Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucleotide: Structure Synthesis Length Unit Abbreviation Codes For Degenerate Bases See Also
Nucleotide: Structure Synthesis Length Unit Abbreviation Codes For Degenerate Bases See Also
Uploaded by
jerni2012Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleotide: Structure Synthesis Length Unit Abbreviation Codes For Degenerate Bases See Also
Nucleotide: Structure Synthesis Length Unit Abbreviation Codes For Degenerate Bases See Also
Uploaded by
jerni2012Copyright:
Available Formats
Nucleotide
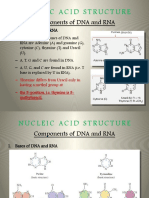
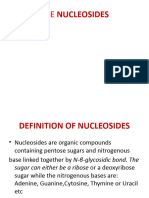
Structural elements of common nucleic acid constituents. The compounds marked nucleoside monophosphate, nucleoside diphosphate and nucleoside triphosphate are all nucleotides. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the monomers, or subunits, of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. The building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a ve-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and at least one phosphate group. Nucleotides serve to carry packets of energy within the cell (ATP). In the form of the nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, GTP, CTP and UTP), nucleotides play central roles in metabolism.[1] In addition, nucleotides participate in cell signaling (cGMP and cAMP), and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions (e.g. coenzyme A, FAD, FMN, NAD, and NADP+).
Structure Synthesis Length unit Abbreviation codes for degenerate bases See also
References External links
Read in another language
Last modied 28 days ago
Mobile Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 Terms of use
Desktop unless otherwise noted.
Privacy
You might also like
- Nucleic Acid ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acid ProjectPramod Etarvi89% (9)
- Nuceic AcidsDocument124 pagesNuceic AcidsMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide: Nucleotides Are Organic Molecules Consisting of A NucleosideDocument10 pagesNucleotide: Nucleotides Are Organic Molecules Consisting of A NucleosideMujahidul HasanNo ratings yet
- Nukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesDocument33 pagesNukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesIkatanti Ratna AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 04 Pekan 2 - Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Biochemistry)Document28 pages04 Pekan 2 - Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Biochemistry)Eren YooNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document9 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 5th LectureDocument24 pagesBIO 001 5th LectureBenjaminNo ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument12 pagesNucleotidesIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids and NucleotidesWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Nukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesDocument33 pagesNukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesAldiansyahHakimNo ratings yet
- NUCLEICACIDSDocument2 pagesNUCLEICACIDSJamiluNo ratings yet
- Dna 1Document31 pagesDna 1Dr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- 471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebDocument10 pages471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebShaikh SalmanNo ratings yet
- The Functions of ATP: Synthesis of New Chemical CompoundsDocument5 pagesThe Functions of ATP: Synthesis of New Chemical CompoundsMohini BajajNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering Class 6Document3 pagesBiochemical Engineering Class 6Vittal PiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument383 pagesBiochemtylermedNo ratings yet
- Nucleosides: - Heterocyclic Nitrogen and Pentose Are Linked by N-Glycosidic BondDocument4 pagesNucleosides: - Heterocyclic Nitrogen and Pentose Are Linked by N-Glycosidic BondVitor MartinsNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Structure: Components of DNA and RNADocument18 pagesNucleic Acid Structure: Components of DNA and RNAShamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2019Document15 pagesChemistry Project 2019Aiasha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Blueprint of Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Blueprint of Protein SynthesislamesaltheamoniqueNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesStructure of Nucleic Acidsplayandhavefun23No ratings yet
- DNA Structure NotesDocument8 pagesDNA Structure NotesSabina BabaievaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument30 pagesNucleic Acidjordanmusyoki19No ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Co-Enzymes Role in Metabolic PathwaysDocument23 pagesCo-Enzymes Role in Metabolic PathwaysHarini BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- A Nucleotide IsDocument1 pageA Nucleotide IsSanny LimNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDocument38 pagesHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsSHIFA ALTAFNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ReportDocument15 pagesNucleic Acid Reportmumu memeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesLecture Nucleic Acidsj9694052No ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleotidesvitro4No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument72 pagesChemistry of Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsBernard100% (1)
- 7 Introduction To Molecular Genetics-Part 1Document29 pages7 Introduction To Molecular Genetics-Part 1MarieFranz ChuaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDocument38 pagesHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsSHIFA ALTAFNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules (Nucleotides)Document12 pagesBiological Molecules (Nucleotides)Raphael OngodiaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- Written: in Biology Group 1Document5 pagesWritten: in Biology Group 1Joel EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NUCLEIC ACID NotesDocument4 pagesNUCLEIC ACID Notestikamam881No ratings yet
- (BCH 211) The Nucleic Acid1-1Document36 pages(BCH 211) The Nucleic Acid1-1destiny gowonNo ratings yet
- Genetics, Lecture 1 &2 Purines & Pyrimidines (Lecture Notes)Document11 pagesGenetics, Lecture 1 &2 Purines & Pyrimidines (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument32 pagesNucleic AcidsAlexander DacumosNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument35 pagesNucleic AcidCheelsy P. ButronNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous Bases, Nucleotides, Nucleic AcidsDocument32 pagesNitrogenous Bases, Nucleotides, Nucleic AcidsShauntelle WinchesterNo ratings yet
- DNA in Cells: Molecular BiologyDocument10 pagesDNA in Cells: Molecular BiologyDe Los Santos AinjelNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 8a LectureDocument36 pagess15 Miller Chap 8a LectureShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- J Fob 2015 05 002Document10 pagesJ Fob 2015 05 002ericktNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme NukleotidaDocument30 pagesMetabolisme Nukleotidappg.putriazzahra00530No ratings yet
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid STRUCTUREDocument5 pagesNucleic Acid STRUCTUREKalel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles: Organisms Are Made of CellsDocument10 pagesBasic Principles: Organisms Are Made of CellsEllu SeethaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidAjagu ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Text 4Document1 pageText 4Tjaša PaukoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet