Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Uploaded by
Seruoa PerezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- GRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandGRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Real NumbersDocument15 pagesReal NumbersAbby LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeDocument30 pagesAristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeKrishnendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- GROUP2 Investigation2Document16 pagesGROUP2 Investigation2ludivina rapisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Rational - NumbersDocument21 pagesChapter - 1 Rational - NumbersAditya GawandeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Language and Symbolshiro100% (1)
- Linear Equation .Lec1Document49 pagesLinear Equation .Lec1Njood AdelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols PDFDocument46 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols PDFNove TrapsiNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Translating ExpressionsDocument2 pagesNOTES - Translating ExpressionsMarnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- C.1 Support MaterialDocument32 pagesC.1 Support MaterialJYF OSTUNINo ratings yet
- Test Prep For Success Glossary of SAT Math TemsDocument10 pagesTest Prep For Success Glossary of SAT Math Temssendra0285No ratings yet
- Limits and Sets: Topic 1Document16 pagesLimits and Sets: Topic 1fleminm1No ratings yet
- Quant Concepts FormulaeDocument31 pagesQuant Concepts FormulaeCAT 2022No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument48 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsPL05CANO, DRAE P.No ratings yet
- Reviewer Math 7 10Document16 pagesReviewer Math 7 10Isidro ComonNo ratings yet
- College and Advanced Algebra (Content)Document269 pagesCollege and Advanced Algebra (Content)Michelle100% (1)
- SAT/ ACT/ Accuplacer Math ReviewDocument40 pagesSAT/ ACT/ Accuplacer Math Reviewaehsgo2college100% (1)
- Real Number SystemDocument32 pagesReal Number SystemJoy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Math 123 Lesson 1.2Document8 pagesMath 123 Lesson 1.2Supitran Reygie BamanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument5 pagesMathematics in Modern WorldvkleintoyNo ratings yet
- Math Lecture 2Document10 pagesMath Lecture 2Leo AnimeNo ratings yet
- Speaking MathematicallyDocument7 pagesSpeaking MathematicallyAngeline LobaNo ratings yet
- Algebra - IntegersDocument5 pagesAlgebra - IntegersSchool Desk SpaceNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers ReviewDocument10 pagesRational Numbers ReviewDaniel ShipNo ratings yet
- Sequence, EquationsDocument6 pagesSequence, EquationsVine AlparitoNo ratings yet
- 5a Patterns and ExpressionsDocument38 pages5a Patterns and ExpressionsFlors BorneaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Cryptography: NumbersDocument7 pagesMathematics and Cryptography: NumbersKarel KouwensNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathai SL Study GuideDocument77 pagesIb Mathai SL Study GuideJohnNo ratings yet
- Maths Ai Study GuideDocument77 pagesMaths Ai Study GuideNaomi BoesonoNo ratings yet
- Double Factorial - WikipediaDocument6 pagesDouble Factorial - WikipediaMLalli5340No ratings yet
- Wollo University: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument4 pagesWollo University: Object Oriented ProgrammingSeyfe EsubalewNo ratings yet
- Class 8 CBSE Rational NumbersDocument11 pagesClass 8 CBSE Rational NumbersMohanaMisraNo ratings yet
- Distance Rate X TimeDocument4 pagesDistance Rate X TimekprdeepakNo ratings yet
- Gec Math Wk2Document51 pagesGec Math Wk2The Negative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument31 pagesNumber SystemJwc Fest2018No ratings yet
- GRE Quant Concepts FormulaeDocument31 pagesGRE Quant Concepts Formulaeshaliniark100% (3)
- R 2 CalculationsDocument30 pagesR 2 Calculationss8nd11d UNINo ratings yet
- Maths Inequalities 2Document9 pagesMaths Inequalities 2KaushikperikaNo ratings yet
- DiscreteDocument16 pagesDiscreteLoraineNo ratings yet
- Quant NotesDocument28 pagesQuant NotesDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Math Lecture 1Document12 pagesMath Lecture 1Leo AnimeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics7 - q2 - Week 8Document10 pagesMathematics7 - q2 - Week 8Nimfa MalizaNo ratings yet
