Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Git Cheat Sheet
Git Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
mariam070Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Git Cheat Sheet
Git Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
mariam070Copyright:
Available Formats
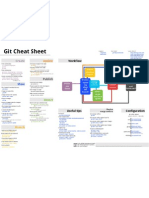
Git Cheat Sheet
http://git.or.cz/
Remember: git command --help Global Git configuration is stored in $HOME/.gitconfig (git config --help)
Commands Sequence
the curves indicate that the command on the right is usually executed after the command on the left. This gives an idea of the flow of commands someone usually does with Git.
CREATE
BROWSE
CHANGE
REVERT
UPDATE
BRANCH
init clone
Create
From existing data
Concepts Git Basics
master origin HEAD HEAD^ HEAD~4 : default development branch : default upstream repository : current branch : parent of HEAD : the great-great grandparent of HEAD
status log show diff branch
reset checkout revert
pull fetch merge am
checkout branch
commit
COMMIT
push
format-patch
PUBLISH
cd ~/projects/myproject git init git add .
From existing repo
git clone ~/existing/repo ~/new/repo git clone git://host.org/project.git git clone ssh://you@host.org/proj.git
Show
Files changed in working directory
Revert
git reset --hard
Return to the last committed state
!
you cannot undo a hard reset
git status git diff
Revert the last commit
Update
Fetch latest changes from origin
Publish
Commit all your local changes
Changes to tracked files What changed between $ID1 and $ID2
git revert HEAD
Creates a new commit
Revert specific commit
git fetch
(but this does not merge them).
git commit -a
Prepare a patch for other developers
git revert $id
Fix the last commit
Creates a new commit
Pull latest changes from origin
git diff $id1 $id2 git log
git pull
History of changes History of changes for file with diffs
git commit -a --amend
(does a fetch followed by a merge)
git format-patch origin git push
(after editing the broken files)
Apply a patch that some sent you
Push changes to origin
Checkout the $id version of a file
git am -3 patch.mbox
git log -p $file $dir/ec/tory/ git blame $file git show $id
git checkout $id $file
(in case of a conflict, resolve and use git am --resolved )
Who changed what and when in a file A commit identified by $ID A specific file from a specific $ID
Branch
Switch to the $id branch
Mark a version / milestone
git tag v1.0
git checkout $id git checkout $branch2 git merge branch1
Resolve Merge Conflicts
Finding regressions
To view the merge conclicts
(complete conflict diff) git diff (against base file) git diff --base $file (against your changes) git diff --ours $file (against other changes) git diff --theirs $file
git show $id:$file git branch
Useful Commands
Merge branch1 into branch2
git bisect start git bisect good $id git bisect bad $id git bisect bad/good git bisect visualize git bisect reset
(to start) ($id is the last working version) ($id is a broken version) (to mark it as bad or good) (to launch gitk and mark it) (once you're done)
All local branches
(star '*' marks the current branch)
Create branch named $branch based on the HEAD
git branch $branch
To discard conflicting patch
Cheat Sheet Notation
Create branch $new_branch based on branch $other and switch to it Delete branch $branch
Check for errors and cleanup repository
git reset --hard git rebase --skip
After resolving conflicts, merge with
git checkout -b $new_branch $other
git fsck git gc --prune
Search working directory for foo()
$id : notation used in this sheet to represent either a commit id, branch or a tag name $file : arbitrary file name $branch : arbitrary branch name
git branch -d $branch
git grep "foo()"
git add $conflicting_file git rebase --continue
(do for all resolved files)
Zack Rusin Based on the work of: Sbastien Pierre Xprima Corp.
