Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Windows 9x
Windows 9x
Uploaded by
scribd388Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Windows 9x
Windows 9x
Uploaded by
scribd388Copyright:
Available Formats
Windows 3.
0, released in 1990
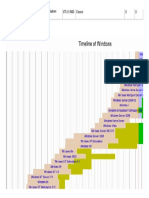
Windows 9x
The next major consumer-oriented release of Windows, Windows 95, was released on August 24, 1995.
While still remaining MS-DOS-based, Windows 95 introduced support for native 32-bit applications,
plug and play hardware, preemptive multitasking, long file names of up to 255 characters, and provided
increased stability over its predecessors. Windows 95 also introduced a redesigned, object oriented user
interface, replacing the previous Program Manager with the Start menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer
shell. Windows 95 was a major commercial success for Microsoft; Ina Fried of CNET remarked that "by
the time Windows 95 was finally ushered off the market in 2001, it had become a fixture on computer
desktops around the world."
[13]
Microsoft published four OEM Service Releases (OSR) of Windows 95,
each of which was roughly equivalent to a service pack. The first OSR of Windows 95 was also the first
version of Windows to be bundled with Microsoft's web browser, Internet Explorer.
[14]
Mainstream
support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2000 and extended support for Windows 95 ended on
December 31, 2001.
[15]
Windows 95 was followed up with the release of Windows 98 on June 25, 1998, which introduced the Windows Driver Model, support for USB
composite devices, support for ACPI, hibernation, and support for multi-monitor configurations. Windows 98 also included integration with Internet
Explorer 4 through Active Desktop and other aspects of the Windows Desktop Update (a series of enhancements to the Explorer shell which were also
made available for Windows 95). In May 1999, Microsoft released Windows 98 Second Edition, an updated version of Windows 98. Windows 98 SE
added Internet Explorer 5.0 and Windows Media Player 6.2 amongst other upgrades. Mainstream support for Windows 98 ended on June 30, 2002
and extended support for Windows 98 ended on July 11, 2006.
[16]
On September 14, 2000, Microsoft released Windows ME (Millennium Edition), the last DOS-based version of Windows. Windows ME incorporated
visual interface enhancements from its Windows NT-based counterpart Windows 2000, had faster boot times than previous versions (which however,
required the removal of the ability to access a real mode DOS environment, removing compatibility with some older programs),
[17]
expanded multimedia
functionality (including Windows Media Player 7, Windows Movie Maker, and the Windows Image Acquisition framework for retrieving images from
scanners and digital cameras), additional system utilities such as System File Protection and System Restore, and updated home networking tools.
[18]
However, Windows ME was faced with criticism for its speed and instability, along with hardware compatibility issues and its removal of real mode
DOS support. PC World considered Windows ME to be one of the worst operating systems Microsoft had ever released, and the 4th worst tech
product of all time.
[19]
Windows NT
You might also like
- Operating Systems CourseworkDocument61 pagesOperating Systems CourseworkEkode JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Programming User RPLIn PCDocument26 pagesProgramming User RPLIn PCselm27No ratings yet
- Windows 3.1x Is A Series of 16-Bit Operating Systems Produced by Microsoft ForDocument12 pagesWindows 3.1x Is A Series of 16-Bit Operating Systems Produced by Microsoft ForJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- A Discussion On MS Windows & DOS (By Sajjad CH.)Document18 pagesA Discussion On MS Windows & DOS (By Sajjad CH.)Sajjad Rasool ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Research Topic Windows 97 From WikiDocument1 pageResearch Topic Windows 97 From WikiAlan_PotatoNo ratings yet
- WindowsDocument4 pagesWindowsReal WrittenNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Windows OSDocument8 pagesCase Study On Windows OSroshani chede0% (1)
- Unit 1 Ms WindowsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Ms WindowsKamal MittalNo ratings yet
- Project IN CS 342: Submitted By: Perez, John Carlo S. Submitted To: Jerome Tan AlvezDocument43 pagesProject IN CS 342: Submitted By: Perez, John Carlo S. Submitted To: Jerome Tan AlvezMichael San LuisNo ratings yet