- Bases For Propositional Logic: NegationDocument9 pagesBases For Propositional Logic: NegationRajiv PaglicawanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Basic Algebraic Operations and EquationsDocument20 pagesWeek 1 - Basic Algebraic Operations and EquationsNajathNo ratings yet
- Numbers and PropertiesDocument7 pagesNumbers and PropertiesPOke wOrlDNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers (Aakash Byjus Notes)Document24 pagesReal Numbers (Aakash Byjus Notes)ganji.karthik.9999No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsNina HNo ratings yet
- What Is A Rational NumberDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Rational NumbernishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Final Module 3 The Language of MathematicsDocument7 pagesFinal Module 3 The Language of Mathematics[G-08] Cristobal, Maria Pauline G.No ratings yet
- Number System 2023Document125 pagesNumber System 2023Pujan Jain100% (1)
- Apti Rules & Tips-1Document17 pagesApti Rules & Tips-1NishadNo ratings yet
- The Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroFrom EverandThe Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Uploaded by
Seruoa PerezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Math Rules For Gmat: Word Problems
Uploaded by
Seruoa PerezCopyright:
Available Formats
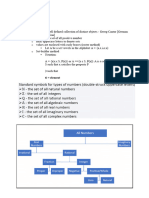
Math Rules for Gmat: Word problems The product of k consecutive integers is always divisible by k factorial (K!
) For any set of consecutive integers with an ODD number of items, the sum of all the integers is ALWAYS a multiple of the number of items. For any set of consecutive integers with an EVEN number of items, the sum of all the items is NEVER a multiple of the number of items. The average of an odd number of consecutive integers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) will always be an integer (3). This is because the middle number will be a single integer. On the other hand, the average of an even number of consecutive integers (1, 2, 3, 4) will never be an integer (2.5), because there is no true middle number. The sum of the elements in the set equals the arithmetic mean (average) number in the set times the number of items in the set. Problem - How many integers are there from 14 to 765, inclusive? Just remember: for consecutive integers, the formula is (Last - First + 1). 765 - 14, plus 1, yields 752.
Functions Inverse proportionality means that the two quantities change by reciprocal factors. Cutting the input in half will actually double the output. Tripling the input will cut the output to one-third of its original value k. Inverse proportionality relationships are of the form y = , where x is the input value and y is the output value, k is called the proportionality constant. This equation can also be written as xy = k, which means that the product of the output and input values is always constant. When it is directly proportional shold be written as x/y = k
linear growth (or decay) that is, they grow at a constant rate. Such quantities are determined by the linear function: y = mx + b
You might also like
- GRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandGRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Real NumbersDocument15 pagesReal NumbersAbby LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeDocument30 pagesAristotle Quant Concepts & FormulaeKrishnendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- GROUP2 Investigation2Document16 pagesGROUP2 Investigation2ludivina rapisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Rational - NumbersDocument21 pagesChapter - 1 Rational - NumbersAditya GawandeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Language and Symbolshiro100% (1)
- Linear Equation .Lec1Document49 pagesLinear Equation .Lec1Njood AdelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols PDFDocument46 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols PDFNove TrapsiNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Translating ExpressionsDocument2 pagesNOTES - Translating ExpressionsMarnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- C.1 Support MaterialDocument32 pagesC.1 Support MaterialJYF OSTUNINo ratings yet
