Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operation Management Workbook For Students
Operation Management Workbook For Students
Uploaded by
lravi4uOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Operation Management Workbook For Students
Operation Management Workbook For Students
Uploaded by
lravi4uCopyright:
Available Formats
Operations Management
2
nd
Edition
WORKBOOK
Icfai Center for Management Research
Road # 3, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad 500 034
ISBN 81-314-1126-5
Ref. No. OM WB 03 2K7 35
For any clarification regarding this book, students may please write to Icfai giving the above
reference, and page number.
While every possible care has been taken in preparing this book, Icfai welcomes suggestions
from students for improvement in future editions.
Icfai, March 2007. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used
in a spreadsheet, or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic,
mechanical, photocopying or otherwise without prior permission in writing from
Icfai.
Operations Management (2
nd
Edition) Workbook
Contents
Part A
Multiple Choice Questions 3-67
Multiple Choice Answers and Explanations 71-136
Part B
Paper I
Paper I Model Test 1 139-148
Paper I Model Test 2 149-159
Paper I Model Test 1 Answers and Explanations 163-172
Paper I Model Test 2 Answers and Explanations 173-184
Paper II
Paper II Model Test 1 187-196
Paper II Model Test 2 197-207
Paper II Model Test 1 Answers and Explanations 211-221
Paper II Model Test 2 Answers and Explanations 222-231
iv
Detailed Contents
Part One: Introduction to Operations Management
1. OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT AN OVERVIEW
Operations Management Decisions
The Historical Evolution of Operations Management
Computers and Advanced Operations Technology
2. OPERATIONS STRATEGY
Operations Strategy as a Competitive Weapon
Elements of Operations Strategy
Developing an Operations Strategy
Financial and Economic Analysis in Operations
3. FORECASTING DEMAND
Forecasting in Operations
Forecast Components
Demand Forecasting Process
Forecasting Methods
Selecting a Forecasting Method
Measures of Forecasting Accuracy
Monitoring and Controlling Forecasts
Part Two: Design of Facilities and Jobs
4. ALLOCATING RESOURCES TO STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES
Allocation Decisions in Operations Strategy
Linear Programming in Operations Management
Formulation of Linear Programming Problems
Solution of Linear Programming Problems
The Transportation Problem in Linear Programming
5. DESIGN OF PRODUCTION PROCESSES
Process Planning and Design
Major Factors Affecting Process Design Decisions
Types of Process Designs
Process Planning Aids
Selecting the Type of Process Design
v
6. FACILITY LOCATION AND LAYOUT
Importance of Location
Factors Affecting the Location Decisions
General Steps in Location Selection and Location Decision Process
Location Evaluation Methods
Locating Service Facilities
Facility Layout
Basic Layout Formats
Developing a Process Layout
Developing a Product Layout
Developing a Cellular Manufacturing Layout
Japanese Approaches and Trends in Manufacturing Layouts
Service Facility Layouts
7. JOB DESIGN
Job Design Fundamentals
Considerations in Job Design
Work Environment
Uses of Job Design
8. WORK MEASUREMENT
Uses of Setting Work Standards
Work Measurement Techniques
Part Three: Operations Planning and Control
9. AGGREGATE PLANNING AND CAPACITY PLANNING
Overview of Planning Activities
The Aggregate Planning Process
Strategies for Developing Aggregate Plans
Aggregate Planning Techniques
Master Production Schedule
Implementing Aggregate Plans and Master Schedules
Capacity Planning
10. FUNDAMENTALS OF INVENTORY CONTROL
Purpose of Inventories
Inventory Costs
Inventory Systems
Economic Order Quantity Model
Inventory Classifications Models
vi
11. PURCHASE MANAGEMENT
Importance of Purchasing
Organizing Purchasing
Responsibilities of a Purchasing Manager
Purchasing Process
Duties of Buyers
Make-or-Buy Decisions
Ethics in Buying
12. MATERIALS MANAGEMENT
Necessity of Materials Management
Functions of Materials Management
Materials Management Technology
Materials Management Techniques
13. MATERIALS REQUIREMENT PLANNING
Fundamentals of Materials Requirement Planning
Components of an MRP System
Advantages and Disadvantages of an MRP System
Problems in Implementing MRP Systems
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)
14. OPERATIONS SCHEDULING
Purpose of Scheduling
Scheduling Methods
Scheduling Activities
Scheduling by Type of Operations
Scheduling Personnel in Service Operations
Scheduling Techniques
15. ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING
Evolution of ERP
Business Process Reengineering
Business Modeling for ERP
ERP Implementation
ERP and Competitive Advantage
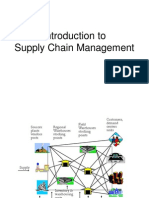
16. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Business Drivers in Supply Chain Performance
Principles of Supply Chain Management
Forces Shaping Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management Framework
Customer Focus in Supply Chain Management
Electronic Supply Chain Management
vii
17. JUST-IN-TIME (JIT) MANUFACTURING SYSTEM
The Concept of the JIT System
Advantages of JIT Systems
Characteristics of JIT Systems
18. PRODUCTIVITY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Productivity
The Strategic Role of Quality
Role of Inspection in Quality Control
The Cost of Quality
Statistical Concepts in Quality Control
Computers in Quality Control
Concept of TQM
19. FACILITIES AND MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
Facilities Management
Necessity of Maintenance Management
Types of Maintenance
Economics of Maintenance
Evaluation of Preventive Maintenance Policies
Maintenance Planning
Modern Approaches to Preventive Maintenance
Recent Trends in Maintenance
20. PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Necessity of Project Management
Network Modeling
Project Planning Methods
Project Crashing
Part Four: Technology and Globalization in Operations Management
21. TRENDS IN OPERATIONS TECHNOLOGY
Automation
Overview of Manufacturing Activities
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
22. GLOBALIZATION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Significance of Globalization
Sources of Global Competitive Advantage