You might also like
- Entity Framework Core Cheat Sheet.Document3 pagesEntity Framework Core Cheat Sheet.Osempu100% (2)
- Understand JavaScript's "This" With Clarity, and Master It - JavaScript Is SexyDocument55 pagesUnderstand JavaScript's "This" With Clarity, and Master It - JavaScript Is Sexyutkarsh9978No ratings yet
- Maven Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMaven Cheat SheetMonica GellerNo ratings yet
- ASME RAM 1 2013 Reliability, Availability PDFDocument25 pagesASME RAM 1 2013 Reliability, Availability PDFJiss Mathew50% (2)
- Git Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageGit Quick ReferenceJuan Pablo Justiniano100% (1)
- Git Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGit Cheat SheetshawnjgoffNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet Git Commands 01Document2 pagesCheatsheet Git Commands 01giannis9pavlopoulos9No ratings yet
- A Git Cheat Sheet (Git Command Reference) - A Git Cheat Sheet and Command ReferenceDocument14 pagesA Git Cheat Sheet (Git Command Reference) - A Git Cheat Sheet and Command ReferenceMohd AzahariNo ratings yet
- Git Cheat Sheet EducationDocument2 pagesGit Cheat Sheet EducationWaldon Hendricks50% (2)
- AngularCheatSheet DNCMagazineDocument14 pagesAngularCheatSheet DNCMagazineFernando De FreitasNo ratings yet
- Git CheatsheetDocument2 pagesGit Cheatsheetgines100% (3)
- Git Cheatsheet r2v1 PDFDocument6 pagesGit Cheatsheet r2v1 PDFRakotomalala Mamy TianaNo ratings yet
- GIT Basics PDFDocument126 pagesGIT Basics PDFCosticã Pardaillan Lupu100% (1)
- Git Concepts SimplifiedDocument27 pagesGit Concepts SimplifiedChin BimNo ratings yet
- Git CheatsheetDocument1 pageGit CheatsheetIndrajeetNo ratings yet
- Linux Certification Practice Quiz 1-3Document9 pagesLinux Certification Practice Quiz 1-3LHNo ratings yet
- Top GIT Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesTop GIT Interview QuestionmagillaniNo ratings yet
- Real Questions, 100% Passing Guaranteed: 1Z0-808 Exam: Java SE 8 Programmer IDocument11 pagesReal Questions, 100% Passing Guaranteed: 1Z0-808 Exam: Java SE 8 Programmer IMohammed Al ataNo ratings yet
- Git CheatsheetDocument1 pageGit CheatsheetVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Programming in ColdFusionFrom EverandObject-Oriented Programming in ColdFusionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Making Changes Reviewing Changes: Version Control Cheat Sheet For Git WorkflowsDocument1 pageMaking Changes Reviewing Changes: Version Control Cheat Sheet For Git Workflowsfelm07No ratings yet
- Getting Started With BitbucketDocument9 pagesGetting Started With BitbucketAmit Sharma100% (1)
- Spring FrameworkDocument973 pagesSpring Frameworkbabith100% (1)
- Git Cheatsheet EN Grey PDFDocument2 pagesGit Cheatsheet EN Grey PDFCarlos Ivan CastroNo ratings yet
- The Essential Debugging JavaScript Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesThe Essential Debugging JavaScript Cheat Sheetlugordon100% (2)
- React Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesReact Cheat SheetVikram BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Cucumber Regular Expressions Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCucumber Regular Expressions Cheat SheetJoão SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!Document50 pagesBootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!BL Pipas100% (2)
- Restful Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesRestful Cheat SheetErique Bomfim100% (1)
- Regex Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesRegex Cheat SheetjohnsolarpanelsNo ratings yet
- Java Training-Spring FrameworkDocument57 pagesJava Training-Spring FrameworkDuy Chuong HuynhNo ratings yet
- VSCode Shortcuts CheatSheetDocument51 pagesVSCode Shortcuts CheatSheetMarko TodorovicNo ratings yet
- Java Concurency in PracticeDocument234 pagesJava Concurency in PracticeDagim NewayNo ratings yet
