Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Hematemesis Melena Hematochezia Occult Bleeding
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Hematemesis Melena Hematochezia Occult Bleeding
Uploaded by
Kusuma Edhi KuncoroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Hematemesis Melena Hematochezia Occult Bleeding
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Hematemesis Melena Hematochezia Occult Bleeding
Uploaded by
Kusuma Edhi KuncoroCopyright:
Available Formats
GASTROINTESTINAL
BLEEDING
Hematemesis
Melena
Hematochezia
Occult bleeding
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Clinical manifestations of GI bleeding
depends upon extent & rate
Postural hypotension suggests acute
hemorrhage & intravascular volume
depletion
Fatigue & exertional dyspnea typical
symptoms with slow, chronic blood loss
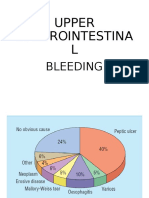
ETIOLOGY OF UGI BLEEDING
Differential diagnosis is extensive
Major causes;
PUD
Esophageal/Gastric Varices
Esophagitis
Mallory-Weiss tear
ETIOLOGY OF LOWER BLEED
Anal and rectal lesions
Colonic lesions
Diverticula
HISTORY
Consider factors that may cause false +
FOBT
Postural hypotension helps determine need
for hospitalization
H/O PUD, recent use of NSAIDs
Weight loss & change in bowel habits
H/O liver disease, ETOH abuse,
inflammatory bowel disease
PHYSICAL
Orthostatic changes in pulse & BP
Cardiopulmonary
Skin
Examine oral cavity & nasopharynx
Lymph nodes
Abdomen
Digital rectal
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
CBC
PT, PTT
Other lab tests relevant to physical findings
Upper endoscopy if stable
Colonoscopy
INDICATIONS FOR
ADMISSION & REFERRAL
Admit pts with h/o recent brisk bleeding &
orthostatic changes
Admit pts with less sever blood loss who have
comorbid conditions aggravated by anemia
Profound anemia with no evidence of blood loss
Refer pts who are candidate for endoscopy or
colonscopy when source of bleeding is elusive
You might also like
- CirrhosisDocument54 pagesCirrhosisYani88% (8)
- Biliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract Disease - Emmet AndrewsBoneyJalgarNo ratings yet
- Gi BleedDocument28 pagesGi BleedligitafitranandaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: PCOM Internal Medicine Residents 2004Document30 pagesGastrointestinal Bleeding: PCOM Internal Medicine Residents 2004nesakusumaNo ratings yet
- Upper Gi BleedingDocument36 pagesUpper Gi BleedingHalimatul SaadiahNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AlterationsDocument40 pagesGastrointestinal AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestina L: BleedingDocument35 pagesUpper Gastrointestina L: BleedingayuNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: CPT Donald C Palma MCDocument28 pagesGastrointestinal Disorders: CPT Donald C Palma MCJorge RabajaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Signs in Acute Abdominal PainDocument40 pagesSymptoms and Signs in Acute Abdominal PainPoh TseNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Jaundice 2020Document4 pagesObstructive Jaundice 2020Choden JamyangNo ratings yet
- Edema: Leyi Gu Renal Division, Renji HospitalDocument27 pagesEdema: Leyi Gu Renal Division, Renji HospitalIdham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Gi BleedDocument33 pagesGi BleedMuhammad ArmghanNo ratings yet
- Upper Gi BleedDocument47 pagesUpper Gi BleedAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Inzar Yasin Ammar LabibDocument47 pagesPrepared by Inzar Yasin Ammar LabibJohn Clements Galiza100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis: DR Alex MogereDocument51 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: DR Alex MogereGladys Maina100% (1)
- Fluid Volume DisturbancesDocument25 pagesFluid Volume Disturbancesmoonlight ariNo ratings yet
- GI Bleeding:: From Mouth To RectumDocument31 pagesGI Bleeding:: From Mouth To RectumBendy Dwi IrawanNo ratings yet
- UremiaDocument52 pagesUremiamgopigio5No ratings yet