Difficulties in Managing Globalization
Changes in Operations Strategy Necessary due to Globalization
Managing Globalization
Operations in Global Business Strategy
Part A Multiple Choice Questions: Relevant Chapters
Chapters Title Multiple Choice Questions
Chapter 1 Operations Management An Overview 1-16
Chapter 2 Operations Strategy 17-40
Chapter 3 Forecasting Demand 41-86
Chapter 4 Allocating Resources to Strategic Alternatives 87-113
Chapter 5 Design of Production Processes 114-140
Chapter 6 Facility Location and Layout 141-186
Chapter 7 Job Design 187-200
Chapter 8 Work Measurement 201-216
Chapter 9 Aggregate Planning and Capacity Planning 217-243
Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Inventory Control 244-278
Chapter 11 Purchase Management 279-300
Chapter 12 Materials Management 301-333
Chapter 13 Materials Requirement Planning 334-360
Chapter 14 Operations Scheduling 361-408
Chapter 15 Enterprise Resource Planning 409-425
Chapter 16 Supply Chain Management 426-443
Chapter 17 Just-In-Time (JIT) Manufacturing System 444-460
Chapter 18 Productivity and Quality Management 461-493
Chapter 19 Facilities and Maintenance Management 494-529
Chapter 20 Project Management 530-557
Chapter 21 Trends in Operations Technology 558-582
Chapter 22 Globalization and Operations Management 583-600
This section consists of multiple-choice questions that test the students
understanding of the basic concepts discussed in the textbook. Answering these
questions will help students quickly recollect the theories theyve learnt and apply
them to real-life business situations.
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions
1. On the basis of Hawthorne studies, Elton
Mayo and his team concluded that
________had a major impact on employee
productivity.
a. Physical work conditions
b. Importance and recognition given to
employees
c. Job content
d. Fear of losing job
2. Which company first adopted the concept
of scientific management in the assembly
line production system?
a. General electric
b. Ford motors
c. General motors
d. Westinghouse
3. The computerization of operations began
when the first computer was installed in
General Electric Appliance Park in 1954.
What was the basic objective of computer
applications then?
a. Reducing manpower
b. Reducing clerical costs
c. Enhancing worker safety
d. Increasing production
4. Operations management involves the
functions of planning, organizing,
controlling etc, in production systems. The
activity of encouraging employees through
praise, recognition and other intangibles is
part of which function?
a. Controlling
b. Motivating
c. Coordinating
d. Organizing
5. Decisions on production and process
design, facility location and layout etc, are
part of which decision category?
a. Strategic decisions
b. Tactical decisions
c. Operational decisions
d. All of the above
6. Which of the following decision do not
fall within the basic scope of operations
management?
a. Analyzing the firms financial position
b. Designing a new assembly line
c. Determining the location of a new
distribution center
d. Improving product quality
7. Division of labor or specialization is an
outcome of ____________.
a. Industrial revolution
b. World War II
c. Scientific management
d. Computerization of production systems
8. The decision of an operations manager
about what products to make and when is
part of which function?
a. Organizing
b. Directing
c. Planning
d. Coordinating
9. The decisions that operations managers
take can be broadly classified into various
categories. What is the usual time-frame
for tactical decisions?
a. Seven years or more
b. One or two years
c. Two to four months
d. A couple of weeks
10. Operations Management deals with which
of the following?
a. Design of products
b. Design of services
c. Acquisition of resources
d. All of the above
11. Operations Management involves the
activities of planning, organizing,
controlling, directing, and coordinating in
production systems. These systems convert
resource inputs into products or services.
Centralization and/or decentralization of
operations fall under which of the
following activities?
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions
Operations Management
4
a. Planning
b. Organizing
c. Directing
d. Controlling
12. The term Production Management was
replaced by a more general term
Operations Management in the 1970s.
What led to the enlargement of the field
and use of the new term?
i. Inclusion of purchasing function
ii. Inclusion of dispatch and other related
activities
iii. Inclusion of services related concepts and
procedures
iv. Inclusion of manufacturing technologies
a. i, ii, iii
b. iii, iii, iv
c. i, iii, iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
13. Operations Research uses mathematical
techniques to solve complex problems.
When was the concept of operations
research first introduced?
a. In the early 1940s during World War II
b. In the late 1920s during Hawthorne studies
c. In 1911 for the moving assembly line
production by Ford
d. In the 1880s at Midvale Steel Works
14. Who was involved in the Hawthorne
experiments at the Western Electric plant?
a. Frederick Taylor
b. Henry Ford
c. Elton Mayo
d. Adam Smith
15. Which of the following technologies helps
perform tasks that are repetitive or
hazardous for a human being to perform?
a. CAD
b. FMS
c. Expert systems
d. Moving assembly line
16. Computerization has significantly
improved the production process. Which
of the following is not an advantage of
computerization in the production process?
a. Rise in quality of products
b. Reduction in labor costs
c. Higher maintenance costs
d. Greater efficiency of the production
process
17. Which of the following are among the key
objectives of an operations manager?
i. Maximizing customer satisfaction
ii. Minimizing inventory
iii. Maximizing resource utilization
a. i & ii
b. ii & iii
c. i & iii
d. i, ii & iii
18. Product design is one of the factors that an
operations manager must consider while
designing a production system. Product
design can be based on a customized or a
standard production design system. What
does a customized product design system
primarily focus on?
a. Quality and on-time delivery
b. Reducing costs
c. Costs and quality
d. Mass production
19. Which of the following is not categorized
among indirect costs?
