Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Final Exam Key
Uploaded by
brookCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry Final Exam Key
Uploaded by
brookCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY 341
Final Exam December 13, 1999 NAME KEY
Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9
15 pts 12 pts 18 pts 15 pts 32 pts 32 pts 10 pts 10 pts 16 pts TOP 10 reasons Scott wanted to be the organic SI Guy . . . 10. 9. 8. 7. 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. To learn more Organic Chemistry To make fun of Fergie To find out how to synthesize Viagra It's too cold to golf So someone would actually listen to him talk He is a sadist Where else could he find friends? Organic is where it's all happenin' He's a chemistry geek
Problem 10 15 pts Problem 11 12 pts Problem 12 12 pts Given 1 pts 1
and the number 1 reason Scott wanted to be the organic SI Guy . . . 1. To pick up women
TOTAL
200 pts
Words of Wisdom from the SI Guy . . . #1) #2) #3) There are 3 ways to get something done - 1. Do it yourself. 2. Pay someone to do it. 3. Forbid your children to do it. There are 3 types of people in this world - 1. Those that can count. 2. Those that can't. English is totally overdid.
If you need scrap paper or more room, use the back of the test pages. Please read through each problem carefully. Enter your answers in the spaces provided.
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
1. Name the following structures (IUPAC) or provide the structure that corresponds to the name for the following. (15 points)
a) 1-(2-methylpropyl)-1,4-cyclohexadiene
Cl b) (R)-2-chloro-3-ethylpentane
c)
(R)-2,4-dimethyl-2-hexene
Br Br d) a meso form of 2,3-dibromobutane Br or Br
e)
trans-hept-4-en-2-yne
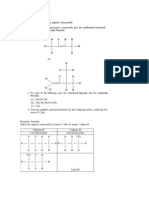
2. Circle the most stable molecule in each pair below. (12 points)
CH3 Br CH3 CH3
CH3 Br
CH3 H H CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 H3C H H CH CH3 3
page 2 of 10
OH
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
3. Circle all of the following pairs which represents resonance forms. (18 points)
O (a)
OH (b)
O (c)
OH
OH
OH O (d) N O N (e) OH
(f) H O
N N N H
N N N
4. What is the relationship between the following pairs of molecules? (15 points)
check one identical
OH HO Cl Cl HO OH
enantiomers diastereomers constitutional isomers
conformers
X
HO Br Cl OH
X
Cl CH3 C C HO H H N H OH CH3 CH3 Br OH H C C HO CH3 H H N
HO
HO
OH
page 3 of 10
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
5. Fill in the boxes for the major organic products of the following reactions. Indicate stereochemistry clearly where necessary. (32 points)
O O OH 1) BH3 2) H2O2, NaOH
1) HBr (1 eq) 2) (CH3)2CuLi H2 Lindlar catalyst 1) NaNH2 2) 1-bromo-2-methylpropane Cl
O3 then + Zn, H3O Cl 1) HCl (1 eq) 2) HBr (1 eq) Br
page 4 of 10
Cl2 (excess) Cl Br Cl
H2 Pd/C
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
6. Fill in the boxes for the major organic products of the following reactions. Indicate stereochemistry clearly where necessary. (32 points)
OH O O OH
Br 1) BH3 2) H2O2, NaOH HBr 1) Hg(OAc)2 2) NaBH4 KMnO4 H3O+
1) OsO4 2) NaHSO3
OH
OH
OH or Br
NBS, light
Cl2, H2O
H2 Pd/C
Br Cl
page 5 of 10
OH
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
7. The two tosylates shown below react differently under identical reaction conditions. One will undergo a facile SN2 reaction while the other will easily eliminate via an E2 mechanism. Draw the structure of the major product for each reaction. (10 points)
OCH3 CH3
OTos CH3
NaOCH3 DMSO
OTos CH3
NaOCH3 DMSO CH3
8. The following substitution reaction is described by the accompanying reaction diagram. Show on the diagram with arrows, the activation energy for the rate determining step and G. (10 points)
OTos CH3
Some nucleophile
substitution product
G G reaction progress
(a) Does the reaction take place by a SN1 or a SN2 mechanism? (b) Check the box for the statement that is true about the reaction. A racemic mixture of enantiomers will be produced.
SN1
A mixture of two diastereomers, both racemic will be produced.
A mixture of two diastereomers, both chiral will be produced. A single stereoisomer will be produced.
page 6 of 10 Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
9. Fill in the missing structure or reagents where necessary. (16 points)
OH PBr3 Br 1) Mg 2) D O 2 D
Tos-Cl base
OTos
NaCN HMPA
CN
10. Starting from ethynyl benzene, synthesize the molecule shown using any other reagents you need. More than one step will be necessary. Show all reagents and intermediate structures along the way. (15 points)
H2 / Lindlar or Li / NH3
(CH2=CH)2CuLi
Br HBr
page 7 of 10
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
11. Below is the IR and 1H NMR spectra for an unknown compound with a molecular formula C5H10O. In the 13C NMR, four resonances appear at 210, 45, 22, and 16 ppm.
