Professional Documents
Culture Documents
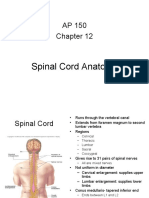
Central Nervous System
Uploaded by
Zeeshan Munir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesCentral nervous system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCentral nervous system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesCentral Nervous System
Uploaded by
Zeeshan MunirCentral nervous system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Muhammad Usman Munir
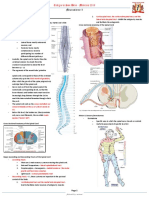
Muscle Spindle:
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of
a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this
muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous
system via sensory neurons.
Muscle spindles are found within the belly
of muscles, embedded in extrafusal muscle
fibers. these are composed of intrafusal muscle
fibers.
Upper Motor Neuron Lesion
An upper motor neuron lesion is a lesion of
the neural pathway above the anterior horn
cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of
the cranial nerves.
occur in conditions affecting motor neurons in
the brain or spinal cord such as:
stroke
multiple sclerosis
traumatic brain injury
cerebral palsy
Types:
1. Cotico-spinal Tract Lesions
2. Extra Cortico-Spinal Tract Lesions
Corticospinal Tract Lesions:
Loss of fine skilled voluntary movement of distal body parts.
(writing/drawing)
Loss of superficial abdominal reflex
Loss of cremasteric reflex
Loss of fasciliated responses
+ve Babinski sign (pathological version of plantar reflex
characterised by upgoing of big toe & fanning out of rest of the
toes when lateral border of foot is scratched)
Extra Corticospinal Tract Lesions:
Spastic paralysis (Hypertonia)
Clasp knife Rigidity (Rigid Limb)
Disused Atrophy
Exaggerated Deep Reflexes
Clonus (involuntary, rhythmic muscular
contractions & relaxations)
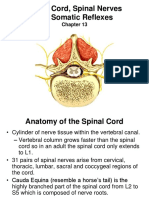
Lower Motor Neuron Lesion
A lower motor neuron lesion is
a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from
the anterior horn of the spinal cord to the
relevant muscles.
One major characteristic used to identify a lower
motor neuron lesion is flaccid paralysis
paralysis accompanied by loss of muscle tone.
Symptoms:
Flaccid paralysis
Loss of superficial reflexes
Loss of deep reflexes
Muscular atrophy
No Babinski sign
Fasciculation
Fibrillation
CORTICOSPINAL (Pyramidal) TRACT
You might also like
- MNs and MTsDocument32 pagesMNs and MTsJoanna RiveraNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument34 pagesApplied Anatomy of Spinal CordSuhana PathanNo ratings yet
- UMNDocument20 pagesUMNMuzayyinatulhayatNo ratings yet
- Kuliah UMN - LMN DR - VaniaDocument22 pagesKuliah UMN - LMN DR - Vania22p20015No ratings yet
- The Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainDocument78 pagesThe Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainMartha MulusaNo ratings yet
- 3.the Extrapyramidal TractDocument11 pages3.the Extrapyramidal Tractnanqo tanqoNo ratings yet
- Radicular Syndrome Kuliah BlokDocument32 pagesRadicular Syndrome Kuliah BlokNisha AnggiaNo ratings yet
- Radicular Syndrome Kuliah BlokDocument32 pagesRadicular Syndrome Kuliah BlokChRist LumingkewasNo ratings yet
- Sensory DisturbancesDocument155 pagesSensory DisturbancesCharles Okoh100% (1)
- DrMBA Medulla SpinalisDocument25 pagesDrMBA Medulla SpinalisAyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Neuro ADocument30 pagesNeuro Akazeem100% (1)
- Motor Pathways (1) 2019Document24 pagesMotor Pathways (1) 2019Sindile MchunuNo ratings yet
- Motor System: ZHAO Xinyu Department of Neurology The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou UniversityDocument29 pagesMotor System: ZHAO Xinyu Department of Neurology The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou Universityapi-19916399No ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of SpasticityDocument18 pagesThe Pathophysiology of SpasticityjpwchardonNo ratings yet
- Lower Motor NeuronDocument33 pagesLower Motor NeuronMarin SergiuNo ratings yet
- Basic Neuroanatomy and Function: Tract and Anterior Corticospinal Tract)Document47 pagesBasic Neuroanatomy and Function: Tract and Anterior Corticospinal Tract)Shourya PratapNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Umn LMN SensoryDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Umn LMN Sensoryapi-241050485No ratings yet
- Diseases of The Spinal Cord by Dr. WongelDocument51 pagesDiseases of The Spinal Cord by Dr. Wongelmogesie1995No ratings yet
- UMN Vs LMN RevisiDocument28 pagesUMN Vs LMN RevisiYeniNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Motor NeuronDocument22 pagesUpper and Lower Motor NeuronSry Hartaty WahidNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument22 pagesSpinal Cord AnatomyAbdallah ElshayahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Conditions of The Lower ExtremityDocument48 pagesClinical Conditions of The Lower Extremityim. EliasNo ratings yet
- Motor TractsDocument29 pagesMotor TractsbnmjgcNo ratings yet
- Motor TestingDocument57 pagesMotor TestinghemaanandhyNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument7 pagesSpinal CordRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Motor Functions of Spinal CordDocument51 pagesMotor Functions of Spinal CordZoafshan Ashfaque100% (1)
- Injury of Peripheral NerveDocument113 pagesInjury of Peripheral NerveRey AlwiwikhNo ratings yet
- 10-Physiology Extraocular MusclesDocument154 pages10-Physiology Extraocular MusclesYoussefNo ratings yet
- 23 - Umn - LMN-2019Document30 pages23 - Umn - LMN-2019sara khanNo ratings yet