a. Administrative costs
b. Maintenance costs
c. Labor costs
d. Rentals
20. Who generally develops corporate
objectives that are unique to each
organization?
a. Frontline managers
b. Top-level managers
c. Middle level managers
d. Production supervisors
21. What factors must managers consider
while formulating corporate objectives?
a. Market conditions
b. Political environment
c. Economic environment
d. All of the above
Part A
5
22. Rainbow Electronics manufactures a
limited number of models of television
sets. What kind of product design system
does the company have?
a. Customized production design
b. Standardized product design
c. Stock-to-order
d. Assemble-to-order
23. Feasibility studies are part of the new
product development process. The
feasibility test generally focuses on which
of the following aspects?
i. Technical feasibility
ii. Marketing feasibility
iii. Economic feasibility
iv. Production feasibility
a. i & ii
b. ii & iii
c. i & iii
d. iii & iv
24. Large organizations are often divided into
separate operating divisions that operate as
autonomous business units with
independent control. What are such units
called?
a. Subsidiary units
b. Strategic business units
c. Franchise centers
d. Sister concerns
25. Nucor, a steel producer, competes
successfully with larger integrated steel
producers by processing steel scrap rather
than producing steel from iron ore. What
advantage does the company gain through
this kind of production process?
a. Production flexibility
b. Better quality
c. Lower costs
d. Batch process facility
26. Selecting product design, production
system, and inventory policy for finished
goods fall under which component of
operations strategy?
a. Designing the production system
b. Product/service design and development
c. Technology selection and process
development
d. Allocation of resources to strategic
alternatives
27. Which among the following products are
generally customized as per user
requirements?
i. Industrial boilers
ii. Turbines
iii. Televisions
iv. Ceiling fans
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. iv and i
28. Which stage of the product life cycle is
characterized by exponential growth of
sales volume?
a. Introduction stage
b. Growth stage
c. Maturity stage
d. Decline stage
29. Pick the statement that pertains to the
relationship between the role of operations
department and the product life cycle.
a. The role of operations department
increases as the product moves up the
lifecycle
b. The role of operations department
decreases as the product moves up the
lifecycle
c. There is no change in the role of
operations department across the lifecycle
d. The role of operations department
increases or decreases as the product
moves up the lifecycle
30. What is the basic use of a prototype during
the new product development process?
a. A prototype is used to test the technical
and economical feasibility
b. A prototype helps test the product
performance under standard conditions
c. A prototype is developed as part of test
marketing
d. None of the above
Operations Management
6
31. Availability of raw materials and nearness
to markets are some of the factors that are
considered while making decisions
regarding plant location. Which
component of operations strategy deals
with decisions such as plant location?
a. Allocation of resources to strategic
alternatives
b. Technology selection and process
development
c. Product design and development
d. Facility planning
32. Developing an operations strategy is an
important function of an operations
manager. The operations strategy should
basically be in accordance with which of
the following?
a. Organization strategy
b. Marketing strategy
c. Competitor strategy
d. Both a and c
33. How is strategic planning different from
operations planning?
a. Strategic planning is concerned with long-
term planning while operational planning
involves short-term day-to-day planning
b. Strategic planning is concerned with short-
term day-to-day planning while
operational planning involves long-term
planning
c. Operational planning involves selection of
target markets and distribution channels
d. Both strategic planning and operational
planning are long-term in nature
34. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of operations strategy?
a. It should be fixed so as to support a
product through its entire lifecycle
b. It should accommodate future changes in
market demand
c. It should focus on having short-term
operational superiority over competitors
d. It should be consistent with strategies in
other functional areas such as marketing,
finance and human resources
35. HDFC Bank offers deposits, loans,
insurance products, mutual funds, trading
in stocks, etc, under one roof and positions
itself as a financial supermarket. Which
type of competitive advantage strategy
does the bank seek to focus on?
a. Quality
b. Product variety
c. Convenience
d. Low cost
(Questions 36 to 39) The given data below
shows the initial investment of three projects
and their payback periods. Use this data to
answer the following four questions.
Project Initial
investment
Expected annual
income from the
project
A Rs.10,00,000 Rs.2,00,000
B Rs.12,00,000 Rs.2,50,000
C Rs.8,00,000 Rs.1,50,000
36. Calculate the payback period for Project A
a. 5 years
b. 4 years
c. 3 years
d. 6 years
37. What is the payback period for Project B?
a. 5.0 years
b. 4.8 years
c. 3.8 years
d. 4.5 years
38. Calculate the payback period for Project C.
a. 5.0 years
b. 4.8 years
c. 5.3 years
d. 4.5 years
39. Based on the results for product A, B and
C, which is the best investment in terms of
faster returns?
a. Project A
b. Project B
c. Project C
d. Either project A or C
40. Allocation of resources to strategic
alternatives is a component of operations
strategy. What is the main objective of this
component?
a. To minimize efficiency
b. Optimize the use of resources for best
strategic use
Part A
7
c. Ensure capacity expansion
d. Maintain proximity to resources
41. Demand for a commodity is most likely to
depend upon which of the following?
i. The price of the commodity
ii. The prices of the available complimentary
goods
iii. The customer tastes and preferences
iv. Price of substitutes
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, iii, and iv
42. _________is the ability of an organization
to adjust quickly to true changes in the
base level of demand.
a. Stability
b. Responsiveness
c. Repetitiveness
d. Controlling
43. The numerical difference between forecast
demand and actual demand is called
___________.
a. Standard deviation
b. Forecast error
c. Forecast variance
d. Forecast noise
44. A forecast made by using exponential
smoothing was found to be over-optimistic
to the most recent trends in demand.
