Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Printf : Java Method Quick Reference
Uploaded by
namnblobOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Printf : Java Method Quick Reference
Uploaded by
namnblobCopyright:
Available Formats
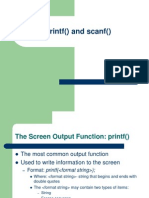
Java printf( ) Method Quick Reference
System.out.printf( format-string [, arg1, arg2, ] );
Format String: Composed of literals and format specifiers. Arguments are required only if there are format specifiers in the format string. Format specifiers include: flags, width, precision, and conversion characters in the following sequence: % [flags] [width] [.precision] conversion-character Flags:
+ 0 , : : : : :
( square brackets denote optional parameters )
left-justify ( default is to right-justify ) output a plus ( + ) or minus ( - ) sign for a numerical value forces numerical values to be zero-padded ( default is blank padding ) comma grouping separator (for numbers > 1000) space will display a minus sign if the number is negative or a space if it is positive
Width: Specifies the field width for outputting the argument and represents the minimum number of characters to be written to the output. Include space for expected commas and a decimal point in the determination of the width for numerical values. Precision: Used to restrict the output depending on the conversion. It specifies the number of digits of precision when outputting floating-point values or the length of a substring to extract from a String. Numbers are rounded to the specified precision. Conversion-Characters: d: f: c: s: h: n : decimal integer [byte, short, int, long] floating-point number [float, double] character Capital C will uppercase the letter String Capital S will uppercase all the letters in the string hashcode A hashcode is like an address. This is useful for printing a reference newline Platform specific newline character- use %n instead of \n for greater compatibility
Examples:
System.out.printf("Total is: $%,.2f%n", dblTotal); System.out.printf("Total: %-10.2f: ", dblTotal); System.out.printf("% 4d", intValue); System.out.printf("%20.10s\n", stringVal); String s = "Hello World"; System.out.printf("The String object %s is at hash code %h%n", s, s);
String class format( ) method: You can build a formatted String and assign it to a variable using the static format method in the String class. The use of a format string and argument list is identical to its use in the printf method. The format method returns a reference to a String. Example:
String grandTotal = String.format("Grand Total: %,.2f", dblTotal);
You might also like
- Printf : Java Method OverviewDocument2 pagesPrintf : Java Method Overviewakula pranathiNo ratings yet
- Java Printf Method Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageJava Printf Method Quick ReferencePhiokham SuriyaNo ratings yet
- CSCI 230 Basic I/O – printfDocument19 pagesCSCI 230 Basic I/O – printfAnjali NaiduNo ratings yet
- How String WorksDocument13 pagesHow String WorksSagar Morje100% (1)
- C - PrintfDocument3 pagesC - PrintffabioscanNo ratings yet
- Basic Input and OutputDocument15 pagesBasic Input and OutputBiebe Ann Cabunilas CagangNo ratings yet
- Number Input Output Statement2Document22 pagesNumber Input Output Statement2brando05633757No ratings yet
- Built-in string methodsDocument6 pagesBuilt-in string methodsbeappyNo ratings yet
- Input / Output: S.Vaishnavi Programming For Problem SolvingDocument48 pagesInput / Output: S.Vaishnavi Programming For Problem SolvingkavyaNo ratings yet
- PrintfDocument10 pagesPrintfkayak7No ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument12 pagesChapter Sixn64157257No ratings yet
- C Programming - Managing Input and Output OperationsDocument8 pagesC Programming - Managing Input and Output Operationsneo_4110% (1)
- CIO Basic Operators and Data TypesDocument44 pagesCIO Basic Operators and Data TypesTed ChanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4Abel IngawNo ratings yet
- Sololearn CDocument55 pagesSololearn CHarALevelComputing JNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4Abel IngawNo ratings yet
- Data Type in C++: Signed, Unsigned, Short, and Long (Type Modifiers)Document4 pagesData Type in C++: Signed, Unsigned, Short, and Long (Type Modifiers)ashimsarkar2006No ratings yet
- 1dIayG QDTulYf2Lnvk8Uz6O3leFmqFdC 2Document16 pages1dIayG QDTulYf2Lnvk8Uz6O3leFmqFdC 2Learn With BroNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference CDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Csidbom100% (1)
- C Reference Card (ANSI) : C 1999 Joseph H. Silverman Permissions On Back. v1.3Document2 pagesC Reference Card (ANSI) : C 1999 Joseph H. Silverman Permissions On Back. v1.3LGavri100% (1)
- Formatted and Unformatted FunctionsDocument29 pagesFormatted and Unformatted FunctionsSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- LexDocument41 pagesLexvarsoliwalaNo ratings yet
- Basic I/O - Scanf : CSCI 230Document10 pagesBasic I/O - Scanf : CSCI 230Gaurav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- C Mod 3Document24 pagesC Mod 3arafaiic2022No ratings yet
- CprogrammingICTweek3Document28 pagesCprogrammingICTweek3Mr. CreeperNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4: Managing Input and Output OperationDocument55 pagesChapter-4: Managing Input and Output Operationvinod_msNo ratings yet
- 2 UnitDocument20 pages2 Unitsheenafarhana03No ratings yet
- The Attack and Defense of ComputersDocument61 pagesThe Attack and Defense of ComputersAman SardanaNo ratings yet
