Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IV. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factors
IV. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
Min-Joo Esther ParkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IV. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factors
IV. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
Min-Joo Esther ParkCopyright:
Available Formats
IV.
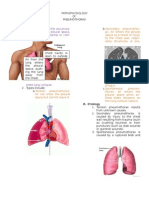
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 1. Schematic diagram
Book Based Pathophysiology &o! #odi$ia%le " Predisposi!g 'actors "ge especially infants Immunocompromised #ommon #olds "ny #hest Injury
"llo$s air to enter the pleural space
Precipitati!g"#odi$ia%le $actors Environment Exposure to Pathologic Microorganism aspiration of foods or fluids Lung Disease Injury/accidents mo!ing
Manifestations+ Depends on its si,e and the integrity of the underlying lung*
Penetration into the pleural space %y an o%ject external to the chest $all &such ash !nife/needle' (pen Pneumothorax
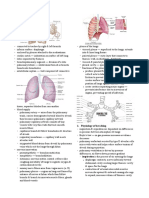
P!e(mothora)
Internal Mechanism &such as %ro!en ri% or %le% rupture of the lung' air or %lood enters the pleural space*
Increase intrathoracic pressure and reduction in vital capacity
Large Pneumothorax Penetrating /)on penetrating injuries Injury to the chest or respiratory structures -ypoxemia .asoconstriction of the %lood vessels in the affected lung*
#losed Pneumothorax
"ir filled %le%/%lister on the lung surface ruptures
34
0ractured/ dislocated ri%s that penetrates the pleura
#hest 1rauma
(ther #omplication -emothorax
Medical Procedure such as intra thoracic needle aspirations2 intu%ation2 and positive pressure ventilation
#ardio pulmonary resuscitation &#P3'
"ir enters the pleural space %ut does not leave 3apid increase of pressure in chest $ith compression atelectasis of unaffected lung
Manifestations+ Ipsilateral chest pain Inc* in 33 Dyspnea Inc* -3 "symmetry of chest -yperresonant sound upon percussion 6reath sounds decreased/a%sent over the area of the pneumothorax*
pontaneous Pneumothorax
1raumatic Pneumothorax
hift in mediastinum to the opposite side of the chest and compression of the vena cava $ith impairment of venous return to the heart Intrapleural pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure*
4n!no$n cause "ir filled %le%s rupture on 1(P of the lungs*
Lung Disease 1rapping of gases 5 Destruction of lung tissue econdary pontaneous Pneumothorax
-istory of endometriosis "ir may gain access to the peritoneal #avity during menstruation and then enter the pleural cavity through diaphragmatic Defect* #atamenial Pneumothorax 3/
1ension Pneumothorax
Primary pontaneous Pneumothorax
Manifestations+ tructures in the mediastinal space shift to$ard the opposite side of the chest* Distention of nec! veins Intrapleural pressure u%cutaneous emphysema exceeds atmospheric #linical signs of shoc! pressure*
Partial/total loss of lung function -ypoxemia Life threatening
You might also like
- Zibu SymbolsDocument4 pagesZibu SymbolsNagarajan86% (7)
- Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsDocument1 pagePneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsJoshua Villarba80% (5)
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 pagesPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Cot 2012Document410 pagesCot 2012AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"jhonroks78% (9)
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural Effusionarvinian01100% (2)
- Pathophysiology HemothoraxDocument1 pagePathophysiology HemothoraxFlauros Ryu Jabien50% (4)
- NCP: DysrhythmiasDocument12 pagesNCP: DysrhythmiasJavie100% (3)
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocument4 pagesIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771No ratings yet
- Tactical Casualty Combat Care Handbook v5 PDFDocument133 pagesTactical Casualty Combat Care Handbook v5 PDFJose Torres100% (5)
- FNCP NewDocument29 pagesFNCP NewKhim Margarette DionisioNo ratings yet
- pg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument2 pagespg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case Studyikemas100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PneumothoraxDocument1 pagePathophysiology of PneumothoraxDizah Faye OsboroNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyIris Caberte100% (3)
- NCP Increased IcpDocument2 pagesNCP Increased IcphelloaNo ratings yet
- CHF NCPDocument8 pagesCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPamela DomingoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFYhenlee Rhizelle MarquezNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Hemothorax HandoutsDocument2 pagesHemothorax HandoutsJunathan L. DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumothoraxDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Pneumothoraxoxidalaj84% (19)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- List of Prioritized Nursing ProblemsDocument1 pageList of Prioritized Nursing ProblemsdanaNo ratings yet
- Ventilatory Assistance MechanicalDocument18 pagesVentilatory Assistance Mechanicalmardsz100% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- NCP For CHFDocument2 pagesNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- The Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Document5 pagesThe Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Edmar Francis SabileNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- PneumothoraxDocument57 pagesPneumothoraxCamille Marquez100% (9)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanJayalakshmi David50% (2)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824No ratings yet