- Python Decorators PDFDocument6 pagesPython Decorators PDFRajendra BuchadeNo ratings yet
- Es6 Cheatsheet PDFDocument3 pagesEs6 Cheatsheet PDFZaha Kelloud100% (1)
- Javascript Programs OnlyDocument48 pagesJavascript Programs OnlyLokesh VermaNo ratings yet
- GroovyDocument904 pagesGroovyhugoknight0710No ratings yet
- Spring Web FlowDocument6 pagesSpring Web FlowThuy NhoNo ratings yet
- DB2 IntroductionDocument423 pagesDB2 IntroductionPriya EkambaramNo ratings yet
- ISPF TrainingDocument40 pagesISPF TrainingAntony100% (1)
- Terraform Cheat Sheet-1 220722 122745Document2 pagesTerraform Cheat Sheet-1 220722 122745pappypavanNo ratings yet
- Notes On Selenium WebDriverDocument12 pagesNotes On Selenium WebDrivervvenkat123No ratings yet
- Search and Replace: ST ND RDDocument1 pageSearch and Replace: ST ND RDperaNo ratings yet
- Junit Testing Framework ArchitectureDocument10 pagesJunit Testing Framework ArchitectureRekha Perumal VijayanNo ratings yet
- Entity FrameworkDocument154 pagesEntity FrameworkraoNo ratings yet
- Narayanan Palani - Selenium Webdriver Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesNarayanan Palani - Selenium Webdriver Cheat SheetHaleem.No ratings yet
- Selenium Cheat Sheet - Download in PDF & JPG Format - IntellipaatDocument7 pagesSelenium Cheat Sheet - Download in PDF & JPG Format - Intellipaatjbala64No ratings yet
- Docker Commands Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDocker Commands Cheat SheetVikram ReddyNo ratings yet
- Git MaterialDocument23 pagesGit MaterialSrinath SaiNo ratings yet
- C 6 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageC 6 Cheat SheetEmilyNo ratings yet
- Git Basic GoodDocument20 pagesGit Basic GoodRajendra Kumar100% (1)
- Entity Framework Interview Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesEntity Framework Interview Questions With AnswersShivprasad Koirala100% (5)
- Regular ExpressionsDocument9 pagesRegular ExpressionsThi HaNo ratings yet
- Git Cheat Sheet - Wall Skills1Document1 pageGit Cheat Sheet - Wall Skills1jesusNo ratings yet
- GitcheatsheetDocument1 pageGitcheatsheetBob YaoNo ratings yet
- Quickref Me GitDocument3 pagesQuickref Me GitDaksh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Objective C SuccinctlyDocument111 pagesObjective C Succinctlytwenty_sevenNo ratings yet
- Andy in AlgeriaDocument227 pagesAndy in Algeriakzelda97% (68)
- Cplusplus SuccinctlyDocument123 pagesCplusplus SuccinctlykzeldaNo ratings yet
- Launching Hiren's BootCD From USB Flash Drive - HBCD Fan & Discussion PlatformDocument5 pagesLaunching Hiren's BootCD From USB Flash Drive - HBCD Fan & Discussion PlatformkzeldaNo ratings yet
- GitcheatsheetDocument1 pageGitcheatsheetBob YaoNo ratings yet
- Sed - An Introduction and TutorialDocument42 pagesSed - An Introduction and TutorialkzeldaNo ratings yet
- File Transfer Protocol, Active FTP, Passive FTPDocument6 pagesFile Transfer Protocol, Active FTP, Passive FTPkzeldaNo ratings yet
- تعلم كيف تتكلم تسأل تجيب بالإنجليزية في ثلاثة أسابيعDocument53 pagesتعلم كيف تتكلم تسأل تجيب بالإنجليزية في ثلاثة أسابيعkzelda100% (2)
- Data Table To ExcelDocument2 pagesData Table To ExcelkzeldaNo ratings yet
- Vbox OptionsDocument7 pagesVbox OptionskzeldaNo ratings yet
- JQuery HowToDocument73 pagesJQuery HowTokzeldaNo ratings yet
- 10 Jquery SnippetsDocument4 pages10 Jquery Snippetskzelda100% (1)
- CSS Line-HeightDocument99 pagesCSS Line-HeightRihards KubilisNo ratings yet
- Importer Un Fichier Excel Dans Une ApplicationDocument1 pageImporter Un Fichier Excel Dans Une ApplicationkzeldaNo ratings yet
- CSS CascadeDocument111 pagesCSS CascadeRihards KubilisNo ratings yet
- Lire Des Fichiers DBF À Partir DuDocument1 pageLire Des Fichiers DBF À Partir Dukzelda100% (1)
- Am Civ 2009Document287 pagesAm Civ 2009kzeldaNo ratings yet
- Rescue CD PXEDocument12 pagesRescue CD PXEkzeldaNo ratings yet
