Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Submitted By: Group 6
Uploaded by
Pratik MehtaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Submitted By: Group 6
Uploaded by
Pratik MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
Submitted by: Group 6
What is insurance?
The definition of insurance can be made from two
points:
Functional definition.
Contractual definition.
FUNCTIONAL DEFINITION
Insurance is a co-operative device to spread the
loss caused by a particular risk over a number of
persons who are exposed to it and who agree to
insure themselves against the risk.
Contractual Definition
In the words of justice Tindall, Insurance is a
contract in which a sum of money is paid to
the assured as consideration of insurers
incurring the risk of paying a large sum upon
a given contingency.
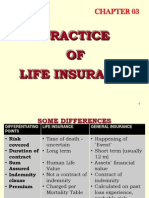
TYPE OF INSURANCE
INSURANCE
LIFE
INSURANCE
GENERAL
INSURANCE
LIFE INSURANCE
Life insurance is a written contract between the
insured and the insurer, that provides for the
payment of the insured sum on the date of the
maturity of the contract or on the unfortunate
death of the insured, whichever occurs earlier.
GENERAL INSURANCE
General insurance or non-life
insurance policies, including automobile
and homeowners policies, provide
payments depending on the loss from a
particular financial event. General
insurance typically comprises any
insurance that is not determined to be
life insurance.
TYPES OF GENERAL
INSURANCE
Health insurance
Business insurance
Automobile insurance
Fire insurance etc.
HEALTH INSURANCE
Just like one looks to safeguard ones
wealth, these policies ensure guarding
the insurer's health against any
calamities that may cause long term
harm to ones life and even hamper ones
earning ability for a lifetime. Some
examples of this type of policy are
mediclaim policy, personal accident,
group accident, traffic accident, etc.
Business Insurance
Risks of loss of profits/business, goods, plant
and machinery are most profound in case of
business. Under this head they cover the
most widely used policies that cover a
business from any loss of the above kind.
Some of these policies are burglary
insurance, shopkeepers insurance, key-man
insurance, marine insurance, public liability
insurance, workmen compensation
insurance, air transit insurance, fidelity
guarantee insurance etc.
Automobile Insurance
Auto Policy is required to be taken to
cover the risks that arise to the owner,
vehicle and third party. This includes the
Compulsory Vehicle Policy (In India, by the
Motor Vehicles Act, every car owner is
required to covered against Act risks) and
the Comprehensive Vehicle Policy.
FIRE INSURANCE
This policy is required to be
taken to prevent any loss of
profits / property from incidental
fire. Eg: fire insurance and fire
consequential loss policy.
HISTORY OF INSURANCE IN INDIA
5/12/2014 12
Phase Period Industry
Phase I
a. Life Insurance
b. General Insurance
1818 to 1956
(about 138 yrs)
1850 to 1972
(about 122 yrs)
Many (245) private sector companies only,
competitive market.
Many (107) private sector companies only,
competitive market.
Phase II
a.Life Insurance
b.General Insurance
1956 to 2000
(about 44 yrs)
1972 to 2000
(about 28 yrs)
Nationalization, public sector or State
monopoly, only one company.
Nationalization, public sector monopoly, only
one company with its four subsidiaries.
Phase III
Life Insurance and
General Insurance
After 2000
Opened to the entry of private domestic and
foreign companies, mixed sector of public and
private sector units, oligopoly of public sector
companies (14 life insurance and 12 general
insurance companies)
HISTORY OF INSURANCE IN INDIA contd..
5/12/2014 13
-1818 First life insurance company Oriental Life Insurance
Company (in Calcutta).
- 1850 First general insurance company Tritan Insurance
Company (in Calcutta)
- Till 1956/1972 life and general insurance industry grown in
terms of number of companies (life 245 and General 107 with
complete private sector ownership), the volume of premium,
investible resources, and so on. And both type of insurance
companies were competitive.
- The insurance was regulated through the Insurance Act, 1938.
- The picture changed after the Independence.
HISTORY OF INSURANCE IN INDIA contd..
5/12/2014 14
- In 1956, 245 Indian and Foreign life insurers and provident
societies were nationalized, and new single entity namely
LIC was established by passing the LIC Act, 1956.
- Similarly, in 1972, 107 general insurers were nationalized
through the passing of General Insurance Business
(Nationalisation) Act, 1972.