- Jaundice: DremsaidDocument42 pagesJaundice: DremsaidabdallhNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN Review GastrointestinalDocument23 pagesCCRN-PCCN Review GastrointestinalGiovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding in NewbornDocument28 pagesGastrointestinal Bleeding in NewbornHafiz AwaisNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolytes 2Document22 pagesFluid Electrolytes 2QueenClerk VillarteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Stomach NotesDocument5 pagesNursing Stomach Noteslucas dibenedettoNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Inzar Yasin Ammar LabibDocument47 pagesPrepared by Inzar Yasin Ammar LabibdiaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Upper GI BleedDocument42 pagesApproach To A Patient With Upper GI BleedMuhammad Naveed AslamNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Liver Disease - Orla CrosbieDocument46 pagesAcute and Chronic Liver Disease - Orla CrosbiewasimqureshiNo ratings yet
- Student Copy of Gastrointestinal Problems SP 2010 IggyDocument80 pagesStudent Copy of Gastrointestinal Problems SP 2010 IggyJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Atul Sharma Uppergi Fcccm23Document47 pagesAtul Sharma Uppergi Fcccm23Atul SharmaNo ratings yet
- CPC Edit RMDocument39 pagesCPC Edit RMSoumya GuptaNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument43 pagesGerdNidhi shriNo ratings yet
- Acute Chronic Kidney InjuryDocument29 pagesAcute Chronic Kidney InjuryPriya GKNo ratings yet
- 1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3Document84 pages1100 Ultrasound of The Acute Abdomen 15 3gp1promo2016No ratings yet
- Middle Age Man With Nephrotic Syndrome, Ascitis and Edema: Raika Jamali MDDocument66 pagesMiddle Age Man With Nephrotic Syndrome, Ascitis and Edema: Raika Jamali MDyusnafratilova16No ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument52 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseAna Cotoman100% (1)
- New Upper Gi BleedDocument35 pagesNew Upper Gi Bleedapi-195799092No ratings yet
- Liver CirhosisDocument72 pagesLiver CirhosisamadoorahmedNo ratings yet
- PembahasanDocument1,129 pagesPembahasanatc100% (1)
- EdemaDocument27 pagesEdemaAyyappan JayavelNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Varices AMJDocument35 pagesEsophageal Varices AMJAli Al.JuffairiNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument57 pagesPortal Hypertension: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNo ratings yet
- CIRRHOSIS v1Document41 pagesCIRRHOSIS v1anil sahNo ratings yet
- 01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersDocument51 pages01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersRere AnugrahNo ratings yet
- UgumDocument50 pagesUgumhailu henockNo ratings yet
- EdemaDocument27 pagesEdemarapadilNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument60 pagesAcute PancreatitisHara TsolakidouNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: DR Phillipo Leo ChalyaDocument19 pagesIntussusception: DR Phillipo Leo ChalyaSibabaong'ombe MasakaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Distention and AscitesDocument49 pagesAbdominal Distention and AscitesNinaNo ratings yet
- Managing Common Ward CallsDocument55 pagesManaging Common Ward CallsShuvashis TituNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Chronic Renal FailureDocument48 pagesAcute Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failurekimchi girlNo ratings yet
- Budd Chiari Syndrome: by DR - Kamran M SaeedDocument41 pagesBudd Chiari Syndrome: by DR - Kamran M SaeeddockmsNo ratings yet
- Upper Gi BleedingDocument37 pagesUpper Gi Bleedingfathima AlfasNo ratings yet
- C5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)Document44 pagesC5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)coco brillqnteNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Saluran CernaDocument21 pagesPerdarahan Saluran CernaAmalia Hendar PangestutiNo ratings yet
- CKD Case PresentationDocument25 pagesCKD Case PresentationMohamed Anwer NaleefNo ratings yet
