Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizational Theory, Design, and Change
Organizational Theory, Design, and Change
Uploaded by
SpUnky Rohit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views18 pagesfree
Original Title
Plan Strategy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfree
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views18 pagesOrganizational Theory, Design, and Change
Organizational Theory, Design, and Change
Uploaded by
SpUnky Rohitfree
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall 1
Organizational Theory,
Design, and Change
Sixth Edition
Gareth R. Jones
Chapter 10
Types and Forms
of Organizational
Change
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 2
What is Organizational Change?
Organizational change: the process by
which organizations move from their
present state to some desired future state
to increase their effectiveness
Goal is to find improved ways of using
resources and capabilities in order to increase
an organizations ability to create value
Targets of change include improving
effectiveness at four different levels
Human resources
Functional resources
Technological capabilities
Organizational capabilities
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3
Targets of Change
Human Resource changes include:
Investment in training and development
Socializing employees into the
organizational culture
Changing organizational norms and
values to motivate a multicultural and
diverse workforce
Promotion and reward systems
Changing the composition of the top-
management team
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 4
Targets of Change
Functional Resources changes Include:
Transferring resources to the functions
where the most value can be created in
response to environmental change
An organization can improve the value that
its functions create by changing its
structure, culture, and technology
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Targets of Change
Technological capabilities changes
include:
Efforts intended to give an organization
the capacity to change itself in order to
exploit market opportunities
Adoption and use of new technologies
Development of new products/
technologies and the changing of existing
ones
Technological capabilities are a core
competence
5
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 6
Targets of Change
Organizational capabilities changes
include:
Changing organizational design
Culture and structure
Changing strategy
Changes that permeate entire
organization
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7
Figure 10.1: Forces for and
Resistances to Change
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 8
Levin's Force-Field
Theory of Change
Argues that two sets of opposing forces within an
organization determine how change will take place
Forces for change and forces making organizations
resistant to change
When forces for and against change are equal, the
organization is in a state of inertia
To change an organization, managers must increase
forces for change and/or decrease forces resisting change
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 9
Types of Change in Organizations
Evolutionary change: change that
is gradual, incremental, and narrowly
focused
Revolutionary change: change
that is sudden, drastic, and broadly
focused
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 10
Developments in
Evolutionary Change
Sociotechnical systems theory: a theory
that proposes the importance of changing
role and task or technical relationships to
increase organizational effectiveness
Total quality management (TQM): an
ongoing and constant effort by all of an
organizations functions to find new ways to
improve the quality of the organizations
goods and services
Flexible workers and Flexible work
teams
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 11
Developments in
Revolutionary Change
Reengineering: the process by which
managers redesign how tasks are bundled
into roles and functions to improve
organizational effectiveness
Focuses on business processes versus functions
Deliberately ignores the existing arrangement of
tasks, roles, and work activities
E-engineering: refers to companies
attempts to use information systems to
improve their performance
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12
Developments in
Revolutionary Change (cont.)
Restructuring: changing task and authority
relationships and redesigning organizational
structure and culture to improve organizational
effectiveness
Downsizing: the process of streamlining the
organizational hierarchy and laying off managers
and workers to reduce bureaucratic costs
Innovation: the process by which organizations
use their skills and resources to:
Create new technologies
Develop new goods and services
Better respond to the needs of their customers
One of the most difficult instruments of change to manage
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 13
Figure 10.2: Levin's Force-Field
Theory of Change
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 14
Figure 10.5: Levin's Three-Step
Change Process
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 15
Managing Change:
Action Research
Action research: a
strategy for generating
and acquiring
knowledge that
managers can use to
define an
organizations desired
future state
Used to plan a change
program that allows the
organization to reach
that state
Helps in the unfreezing,
changing, and refreezing
process
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 16
Organizational Development (OD)
Organizational development (OD):
a series of techniques and methods
that managers can use in their action
research program to increase the
adaptability of their organization
Goal is to improve organizational
effectiveness and to help people in
organizations reach their potential and
realize their goals and objectives
Can be used to unfreeze, change, and
refreeze attitudes and behaviors
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 17
Organizational Development
(cont.)
OD techniques to deal with resistance
to change
Education and communication: inform
workers about change and how they will
be affected
Participation and empowerment:
involve workers in change
Facilitation: help employees with change
Bargaining and negotiation
Manipulation: change the situation to
secure acceptance
Coercion: force workers to accept change
10- Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 18
Organizational Development
(cont.)
