Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M Albanese
Uploaded by
leozalkiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M Albanese
Uploaded by
leozalkiCopyright:
Available Formats
Small Wastewater Treatment
Systems
By Michael Albanese, P.Eng.
H2FLOW EQUI PMENT I NC.
www.h2flow.com
Why do you need one?
Typical Reasons
Enviromental Regulations
New Development
Failing Septic Systems
Cost of Sewers & Pumping to Closest Municipality
Centralized Operations may be costly
Politics
Autonomy
Keeping the Water
Reuse
What are you looking for?
A low cost, highly efficient wastewater treatment system capable
of consistently producing:
<5-10 mg/ L BOD
<5-10 mg/ L TSS
<0.5-2 mg/ L NH3
<0.1-0.5 mg/ L TP
<200 FColi / 100ml
TN ?
.. with minimal electrical cost, high degree of automation, low
operator attention and minimal sludge production !!!!
(I WI LL ORDER ONE OF THOSE, THANKS VERY MUCH..)
Definitions
On-Site systems for 0 to 5m3/ day and can be
up to 20 m3/ day
A small wastewater plant is usually referred
to flows between 10 to 300 m3/ day but can
range up to 3800 m3/ day
We will focus on 20m to 300m3/ day range
5
th
Wheel Truck Stop WWTP Dorchester, ON 45m3/ day SBR
What is a Package Plant?
Term package plant is loosely used
I ndustry definition is a transportable plant that comes
pre-assembled ready for plug and play, made in steel
or pre-cast tankage
Sometimes this term is also used to refer to small
pre-engineered plants which are poured in place
concrete. Should be referred to as Pre-Engineered
plants
Sentinel WWTP 33m3/ day SBR
Photos Courtesy of Fluidyne
Package & Pre-Engineered
Plants
PACKAGE PLANT
(usually up to 200m3/ day)
Steel or Pre-cast Tanks
PRE-ENGI NEERED PLANT
(usually up to 3800m3/ day)
Poured I n Place Concrete Tanks
Photo Courtesy of Eimco Water I nc. Photo Courtesy of Eimco Water I nc.
Package & Pre-Engineered Plants
PACKAGE PLANT
(usually up to 200m3/ day)
Steel or Pre-cast Tanks
PRE-ENGI NEERED PLANT
(usually up to 3800m3/ day)
Poured I n Place Concrete Tanks
Photo Courtesy of Eimco Water I nc.
Types of Small Plants
Most Common Biological Processes:
Extended Aeration
RBC (Rotating Biological Contactor)
SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor)
I SAM (Modified SBR)
MBR (Membrane Bio Reactor)
Others (Contact Stabilization,
Lagoon) not discussed as they are
not common or no longer marketed
Extended Aeration
Rectangular up to 400 m3/ d
Concentric Design > 400m3/ d
Very popular up to recent years
Usually Consists of :
- Aeration Tank ( outboard)
- Clarifier ( internal tank)
PLUS
- Aerobic Digester
- Disinfection
- Equalization Chamber
- Tertiary Filters
Continuous Flow Discharge
Declined in popularity as better
processes went on the market
Photo Courtesy of Permastore Ltd.