- Submited by Usha K. Agashe Guided by Mr. Dev ShahareDocument17 pagesSubmited by Usha K. Agashe Guided by Mr. Dev Shahareᗬᗴᐻ ᔤᗩᕼᕢᖆᘍNo ratings yet
- Joomla ContentDocument21 pagesJoomla ContentAlelieAnn ManuelNo ratings yet
- Office Productivity Week 5Document7 pagesOffice Productivity Week 5Erizza PastorNo ratings yet
- Ebook On Evolution of Computer Operating SystemDocument7 pagesEbook On Evolution of Computer Operating SystemRonaldo EtuNo ratings yet
- Microsoft WindowsDocument2 pagesMicrosoft WindowsMitko DimitrovNo ratings yet
- Virtual BookDocument19 pagesVirtual Bookstoragejack3264No ratings yet
- Omputer Systems Servicing NCII (G11) : (Learning Activity)Document14 pagesOmputer Systems Servicing NCII (G11) : (Learning Activity)Tabata Qbz TawinNo ratings yet
- Windows Nores - 2022Document11 pagesWindows Nores - 2022Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Evolution of WindowsDocument10 pagesEvolution of Windowsstrictpond80005No ratings yet
- Window Sine 2000 To 2005: Microsoft Windows 2000Document15 pagesWindow Sine 2000 To 2005: Microsoft Windows 2000Anonymous SHu6DB4tyNo ratings yet
- History of Microsoft WindowsDocument2 pagesHistory of Microsoft WindowsPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- From Windows 1 To Windows 10Document11 pagesFrom Windows 1 To Windows 10Mrj NionesNo ratings yet
- Microsoft WindowsDocument13 pagesMicrosoft Windowsgaurav775588No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 WINDOWS Operating SystemDocument7 pagesUNIT 4 WINDOWS Operating SystemsandeepNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows 95: "OSR2" Redirects Here. For The Gene, See - "Windows 4.0" Redirects Here. Not To Be Confused WithDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Windows 95: "OSR2" Redirects Here. For The Gene, See - "Windows 4.0" Redirects Here. Not To Be Confused WithAmor BalbonNo ratings yet
- Windows HistoryDocument17 pagesWindows HistoryMiftah ToleNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument9 pagesComputer SoftwareRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- MS JourneyDocument23 pagesMS Journeymanu.garg15No ratings yet
- 10 Different Types of OS LectureDocument45 pages10 Different Types of OS LectureErjan PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Study of Windows 2000 Operating SystemDocument15 pagesStudy of Windows 2000 Operating SystemGaurav50% (2)
- 7 Op Week 5 Windows - Leilani - MildredDocument8 pages7 Op Week 5 Windows - Leilani - MildredDonna Marie ArcangelNo ratings yet
- Operating System Definition and Function: o o o oDocument10 pagesOperating System Definition and Function: o o o oJagjit GillNo ratings yet
- Windows Operating SystemDocument8 pagesWindows Operating System08BSc.ITARNAV PATELNo ratings yet
- Windows 2000: Wwe 2K Windows NTDocument21 pagesWindows 2000: Wwe 2K Windows NTOrlando FelixNo ratings yet
- Windows HistoryDocument22 pagesWindows HistoryXOsarNo ratings yet
- Window Os Group 3Document20 pagesWindow Os Group 3Rhomes AbadinesNo ratings yet
- SundaramDocument4 pagesSundaramManaswi GargNo ratings yet
- Microsft Windows Operating System PresentationDocument16 pagesMicrosft Windows Operating System Presentationletsjoy100% (2)
- Microsoft OS VersionsDocument17 pagesMicrosoft OS Versionskarlajoy.sucgang-22No ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows Operating Systems For PCsDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Windows Operating Systems For PCsNafta PutraNo ratings yet
- Windows Me: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesWindows Me: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAmor BalbonNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Windows PDFDocument15 pagesCase Study On Windows PDFJPC RTK100% (1)
- ASSIGNMEMT Ict ShujjatDocument15 pagesASSIGNMEMT Ict ShujjatShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Basics of PC and Windows: 1.1 Microsoft WindowDocument31 pagesChapter One Basics of PC and Windows: 1.1 Microsoft WindowFilma FiliNo ratings yet
- What Is Operating SystemDocument20 pagesWhat Is Operating SystemMd. Rashedul Islam 1511108042No ratings yet
- Microsoft Window Operating System & Its AdvancementsDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Window Operating System & Its AdvancementsDev SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1985: Windows 1.0Document7 pages1985: Windows 1.0adzrulNo ratings yet