- The existing 107 insurers were amalgamated and grouped into
Five companies, viz., National Insurance Company (NIC),
New India Assurance Company (NIAC), Oriental Insurance
Company (OIC), United India Insurance Company (UIIC),
and General Insurance Corporation (GIC).
- Then insurance industry transformed into monopoly and
Oligopolistic state or public sector insurance industry in India.
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) was formed in
September 1956 by an Act of Parliament, LIC Act 1956 with
a contribution of Rs. 50 million.
The then Finance Minister Mr. C. D. Deshmukh while
piloting the bill for nationalization outlined the objectives of
LIC thus: To conduct the business with utmost economy with
the spirit of trusteeship; to charge premium no higher than
warranted by strict actuarial considerations; to invest the
funds for obtaining maximum yield for the policy holders
consistent with safety of capital; to render prompt and
efficient service to policy holders thereby making Insurance
widely popular.
5/12/2014 15
LIC OF INDIA contd
Presently the LIC has a network of seven zones; 100 divisions and
2,048 branches, personnel exceed seven lakhs employees and
over six lakhs agents.
Vision: A trans-nationally competitive financial conglomerate of
significance to societies and Pride of India.
Mission: To explore and enhance the quality of the life of people
through financial security by providing products and services of
aspired attributes with competitive returns and by rendering
resources for economic development.
Values: Caring and Courtesy, Initiatives and Innovation, Integrity
and Transparency, Quality and Returns, Participation and
Relationship, and Trustworthiness and Reliability
Culture: Agility (quickness), Adaptability, Collaboration,
Commitment, Discipline, Empowerment, Sensitivity, and
Excellence.
5/12/2014 16
LIC OF INDIA contd
Objectives
Spread Life Insurance widely and in particular to the rural
areas.
Maximise mobilization of peoples savings by making
insurance-linked savings adequately attractive.
Deployment of funds to the best of advantage of the investors
as well as the community as whole, keeping in view national
priorities and obligations of attractive return.
Conduct of business at most economy and with the full
realisation that the money belongs to the policyholders.
Act as trustee of the insured public in their individual and
collective capacities.
5/12/2014 17
PRINCIPLES AND INVESTMENT POLICY OF LICs
1. Security of funds, and
2. Maximization of return of investment,
5/12/2014 18
Investment Policy
1. Central Govt. marketable securities being not less than 20%
2. Loans to Housing Bank including above (1) being not less than 25%
3. State Govt. securities including Govt. Guaranteed marketable
securities, inclusive of (2) above being not less than 50%
4. Socially oriented sectors including public sector, co-operative sector
house building by policyholders, own house scheme, inclusive of (3)
above not less than 75%
5. Private corporate sector, loans to policyholders for construction and
acquisition of immovable property 25%
INVESTMENT POLICY OF
LICs
5/12/2014 19
INVESTMENT POLICY OF
LICs contd
5/12/2014 20
Working of insurance
LIC Products & Plans
Jeevan Anurag Komal Jeevan
CDA Endowment Vesting at
21
Marriage Endowment Or
Educational Annuity Plan
CDA Endowment Vesting
18
Jeevan Kishore Jeevan Chhaya
Child Career Plan Child Future Plan
Child Fortune Plus
Jeevan Aadhar
Jeevan Vishwas
The Endowment Assurance Policy
The Endowment Assurance Policy-Limited Payment
Jeevan Mitra(Double Cover Endowment Plan)
Jeevan Mitra(Triple Cover Endowment Plan)
Jeevan Anand
New Janaraksha Plan
Jeevan Amrit
Jeevan Shree-I
Jeevan Pramukh
The Money Back Policy-20 Years
The Money Back Policy-25 Years
Jeevan Surabhi-15 Years
Jeevan Surabhi-20 Years
Jeevan Surabhi-25 Years
Bima Bachat
jeevan Bharati-1
The Whole Life Policy
The Whole Life Policy- Limited Payment
The Whole Life Policy- Single Premium
Jeevan Anand
Jeevan Tarang
Two Year Temporary Assurance Policy
The Convertible Term Assurance Policy
Anmol Jeevan-I
Amulya Jeevan-I
Jeevan Saathi Plus
Jeevan Saathi
Jeevan Nidhi
Jeevan Akshay-VI
New Jeevan Dhara-I
New Jeevan Suraksha-I
Wealth Plus
Market Plus I
Profit Plus
Money Plus-I
Child Fortune Plus
Jeevan Saathi Plus
MAJOR PLAYERS
PRIVATE SECTOR COMPANIES
-Several leading private sector companies have entered in the field
of insurance sector, both in life and non-life insurance.