- Test Prep For Success Glossary of SAT Math TemsDocument10 pagesTest Prep For Success Glossary of SAT Math Temssendra0285No ratings yet
- Limits and Sets: Topic 1Document16 pagesLimits and Sets: Topic 1fleminm1No ratings yet
- Quant Concepts FormulaeDocument31 pagesQuant Concepts FormulaeCAT 2022No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument48 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsPL05CANO, DRAE P.No ratings yet
- Reviewer Math 7 10Document16 pagesReviewer Math 7 10Isidro ComonNo ratings yet
- College and Advanced Algebra (Content)Document269 pagesCollege and Advanced Algebra (Content)Michelle100% (1)
- SAT/ ACT/ Accuplacer Math ReviewDocument40 pagesSAT/ ACT/ Accuplacer Math Reviewaehsgo2college100% (1)
- Real Number SystemDocument32 pagesReal Number SystemJoy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Math 123 Lesson 1.2Document8 pagesMath 123 Lesson 1.2Supitran Reygie BamanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument5 pagesMathematics in Modern WorldvkleintoyNo ratings yet
- Math Lecture 2Document10 pagesMath Lecture 2Leo AnimeNo ratings yet
- Speaking MathematicallyDocument7 pagesSpeaking MathematicallyAngeline LobaNo ratings yet
- Algebra - IntegersDocument5 pagesAlgebra - IntegersSchool Desk SpaceNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers ReviewDocument10 pagesRational Numbers ReviewDaniel ShipNo ratings yet
- Sequence, EquationsDocument6 pagesSequence, EquationsVine AlparitoNo ratings yet
- 5a Patterns and ExpressionsDocument38 pages5a Patterns and ExpressionsFlors BorneaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Cryptography: NumbersDocument7 pagesMathematics and Cryptography: NumbersKarel KouwensNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathai SL Study GuideDocument77 pagesIb Mathai SL Study GuideJohnNo ratings yet
- Maths Ai Study GuideDocument77 pagesMaths Ai Study GuideNaomi BoesonoNo ratings yet
- Double Factorial - WikipediaDocument6 pagesDouble Factorial - WikipediaMLalli5340No ratings yet
- Wollo University: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument4 pagesWollo University: Object Oriented ProgrammingSeyfe EsubalewNo ratings yet
- Class 8 CBSE Rational NumbersDocument11 pagesClass 8 CBSE Rational NumbersMohanaMisraNo ratings yet
- Distance Rate X TimeDocument4 pagesDistance Rate X TimekprdeepakNo ratings yet
- Gec Math Wk2Document51 pagesGec Math Wk2The Negative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument31 pagesNumber SystemJwc Fest2018No ratings yet
- GRE Quant Concepts FormulaeDocument31 pagesGRE Quant Concepts Formulaeshaliniark100% (3)
- R 2 CalculationsDocument30 pagesR 2 Calculationss8nd11d UNINo ratings yet
- Maths Inequalities 2Document9 pagesMaths Inequalities 2KaushikperikaNo ratings yet
- DiscreteDocument16 pagesDiscreteLoraineNo ratings yet
- Quant NotesDocument28 pagesQuant NotesDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Math Lecture 1Document12 pagesMath Lecture 1Leo AnimeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics7 - q2 - Week 8Document10 pagesMathematics7 - q2 - Week 8Nimfa MalizaNo ratings yet
- Bases For Propositional Logic: NegationDocument9 pagesBases For Propositional Logic: NegationRajiv PaglicawanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Basic Algebraic Operations and EquationsDocument20 pagesWeek 1 - Basic Algebraic Operations and EquationsNajathNo ratings yet
- Numbers and PropertiesDocument7 pagesNumbers and PropertiesPOke wOrlDNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers (Aakash Byjus Notes)Document24 pagesReal Numbers (Aakash Byjus Notes)ganji.karthik.9999No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsNina HNo ratings yet
- What Is A Rational NumberDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Rational NumbernishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Final Module 3 The Language of MathematicsDocument7 pagesFinal Module 3 The Language of Mathematics[G-08] Cristobal, Maria Pauline G.No ratings yet
- Number System 2023Document125 pagesNumber System 2023Pujan Jain100% (1)
- Apti Rules & Tips-1Document17 pagesApti Rules & Tips-1NishadNo ratings yet
- The Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroFrom EverandThe Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)