- Evolution in Operating SystemsDocument14 pagesEvolution in Operating SystemsBush Reece MauriceNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Windows Ms. Jaya Gangwani Unit V: Case Study On WindowsDocument15 pagesCase Study On Windows Ms. Jaya Gangwani Unit V: Case Study On WindowsArpit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- CSC134Document10 pagesCSC134RashNo ratings yet
- Case Study On WindowsDocument7 pagesCase Study On Windowsbp20112003No ratings yet
- Introduction To WindowsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To WindowspNo ratings yet
- Windows XP HistoryDocument6 pagesWindows XP HistoryRohit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Windows NT LineageDocument2 pagesWindows NT LineageSaira UsmanNo ratings yet
- MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System)Document5 pagesMS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System)blessing pakachenaNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Presented ToDocument23 pagesGroup Members: Presented Todawood ahmedNo ratings yet
- History of Microsoft WindowsDocument23 pagesHistory of Microsoft WindowsLutfi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- CSS10 Q2 Mod2 - Full NotesDocument8 pagesCSS10 Q2 Mod2 - Full NotesJade ivan parrochaNo ratings yet
- Computer TerminologyDocument8 pagesComputer Terminologyrosyprincess18No ratings yet
- Baysic W#4Document2 pagesBaysic W#4baysic.136511130206No ratings yet
- Pro Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): Powerful Tools and Practices for Cross-Platform Development and CollaborationFrom EverandPro Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): Powerful Tools and Practices for Cross-Platform Development and CollaborationNo ratings yet
- K 31Document1 pageK 31scribd388No ratings yet
- Government and Administration: Population Density Map of KeralaDocument1 pageGovernment and Administration: Population Density Map of Keralascribd388No ratings yet
- Temple FestivalsDocument1 pageTemple Festivalsscribd388No ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicsscribd388No ratings yet
- Culture: A Kathakali ArtistDocument1 pageCulture: A Kathakali Artistscribd388No ratings yet
- Religion in Kerala Hinduism 56.2% Islam 24.7% Christianity 19.0% Others 0.1%Document1 pageReligion in Kerala Hinduism 56.2% Islam 24.7% Christianity 19.0% Others 0.1%scribd388No ratings yet
- SubdivisionsDocument1 pageSubdivisionsscribd388No ratings yet
- Economy: Tempore Justices As of 2012Document1 pageEconomy: Tempore Justices As of 2012scribd388No ratings yet
- Railways: The Main Portico of The TrivandrumDocument1 pageRailways: The Main Portico of The Trivandrumscribd388No ratings yet
- Fisheries: A Typical Paddy Field in KeralaDocument1 pageFisheries: A Typical Paddy Field in Keralascribd388No ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna: Southwest Monsoon Clouds Over AlappuzhaDocument1 pageFlora and Fauna: Southwest Monsoon Clouds Over Alappuzhascribd388No ratings yet
- Coconut Palms Can Be Found All Over Kerala Bharathappuzha RiverDocument1 pageCoconut Palms Can Be Found All Over Kerala Bharathappuzha Riverscribd388No ratings yet
- Pre HistoryDocument1 pagePre Historyscribd388No ratings yet
- Climate: Periyar RiverDocument1 pageClimate: Periyar Riverscribd388No ratings yet
- Geography: Post Colonial PeriodDocument1 pageGeography: Post Colonial Periodscribd388No ratings yet
- Colonial EraDocument1 pageColonial Erascribd388No ratings yet
- Tipu Sultan's Fort at Palakkad View From Outside The Northern WallDocument1 pageTipu Sultan's Fort at Palakkad View From Outside The Northern Wallscribd388No ratings yet
- Etymology: Ancient Religious TextsDocument1 pageEtymology: Ancient Religious Textsscribd388No ratings yet
- Neacyndi) .: Early Medieval PeriodDocument1 pageNeacyndi) .: Early Medieval Periodscribd388No ratings yet
- Usage Share: The Windows Family TreeDocument1 pageUsage Share: The Windows Family Treescribd388No ratings yet
- Location of Kerala (Marked in Red) in India: Coordinates (Trivandrum) : 8.5074°N 76.973°E Country IndiaDocument1 pageLocation of Kerala (Marked in Red) in India: Coordinates (Trivandrum) : 8.5074°N 76.973°E Country Indiascribd388No ratings yet
- See AlsoDocument1 pageSee Alsoscribd388No ratings yet