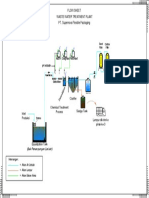
Extended Aeration
Clarifier
I nfluent
Aeration Tank
Aerobic Digester
Tertiary Filters
Equalization Chamber
Disinfection
Effluent
Sample Plan Layout
Rotating Biological Contactor
Declined in popularity due
to mechanical issues and
low effluent quality
Usually Consists of :
- Primary Tank
- Rotaring Disk
- Secondary Clarifier
PLUS
- Aerobic Digester
- Disinfection Chamber
- Tertiary Filters
Continuous Flow Discharge
Needs to be covered
Low operator attention
Rotating Biological Contactor
RBC
Aerobic
Digester
Secondary
Clarifier
Disinfection
Tertiary
Filters
Primary Clarifier
Equalization
Chamber
I nfluent
Effluent
Sample Plan Layout
Sequencing Batch Reactor
Modified Exended Air Process
Mostly Rectangular
Batch Discharge
Various Variations
Usually Consists of :
- Selector Tanks
- Upstream Equalization Tank
or Two Tanks in series
- Tank for
React/ Settle/ Decant
PLUS
- Aerobic Digester
- Post Equalization Chamber
- Disinfection
- Tertiary Filters
I nglewood WWTP - Region of Peel 243m3/ day SBR
Coldwater WWTP Springwater Township 300m3/ day SBR
Sequencing Batch Reactor
SBR Steps: Fill, React, Settle, Decant & I dle
Sequencing Batch Reactor
SBR
Aerobic
Digester
Post Equa-
lization
Chamber
Disinfection
Tertiary
Filters
Optional Selector Tank
Equalization
Chamber
I nfluent
Effluent
Single Train Layout
Sequencing Batch Reactor
SBR
P
o
s
t
E
q
u
a
l
i
z
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
i
n
f
e
c
t
i
o
n
Tertiary
Filters
Optional Selector Tank
I nfluent
Effluent
Dual Train Layout
SBR
Aerobic
Digester
Modified Sequencing Batch
Reactor (I SAM)
Rectangular
Batch Discharge with
Fill, I nteract, Settle, Decant
Usually Consists of :
- Anaerobic Trash Trap Tanks
- Equalization Tank
- React/ Settle/ Decant Tank
PLUS
- Post Equalization Chamber
- Disinfection
- Tertiary Filters
Low sludge production
Modified Sequencing Batch
Reactor (I SAM)
Post Equa-
lization
Chamber
Disinfection
Tertiary
Filter
Surge
Anoxic Mix
Equal. Tank
Anaerobic
Chamber/
Thrash Trap
I nfluent
Effluent
SBR
Sample Plan Layout
Membrane Bio Reactor
Mostly Rectangular
Continuous Discharge
Various Variations
- Selector / Anoxic Zone
- Aeration Zone
- Membranes as Clarifier
PLUS
- Aerobic Digester
- Disinfection
NO Tertiary Filters
Smallest Footprint
Some MBR models can
thicken sludge
Aeration Zone
MBR Zone
Anoxic Zone
Membrane Bio Reactor
MBR
Aerobic
Digester
Disinfection
Optional Anoxic Selector Tank
Equalization
Chamber
I nfluent
Effluent
Sample Plan Layout
Membrane Bio Reactor
38 m3/ day Footrpint Based on
EI MCO WATER/ KUBOTA MBR
Design I ssues
Large fluctuations in flow and BOD loads
- (watch your pump sizing!)
Effluent Limits may determine which technology
External Loads like Septage this is high BOD load we
need to design for it
Sludge Production and Disposal - usually removed by vac
truck, but if you can produce less that reduces frequency
Odour considerations if neighbours are nearby
Pretreatment; Screening, Grinding or Trash Trap
Downstream processes; Filters and Disinfection
Large fluctuations in loads
Hydraulic shock loads and large variation in flows
from small communities are accentuated by the use
of oversized pumps where wastewater is pumped.
Example: Based on per capita unit flow, you determine you need a
30m3/ day plant for a community.
Smallest sewage pump (2) is rated for 120 lpm @20ft head
When pump is on it equates to 173m3/ d !
(about 6 times ADF). Designing for 8-10 is not uncommon, by
using equalization tanks.
Pretreatment
Fine screening is
recommended (and is a must
for MBR)
Grinding can be adequate for
SBR, ExAir, RBC
Trash trap works well for
SBR, ExAir
Grit removal may be
required but for small
systems it is typically not
included or use Trash trap
Size for I nstantaneous Peak
Flow not ADF
Channel Grinder Photo Courtesy of Franklin Miller Corp.
Pretreatment Screening
I f screening, then fine
screening is recommended
(6mm openings)
2 or 3mm if going with MBR
Removes grease balls!
Screw Screen popular choice
Will have to dispose of
removed screened material
Bagger Unit can help with
odours and housekeeping
Can be located outdoors (no
building) but must equip
screening unit with heat
tracing and insulation.
Screw Screen Photo Courtesy of Parkson Corp.
Tertiary Filters
Pressure filter type or
Continuous Backwash Type
Not needed for MBR
Size for I nstantaneous Peak
Flow not ADF
Watch Volume of Backwash!
Dynasand Photo Courtesy of Parkson Corp.
Snow Valley Ski Hill WWTP Pressure Filters
Disinfection
UV or Chlorine are typical
With Chlorine, Dechlorination is
needed more and more
UV is simple, no chemicals, less
operator attendance
Can be inside or outside building
Size for I nstantaneous Peak Flow
UV unit indoors Photo Courtesy of Trojan I nc.