Which of the following is the most suitable
corrective action possible to make the
forecast more realistic?
a. Increase the value of
b. Decrease the value of
c. Shift to some other forecasting method
d. Ensure that remains constant
45. If the demand for a product is stable and is
representative of the future, what should
be the value of used to forecast the
demand for the product?
a. Low
b. High
c. Medium
d. Can take any value
46. Organizations generally use demand
forecasts to develop which of the
following plans?
a. Financial plans
b. Facilities plans
c. Marketing plans
d. All of the above
47. Which of the following methods is
judgmental and subjective in nature and
based on the estimates and opinions of
individuals?
a. Time series methods
b. Delphi method
c. Exponential smoothing
d. Regression analysis
48. Which of the following statements is not
true about demand?
a. Dependent demand is forecasted
b. If a manufacturer produces tires, the
demand for the tires is a dependent
demand
c. MRP systems help determine demand for
items with dependent demand
d. Exponential smoothing is used to
determine independent demand
49. Which of the following statements about
demand forecasting is not true?
a. Forecasts are more accurate for shorter
time horizons
b. Regression analysis produces more
accurate forecasts than moving average
c. A 6-month moving average forecast is
more accurate than a 3-month moving
average forecast
d. Forecasts are created using only
quantitative data
50. Identify the statistical techniques that use
historical data collected over a period of
time to predict future demand.
a. Time-series methods
b. Qualitative methods
c. Nonparametric methods
d. Causal methods
Operations Management
8
51. Which of the following is not considered
by operations managers before selecting a
method for forecasting the future demand?
a. Cost and accuracy
b. Data availability
c. Projected time span
d. Plant capacity
52. Which of the following measures provide
information on the extent of forecast error
in relative terms?
a. Mean absolute deviation
b. Mean square error
c. Mean forecast error
d. Mean absolute percentage error
53. Which of the following decisions
undertaken by operations managers does
not generally require long-range forecast?
a. Capacity planning
b. New product development
c. Spare parts inventory
d. Capital funds
54. Demand for a product is influenced by
many factors. Which of the following is
not a factor that influences product
demand?
a. Price of the product
b. Price of the substitutes
c. Income levels of the consumers
d. Extent of accuracy of demand forecasts
55. Which of the following is not a
consequence of underestimation of
demand?
a. Increase in supply lead time
b. Increase in loss of orders
c. Increase in customer switching
d. Increased locking up of working capital as
inventory
56. Which of the following demand estimates
are very detailed and used to plan and
schedule production operations?
a. Short-term demand
b. Medium-term demand
c. Long-term demand
d. All of the above
57. Raw materials demand forecast is derived
from which of the following type of
forecast?
a. Short-term demand forecast
b. Aggregate product demand forecast
c. Labor demand forecast
d. All of the above
58. Forecasting demand has a direct impact on
which of the following two functions of
management.
a. Planning and organizing
b. Directing and control
c. Organizing and staffing
d. Planning and controlling
59. In Delphi method, independent opinions
and predictions are made by a panel of
experts and summarized by a competent
mediator. The success of this method is
not dependent on which of the following?
a. The presence of a socially dominant
individual
b. The geographical distance between the
experts
c. Tendency towards groupthink
d. Competency of coordinator
60. The demand for generator sets for twelve
consecutive months from January to
December is given as 78, 80, 85, 82, 84,
85, 87, 88, 86, 89, 86, 87. Calculate the
approximate demand for January of the
next year using the simple moving
averages method. Assume the time period
to be a six month moving average.
a. 82
b. 83
c. 86
d. 87
61. The sum of weights used in weighted
moving average method should be equal to
_________.
a. 1
b. 10
c. 100
d. Zero
62. How are weights in the weighted moving
average method calculated?
Part A
9
a. Simple moving average method
b. Future forecast
c. Trial & error
d. Exponential smoothing
63. Which of the following forecasting
methods are used when the demand for a
product is influenced by seasonal
tendencies?
a. Delphi method
b. Simple moving average method
c. Exponential smoothing
d. All of the above
64. Which of the following is not a benefit
that an operations manager gains when
using the exponential smoothing method?
a. Easy availability of standard software
packages
b. Less computational requirements
c. Larger data storage space
d. Greater accuracy in forecasts
65. Maximum weightage is given in the
exponential smoothing method for demand
values in which of the following time
periods?
a. Latest time period
b. Earliest time period
c. Average of latest and oldest time periods
d. Sum of latest and oldest time periods
66. What is the formula for calculating the
weighted moving average?
a. WMA
t
=
=
n
1 t
t t
A C
b. WMA
t+1
=
=
n
1 t
t t
A C
c. WMA
t+1
=
+
=
1 n
1 t
t t
A C
d. WMA
t-1
=
=
1 - n
1 t
t t
A C
67. Why is the constant used in exponential
smoothing method?
i. To show effects of past demand
ii. To smooth out the effects of any noise
iii. To predict future trends in demand
a. Only i
b. Only ii
c. i and ii
d. i, ii, and iii
68. In the equation Y = a + bX, what is a
termed as?
a. Value of the dependent variable
b. Value of the independent variable
c. Slope of the line
d. Y intercept or constant value
69. What is the relation between the slope of
the line and the trend line in regression
analysis?
a. If the slope is positive, then the trend line
increases positively
b. If the slope is positive, then the trend line
decreases negatively
c. There is no relationship between the slope
and the trend line
d. If the slope is negative, then the trend line
increases positively
70. If the sales of a refrigerator model rose
from 15000 units to 20000 units between
two consecutive time periods due to 5%
increase in advertising expenditure. What
is the value of the slope?
