Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iron Profile Estimation in Children With Behaviour Disorder
Iron Profile Estimation in Children With Behaviour Disorder
Uploaded by
inggrit06Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iron Profile Estimation in Children With Behaviour Disorder
Iron Profile Estimation in Children With Behaviour Disorder
Uploaded by
inggrit06Copyright:
Available Formats
OCTOBER 2010
DELHI PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL Vol. 13 No. 2
Original Article
Iron Profile Estimation in Children of Behavioral Disorders
Shruti. Srivastava*, Bhatia MS**, Rusia U***, Rusia A**** *Lecturer, **Professor and Head, ***Professor, Department of Pathology, ****Resident Department of Psychiatry, U.C.M.S & Guru Tegh Bahadur Hospital, University of Delhi, Delhi-110095
Abstract Background: Iron deficiency causes abnormal dopaminergic neurotransmission and may contribute to behavioral disorders. Objective: Iron Profile Estimation in Children (5-14 yrs) of Behavioral Disorders. Design : Cross-sectional study. Setting: Child Guidance Clinic of University College of Medical Sciences and Guru Tegh Bahadur Hospital. The sample consisted of Forty children in the age group of 5 to 14 years suffering from behavioral disorders. Haemoglobin , Mean Corpuscular Volume, Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, Serum Iron ,Total Iron Binding Capacity, Peripheral smear, Percentage transferrin saturation , serum ferritin estimations were done. The behavioral symptoms were scored on Achenback Child Behavior Checklist. Results: Iron deficiency anemia was present in 75% of the children with behavioral symptoms. Serum ferritin was abnormal (<20micrograms/litre) in 67.8% of the children. There was statistically significant association between pica and iron deficiency anemia(p<0.001).Serum ferrittin levels correlated negatively with behavioral symptoms (r=-.067), though not significant. Key words: Iron deficiency Anemia, Serum ferritin Introduction The WHO estimates that more than two billion people in the world are anemic, which is about one third of the World population.1 UNICEF reports that 90% of all types of anemia in the world are due to iron deficiency.The estimated prevalence of Iron deficiency anemia among pregnant women and young children being 49.7% and 74% respectively.2 Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects 5% to 10% of school-aged children .The disorder is characterized by inappropriate impulsivity, overactivity, inattention, and altered executive functions. The symptoms of ADHD may be caused by dopamine dysfunction. Iron is a coenzyme of dopamine synthesis. In the brain, iron is bound to ferritin, the levels of which are decreased by iron deficiency and increased by iron supplementation. Low ferritin levels in childhood have been reported to affect the development of the central nervous system, leading to mental retardation and behavioral disorders3. Material and Methods In this cross-sectional hospital based study, we estimated iron profile in children with behavioral disorders. Forty consecutive children in the age group of 5-14 years were diagnosed as behavioral disorders including ADHD by psychiatrists using ICD - 10 Criterion in a tertiary care teaching hospital. All children were recruited after taking informed consent from parents or legal guardians. The children with other physical or neurological diagnosis were excluded. The Child Behaviour Checklist developed by T M Achenbach was administered to all the forty children for the evaluation of their behavioral problems. It has 113 item behavioral problem checklist with a seven part social competence checklist. The CBCL has been tested in large populations and is fairly easy to administer. It is used in both clinical settings and research. A limitation of the CBCL is that syndromes from the scale do not necessarily correspond with DSM-IV .After the completion of
339
Delhi Psychiatry Journal 2010; 13:(2) Delhi Psychiatric Society
DELHI PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL Vol. 13 No. 2
OCTOBER 2010
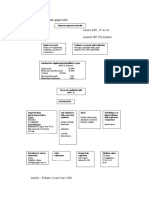
CBCL, serum ferritin levels were measured using commercially available kits (based on immunoenzymatic calorimetric method), as were blood hemoglobin, Mean Corpuscular Volume, Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin , Serum Iron, Total Iron Binding Capacity, Peripheral smear, Percentage transferrin saturation levels. The following criteria were used for diagnosing Iron deficiency anemia: 1. Hemoglobin < 11g/dl (3-6 years) and < 12g/ dl (6-12 years) 2. Percentage transferring saturation < 16% and/or serum ferritin <16 micrograms/litre Statistical analyses were performed using the t test and X2 test for between-group comparison of biological measures and Pearson test for correlations between symptom severity and serum ferritin levels. The mean age of the sample was 9.72 + 3.19 years with 65% male and 35% female children. Table-I. Distribution of hemoglobin in patients with behavioral disorders (N = 40)
Age (years)/ Sex 3-5 F M 6-9 F M 10-14 F M Number Hb Average 9.7 12.1 9.1 10.7 9.6 11.6 11.0 10.3 11.3 Comparison with Normal Values D N D D D N D D D
Table-II . Compete blood counts of patients with behavioral disorders (N= 40).