- October 2013 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 NT 6.3.9600 Current 11 11Document1 pageOctober 2013 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 NT 6.3.9600 Current 11 11scribd388No ratings yet
- KeralaDocument1 pageKeralascribd388No ratings yet
- Alternative ImplementationsDocument1 pageAlternative Implementationsscribd388No ratings yet
- Version History: Early VersionsDocument1 pageVersion History: Early Versionsscribd388No ratings yet
- Timeline of ReleasesDocument1 pageTimeline of Releasesscribd388No ratings yet
- SecurityDocument1 pageSecurityscribd388No ratings yet
- Windows 3.0 and 3.1: Windows 1.0, The First Version, Released in 1985Document1 pageWindows 3.0 and 3.1: Windows 1.0, The First Version, Released in 1985scribd388No ratings yet
- Windows CEDocument1 pageWindows CEscribd388No ratings yet
- Prueba 3Document9 pagesPrueba 3Guillermo AndradeNo ratings yet
- ECG-SE-1515-Connect A Treadmill To ECG Workstation SE-1515-1.0Document8 pagesECG-SE-1515-Connect A Treadmill To ECG Workstation SE-1515-1.0JuanMa SERVYTRONIXNo ratings yet
- DFM 1600Document2 pagesDFM 1600amirin_kingNo ratings yet
- HDL Manual 2019 5th Sem E&CE 17ECL58Document77 pagesHDL Manual 2019 5th Sem E&CE 17ECL58vishvakirana100% (1)
- (E18-E19) AC Motor Control by Inverter Trainer PDFDocument2 pages(E18-E19) AC Motor Control by Inverter Trainer PDFLuis Eduardo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- 63230-401-203 A4 en PDFDocument108 pages63230-401-203 A4 en PDFtamamengka renaldyNo ratings yet
- Linux 2.6 For Embedded Systems-: Closing in On Real TimeDocument4 pagesLinux 2.6 For Embedded Systems-: Closing in On Real Timeapi-19417993100% (1)
- WellGate 2504 and WellGate 2540 P2P Hotline ApplicationDocument17 pagesWellGate 2504 and WellGate 2540 P2P Hotline ApplicationMuhammad Shahroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Automated Assembly SystemsDocument4 pagesAutomated Assembly Systemsዘረአዳም ዘመንቆረርNo ratings yet
- System Imaging and SW Update Admin v10.6Document102 pagesSystem Imaging and SW Update Admin v10.6tseiple7No ratings yet
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide PDFDocument106 pagesConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide PDFdownloadpostaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Generator Alignment: Alan Luedeking, Ludeca IncDocument7 pagesTurbine Generator Alignment: Alan Luedeking, Ludeca IncEliyanto E BudiartoNo ratings yet
- Line Follower RobotDocument4 pagesLine Follower Robotmari_euNo ratings yet
- Project Time ScheduleDocument12 pagesProject Time Schedulemissle2007No ratings yet
- Virtualization (VT-X - AMD-V) - Enabling Virtualization On Your Computer For Running 2N® Access Commander - FAQ - 2N WIKIDocument4 pagesVirtualization (VT-X - AMD-V) - Enabling Virtualization On Your Computer For Running 2N® Access Commander - FAQ - 2N WIKIErick Luna RojasNo ratings yet
- CNC Machine Tools and Control SystemsDocument39 pagesCNC Machine Tools and Control Systemsp_a_jeevaNo ratings yet
- KR87 InstallDocument66 pagesKR87 InstallZheng Long0% (1)
- 14 B2 CD 01Document602 pages14 B2 CD 01fischettipNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledRahmad Fitri YantoNo ratings yet
- Tds-11sa Top DriveDocument2 pagesTds-11sa Top DriveJuan Pablo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet BPA241 Counting Scale For Mettler ToledoDocument2 pagesDatasheet BPA241 Counting Scale For Mettler ToledoAnubhav LakhmaniNo ratings yet
- Atmel 24C1024Document19 pagesAtmel 24C1024vax1No ratings yet
- The MMT All-Sky CameraDocument7 pagesThe MMT All-Sky CameraJairo AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Considerations For Selecting and Using Multimode FiberDocument32 pagesConsiderations For Selecting and Using Multimode FiberPop-Coman SimionNo ratings yet
- Portable Ground Control Station: A Universal Off-The Shelf SolutionDocument3 pagesPortable Ground Control Station: A Universal Off-The Shelf SolutionantsouNo ratings yet
- Intel ChipsetDocument159 pagesIntel Chipsetzaki marufanNo ratings yet
- CSEC ElectricalElectronicTechnology SBAForm LabBookandLaboratoryExercisesDocument38 pagesCSEC ElectricalElectronicTechnology SBAForm LabBookandLaboratoryExercisesPercival J Sayers67% (3)
- 2-32-1378907628-4. The Consumers .Full PDFDocument12 pages2-32-1378907628-4. The Consumers .Full PDFJaseem CTNo ratings yet
- HitFilm 4 Pro User GuideDocument312 pagesHitFilm 4 Pro User GuideM Irvan SukandarNo ratings yet