a. 33.33
b. 6.67
c. 3.33
d. 250
71. Short-range decisions vary from
purchasing, job scheduling, and project
assignment to machine scheduling. Which
of the following forecasting methods can
be used for such decisions?
a. Exponential smoothing
b. Linear regression analysis
c. Multiple regression analysis
d. Delphi method
72. Identify the forecasting method that can be
used when data collection proves very
expensive.
a. Moving averages method
b. Delphi method
Operations Management
10
c. Regression analysis
d. Exponential smoothing
73. Which of the following forecasting
methods give 100% accurate forecasts?
a. Qualitative methods
b. Time series methods
c. Causal methods
d. None of the above
74. Identify the relationship between cost of
forecasting and accuracy of forecasting.
a. Cost is directly proportional to extent of
accuracy
b. Cost is indirectly proportional to extent of
accuracy
c. Accuracy is independent of costs
d. Cost is inversely proportional to extent of
accuracy
(Questions 75 to 79) Use the data given in the
table below to answer the following five
questions related to forecast errors.
Demand Forecast Actual Demand
500 510
510 510
520 515
540 550
550 545
75. Calculate the Mean Absolute Deviation
(MAD).
a. 5
b. 6
c. 30
d. 20
76. The Mean Square Error (MSE) for the
given data is ______________.
a. 250
b. 100
c. 50
d. 75
77. Calculate the mean forecast error.
a. 2
b. 10
c. 7
d. 5
78. Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE)
for the given data is __________.
a. 5.72
b. 3.14
c. 1.14
d. 2.56
79. Calculate the Tracking Signal (TS).
a. 1.67
b. 2.67
c. 3.67
d. 4.67
80. For forecasting purposes, firms need to
take into consideration various factors or
components. Which of the following is
associated with average sales over a given
period of time?
a. Trend component
b. Seasonal component
c. Cyclical component
d. Base demand
81. The demand for luxury products may be
linked with the business cycle, as sales
usually increase during the boom phase
and slow-down during recession. What
component of forecasting is described
here?
a. Trend component
b. Seasonal component
c. Cyclical component
d. Base demand
82. When LG increased the advertising budget
by 40%, the sales of its televisions
doubled. On this basis, LG prepared an
aggressive demand forecast for the next
year. What component of demand did LG
consider as part of its forecast?
a. Cyclical component
b. Promotional component
c. Trend component
d. Irregular component
83. Which of the following is an example of
the trend component of forecast?
Part A
11
a. The demand for gold has reduced as the
price of gold has increased
b. The promotional expenditure of Airtels
GSM service was hiked based on demand
forecast
c. The demand for camera mobile phones in
India has increased steeply since 2001
d. The demand for wrist watches has been
fluctuating for quite some time
84. Identify the correct sequence of steps taken
as part of the demand forecasting process.
a. Identify influencing factors understand
objectives identify customer segments
select forecasting technique
b. Identify influencing factors identify
customer segments understand objectives
select forecasting technique
c. Identify customer segments understand
objectives identify influencing factors
select forecasting technique
d. Understand objectives identify
influencing factors identify customer
segments select forecasting technique
85. Which of the following demand
forecasting techniques is divided into static
and adaptive methods?
a. Qualitative methods
b. Time series methods
c. Causal methods
d. All of the above
86. Trend and seasonal components play an
important role in demand forecasting. In
which of the following forecasting
methods are estimates of trend and
seasonal components assumed to not vary
from year to year?
a. Exponential smoothing
b. Static forecasting method
c. Regression analysis
d. Simple moving average
87. Constrained optimization models are
useful techniques enabling operations
managers to compute the amount of
resources to be allocated to each strategic
alternative. Which of the following is not a
benefit of using a constrained optimization
model?
a. Feasible solutions are reduced to
manageable numbers
b. Provides optimal solution for the whole
organization
c. Enables decision-makers to perform what-
if analysis
d. Provides optimal solutions that are always
practical
88. Constrained optimization models consist
of three major components. Which of the
following is not a component of these
models?
a. Decision variables
b. Nature of demand
c. Objective functions
d. Constraints
89. Linear programming is a mathematical
constrained optimization model used to
maximize or minimize the linear functions
of a large number of variables, subject to
certain constraints. Linear programming
cannot help obtain solutions for which of
the following?
a. Profitability
b. Cost effectiveness
c. Motivation
d. Productivity
90. Identify the term that describes the
solution satisfying all the restrictions of a
linear programming problem.
a. Initial solution
b. Basic solution
c. Feasible solution
d. Final solution
91. In linear programming, a statement such as
the number of labor hours available is
600 is identified as a ___________.
a. Constraint
b. Slack variable
c. Objective function
d. Decision variable
92. Identify the mathematical technique used
to determine the optimal utilization of
resources in an organization.
Operations Management
12
a. Exponential smoothing
b. Regression analysis
c. Linear programming
d. Decision tree analysis
93. When arriving at production plan decisions
by using linear programming, which of the
following is not considered a constraint?
a. Market
b. Capacity
c. Destination requirements
d. Inventory space
(Questions 94 to 98) Atul Tele-Products
manufactures two telephone models using two
different raw material grades. One (x) is of
superior quality and the other (y) inferior
(second grade). The profit per unit for the
model using superior quality raw material is
Rs.200 and that of the other is Rs150. The
maximum demand for both telephones is 600
units. Production should not exceed demand
and total machine time available for both types
of telephones together is 650 hours. Besides,
one superior quality telephone can be produced
in two hours while one unit of inferior quality
telephone can be produced every hour. Answer
the following five questions using the
information given above.