-There are several MNCs, in Joint Venture with Indian private
sector firms, have started operations in a big way.
5/12/2014 30
Private Players in the Life Insurance Business
Regd.
No.
Date of
Regd.
Name of the
Company
Who Owns it (in percentage)
101 23.10.00 HDFC Standard Life Standard Life, UK - 18 and HDFC 82
104 15.11.00 Max New York Life New York Life - 26 and Max India 74
105 24.11.00 ICICI Prudential Life Prudential, UK - 26 and ICICI Bank 74
107 10.01.01 Om Kotak Mahindra Old Maruthi, South Africa 26 and Kotak
Mahindra 74
109 31.01.01 Birla Sunlife Sun Life of Canada26 and Birla Capital 74
110 12.02.01 Tata AIG AIG, US 26 and Tatas 74
111 30.03.01 SBI Life Cardif SA, France 26 and State Bank of
India 74
114 02.08.01 ING Vysya ING, Holland26 and GMR Group, Hyd54
and ING Vysya Bank20
Regd.
No.
Date of
Regd.
Name of the
Company
Who Owns it (in percentage)
116 03.08.01 Allianz Bajaj Allianz AG, Germany 26 and Bajaj Auto 74
117 06.08.01 Metlife Metlife, US26, Shapoorji Pallonji30 and J&K
Bank25
121 03.01.02 AMP Sanmar AMP, Australia26 and Sanmar Group, Chennai
74
122 03.01.02 Aviva Aviva PLC, UK 26 and Dabur Investments 74
*** *** Reliance Life
*** *** Bharathi AXA
127 06.02.04
Sahara India
Insurance
128 07.11.05 Shriram Life
Insurance
Private Players in the Life Insurance Business
CURRENT SCENARIO contd.
MARKET SHARE
Growing at the rate of 15-20% annually
75% population has no insurance
Adds 7% to countrys GDP
LIC market share come down to 75% and private insurers
increased over 24%
Annuity or pension product have over 33% of market
Unity linked insurance scheme have monopoly
GENERAL INSURANCE CORPORATION (GIC)
Prior nationalization there were 68 Indian insurers (including
LIC) and 45 non-Indian insurers did the business.
In Nov. 1972, the general insurance business was nationalized
by the General Insurance Business (Nationalized), Act 1972
(GIBNA) and vested in the hand of the GIC and its four
subsidiaries viz.
1. National Insurance Co. Ltd.,
2. New India Assurance Co. Ltd.,
3. Oriental Fire and General Insurance Co. Ltd., and
4. United India Insurance Co. Ltd.
GIC was incorporated as a holding company in 1992.
General Insurance Business is completely owned by the
government.
The paid up capital of GIC was fully subscribed by the
Government and of four subsidiaries.
It was controlled by a single organization with four subsidiaries.
5/12/2014 34
G I C contd
GICs four subsidiaries:
1. National Insurance Co. Ltd.,
2. New India Assurance Co. Ltd.,
3. Oriental Fire and General Insurance Co. Ltd., and
4. United India Insurance Co. Ltd.
The Govt of India took over Control, supervision, and policy
making is with GIC.
The premium income for GIC comes mainly through the obligatory
reinsurance premium on a quota share basis from subsidiaries on
their direct business in India (almost 20% of subsidiaries business
come to GIC).
5/12/2014 35
G I C contd
TYPES AND STRUCTURE OF BUSINESS
- General insurance policies are not financial claims.
- There is no guarantee of renewal of policy on the same terms or
on any terms.
- The contract is short-term contract.
- The general insurance companies do not collect savings.
- Policy claims are unpredictable.
- Assets are held in relatively liquid form.
- GIC meets the requirements of industrial, manufacturing,
commercial, services, household, and agricultural sectors
through wide rage of 115 products, granting insurance coverage.
- GIC has been promoting insurance cover in the field of
livestock, poultry, sericulture, horticulture, pump sets, and
personal accidents.