Parameter Hb (g/dl) MCV (fl) Serum Iron (micrograms/dl) TIBC (micrograms/dl) % TS Serum ferritin(micrograms/l) Range 3.4-13.9 55-95.5 19-134 229-533 4.7-33.3 3-115 Mean + S.D. 10.73 + 2.57 77.73 + 10.46 65.625 + 29.31 339.87 + 78.25 19.23 + 9.18 34.94 + 27.03
Conclusion There is a need for correction of Iron deficiency anemia at a war footing especially in a developing country like India as it leads to behavioral problems. References 1. World Health Organization. Iron deficiency anemia, assessment , prevention and control. A guide for program managers. WHO, Geneva, 2001. 2. Shali T, Singh C, Goindi G. Prevalence of anemia amongst pregnant mothers and children in Delhi. Indian J Pediatr. 2004; 71 : 946. 3. Grantham-McGregor S., Ani C. A review of studies on the effect of iron deficiency on cognitive development in children. J Nutr. 2001; 131 : 649S-668S. 4. Bhatia MS, Rai S, Singhal PK, Nigam VR, Bohra N, Malik SC. Pica:Prevalence and etiology. Indian Pediatr. 1988; 25 : 1165-70. 5. Geissler PW, Mwaniki DL, ThiongO F, Michaelsen KF, Friis H. Geophagy, iron status and anemia among primary school children in Western Kenya. Trop Med Int Health, 1988; 3(7) : 529-34. 6. Konofal E, Lecendreaux M, Arnulf I, Mouren MC. Iron deficiency in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004; 158 : 1113-1115. 7. Oner O, Alkar OY, Oner P. Relation of ferritin levels with symptom ratings and cognitive performance in children with attention deficithyperactivity disorder. Pediatr Int. 2008; 50(1) : 40-4. 8. Millichap JG, Yee MM, Davidson SI. Serum ferritin in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatr Neurol. 2006 Mar; 34(3) : 200-3.
5 1 4 11 5 6 24 8 16
Results and Discussion Iron deficiency anemia was present in 75% of the children with behavioral disorders. Serum ferritin was abnormal (<20micrograms/litre) in 67.8% of the children. There was statistically significant association between pica and iron deficiency anemia (Chi square test df = 1, p < 0.001). Similar findings have been observed in other studies.4,5 Serum ferrittin levels correlated negatively with behavioral symptoms (r = -.067, N = 40, p > 0.05), though not significant. Some of the previous studies have found low serum ferritin levels to correlate with higher behavioral symptoms and more cognitive deficits.6,7 Another study by Millichap JG did not find serum ferritin levels to play causative role in ADHD.
