Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Worksheet 2
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Worksheet 2
Uploaded by
xinying94Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Worksheet 2
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Worksheet 2
Uploaded by
xinying94Copyright:
Available Formats
1
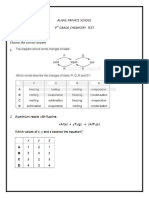
Carboxylic Acids and derivatives ( Acyl Chlorides) Worksheet 2
1 Why is the carbonyl carbon in acyl chlorides more susceptible to attack by nucleophiles?
.
.
...
2 How can you follow the relative ease of hydrolysis of acyl chlorides , halogenoalkanes and
halogenoarenes in the lab? What would you observe?
.
.
..
..
..
Why does ethanoyl chloride undergo hydrolysis more readily than chloroethane?
Why chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis?
.
.
.
5
Write a general equation for the reaction of an acyl chloride with an alcohol and state what
kind of reaction is it?
.
.
6 Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride with ethanol stating the conditions
(a) for the reaction
b) State the three steps involved in this reaction
..
c) Draw the mechanism for this reaction
7 Both Phenols and alcohols have a hydroxyl group. Which of the two is a weaker nucleophile
and why?
8 Draw the mechanism for a reaction of phenoxide ions with ethanoyl chloride
9 Describe the formation of phenyl benzoate from acyl chlorides
.
.
.
.
.
10 What are primary amines?
11 Draw the mechanism for a reaction between a primary amine and an acyl chloride
12 Write an equation for a reaction between ethanoyl chloride and ethyl amine. Name the
product formed.
You might also like
- Corrosion and Damage MechanismDocument83 pagesCorrosion and Damage Mechanismashtax100% (1)
- c2 Higher Revision Questions - Sets 12 3 Higher Tier OnlyDocument110 pagesc2 Higher Revision Questions - Sets 12 3 Higher Tier Onlyapi-320022467No ratings yet
- Chemistry 0620 Tutorial Abdulla Ikram - Teacher ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistry 0620 Tutorial Abdulla Ikram - Teacher Chemistryʀᴏʏᴀʟ ɢɪʀʟNo ratings yet
- ChemicalanalysisDocument90 pagesChemicalanalysismuhammadshadid4No ratings yet
- Initial A Level Assessment PDFDocument18 pagesInitial A Level Assessment PDFsimonbamfordNo ratings yet
- GRADE 9 ADMISSION TEST IDocument3 pagesGRADE 9 ADMISSION TEST IdodoNo ratings yet
- Extraction of MetalsDocument5 pagesExtraction of MetalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Reacting Mass Calculations 1: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 24-October-2016 Chemsheets GCSE 1093Document2 pagesReacting Mass Calculations 1: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 24-October-2016 Chemsheets GCSE 1093George AshcroftNo ratings yet
- A Passage To Africa (Annotated)Document2 pagesA Passage To Africa (Annotated)danieljamesmaherNo ratings yet
- S5 Chemistry End of July Test Exams 2021.Document5 pagesS5 Chemistry End of July Test Exams 2021.kimberlycarls johnNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Part 2 Question 2Document4 pagesElectrolysis Part 2 Question 2danielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Separation and Purification WSDocument3 pagesSeparation and Purification WSchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 4 QPDocument9 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 4 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 2Document7 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 2Asif ArmanNo ratings yet
- SDocument8 pagesSlubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument41 pagesUnit 4-Photosynthesis Questionsareyouthere92100% (3)
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledانور الحاجNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 12 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDocument10 pagesBritish International College: Year 12 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 12 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDocument10 pagesBritish International College: Year 12 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonNo ratings yet
- Group IVDocument5 pagesGroup IVFatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- AQA C2 Past Paper Q&A Part 1Document184 pagesAQA C2 Past Paper Q&A Part 1Junaid AsgharNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hypochlorite: Odyssey Manufacturing CoDocument29 pagesSodium Hypochlorite: Odyssey Manufacturing CoFatemeh kazemiNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding QuestionsDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding QuestionsZak NNo ratings yet
- Gold Chemistry 2Document189 pagesGold Chemistry 2Radulescu Eugen100% (3)
- Preliminary Chemistry 2014 Modules 8.4.3 and 8.4.4 - Solubility, Concentration of Solutions and PrecipitationDocument2 pagesPreliminary Chemistry 2014 Modules 8.4.3 and 8.4.4 - Solubility, Concentration of Solutions and PrecipitationifodifodfNo ratings yet