- NCP For BreathingDocument17 pagesNCP For BreathingCeleste Sin Yee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Pleural Effusionfaula rocamora80% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaNo ratings yet
- Burns - Airway Clearance, Risk For IneffectiveDocument2 pagesBurns - Airway Clearance, Risk For Ineffectivemakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey Sunga100% (1)
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- Case Study Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCase Study Pleural EffusionKhristine Anne FabayNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial PressureElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancemichelle_010379No ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Case StudyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Case Studyjanice ianNo ratings yet
- Burns NCPDocument3 pagesBurns NCPKristian Jonas Lao0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- Pneumothorax Key PointsDocument2 pagesPneumothorax Key PointsJose UringNo ratings yet
- ADAZA BSND 3 OR REQS Concept MAP 3 PDFDocument1 pageADAZA BSND 3 OR REQS Concept MAP 3 PDFKrizle AdazaNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax PDFDocument2 pagesTension Pneumothorax PDFClarissa Aileen Caliva AdoraNo ratings yet
- Hafizah Hoshni PneumothoraxDocument47 pagesHafizah Hoshni PneumothoraxhafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax AmierDocument7 pagesPneumothorax Amieramier90No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives 1. Anatomy of The LungsDocument5 pagesLearning Objectives 1. Anatomy of The LungslaurenNo ratings yet
- JURNAL PNEUMOTHORAKS Edit PDFDocument84 pagesJURNAL PNEUMOTHORAKS Edit PDFAlvikhaabieber Alvinosztarisegfc Stuarst'gNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument10 pagesPneumothoraxThuganamix100% (10)
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction A Case StudyDocument44 pagesIntestinal Obstruction A Case StudyikemasNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument76 pagesAcute Renal Failureikemas100% (7)
- pg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument2 pagespg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case Studyikemas100% (1)
- pg1-33 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument36 pagespg1-33 of Pneumothorax Case StudyikemasNo ratings yet
- Headtotoe 2Document5 pagesHeadtotoe 2api-675533626No ratings yet
- NCM 107 Chest Physiotherapy Checklist 2020Document2 pagesNCM 107 Chest Physiotherapy Checklist 2020acentino121No ratings yet
- 8940Document166 pages8940Basory Ok OkNo ratings yet
- Incision Access UrologyDocument47 pagesIncision Access UrologyHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- Angiology NoteDocument13 pagesAngiology NoteSantosh Bhandari100% (2)
- NAVTA Ovt Nov17 CERadiographDocument8 pagesNAVTA Ovt Nov17 CERadiographabazanhasan6705No ratings yet
- LSMU 6th Year Therapy1stDocument35 pagesLSMU 6th Year Therapy1stSuruchi Jagdish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Breast - Mammary GlandDocument16 pagesBreast - Mammary GlandEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Standard Operating ProtocolsDocument215 pagesRadiographic Standard Operating ProtocolsIsaias Orlando Muchaypiña CanalesNo ratings yet
- P vs. Gonzales, 183 SCRA 309, #80762, March 19, 1990Document17 pagesP vs. Gonzales, 183 SCRA 309, #80762, March 19, 1990marlouierespicioNo ratings yet
- PMBLST of All ConditionsDocument18 pagesPMBLST of All ConditionsMitchell GowNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Manual: NAVM ED P-5065 AFM 160-19Document130 pagesAutopsy Manual: NAVM ED P-5065 AFM 160-19Roger ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Post Mastectomy ExerciseDocument4 pagesPost Mastectomy ExerciseKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- Nclex Review Pneumonia COPD AsDocument11 pagesNclex Review Pneumonia COPD Asmj078No ratings yet
- Nursing Questions1Document17 pagesNursing Questions1أبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- P1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemDocument123 pagesP1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemThenunda തേനുണ്ടNo ratings yet
- MPT - SyllabusDocument44 pagesMPT - Syllabuselan suriyanNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument31 pagesMedical TerminologySusanBernardNo ratings yet
- What Is Chest Physiotherapy? Chest Physiotherapy Is The Removal ofDocument13 pagesWhat Is Chest Physiotherapy? Chest Physiotherapy Is The Removal ofmhalnijen100% (1)
- Yolk Gall EtcDocument5 pagesYolk Gall EtcNaveen BasudeNo ratings yet
- Pathom, Virgilio, NMS, Sketchy Pharm ChecklistsDocument25 pagesPathom, Virgilio, NMS, Sketchy Pharm ChecklistsdasbosiNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacrum SpineDocument59 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacrum Spinekashmala afzalNo ratings yet
- Kundalini Yoga Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesKundalini Yoga Cheat SheetJulia Manko100% (2)
- Standard Points of Acupuncture For Kyusho ApplicationsDocument18 pagesStandard Points of Acupuncture For Kyusho ApplicationsAndriela LemosNo ratings yet
- NP1Document43 pagesNP1Edward Nicko GarciaNo ratings yet