UV unit outdoors Photo Courtesy of Trojan I nc.
SUMMARY
This presentation was mainly an overview of available technologies
for small wastewater treatment plants, plus considerations and
general design issues associated with them. I n conclusion:
Select your treatment system process based on
Capital cost
Operational costs
Site Conditions (Temperature)
Effluent criteria
Sludge production
Footprint
References
Support
Small Wastewater Treatment Systems
Any questions?
By Michael Albanese, P.Eng.
H2FLOW EQUI PMENT I NC.
THANK YOU VERY MUCH !
www.h2flow.com
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EPA Landfill Site Design Guide PDFDocument154 pagesEPA Landfill Site Design Guide PDFLuster09No ratings yet
- Designing A Product Out of Local, Recyclable, Solid Andor Liquid Materials in Making Useful ProductsDocument6 pagesDesigning A Product Out of Local, Recyclable, Solid Andor Liquid Materials in Making Useful ProductsAbi Manahan-DoriaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment by Aerobic Process - Environmental BiotechnologyDocument41 pagesWastewater Treatment by Aerobic Process - Environmental BiotechnologyPrajwal BhanuNo ratings yet
- Transboundary WaterDocument38 pagesTransboundary WaterswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Refinery Waste Water Treatment and ReuseDocument8 pagesRefinery Waste Water Treatment and ReuseMahmood VahidNo ratings yet
- Proposed DWWTP Sitio NagpanaDocument17 pagesProposed DWWTP Sitio NagpanaKiomitNo ratings yet
- Example For Corporate Presentation Veolia PresentationDocument41 pagesExample For Corporate Presentation Veolia PresentationswordprakashNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 Report - ScriptDocument5 pagesGROUP 6 Report - ScriptSALMAN JOHAYRNo ratings yet
- Coursera V8Q9D7MJR72XDocument1 pageCoursera V8Q9D7MJR72XswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Final Report Inter-Provincial Dependency On Agriculture - DVN 2018 - 1548834926Document88 pagesFinal Report Inter-Provincial Dependency On Agriculture - DVN 2018 - 1548834926swordprakashNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,223,687 B1: Windle (45) Date of Patent: May 1, 2001Document10 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,223,687 B1: Windle (45) Date of Patent: May 1, 2001swordprakashNo ratings yet
- B01D 21/02 (2006.01) F04F 10/00 (2006.01) C02F9/00 (2006.01)Document88 pagesB01D 21/02 (2006.01) F04F 10/00 (2006.01) C02F9/00 (2006.01)swordprakashNo ratings yet
- Pilot Project For Development of Argo-Industries: Niraj Acharya Nepal-India Women Friendship SocietyDocument16 pagesPilot Project For Development of Argo-Industries: Niraj Acharya Nepal-India Women Friendship SocietyswordprakashNo ratings yet
- TEPZZ 6Z4589A - T: European Patent ApplicationDocument9 pagesTEPZZ 6Z4589A - T: European Patent ApplicationswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Automatic Log Table Circular Sliding Wood Table Saw Machine: No Model No.& - Description Q 'TY Unit PriceDocument5 pagesAutomatic Log Table Circular Sliding Wood Table Saw Machine: No Model No.& - Description Q 'TY Unit PriceswordprakashNo ratings yet
- SMMB - A Stochastic Markov-Blanket Frame-Work Strategy For Epistasis Detection in GWASDocument8 pagesSMMB - A Stochastic Markov-Blanket Frame-Work Strategy For Epistasis Detection in GWASswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Cannabis AdvertisingDocument19 pagesCannabis AdvertisingswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Research Methods For Business Students CDocument41 pagesResearch Methods For Business Students CVijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- SMMB - A Stochastic Markov-Blanket Frame-Work Strategy For Epistasis Detection in GWASDocument8 pagesSMMB - A Stochastic Markov-Blanket Frame-Work Strategy For Epistasis Detection in GWASswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Niche 1Document87 pagesNiche 1swordprakashNo ratings yet
- GPO Box 935 Bhat Bhateni, Kathmandu 441-8345/444-3316Document39 pagesGPO Box 935 Bhat Bhateni, Kathmandu 441-8345/444-3316Richa ShahiNo ratings yet