- Hotel Room Controllers - HRCPBG28RDocument2 pagesHotel Room Controllers - HRCPBG28RHùng ĐỗNo ratings yet
- A Local Radial Basis Function Method For The Numerical Solution oDocument59 pagesA Local Radial Basis Function Method For The Numerical Solution oCharles ArokiarajNo ratings yet
- T7 ImplementationDocument32 pagesT7 ImplementationabidouNo ratings yet
- CT21 LicDocument4 pagesCT21 LicharyantojogjaboyNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture Lab (CSC451) : Dr. Bibhash Sen Associate Professor Department of CSE, NIT DurgapurDocument3 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture Lab (CSC451) : Dr. Bibhash Sen Associate Professor Department of CSE, NIT DurgapurManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thakur Institute of Management Studies and Research: (Assignment)Document15 pagesThakur Institute of Management Studies and Research: (Assignment)Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil3d Manual - Slope Classification REV01Document19 pagesAutoCAD Civil3d Manual - Slope Classification REV01Renukadevi RptNo ratings yet
- Sony Xperia M2 Aqua - Schematic DiagarmDocument126 pagesSony Xperia M2 Aqua - Schematic Diagarmjeisson posadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Huffman and Entropy CodingDocument31 pagesLesson - Huffman and Entropy CodingSheikh RaselNo ratings yet
- Answer Assignment of PythonDocument21 pagesAnswer Assignment of PythonRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - Thuso MolefeDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae - Thuso MolefeThuso Keabetswe Eric MolefeNo ratings yet
- Apple Vs SamsungDocument2 pagesApple Vs SamsungDiana StrimbeiNo ratings yet
- Data Scientist ReportDocument33 pagesData Scientist ReportsirdquantsNo ratings yet
- Product Matrix: Fortigate Network Security Platform - Top Selling Models MatrixDocument6 pagesProduct Matrix: Fortigate Network Security Platform - Top Selling Models MatrixDavideDeRubeisNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Weather Forecasting To Predict Rainfall Using Big DataDocument8 pagesA Survey On Weather Forecasting To Predict Rainfall Using Big DataSuraj SubramanianNo ratings yet
- MIT Studio Test CoachingDocument4 pagesMIT Studio Test CoachingSilica InstNo ratings yet
- Eastern International University School of EngineeringDocument59 pagesEastern International University School of EngineeringkttcNo ratings yet
- Manual TurboCash (Inglés) PDFDocument326 pagesManual TurboCash (Inglés) PDFJhorlin Alexis Castillo VivasNo ratings yet
- A Model For Assessing COBIT 5 and ISO 27001 Simultaneously: July 2018Document11 pagesA Model For Assessing COBIT 5 and ISO 27001 Simultaneously: July 2018Shah Maqsumul Masrur TanviNo ratings yet
- Máy Cưa Bàn Bosch Gts 254Document137 pagesMáy Cưa Bàn Bosch Gts 254QUYEN TRANNo ratings yet
- University of Madras: Time TableDocument11 pagesUniversity of Madras: Time TableNithish 2867 shift 2No ratings yet
- Dual Beam Antenna Bsa33rbu6b-V1 - 0-211104Document13 pagesDual Beam Antenna Bsa33rbu6b-V1 - 0-211104Yanira FariasNo ratings yet
- FL-SOFT3 User ManualDocument88 pagesFL-SOFT3 User ManualFidel Nicolae RaduNo ratings yet
- Module 5 San Local RepliDocument38 pagesModule 5 San Local RepliMadhura N KNo ratings yet
- History - 1st Generation (1G) SystemsDocument16 pagesHistory - 1st Generation (1G) SystemsAnto RaddeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.3 Detail SurveyDocument3 pagesLecture 4.3 Detail SurveySo Cho Wing100% (1)
- Addition of Name of Child in Birth CertificateDocument7 pagesAddition of Name of Child in Birth Certificatemaakabhawan26No ratings yet
- Skyhaven Flying Club Cirrus Flight Operations Manual v3.0Document14 pagesSkyhaven Flying Club Cirrus Flight Operations Manual v3.0Dan HeeterNo ratings yet
- Crackwise ArticleDocument8 pagesCrackwise ArticleYarko YurechkoNo ratings yet