OD techniques to promote
change
Counseling, Sensitivity training, and
Process consultation
Team building, Intergroup training,
and Organizational mirroring
Total organizational interventions
Organizational confrontation meeting
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 4 Foundations of Organization DevelopmentDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Foundations of Organization DevelopmentMoses Avinash Andrews0% (1)
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SBI BANK Clerk Solved Exam PaperDocument7 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SBI BANK Clerk Solved Exam PaperSpUnky Rohit0% (1)
- Sub: SH Jagdish Kumar DO (Expired) - Detail of Terminal Dues and Dues/loans OutstandingDocument1 pageSub: SH Jagdish Kumar DO (Expired) - Detail of Terminal Dues and Dues/loans OutstandingSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- TDS On SalariesDocument3 pagesTDS On SalariesSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
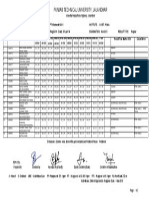
- Punjab Technical University, JalandharDocument1 pagePunjab Technical University, JalandharSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Organisational ChangeDocument209 pagesOrganisational ChangeSasirekha89% (27)
- Strategic Management - An IntroductionDocument26 pagesStrategic Management - An IntroductionSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Punjab Technical University, JalandharDocument1 pagePunjab Technical University, JalandharSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Role of State in Developing Debt MarketsDocument21 pagesPresentation: Role of State in Developing Debt MarketsSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Infosys BYDocument40 pagesA Presentation On Infosys BYSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Corporate Debt Market: Developments, Issues & Challenges: Efficient Allocation of ResourcesDocument11 pagesCorporate Debt Market: Developments, Issues & Challenges: Efficient Allocation of ResourcesManmeetSinghNo ratings yet
- Corporat Bond Market RK v11Document11 pagesCorporat Bond Market RK v11SpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Marketing Aptitude For SBI AssociatesDocument48 pagesMarketing Aptitude For SBI AssociatesShiv Ram Krishna100% (1)
- Natural Resource EnvironmentDocument5 pagesNatural Resource EnvironmentSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Stages of SMDocument3 pagesStages of SMSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- ImfundDocument21 pagesImfundSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Getting Through My Parents Divorce A Workbook For Children Coping With Divorce, Parental Alienation, and Loyalty Conflicts (Andre, KatherineBaker, Amy J. L)Document130 pagesGetting Through My Parents Divorce A Workbook For Children Coping With Divorce, Parental Alienation, and Loyalty Conflicts (Andre, KatherineBaker, Amy J. L)Tessa BaldwinNo ratings yet
- You Can Heal Your LifeDocument11 pagesYou Can Heal Your LifePrateek JhanjiNo ratings yet
- Character Formation 2 ModuleDocument57 pagesCharacter Formation 2 ModuleAlejandro DungcaNo ratings yet
- Dirty DozenDocument28 pagesDirty DozenDarby Morgan100% (1)
- Good Character TraitsDocument5 pagesGood Character TraitsRkantvyasNo ratings yet
- How To Identify and Value Your Inner Voice and Deep Power and Why To Work On Your Mental Toughness Maria MekliDocument40 pagesHow To Identify and Value Your Inner Voice and Deep Power and Why To Work On Your Mental Toughness Maria MekliMaria MEKLINo ratings yet
- Interpersonal CommunicationDocument20 pagesInterpersonal CommunicationnoneNo ratings yet
- Psych 160 Exam #2 Study GuideDocument43 pagesPsych 160 Exam #2 Study GuideAnnaNo ratings yet
- METACOGNICION ForenteinsDocument9 pagesMETACOGNICION ForenteinsPaolaNo ratings yet
- Loa 1 PDFDocument8 pagesLoa 1 PDFAlok PalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 3Document20 pagesChapter-3 3slow dancerNo ratings yet
- Scanning Exercise Alifa Nuzul NabilaDocument3 pagesScanning Exercise Alifa Nuzul NabilaAlifa Nuzul NabilaNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles: Behavioural Indicators VAK Visual Auditory KinestheticDocument8 pagesLearning Styles: Behavioural Indicators VAK Visual Auditory KinestheticMaxiNo ratings yet
- Molly ResearchDocument3 pagesMolly Researchapi-537508541No ratings yet
- Communication ProcessDocument4 pagesCommunication Processanon_189062430No ratings yet
- Assignment Classical & Operant ConditioningDocument15 pagesAssignment Classical & Operant ConditioningHaseeb RoyNo ratings yet
- Pamaran - Assignment 2Document3 pagesPamaran - Assignment 2YURI HARRIS SABLIN PAMARANNo ratings yet
- Running Head: TEACHER INTERVIEW 1: Teacher Interview Satwinder Kaur Ivy Tech Community CollegeDocument7 pagesRunning Head: TEACHER INTERVIEW 1: Teacher Interview Satwinder Kaur Ivy Tech Community Collegeapi-302458103No ratings yet
- Management of StutteringDocument54 pagesManagement of Stutteringpappu71371% (14)
- The Five Minds of A ManagerDocument8 pagesThe Five Minds of A ManagerAashutosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The SelfpauliNo ratings yet
- Case Study I Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderDocument9 pagesCase Study I Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderAisha NoorNo ratings yet
- Technology Students of Using Online LearningDocument3 pagesTechnology Students of Using Online LearningMaria Sofia AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Annual Self EvaluationDocument2 pagesAnnual Self EvaluationUtsav DubeyNo ratings yet
- Diass2 1Document4 pagesDiass2 1nhfdbhddhsdeyterhguyNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Assessment Tool For Spastic Reflexes (SCATS)Document3 pagesSpinal Cord Assessment Tool For Spastic Reflexes (SCATS)indeframe idNo ratings yet
- 001 Ra 10533 1Document60 pages001 Ra 10533 1Ty RonNo ratings yet
- Rúbrica Actitud enDocument1 pageRúbrica Actitud enirenedpmNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology Interactive - Stages of MasteryDocument4 pagesEducational Psychology Interactive - Stages of MasteryMohd AsyrullahNo ratings yet