- 2014 01 15 MahakaliDocument10 pages2014 01 15 MahakaliswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Validation of Kimberly Validation of Kimberly Indigenous Cognitive Assessment Tool For Population in NepalDocument1 pageValidation of Kimberly Validation of Kimberly Indigenous Cognitive Assessment Tool For Population in NepalswordprakashNo ratings yet
- NHSP II FinalDocument160 pagesNHSP II FinalswordprakashNo ratings yet
- NHSP IIIFramework For Improved Health MIS June2017Document28 pagesNHSP IIIFramework For Improved Health MIS June2017swordprakashNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: People. Place. ProsperityDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan: People. Place. ProsperityswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Ingo NPDocument59 pagesIngo NPswordprakashNo ratings yet
- Industrial Waste: Gerald Cyrus Ibal Alyssa MelendrezDocument5 pagesIndustrial Waste: Gerald Cyrus Ibal Alyssa MelendrezCrizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- Flow Diagram SupernovaDocument1 pageFlow Diagram SupernovaHarum Tirta JayaNo ratings yet
- Solution To Urban Runoff in Austin Texas 5Document2 pagesSolution To Urban Runoff in Austin Texas 5api-550649698No ratings yet
- Letter To Liliw, Laguna Re Segregated CollectionDocument9 pagesLetter To Liliw, Laguna Re Segregated CollectionDante Arcigal JrNo ratings yet
- Althon Suds BrochureDocument20 pagesAlthon Suds BrochureNabeel Civil EngineerNo ratings yet
- Sanitery EngineeringDocument56 pagesSanitery EngineeringTAJUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Nijhuis Water Technology - Corporate BrochureDocument15 pagesNijhuis Water Technology - Corporate BrochureMark James AlburoNo ratings yet
- OA Compendium BookDocument258 pagesOA Compendium Bookrynx022423No ratings yet
- Product End-Of-Life Instructions Petit Bloc Bi-FunctionDocument2 pagesProduct End-Of-Life Instructions Petit Bloc Bi-FunctionmayuranNo ratings yet
- BRF PresentationDocument22 pagesBRF Presentationárokszállási norbertNo ratings yet
- KSCSTDocument2 pagesKSCSTNagaraja GuptaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document6 pagesCase Study 1jitenderNo ratings yet
- 3319, Datasheet ActifloCarb en 0915Document2 pages3319, Datasheet ActifloCarb en 0915Anonymous xifNvNNo ratings yet
- Studi Kualitas Air Tanah Dangkal Dan Pendapat Masyarakat Sekitar Tempat Pemrosesan Akhir Sampah Suwung Kecamatan Denpasar Selatan, Kota DenpasarDocument6 pagesStudi Kualitas Air Tanah Dangkal Dan Pendapat Masyarakat Sekitar Tempat Pemrosesan Akhir Sampah Suwung Kecamatan Denpasar Selatan, Kota Denpasarrudy yoga lesmanaNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahDocument10 pagesTinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahHasnanurfajriahNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Envtrenment and Natural ResourcesDocument25 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Envtrenment and Natural ResourcesJade LimbagoNo ratings yet
- Chap:14 Water: by Topaz Group of Class 6EDocument26 pagesChap:14 Water: by Topaz Group of Class 6EBananabandageNo ratings yet
- What Is A Headwater Drainage Feature (HDF) ?: Hdfs Are More Important Than You Think!Document1 pageWhat Is A Headwater Drainage Feature (HDF) ?: Hdfs Are More Important Than You Think!RaúlNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH PROPOSAL FORMAT Sum2022Document21 pagesRESEARCH PROPOSAL FORMAT Sum2022JosephNo ratings yet
- Final Report LSSP ZamboangaDocument250 pagesFinal Report LSSP ZamboangaJerico DelmonteNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Sizing Calculation: A) Total No of UsersDocument4 pagesSeptic Tank Sizing Calculation: A) Total No of UsersShuvam AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Finding The Most Appropriate Method of Water Conservation in Indonesia: A Literature Review StudyDocument15 pagesFinding The Most Appropriate Method of Water Conservation in Indonesia: A Literature Review StudyaiyarahadiNo ratings yet
- 2222222Document4 pages2222222JendaeNo ratings yet
- COT1 Grade-5-PPT Science Q1 W7 Day-3Document105 pagesCOT1 Grade-5-PPT Science Q1 W7 Day-3Ela Mae SantosNo ratings yet