94. If Atul Tele-Products wants to maximize
profits, what should be the objective
function?
a. Maximize Z = 2x + 4y
b. Maximize Z = 200x + 150y
c. Maximize Z = 600x + 650y
d. Maximize Z = 2x + y
95. What is the constraint on machine hours?
a. 2x + y 650
b. x + 2y 650
c. 2x + y 600
d. x + 2y 600
96. What is the constraint on demand?
a. 2x + y 600
b. x + 2y 600
c. x + y 650
d. x + y 600
97. If the number of superior quality
telephones produced in a month is 200 and
inferior quality telephones is 200, then
what is the maximum profit (in rupees)
that the company gets?
a. Rs. 75000
b. Rs. 70000
c. Rs. 76500
d. Rs. 78500
98. What is the appropriate production
combination for the two models to gain
maximum profits?
a. x = 300, y = 300
b. x = 600, y = 0
c. x = 250, y = 100
d. x = 200, y = 200
99. While constructing a linear programming
problem, certain assumptions are made.
Which of these is not such an assumption?
a. Proportionality
b. Optimality
c. Divisibility
d. Additivity
100. If the objective function is a maximizing
function, which of the following can be
considered for it?
a. Profits
b. Inventory
c. Advertising expenditure
d. Production costs
(Questions 101 to 104) The diagram represents
the solution for a linear programming problem
where ABCS is the feasible region. Use the
diagram to answer the following four
questions.
Part A
13
101. Identify the constraint represented by the
line passing through the coordinates
(40, 0) and (0,60).
a. x + y = 40
b. 2x +3y = 120
c. 3x + 2y = 120
d. x + y = 60
102. Identify the corner points of the feasible
region from the above diagram.
a. (0,0), (80,0), (60,0), (40,0)
b. (40,0), (80,0), (60,80), (60,0)
c. (40,0), (80,0), (80,60), (60,0)
d. (0,60), (40,0), (80,0), (80,60)
103. What is the equation of the line passing
through (80,0)?
a. x = 80
b. y = 80
c. x + y = 80
d. x - y = 80
104. Find the minimum value of the objective
function where minimize Z = 20x + 35y.
a. 2100
b. 1600
c. 800
d. 3700
105. Which of the following statements is not
characteristic of linear programming?
a. The linear programming problem should
have a well-defined single objective to
achieve
b. The objective function and constraints of
the linear programming problem must be
linear functions
c. Decision variables of the linear
programming problem should be
continuous in nature
d. The resources considered in the linear
programming problem should have
unlimited supply
106. Identify the correct sequence of steps to
formulate a linear programming problem.
i. Identify the objective function
ii. Identify decision variables
iii. Identify constraints
a. ii, i, and iii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. iii, ii, and i
d. ii, iii, and i
107. Where does the optimum solution lie on
the graph in the graphical method of
solving a linear programming problem?
C
B
A
20
Y
O (0,0)
20
60
80
40
80 X
60
40
S
120
100 120
100
D
Operations Management
14
a. On the X axis
b. On the Y axis
c. In the feasible region
d. Outside the feasible region
108. In the simplex method of solving a linear
programming problem, the lesser than or
equal to inequality is converted into
equality by ___________ to the left hand
side of the inequality.
a. Adding a slack variable
b. Subtracting a slack variable
c. Adding a function
d. Subtracting a function
109. The sequence of steps in moving from one
basic solution to another in a simplex
method is known as ____________.
a. Integration
b. Iteration
c. Allocation
d. Summation
110. Identify the typical objective function of a
transportation problem.
a. To minimize the sum of all quantities
transported
b. To minimize the sum of all production
costs
c. To minimize the sum of all transportation
costs
d. All of the above
111. Which among the following is not a
method used in developing an initial
feasible solution for a transportation
problem?
a. North-West corner method
b. Least cost method
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Stepping stone method
112. Of all the methods used to determine the
initial feasible solution in transportation
problems, which is said to be most
effective?
a. North-West corner method
b. Lest cost method
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Both a & b
113. The concept of linear programming does
not consider any synergetic effects among
decision variables while calculating their
total value for the objective function or the
constraints they are associated with. This
is part of which assumption of linear
programming?
a. Proportionality
b. Additivity
c. Divisibility
d. Certainty
114. Onio Designs provides industrial designing
services to various automobile companies
in India. This is an example of
___________.
a. Job shop production
b. Batch manufacturing
c. Standardized service
d. Customized service
115. In the emerging business scenario, it has
become essential for operations managers
to manage the structure of their
organizations, not merely their operations.
What does the term structure include?
a. Number of plants and their individual
capacities
b. Choices in equipment and process
technology
c. Production control and workforce
management
d. All of the above
116. Keeping other things constant, when the
price of a commodity decreases, the
demand for the commodity __________.
a. Does not change
b. Increases continuously
c. Increases to a certain level
d. Decreases
117. To attain its objective of profit
maximization, L&T decided to acquire a
mine in Australia thereby owning sources
of raw material supplies. What is this
process of expanding ownership called?
a. Horizontal integration
b. Forward integration
c. Backward integration
d. Diagonal integration
Part A
15
118. The factor that is not considered by
operations managers while making their
decisions on backward integration.
a. Level of training for distributor employees
b. Capabilities to consume and market the
products
c. Anticipate changes in net return on assets
d. Availability of funds
119. What are the basic objectives of process
planning and design?
i. To produce products with desired quality
ii. To produce products at the right time
iii. To produce products in required quantities
iv. To produce products below competitor
prices
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. i, ii, and iii
120. Organizations must be flexible to increase
or maintain their market share. The ability
of the production system to shift quickly
from producing one product to another is
called _____________.
a. Product flexibility
b. Demand flexibility
c. Volume flexibility
d. Customer flexibility
121. In an assembly chart, the process of
inspection is generally represented by a
__________.
a. Square
b. Circle
c. Triangle
d. Pentagon
122. Which of the following is not an
advantage of process-focused production?
