Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Albuterol (Salbutamol)
Albuterol (Salbutamol)
Uploaded by
Rye AnchCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Albuterol (Salbutamol)
Albuterol (Salbutamol)
Uploaded by
Rye AnchCopyright:
Available Formats
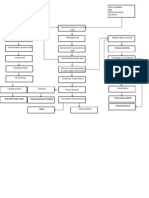
Drug
Route, Dosage & Frequency Inhalation (Children 2-12 years old): 0.10.15 mg/kg/dose 3-4 times a day
Contraindication Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons
Mechanism of Action It relieves nasal congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamol is administered.
Side/Adverse Effect
Nursing Consideration
Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol Classification: Bronchodilator (therapeutic); adrenergics (pharmacologic) Indications control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) bronchospasm exercise-induced bronchospasm -term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm
Nervousness Restlessness Tremor Headache Insomnia Chest pain Palpitation Angina Arrhythmias Hypertension Nausea and vomiting Hyperglycemia Hypokalemia
Assess lung sounds, PR and BP before drug administration and during peak of medication. Observe fore paradoxical spasm and withhold medication and notify physician if condition occurs. Administer PO medications with meals to minimize gastric irritation. Extended-release tablet should be swallowed-whole. It should not be crushed or chewed. If administering medication through inhalation, allow at least 1 minute between inhalation of aerosol medication. Advise the patient to rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to minimize dry mouth. Inform the patient that Albuterol may cause an unusual or bad taste.
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyRye Anch75% (8)
- VancomycinDocument2 pagesVancomycinRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Erce FloraDocument2 pagesErce FloraRye Anch0% (1)
- Bacillus Clausii (Erceflora)Document1 pageBacillus Clausii (Erceflora)Rye Anch88% (8)
- Atorvastatin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAtorvastatin Drug StudyRye Anch88% (17)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Aditional Client PresDocument2 pagesAditional Client PresRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Taking Action To Close The Nursing-Finance Gap: Learning From SuccessDocument3 pagesTaking Action To Close The Nursing-Finance Gap: Learning From SuccessRye Anch100% (1)
- Tramadol Hydrochloride (Ultran, Ultracet)Document1 pageTramadol Hydrochloride (Ultran, Ultracet)Rye AnchNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Hydrochloride (Ultran, Ultracet)Document1 pageTramadol Hydrochloride (Ultran, Ultracet)Rye AnchNo ratings yet
- GiannpathDocument2 pagesGiannpathRye AnchNo ratings yet
- HYDROXYZINE DIHCL (Iterax)Document1 pageHYDROXYZINE DIHCL (Iterax)Rye Anch100% (1)
- Name of Drug Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Amoxicillin Brand NameDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Amoxicillin Brand NameRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Regine Ayanna R. Baltazar Princess Ann B. Belgica John Christopher W. BuenDocument12 pagesRegine Ayanna R. Baltazar Princess Ann B. Belgica John Christopher W. BuenRye AnchNo ratings yet