- Renal NotesDocument11 pagesRenal NotesPatty Pasarilla Passehl100% (2)
- Hepatic Venous Disease 2Document22 pagesHepatic Venous Disease 2Self UpgradeNo ratings yet
- Hematemesis Melena (Upper Gi Bleeding)Document134 pagesHematemesis Melena (Upper Gi Bleeding)Mardoni Efrijon100% (1)
- Upper GI Bleed - SymposiumDocument38 pagesUpper GI Bleed - SymposiumSopna ZenithNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Ischemic Stroke in Young AdultDocument26 pagesIschemic Stroke in Young AdultBill Jones TanawalNo ratings yet
- TextbookofRogaNidanaandVikritiVIgyanDr Gopikrishnas AcharyaDocument72 pagesTextbookofRogaNidanaandVikritiVIgyanDr Gopikrishnas AcharyaArunakumar CNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- 14 CefaleeaDocument52 pages14 Cefaleeagabriela.nicolescuNo ratings yet
- Tibia FracturesDocument15 pagesTibia FracturesmoimoimoibaridacheNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Urine CulturesDocument29 pagesInterpretation of Urine Culturestummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFAsmaa100% (1)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)Document3 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)Muhammad Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Pierre Robin Syndrome A Case ReportDocument2 pagesPierre Robin Syndrome A Case ReportResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder Causes and TreatmentsDocument11 pagesFrozen Shoulder Causes and TreatmentsSylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Ear HematomaDocument3 pagesEar HematomaSafeer GhalibNo ratings yet
- Crigler-Najjar Syndrome - UpToDateDocument31 pagesCrigler-Najjar Syndrome - UpToDateMihaela Alexandra RepeziNo ratings yet
- 1.6+7 Laboratory Investigation and Film Interpretation WITHOUT ANSWERSDocument21 pages1.6+7 Laboratory Investigation and Film Interpretation WITHOUT ANSWERSAlex KamougerosNo ratings yet
- PAROS (Case 3)Document2 pagesPAROS (Case 3)Carl Michael RazoNo ratings yet
- Gridhrasi Case PresentationDocument35 pagesGridhrasi Case PresentationAmogha Kulkarni100% (1)
- Wiki - Week 1 - The Nervous System - CourseraDocument3 pagesWiki - Week 1 - The Nervous System - Courseracharles luisNo ratings yet
- NATVNS Paediatric Glamorgan v7Document5 pagesNATVNS Paediatric Glamorgan v7Nie AfnyNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Infectious DiseaseDocument52 pagesTyphoid Fever: Infectious Disease12. Akshit AtwalNo ratings yet
- 65 - Approach To Patients With CancerDocument1 page65 - Approach To Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Heart Transplantation: Dr. K V Siva KrishnaDocument133 pagesHeart Transplantation: Dr. K V Siva KrishnaRahul K. JagaNo ratings yet
- LP Tumor Mamae OkDocument13 pagesLP Tumor Mamae OkDiban namiNo ratings yet
- Prof. Syakib Acute Kidney Injury - Internal Medicine Emergency Course - Agustus 2019-DikonversiDocument35 pagesProf. Syakib Acute Kidney Injury - Internal Medicine Emergency Course - Agustus 2019-DikonversidrroytambunanNo ratings yet
- Diskusi Topik 2 (PPOK) - Nafisa Zulpa Elhapidi - 406202067Document59 pagesDiskusi Topik 2 (PPOK) - Nafisa Zulpa Elhapidi - 406202067nafisa zulfaelNo ratings yet
- Cataract - GlaucomaDocument2 pagesCataract - GlaucomaggukNo ratings yet
- 4 Pharma General AnestheticsDocument10 pages4 Pharma General AnestheticsisahNo ratings yet
- Froelich Syndrome and HomoeopathyDocument13 pagesFroelich Syndrome and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- CNS DR Najeeb Notes Part 3Document3 pagesCNS DR Najeeb Notes Part 3Dr. Tarush DhawanNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Disease: An Update: EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesKawasaki Disease: An Update: EpidemiologyEmma González de BaideNo ratings yet
- NZ Crisis Handbook - DiagnosingDocument16 pagesNZ Crisis Handbook - DiagnosingSean SmythNo ratings yet
- Botulism As A Bioterrorism AgentDocument24 pagesBotulism As A Bioterrorism AgentFabián FernándezNo ratings yet