- GE19141 PUC Unit 3 LN 2019Document28 pagesGE19141 PUC Unit 3 LN 2019SURIYA M SEC 2020No ratings yet
- The FunctionDocument3 pagesThe Functionstar_shine111No ratings yet
- Computer 12 CH10 NotesDocument11 pagesComputer 12 CH10 Notes9t6vx7psm5No ratings yet
- Formatting Text - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument8 pagesFormatting Text - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaARVINDNo ratings yet
- Changing The Case of A PHP StringDocument10 pagesChanging The Case of A PHP StringDocumentation JunkieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - C Program Managing Input and Output OperationsDocument9 pagesChapter 8 - C Program Managing Input and Output OperationsFreddy MutuaNo ratings yet
- C - ch-4 IO StatementsDocument25 pagesC - ch-4 IO StatementsKalpanaNo ratings yet
- Learn String Manipulation in CDocument19 pagesLearn String Manipulation in CNaneth Masbate-llagunoNo ratings yet
- Input and Output FormattingDocument8 pagesInput and Output FormattingSrijit koirlaNo ratings yet
- Session 7Document11 pagesSession 7Keroro StoneNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PDFDocument69 pagesUnit 4 PDFUday Kumar M100% (1)
- The Basic C StructureDocument8 pagesThe Basic C StructureXian ShengNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of I/ODocument14 pagesFundamentals of I/OBlah BlahNo ratings yet
- C LanguageDocument26 pagesC LanguageMark 42No ratings yet
- AWK Built-in Variables and Formatting ReferenceDocument3 pagesAWK Built-in Variables and Formatting ReferenceHarshali Y. PatilNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Student - SDocument66 pagesLab Manual - Student - SMUHAMMAD HARIZ HAIKAL BIN AZAMKHAIRINo ratings yet
- PPSC Unit 3 Part BDocument25 pagesPPSC Unit 3 Part BHermione GrangerNo ratings yet
- C Standard LibraryDocument8 pagesC Standard Libraryapi-3721555100% (1)
- Unit VDocument9 pagesUnit VMeena VinothNo ratings yet
- Pre Defined Data TypesDocument39 pagesPre Defined Data TypesAusaf Ahmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 Last PartDocument35 pagesModul 2 Last PartrajeshdineshNo ratings yet
- GKS - Formatted and Unformatted Input and Output in CDocument5 pagesGKS - Formatted and Unformatted Input and Output in Carpit vermaNo ratings yet
- CO110 Computer Programming5Document25 pagesCO110 Computer Programming5sauravk2424No ratings yet
- Managing Input and Output OperationDocument35 pagesManaging Input and Output OperationSiddharth Gupta100% (1)
- Constants, Variables, & Data Types: Prepared By:vipul VekariyaDocument46 pagesConstants, Variables, & Data Types: Prepared By:vipul VekariyaJay TadhaniNo ratings yet
- NoteedDocument3 pagesNoteedManis PoggersNo ratings yet
- Tin Hoc Co So 2 Week3 HustDocument41 pagesTin Hoc Co So 2 Week3 Hustvanhoangdz2003No ratings yet
- C Programming Unit - 9 Part II StringsDocument54 pagesC Programming Unit - 9 Part II StringsBina BhandariNo ratings yet
- c suggestionDocument17 pagesc suggestionIndranil ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Caracteres de AsignacionDocument4 pagesCaracteres de AsignacionTakeshi Neko TakanashiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Input and Output OperationsDocument3 pagesLab 3 Input and Output OperationsRAMEYANo ratings yet
- Percentage Grade DefinitionDocument2 pagesPercentage Grade DefinitionnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Torch PointsDocument20 pagesTorch PointsErik130No ratings yet
- Eula Microsoft Visual StudioDocument3 pagesEula Microsoft Visual StudioqwwerttyyNo ratings yet
- Merge TestDocument1 pageMerge TestnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Eula Microsoft Visual StudioDocument3 pagesEula Microsoft Visual StudioqwwerttyyNo ratings yet
- Superintendent Absence Letter 8 31 2010Document1 pageSuperintendent Absence Letter 8 31 2010namnblobNo ratings yet
- Peak Performance Instruction SheetDocument2 pagesPeak Performance Instruction SheetnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Hod Analysis QuestionsDocument5 pagesHod Analysis QuestionsnamnblobNo ratings yet
- 1 BDocument8 pages1 BnamnblobNo ratings yet
- HomeDocument6 pagesHomenamnblobNo ratings yet
- Golden Fabrics Purchase Journal For Month Ended October 31, 2014Document1 pageGolden Fabrics Purchase Journal For Month Ended October 31, 2014namnblobNo ratings yet
- Superintendent Absence Letter 8 31 2010Document1 pageSuperintendent Absence Letter 8 31 2010namnblobNo ratings yet
- 2008 EngDocument2 pages2008 EngNiranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Critter Written Assignment 1Document1 pageCritter Written Assignment 1namnblobNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium OnlineDocument3 pagesEquilibrium OnlinenamnblobNo ratings yet
- WSDT RulesDocument5 pagesWSDT RulesnamnblobNo ratings yet
- 08.10 Home Electricity Bill Record SheetDocument1 page08.10 Home Electricity Bill Record SheetnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Sherlock BBC Piano MedleyDocument14 pagesSherlock BBC Piano Medleymacfpob100% (1)
- Upcoming GamesDocument1 pageUpcoming GamesnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 2012-2013Document5 pagesCourse Outline 2012-2013namnblobNo ratings yet
- Physics Conservation ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics Conservation ProblemsnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Circle of FifthsDocument1 pageCircle of FifthsnamnblobNo ratings yet
- Sherlock BBC Piano MedleyDocument14 pagesSherlock BBC Piano Medleymacfpob100% (1)
- Pedigree WorksheetDocument2 pagesPedigree WorksheetnamnblobNo ratings yet