340
Delhi Psychiatry Journal 2010; 13:(2) Delhi Psychiatric Society
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- EDAIC MOCK TEST For Part 2 Exam From Team Targetedaic 4Document7 pagesEDAIC MOCK TEST For Part 2 Exam From Team Targetedaic 4Ramanan BothuNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Acog Practice Bulletin Summary: Gestational Hypertension and PreeclampsiaDocument4 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin Summary: Gestational Hypertension and PreeclampsiaKevin CasavilcaNo ratings yet
- Primary Chest Wall TumorsDocument13 pagesPrimary Chest Wall Tumorsmhany12345No ratings yet
- 4 Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument30 pages4 Meconium Aspiration SyndromeRana Vandana100% (2)
- Atypical LymphocytesDocument3 pagesAtypical Lymphocytesinggrit06No ratings yet
- Managing Asthma and Allergies in Schools An Opportunity To Coordinate Health CareDocument4 pagesManaging Asthma and Allergies in Schools An Opportunity To Coordinate Health Careinggrit06No ratings yet
- Who NHD 01.3Document132 pagesWho NHD 01.3inggrit06No ratings yet
- Colitis Due To Ancylostoma Duodenale: ReferencesDocument2 pagesColitis Due To Ancylostoma Duodenale: Referencesinggrit06No ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency in Children (8 Years or Younger) : Key Points To RememberDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency in Children (8 Years or Younger) : Key Points To Rememberinggrit06No ratings yet
- RA Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument6 pagesRA Iron Deficiency Anemiainggrit06No ratings yet
- 1 Glomerular DiseasesDocument127 pages1 Glomerular DiseasesCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- PTSD Informative SpeechDocument3 pagesPTSD Informative SpeechMorgan GoadNo ratings yet
- SIMULASI+UAS+D3+KEP+2021 - Hikmah FitriaDocument6 pagesSIMULASI+UAS+D3+KEP+2021 - Hikmah FitriaHikmah FitriaNo ratings yet
- Ciwa-Ar: Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment of Alcohol Scale - RevisedDocument1 pageCiwa-Ar: Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment of Alcohol Scale - RevisedJessica DenningNo ratings yet
- Trigger Finger-An Overview of The Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesTrigger Finger-An Overview of The Treatment OptionsSatrya DitaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson DiseaseDocument30 pagesParkinson DiseaseAndreea OanaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Dan Terapi Ilmu Bedah RSUD Dr. Soetomo. Surabaya.2008Document2 pagesDiagnosis Dan Terapi Ilmu Bedah RSUD Dr. Soetomo. Surabaya.2008tafwidiqbalNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Autoimmune and Paraneoplastic EncefaliteDocument14 pagesAn Overview of Autoimmune and Paraneoplastic Encefaliterafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- Ibbs 2011 IndonesiaDocument80 pagesIbbs 2011 Indonesiarifka yoesoefNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument10 pagesAdult Combined ScheduledrabdulrabbNo ratings yet
- YES NO: Does The Client Consent To An Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Assessment?Document1 pageYES NO: Does The Client Consent To An Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Assessment?aspire centerNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Children PDFDocument11 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Children PDFesdl86No ratings yet
- Arthritis and SaturnDocument4 pagesArthritis and SaturnJatinder SandhuNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ClonazepamDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY ClonazepamP BNo ratings yet
- CHF Ec CadDocument17 pagesCHF Ec CadAkbar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Kalium Durule Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKalium Durule Drug StudymichelleNo ratings yet
- 3 Neurodevelopmental DisorderDocument11 pages3 Neurodevelopmental DisorderLorie Jane De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Rasional - DR DidiDocument42 pagesAntibiotik Rasional - DR DidiZunni HermawatiNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument34 pagesCARDIOKevin Patrick PadolinaNo ratings yet
- Typology of Learners With Special Needs: Learning OutcomesDocument58 pagesTypology of Learners With Special Needs: Learning OutcomesEzraNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture-2, Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument49 pages2.lecture-2, Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Augments Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy On Breast Carcinoma - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesHyperthermia Augments Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy On Breast Carcinoma - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Penatalaksanaan Gagal NafasDocument2 pagesAlgoritma Penatalaksanaan Gagal NafasLion Sangkut Neng EndiNo ratings yet
- VSDDocument4 pagesVSDtikabdullahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination - Eric Sarpong-NtiamoahDocument52 pagesClinical Examination - Eric Sarpong-NtiamoahFathimathNo ratings yet