5/12/2014 36
PRINCIPLES AND INVESTMENT POLICY GIC
1. Central Govt. securities being not less than 20%
2. State Govt. securities and other government guaranteed
securities, including (1) above, being not less than 30%
3. Loans to HUDCO/DDA/GIC-HF and to state govts. For
housing and fire fighting equipment, not less than 15%
4. Market sector not more than 55%
5/12/2014 37
5/12/2014 38
IRDAS MISSION
To protect the interests of the policyholders, to regulate,
promote and ensure orderly growth of the insurance industry
and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
5/12/2014 39
Composition of Authority under IRDA Act, 1999
As per the section 4 of IRDA Act' 1999, Insurance Regulatory
and Development Authority (IRDA, which was constituted by
an act of parliament) specify the composition of Authority.
The Authority is a ten member team consisting of
a. a Chairman;
b. five whole-time members;
c. four part-time members,
(all appointed by the Government of India)
5/12/2014 40
Duties, Powers and Functions of IRDA
Section 14 of IRDA Act, 1999 lays down the duties, powers and
functions of IRDA.
1. Subject to the provisions of this Act and any other law for the
time being in force, the Authority shall have the duty to
regulate, promote and ensure orderly growth of the insurance
business and re-insurance business.
2. Without prejudice to the generality of the provisions
contained in sub-section (1), the powers and functions of the
Authority shall include:
a. issue to the applicant a certificate of registration, renew,
modify, withdraw, suspend or cancel such registration;
5/12/2014 41
Duties, Powers and Functions of IRDA contd
b. protection of the interests of the policy holders in matters
concerning assigning of policy, nomination by policy
holders, insurable interest, settlement of insurance claim,
surrender value of policy and other terms and conditions of
contracts of insurance;
c. specifying requisite qualifications, code of conduct and
practical training for intermediary or insurance
intermediaries and agents;
d. specifying the code of conduct for surveyors and loss
assessors;
e. promoting efficiency in the conduct of insurance business;
5/12/2014 42
Duties, Powers and Functions of IRDA contd
f. specifying the form and manner in which books of account
shall be maintained and statement of accounts shall be
rendered by insurers and other insurance intermediaries;
g. regulating investment of funds by insurance companies;
h. regulating maintenance of margin of solvency;
i. adjudication of disputes between insurers and
intermediaries or insurance intermediaries;
j. supervising the functioning of the Tariff Advisory Committee;
CONCLUSION
Growth of Indian economy is an investment
driven growth
Opens a wide variety of investment
avenues
Companies help to gain knowledge of
products and services
Achieve a better standard for near future
life
Article on
insurance
You might also like
- HDFC LifeDocument66 pagesHDFC LifeChetan PahwaNo ratings yet
- Ic33 Print Out 660 English PDFDocument54 pagesIc33 Print Out 660 English PDFumesh100% (1)
- Legal Framework in InsuranceDocument36 pagesLegal Framework in InsuranceHarshit Srivastava 18MBA0050No ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk ManagementDocument140 pagesInsurance and Risk Managementgg100% (1)
- MCQ Chapter5645644645632Document15 pagesMCQ Chapter5645644645632bharath834No ratings yet
- of InsuranceDocument18 pagesof InsuranceDeepika verma100% (4)
- Unit 5 - Sbaa7001 Insurance Intermediaries and RegulationsDocument45 pagesUnit 5 - Sbaa7001 Insurance Intermediaries and RegulationsGracy100% (1)
- IC-24 - Legal Aspects of Life AssuranceDocument1 pageIC-24 - Legal Aspects of Life Assuranceaman vermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1906Document29 pagesChapter 1906Fozia MehtabNo ratings yet
- Marine Insurance and Fire InsuranceDocument33 pagesMarine Insurance and Fire InsuranceSuzanne Pagaduan CruzNo ratings yet
- Insurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesInsurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Fundamentals of InsuranceDocument16 pagesChapter 2: Fundamentals of InsuranceFaye Nandini SalinsNo ratings yet