(a) The IR stretching frequency at 1720 cm-1 corresponds to what functional group? (4 points)
Carbonyl (Ketone)
(b) What is the structure of this molecule? (8 points)
O
page 8 of 10
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
12. A molecule with the molecular formula C7H7Br displays the following mass spectrum.
(a) How many units of unsaturation are present? (3 points)
(b) What is the structure of the base peak at m/e 91? (3 points)
or
(c) What is the structure of the molecule? (3 points)
Br
(d) Briefly explain why there are two peaks at m/e 170 and 172 of nearly equal amounts. (3 pts)
Bromine exists in nature as roughly a 50:50 mixture of two isotopes which are 2 mass units different. 79 Br and 81Br
page 9 of 10
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
Chem 341
Final Exam
13 December 1999
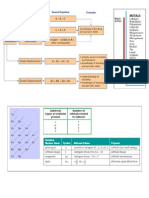
USEFULL DATA Infrared Correlations: C-H stretches: alkanes alkenes alkynes alcohols carbonyl alkyne nitrile 2850 - 2960 cm-1 3020 - 3100 cm-1 3300 cm-1 3400 - 3650 cm-1 1680 - 1750 cm-1 2100 2260 cm-1 2210 - 2260 cm-1 medium/strong medium strong (sharp) broad/strong strong medium medium
O-H stretch: C=O stretch: CC triple bond: CN triple bond
1
H NMR Correlations: (alkanes) (adjacent to sp2 carbon) (Y = O, N, Br, Cl, etc) (alkenes) (benzene rings) (aldehydes) (acids) 0.5 - 1.5 ppm 1.5 - 2.5 ppm 2.5 - 4.5 ppm 4.5 - 6.5 ppm 6.5 - 8.0 ppm 9.5 - 10.0 ppm 11.0 - 12.0 ppm
C-H allylic Y-C-H C=C-H sp2 aromatic O=C-H CO2H
13
C NMR Correlations: (alkanes) (Y = O, N, Br, Cl, etc) (alkenes) (benzene rings) (esters) (aldehydes, ketones) 10 - 60 ppm 40 - 80 ppm 100 - 150 ppm 120 - 160 ppm 175 - 200 ppm 200 - 220 ppm
C Y-C C=C sp2 aromatic O=C-O O=CR2
Atomic Weights C H O Cl Br 12 1 16 35 (75%), 37 (25%) 79 (52%), 81 (48%)
page 10 of 10
Prof. Gregory R. Cook
You might also like
- Calypso C-M-M-GUIDEDocument586 pagesCalypso C-M-M-GUIDEMark Hauser100% (15)
- ChromatographyDocument40 pagesChromatographybrook100% (1)
- Assigning R, S-ConfigurationsDocument1 pageAssigning R, S-ConfigurationsbrookNo ratings yet
- pKa TableDocument6 pagespKa Tablethales94No ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Quiz ADocument2 pagesAlgebra 1 Quiz AbrookNo ratings yet
- Acidity For 118A Leivens DetailsDocument9 pagesAcidity For 118A Leivens DetailsbrookNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Quiz QDocument4 pagesAlgebra 1 Quiz QbrookNo ratings yet
- Radical Chemistry Problem SetDocument2 pagesRadical Chemistry Problem SetbrookNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation TablesDocument6 pagesPhysics Equation TablesSangram NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Tracking Organic ReactionsDocument3 pagesTracking Organic ReactionsbrookNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlyDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlybrookNo ratings yet
- Chirality QuestionsDocument1 pageChirality QuestionsbrookNo ratings yet
- Unlimited Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic C H C H C H They Are Both C H - Ane 4Document4 pagesUnlimited Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic C H C H C H They Are Both C H - Ane 4brookNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemistrybrookNo ratings yet
- Sewing - Slides - Set 1Document22 pagesSewing - Slides - Set 1brookNo ratings yet
- Sewing - Slides - Set 2Document9 pagesSewing - Slides - Set 2brookNo ratings yet
- Precal Midterm SDocument13 pagesPrecal Midterm Sbrook0% (1)
- Doktorarbeit Michael A. K. Vogel Ohne CV - VermerkDocument260 pagesDoktorarbeit Michael A. K. Vogel Ohne CV - VermerkbrookNo ratings yet
- Precal Midterm QADocument3 pagesPrecal Midterm QAbrookNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesChemistry Cheat Sheetbrook92% (39)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)