristian CadaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Inspiration Muscles of Expiration: Principal Accessory Quiet Breathing Active BreathingDocument2 pagesMuscles of Inspiration Muscles of Expiration: Principal Accessory Quiet Breathing Active BreathingDeti ParidlahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Dr. Okon MRCSDocument15 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Dr. Okon MRCSEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة - الثالثة الجاهزة - فسيو - بلك - التنفسي - دفعة - خامسة -Document26 pagesالمحاضرة - الثالثة الجاهزة - فسيو - بلك - التنفسي - دفعة - خامسة -bessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- A&P - PHYSIOLOGY OF RESPIRATION - InspirationDocument32 pagesA&P - PHYSIOLOGY OF RESPIRATION - InspirationYAMINIPRIYAN100% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology - 2021Document39 pagesRespiratory Physiology - 2021Abdikafar AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PresentationDocument18 pagesAnatomy PresentationZaliaSubplace S5357No ratings yet
- Vsp-Ug-5 (RS)Document59 pagesVsp-Ug-5 (RS)6qhx62pr42No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation PDFDocument11 pagesPulmonary Ventilation PDFSrsblackieNo ratings yet
- The Mechanism of Respiration.Document12 pagesThe Mechanism of Respiration.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument340 pagesRespiratory SystemBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- VentilatorsDocument20 pagesVentilatorsYechale TafereNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-1Document84 pagesRespiratory System-1pranjal raiNo ratings yet
- Diaphragmatic Breathing vs. Belly BreathingDocument8 pagesDiaphragmatic Breathing vs. Belly BreathingTatiana JosanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Maysa Fall2015 PDFDocument126 pagesRespiratory Maysa Fall2015 PDFbaasheNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanism of RespirationDocument22 pages1 Mechanism of RespirationAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Respiratory VolumesDocument10 pagesVentilation and Respiratory Volumesalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Intercambio de Oxígeno Y Dióxido de CarbonoDocument2 pagesIntercambio de Oxígeno Y Dióxido de CarbonoAna CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Lung Biomechanics of BreathingDocument55 pagesStructure of The Lung Biomechanics of BreathingMohd Yunus KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Retraction: Intercostal and Epigastric - Dea Natalia - 130110110190 - E3/RespiDocument2 pagesRetraction: Intercostal and Epigastric - Dea Natalia - 130110110190 - E3/RespiMarshel BudiarsaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationapi-276992608No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument43 pagesRespiratory SystemAbuhuraira RafiqNo ratings yet
- How The Lungs Work?Document1 pageHow The Lungs Work?John Marlo CatibogNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of RespirationDocument17 pagesMechanics of Respirationezeudunicholas16No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Physiology: By: Jammaella Vernice T. G Omez, PTRPDocument87 pagesPulmonary Physiology: By: Jammaella Vernice T. G Omez, PTRPRhea Anne DemoticaNo ratings yet
- Lung Capacities / Volumes: Danielle AlleyneDocument18 pagesLung Capacities / Volumes: Danielle AlleyneDanielle M A AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm ArishaDocument3 pagesDiaphragm ArishaAreesha ZubairNo ratings yet
- Preclinical Speech Science Chapter 2 PowerPointDocument90 pagesPreclinical Speech Science Chapter 2 PowerPointNatalieNo ratings yet
- Exame Fisico #3Document24 pagesExame Fisico #3unidade uapsfNo ratings yet
- Respi NotesDocument10 pagesRespi NotesAllyza Marie PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Thoracic Cavity: Atmospheric Pressure Intrapulmonary PressureDocument4 pagesThe Thoracic Cavity: Atmospheric Pressure Intrapulmonary PressureNylaxor Erbmeicet OicacaNo ratings yet
- 18 - Mechanics of Respiration - Prof. Abdelrahman Fahmy - 2020Document5 pages18 - Mechanics of Respiration - Prof. Abdelrahman Fahmy - 2020Hossam BaniisNo ratings yet
- Chest PBLDocument2 pagesChest PBLRamish IrfanNo ratings yet
- AND Lung Ventilation: VolumesDocument27 pagesAND Lung Ventilation: VolumesShaina OturdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Mechanics of Breathing-1Document35 pagesChapter 2 - Mechanics of Breathing-1lolazoNo ratings yet
- Breathing MechanismsDocument5 pagesBreathing MechanismsStephan SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Jalan NafasDocument54 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Jalan NafasFajhriaLeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory System-2020Document27 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory System-2020Izlan AidilNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument54 pagesRespiratory Assessmentraima ayazNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Departement of Physiology Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument142 pagesRespiratory System: Departement of Physiology Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara292Vien HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Breathing Movement Bio 2022-2023Document24 pagesBreathing Movement Bio 2022-2023Kara NewmanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pages2.4 The Parts of The Respiratory SystemAmelia MayNo ratings yet
- Breathing Mechanism: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerDocument18 pagesBreathing Mechanism: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerRJ Noor JanNo ratings yet
- Ad TheDocument2 pagesAd TheHIKRIENo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Renal ReviewDocument39 pagesRespiratory and Renal ReviewTony PadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: DR T. Mpofana Mpofana@ukzn - Ac.zaDocument50 pagesRespiratory System: DR T. Mpofana Mpofana@ukzn - Ac.zaSindile MchunuNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercises: Mazyad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBreathing Exercises: Mazyad AlotaibiekaNo ratings yet
- g8 Breathing SystemDocument16 pagesg8 Breathing Systemhiroshikit12No ratings yet
- Breathe In, Breathe Out: Learning About Your LungsFrom EverandBreathe In, Breathe Out: Learning About Your LungsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)