- Risks and Rewards For The Insurance Sector: The Big Issues, and How To Tackle ThemDocument26 pagesRisks and Rewards For The Insurance Sector: The Big Issues, and How To Tackle ThemPie DiverNo ratings yet
- Insurance ManagementDocument76 pagesInsurance ManagementDurga Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Claim Settlement of GICDocument51 pagesClaim Settlement of GICSusilPandaNo ratings yet
- A Cat Bond Premium Puzzle?: Financial Institutions CenterDocument36 pagesA Cat Bond Premium Puzzle?: Financial Institutions CenterchanduNo ratings yet
- 88 - IC-Marketing-and-Public-RelationsDocument1 page88 - IC-Marketing-and-Public-RelationsVINAY S N33% (3)
- Rishi Project BookDocument93 pagesRishi Project BookAnvesh Pulishetty -B100% (1)
- IF7 Syllabus 2008Document3 pagesIF7 Syllabus 2008TelehealthNo ratings yet
- Report On BhartiDocument57 pagesReport On BhartiWendy CannonNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance Principle and Practice CPCUDocument9 pagesReinsurance Principle and Practice CPCUNguyen Quoc HuyNo ratings yet
- Motor Insurance Study Material FinalDocument67 pagesMotor Insurance Study Material FinalsekkilarjiNo ratings yet
- Insurance ProjDocument20 pagesInsurance ProjMahesh ParabNo ratings yet
- History of Insurance Legislation in IndiaDocument17 pagesHistory of Insurance Legislation in IndiaSagar Bhadrige83% (6)
- Origin of InsuranceDocument39 pagesOrigin of InsuranceNeha Sahitya100% (1)
- Company ProfileDocument44 pagesCompany ProfileBheeshm SinghNo ratings yet
- Legal Principles of InsuranceDocument7 pagesLegal Principles of Insurancemustansir53No ratings yet
- Ethics in Insurance SectorDocument40 pagesEthics in Insurance SectorRohan DhamiNo ratings yet
- Types of NBFCDocument16 pagesTypes of NBFCathiraNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Insurance Management SystemDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Insurance Management SystemAncy KalungaNo ratings yet
- Classification of InsuranceDocument5 pagesClassification of InsuranceRajendranath BeheraNo ratings yet
- Insurance Industry RM1Document62 pagesInsurance Industry RM1Raj Kumar RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Broker Tenders Guide 2015 WEBDocument32 pagesBroker Tenders Guide 2015 WEBLestijono LastNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of Indian BusinessDocument124 pagesLegal Aspects of Indian BusinessGuruKPO100% (3)
- Credit Point SystemDocument3 pagesCredit Point Systemshanmuga89No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document22 pagesChapter 5anis abdNo ratings yet
- Role of Acturies in InsuranceDocument12 pagesRole of Acturies in InsurancePrajakta Kadam67% (3)
- Fire InsuranceDocument34 pagesFire InsuranceSaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- ReinsuranceDocument14 pagesReinsuranceKrishnanunni VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Final PPT Motor TP Insurance & ClaimsDocument57 pagesFinal PPT Motor TP Insurance & ClaimsPRAKASH100% (1)
- Miscellaneous Manual 1Document507 pagesMiscellaneous Manual 1shrey12467% (3)
- Executive SummaryDocument53 pagesExecutive SummaryRohit VkNo ratings yet
- Fire ClausesDocument62 pagesFire ClauseschriscalarionNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous InsuranceDocument27 pagesMiscellaneous InsuranceRavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument13 pagesInsuranceShelly GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance Glossary 3Document68 pagesReinsurance Glossary 3أبو أنس - اليمنNo ratings yet
- Industrial Project On Reliance Life Insurance Company LimitedDocument116 pagesIndustrial Project On Reliance Life Insurance Company LimitedTimothy Brown100% (1)
- Green Delta Insurance PDFDocument98 pagesGreen Delta Insurance PDFSayeedMdAzaharulIslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Principles & Practice of Life InsuranceDocument21 pagesChapter 03 - Principles & Practice of Life InsuranceShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Motor Tariff Gist - Study MaterialDocument9 pagesMotor Tariff Gist - Study MaterialSadasivuni007No ratings yet
- III AssociateDocument2 pagesIII Associateagupta_118177No ratings yet