- Lesions of Upper Motor Neurons and Lower Motor NeuronsDocument9 pagesLesions of Upper Motor Neurons and Lower Motor NeuronsJessy Ahmed El DamacyNo ratings yet
- 1.12 Cervical and Low Back Pain and RadiculopDocument42 pages1.12 Cervical and Low Back Pain and RadiculopsiusiuwidyantoNo ratings yet
- 3motor TestingDocument74 pages3motor Testing2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument207 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjuriesAashka MahetaNo ratings yet
- Umnl & LMNLDocument13 pagesUmnl & LMNLTammy BoudNo ratings yet
- Motor Functions of Spinal CordDocument43 pagesMotor Functions of Spinal CordEugeniu CoretchiNo ratings yet
- Motor PathwaysDocument21 pagesMotor PathwaysSharan MurugaboopathyNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal SystemDocument52 pagesPyramidal SystemKowsalya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Khan Academy Notes - Organ Systems - v2Document104 pagesKhan Academy Notes - Organ Systems - v2Thunder Blast100% (2)
- Corticospinal Tract - Pyramidal TractDocument52 pagesCorticospinal Tract - Pyramidal TractdrgokuNo ratings yet
- Structure Descending (Pyramidal, LMN, UMN) : Denpasar, 27 April 2018 Putu Gede Sudira (PSPD FK UNUD) PS FisioterapiDocument31 pagesStructure Descending (Pyramidal, LMN, UMN) : Denpasar, 27 April 2018 Putu Gede Sudira (PSPD FK UNUD) PS FisioterapiAditya Pramana KasidiNo ratings yet
- Neuropathy: By: Rey MartinoDocument18 pagesNeuropathy: By: Rey Martinorey martinoNo ratings yet
- Biology Organ SystemsDocument105 pagesBiology Organ SystemsLynther Myle ArizoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury, DisordersDocument54 pagesSpinal Cord Injury, DisordersChananNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neurological EmergenciesMAY2013Document69 pagesApproach To Neurological EmergenciesMAY2013PhaimNo ratings yet
- SPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Document51 pagesSPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Sheikh Muhammad MuhallilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Spinal CordDocument57 pagesChapter-Spinal Cordsimi yNo ratings yet
- Sciatic Nerve: by Name: Ahmed Abdalla Mahmoud Salem ID: 052608064Document35 pagesSciatic Nerve: by Name: Ahmed Abdalla Mahmoud Salem ID: 052608064Ahmed El-MalkyNo ratings yet
- TractsDocument42 pagesTractsVijayabala JeevaganNo ratings yet
- ReflexDocument26 pagesReflexr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Nerve Injury: Departemen Neurologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Islam Sumatera UtaraDocument27 pagesNerve Injury: Departemen Neurologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Islam Sumatera UtaraDea indah damayantiNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument37 pagesSpinal Cordyazan.fadi123No ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Document5 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Shab GeNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramDocument63 pagesSistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramUpuUt Putrhie MinchuuetNo ratings yet
- Motor TestingDocument58 pagesMotor Testingsarguss14100% (2)
- Motor Neuron DiseaseDocument23 pagesMotor Neuron DiseaseNaman MishraNo ratings yet
- Lumbar DermatomesDocument16 pagesLumbar DermatomesMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Spine Emergencies: Presenter: Nur Aizat Supervisor: Dr. FakhriyDocument42 pagesSpine Emergencies: Presenter: Nur Aizat Supervisor: Dr. FakhriyZainal HussainNo ratings yet
- Spinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsFrom EverandSpinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesFrom EverandBioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachFrom EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachNo ratings yet
- Case Study GuideDocument2 pagesCase Study GuideZeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Gapinc 120612081836 Phpapp02Document11 pagesGapinc 120612081836 Phpapp02Zeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Case Study No 18 Strategic Management by Michael A Hitt: Prepared by Roll Number 10735 Fawadhussain, 2014Document27 pagesCase Study No 18 Strategic Management by Michael A Hitt: Prepared by Roll Number 10735 Fawadhussain, 2014Zeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process of Denim FabricDocument22 pagesManufacturing Process of Denim FabricGarmentLearner100% (3)
- Denim Manufacturing: Technology and InnvoationDocument11 pagesDenim Manufacturing: Technology and InnvoationShafaqat AliiNo ratings yet
- 114959Document10 pages114959Vikas JagwaniNo ratings yet
- Case Google IncDocument7 pagesCase Google IncZeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Personality and Consumer BehaviorDocument33 pagesChapter 5 Personality and Consumer BehaviorZeeshan Munir100% (1)
- Consumer Decision Making and Beyond: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionDocument44 pagesConsumer Decision Making and Beyond: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionZeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Homework: Pg. 217 5-3 Pg. 218 5-5Document10 pagesChapter 5 Homework: Pg. 217 5-3 Pg. 218 5-5Zeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Global Economic Issues and Policies: Balance of Payments and Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument42 pagesGlobal Economic Issues and Policies: Balance of Payments and Foreign Exchange MarketsZeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- Capacity PlanningDocument30 pagesCapacity PlanningZeeshan Munir100% (1)