a. Small work-in-process inventory
b. Less manufacturing cycle time
c. Low initial investment
d. Better product mix available to meet
customer demand
123. Which of the following is not an
advantage of the product focused
production system?
a. Lower unit costs
b. Lower initial investments
c. Ease of planning
d. Reduced worker training
124. ABC Corp. to match the diversity in
customer orders wants to produce products
in small batches. Which type of process
design would be economically feasible for
ABC?
a. Assembly line
b. Continuous processing
c. Discrete unit processing
d. Job shop process
125. Which of the following forms the basis for
designing factory buildings and facility
layouts?
a. Operations strategy
b. Production planning
c. Process planning
d. Product design
126. When Hindustan Smelters Ltd. decided to
manufacture lead ingots, the management
decided to develop a process plan for the
same. Which of the following factors
should the operations manager at
Hindustan Smelters Ltd. keep in mind
when developing a process plan?
a. Nature of demand
b. Degree of vertical integration
c. Employee skill level requirements
d. Quality level and degree of customer
contact
127. Demand for Pepsi cola is seasonal. It has a
very high demand during summer and
minimal demand during winter season.
Which of the following assumptions is
false with respect to the seasonality of
demand of Pepsi cola?
a. As demand is seasonal Pepsi cola should
not be produced in winter season
b. Pepsi cola should be produced throughout
the year but with varying outputs
c. Finished goods inventory must be stocked
to meet high demand during summer
d. All the above statements are false.
Operations Management
16
128. Which of the following is not a factor
affecting backward integration?
a. Cost of producing components versus cost
of buying them
b. Investments necessary to produce
components in-house
c. Anticipated changes in net return on
assets, if production of components is
undertaken
d. Ability of the organization to market its
products
129. Identify which of the following is not an
advantage of vertical integration.
a. It reduces the over-dependency on the
purchasing function
b. It helps decentralize the overheads
c. It helps in pooling the R&D and design
efforts
d. It helps in achieving economies of scale
130. Assume that Eastside, a readymade
garment retailer, acquired a textile mill to
produce different fabrics. What kind of
integration strategy has the retailer
adopted?
a. Forward integration
b. Backward integration
c. Horizontal integration
d. Lateral integration
131. There are various types of process designs
that are generally used by organizations. In
which type of process design, products or
services tend to flow along linear paths
without backtracking or sidetracking?
a. Product-focused systems
b. Process-focused systems
c. Group technology
d. All the above
132. Steel and Chemical industries generally
implement which type of process design?
a. Discreet unit manufacturing
b. Process manufacturing
c. Job shop process
d. Both a & c
133. Which of the following process design
systems entail high initial investment?
a. Product-focused systems
b. Process-focused systems
c. Group technology
d. All of the above
134. What are the characteristics of process
focused systems?
i. Operations are grouped according to the
type of processes
ii. Production is performed on products on a
start and stop basis
iii. Products move from department to
department in batches
iv. Products are produced irrespective of
diversity in customer orders
a. i and ii
b. iii and iv
c. i, ii, and iii
d. ii, iii, and iv
135. Coding of parts in a manufacturing plant is
done to ensure the identification of each
part and its characteristics. What is the
difficulty in adopting this approach?
a. It provides a clear picture of the steps
involved in producing the part
b. It results in standardization of part design
c. It leads to grouping of the parts into
families
d. It requires high employee skills
136. Which of the following is not an
advantage of cellular manufacturing?
a. Lesser machine changeover time
b. Lower cost of training
c. Reduction in material handling costs
d. Increase in the in-process inventory
137. Which of the following types of charts
indicate operations by circles and
inspections by squares?
a. Assembly charts
b. Gantt charts
c. Flow charts
d. None of the above
138. Which type of production systems has high
diversity in product design and small batch
size?
Part A
17
a. Job shop production systems
b. Cellular manufacturing systems
c. Batch production systems
d. Product focused systems
139. Which of the following is not true about a
product-focused system?
a. Presence of initial fixed costs
b. Presence of low variable costs
c. The total cost of production increases as
the output volume increases
d. Low variations in products
140. In what way is a typical product-focused
system distinct when compared to a
process focused system?
a. Lower fixed costs and higher variable
costs
b. Higher fixed costs and lower variable
costs
c. Higher fixed costs and higher variable
costs
d. Lower fixed costs and lower variable costs
141. Which of the following reasons persuade
companies to set up facilities in export
promotion zones, technology parks and
industrial estates?
i. Tax holidays and exemption from import-
export barriers
ii. Availability of infrastructure
iii. Low loan interest rates
iv. Low cost of manpower
a. i and iv
b. ii, iii, iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. ii and iv
142. Which of the following is a major factor in
selection of a location for an aluminum
factory?
a. Proximity to final consumer
b. Proximity to input sources
c. Proximity to sea port
d. All of the above
143. For which of the following industries is
proximity to markets a must?
a. Telecom industry
b. Textile industry
c. Healthcare industry
d. Call center
144. What do you understand by the term
facility layout?
a. A list of facilities provided by the
organization to the consumers
b. The physical distribution of various
departments for ease in production
c. The location of employees inside the
organization
d. Layout of safety equipment in an
organization
145. Layouts are differentiated by the types of
workflow they entail. Workflow in turn is
dictated by the nature of the product.