- 2023 - Paper-50Document19 pages2023 - Paper-50Wijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- Salt Preparation ChemDocument2 pagesSalt Preparation ChemAhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Electrolysis 2023 BookDocument8 pagesAssignment of Electrolysis 2023 Bookaxmedbadali561No ratings yet
- 13.1 STRUCTURE BONDING Copy 2Document8 pages13.1 STRUCTURE BONDING Copy 2Arman JavedNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Database Part 1Document12 pages5.4 Database Part 1Mags KasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FinalDocument17 pagesChemistry FinalHashika ChanuthNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 9 Paper Jun 2000Document7 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 9 Paper Jun 2000Nabeeha07No ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Group 7Document9 pagesTopic 4 - Group 7Abirame SivakaranNo ratings yet
- Science MLL Light 22Document9 pagesScience MLL Light 22gauravNo ratings yet
- C3Document12 pagesC3Eunice YeohNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Transition Metals - Complex IonsDocument12 pages5.4 Transition Metals - Complex IonsAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Chemistry: C3 Chapter 1 HigherDocument25 pagesExampro GCSE Chemistry: C3 Chapter 1 HigherSamuel KalemboNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPaangijain646No ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 22Document19 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 22Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal ComplexDocument25 pagesTransition Metal Complexpaulcampbell37No ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Document20 pagesA-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Jesus ChristNo ratings yet
- UdkdfhvkdhfnfDocument12 pagesUdkdfhvkdhfnfG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 17Document16 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 17Lutaaya Paul BamutaliraNo ratings yet
- AsdfasdfehjhgfdfdsDocument81 pagesAsdfasdfehjhgfdfdsFrank Kleber García YaretaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriaDocument6 pagesChemical EquilibriaHajra NasirNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - RevisionDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - RevisionannnyyyaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesChlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and Answersideal writersNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - RevisionDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - RevisionannnyyyaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chu I PH N NG Nhóm HalogenDocument3 pagesChu I PH N NG Nhóm Halogent.uyenNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Reacting Masses 3Document2 pagesTask 1 Reacting Masses 3harishthestudent2No ratings yet
- Directions: Answer The Following Questions During The Mini-Lesson And/or Videos.Document1 pageDirections: Answer The Following Questions During The Mini-Lesson And/or Videos.api-16881361No ratings yet
- 07 - Intro To Electrode Potentials - Student SheetDocument3 pages07 - Intro To Electrode Potentials - Student SheetAyaan Asim KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument10 pagesChemical EnergeticsShahmeer MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & CompoundsDocument18 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compoundsmohamedyanaal2020No ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Switching Power Converters: A Hands-on GuideFrom EverandTroubleshooting Switching Power Converters: A Hands-on GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Advanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationFrom EverandAdvanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- 94 Text 1Document4 pages94 Text 1xinying94No ratings yet
- 94 Text 2Document4 pages94 Text 2xinying94No ratings yet
- 96 Text 1Document19 pages96 Text 1xinying94No ratings yet
- 95 Text 1Document19 pages95 Text 1xinying94No ratings yet
- 03 Text4Document4 pages03 Text4xinying94No ratings yet
- 04 Text 4: Failed School Reforms, Traces The Roots of Anti-Intellectualism in Our SchoolsDocument5 pages04 Text 4: Failed School Reforms, Traces The Roots of Anti-Intellectualism in Our Schoolsxinying94No ratings yet
- 03 Text1Document4 pages03 Text1xinying94No ratings yet
- 04 Text2Document5 pages04 Text2xinying94No ratings yet
- 00 Text 1234Document20 pages00 Text 1234xinying94No ratings yet
- 02 Text2Document4 pages02 Text2xinying94No ratings yet
- 02 Text1Document4 pages02 Text1xinying94No ratings yet
- 02 Text4Document4 pages02 Text4xinying94No ratings yet
- Antibody 1234Document108 pagesAntibody 1234xinying94No ratings yet
- 1 20《经济学家》读译参考Document62 pages1 20《经济学家》读译参考xinying94No ratings yet