- Principles of Life InsuranceDocument63 pagesPrinciples of Life InsuranceKanishk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic of Reinsurance 03 June 21 Munch ReDocument24 pagesBasic of Reinsurance 03 June 21 Munch ReFernand DagoudoNo ratings yet
- Claim Procedure and Terms & Conditions For Personal Accident InsuranceDocument11 pagesClaim Procedure and Terms & Conditions For Personal Accident InsuranceMayur AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Business Interruption: Coverage, Claims, and Recovery, 2nd EditionFrom EverandBusiness Interruption: Coverage, Claims, and Recovery, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Insurance Policy Administration Systems A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandInsurance Policy Administration Systems A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- Cost and MGT Accting I Distance Module 1Document152 pagesCost and MGT Accting I Distance Module 1Firiehiwot BirhanieNo ratings yet
- ENTRANCE CONFERENCE AGENDA DiscussionDocument6 pagesENTRANCE CONFERENCE AGENDA DiscussionRay Vincent ChanNo ratings yet
- Relevant Cost Part 1 of 2Document25 pagesRelevant Cost Part 1 of 2simsonNo ratings yet
- Sbaa7001 Banking and Insurance Management II MBA - BATCH (2019-2021) Semester Iii - August 2020 School of Management StudiesDocument38 pagesSbaa7001 Banking and Insurance Management II MBA - BATCH (2019-2021) Semester Iii - August 2020 School of Management StudiesGracyNo ratings yet
- Sol Chap 5-7Document56 pagesSol Chap 5-7Anonymous QEcQfTeHl100% (1)
- Freight, Demurrage & Defence: Claims Handling Scope of CoverDocument2 pagesFreight, Demurrage & Defence: Claims Handling Scope of CoverKASHANNo ratings yet
- Choice IntroductionDocument22 pagesChoice IntroductionMonu SinghNo ratings yet
- 1601-EQ Final Jan 2018 Rev DPADocument2 pages1601-EQ Final Jan 2018 Rev DPAjose80% (5)
- Axa PhilDocument13 pagesAxa PhilKat EspanoNo ratings yet
- CRM in Financial Services: Best Practices, Trends and Strategy For The New EconomyDocument23 pagesCRM in Financial Services: Best Practices, Trends and Strategy For The New EconomySwarnajeet GaekwadNo ratings yet
- Allianz ESG Integration FrameworkDocument51 pagesAllianz ESG Integration FrameworkKhalilBenlahccenNo ratings yet
- Santa Fe Tour 2010Document3 pagesSanta Fe Tour 2010adventurecanada100% (3)
- PLI Premium Calculator NewDocument63 pagesPLI Premium Calculator NewvivekNo ratings yet
- SIP InterimDocument12 pagesSIP InterimSai KiranNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument19 pagesCase StudyAfsheen Danish NaqviNo ratings yet
- Liberty Mutual PresentationDocument21 pagesLiberty Mutual PresentationTeodora KotevskaNo ratings yet
- Securities Analysis and Portfolio Management PDFDocument64 pagesSecurities Analysis and Portfolio Management PDFShreya s shetty100% (1)
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelNiky SharyfNo ratings yet
- Chicago Booth Factsheet 2020-2021Document7 pagesChicago Booth Factsheet 2020-2021Suseen BabuNo ratings yet
- Sun Life Assurance v. CADocument2 pagesSun Life Assurance v. CAJellynNo ratings yet
- 2019 Membership Info - GlobalDocument14 pages2019 Membership Info - GlobalhuihudsonNo ratings yet
- Film FinancingDocument10 pagesFilm Financingjaikishan86100% (2)
- WTC 9/11 Cleanup Cases - Final Settlement Agreement As AmendedDocument104 pagesWTC 9/11 Cleanup Cases - Final Settlement Agreement As AmendedGeorge W. ConkNo ratings yet
- TMBI v. Mitsui DigestDocument4 pagesTMBI v. Mitsui DigestKaren Panisales100% (1)
- May20 Vn8157 Abu AaronDocument11 pagesMay20 Vn8157 Abu Aaronkhazwan85No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document70 pagesChapter 1Michael P. CelisNo ratings yet
- MWA Supplemental Report PDFDocument6 pagesMWA Supplemental Report PDFSoMa2022No ratings yet
- Banc AssuranceDocument67 pagesBanc Assuranceshruti pendhariNo ratings yet
- JAIIB Exam Previous Year Question Papers Free Download - 2014-2015 StudyChaChaDocument7 pagesJAIIB Exam Previous Year Question Papers Free Download - 2014-2015 StudyChaChaவன்னியராஜா78% (9)
- Summary of The Key Articles in UCP 600Document6 pagesSummary of The Key Articles in UCP 600Jhoo AngelNo ratings yet