Which of the following statements is true
about product layout?
a. Equipment is dedicated to the manufacture
of a narrow product line
b. Equipment is flexible to produce a wide
range of products
c. Material handling cost increases
significantly
d. It is used for manufacturing customized
products
146. Which of the following involves the use of
layout planning tools like templates and
two-dimensional cut-outs of equipment
drawn to scale?
a. Graphic and schematic analysis
b. Load distance model
c. Computer models
d. CRAFT model
147. Cotton yarn manufacturing units are
generally concentrated in select areas of
the country as yarn production requires
certain ideal levels of humidity. What
factor influences selection of plant location
in this case?
a. Site cost
b. Conducive politico-economic situation
c. Suitability of climate
d. Availability of amenities
148. Which of the following is not a primary
objective of facility location and layout
decisions?
Operations Management
18
a. To set up a plant of the right size and right
design
b. To serve the customer better
c. To optimize production cost
d. To use best available technology
149. Which of the following is not an
advantage of selecting an optimum
location for a plant?
a. Reduction of transportation costs of raw
material and finished goods
b. Competitive advantage due to proximity to
market
c. Low labor-cost
d. Cost of technology
150. Which of the following types of layout is
used when the product manufactured is
bulky, heavy or fragile?
a. Product layout
b. Process layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Group technology layout
151. Which of the following techniques is not
associated with taking suitable location
decisions?
a. Cost-profit-volume analysis
b. Factor analysis
c. Linear programming
d. CRAFT analysis
152. Which of the following organizations
selects a particular location from a market-
oriented approach?
a. A retailer
b. A manufacturer
c. A software development center
d. A content development center
153. Which of the following is not a type of
facility layout?
a. Process layout
b. Product layout
c. Employee layout
d. Hybrid layout
154. It is also called the cellular manufacturing
layout. Identify the layout from the
following.
a. Process layout
b. Grouping technology layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Hybrid layout
155. In which of the following situations is
there no need for selecting a facility
location?
a. When a business has just started
b. When expansion of the existing plant is
possible
c. When a business wants to establish new
branches/plants
d. When government regulations mandate
that the business has to shift its location
156. Firms conduct facility location analysis
where they evaluate different locations and
finally choose an optimum location to start
operations. Arrange the following
activities related to facility location
planning in a logical sequence.
i. Design layout
ii. Select location
iii. Search for a location
iv. Revise layout
a. i, ii, iii, iv
b. ii, iii, i, iv
c. iii, ii, i, iv
d. iv, iii, ii, i
157. Rahul wanted to set up a small scale
printing press to print books for
individuals interested in publishing their
work for a small audience. Which is the
right location for Rahul to establish a
printing press to cater to this kind of
market?
a. Near paper mills
b. In a town/city
c. In a village where cost of labor is cheap
d. Near the manufacturer of printing
machines
158. There are many factors affecting the
selection of a facility location. Which of
the following factors would deter a firm
from setting up operations in a particular
location?
a. Low labor costs
b. High transportation costs
c. Availability of public utility services
d. Benefit of tax holidays
Part A
19
159. The basic raw material for a cement
manufacturing unit is limestone and the
major consumers are the government, real
estate and individual consumers. Which is
the best possible location to build a cement
plant?
a. Close to sea port
b. Close to cities where consumption is high
c. Close to the raw material source
d. Within special economic zones or export
processing zones
160. Process layouts are also known as ______.
a. Functional layouts
b. Fixed position layout
c. Flow-shop layouts
d. Straight-line layouts
161. Many auto-ancillary units have set up
facilities close to facilities of auto majors
like Hyundai and Ford near Chennai.
Which of the following factors would have
primarily led to this decision?
a. Site cost
b. Proximity to markets
c. Need for safety requirements
d. Availability of services like electricity,
drainage, and waste disposal
162. Which of the following is not considered a
benefit derived by companies setting up
operations in special export zones (SEZ)?
a. Good infrastructure support
b. Tax holidays
c. Low interest loans
d. Availability of prime real estate
163. Companies can follow certain guidelines
when trying to analyze possible locations
and identify an optimal one since it is
expensive and time-consuming. What is
the correct sequence of guidelines a
company can follow when evaluating
locations?
a. Define location objectives relate
objectives to criteria Identify relevant
decision criteria evaluate alternative
locations select the best location
b. Identify relevant decision criteria define
location objectives relate objectives to
criteria evaluate alternative locations
select the best location
c. Define location objectives identify
relevant decision criteria relate
objectives to the criteria evaluate
alternative locations select the best
location
d. Define location objectives identify
relevant decision criteria evaluate
alternative locations relate objectives to
criteria select the best location
164. Though there is no standard procedure,
certain guidelines can be used for making
a location decision. The first guideline is to
define location objectives. Whose views
and requirements are not considered when
defining them?
Cost Volume Relationships of Two Locations
V
0
Volume of sales
C
o
s
t
Revenue
TC
2
TC
1
FC
1
FC
2
Operations Management
20
a. Owners and promoters
b. Employees
c. Customers
d. Competitors
(Questions 165 & 166) The above figure
presents cost-volume-profit analysis. Based on
the figure, answer the following two questions.
165. Which of the following is similar for the
two locations?
a. Revenue
b. Fixed cost
c. Variable cost
d. Total cost
166. If fixed cost at a location is Rs.500,000,
variable cost per unit Rs.30, and price per
unit Rs.50. Calculate the number of units a
firm should produce to break even?
a. 20,000
b. 10,000
c. 25,000
d. 15,000
(Questions 167 to 169) The table below gives
details about fixed costs and variable costs for
three different locations. Answer the following
three questions using information given in the
table.
Location Fixed cost /Yr Variable cost /
Unit
Chandigarh Rs. 4,00,000 300
Gurgaon Rs. 4,50,000 285
Delhi Rs. 5,00,000 275
167. Which of the following locations would
have the highest total cost per year if
annual output of a firm located there is
1000 units?
a. Chandigarh
b. Gurgaon
c. Delhi
d. Both Delhi and Gurgaon
168. Which of the following locations would
have the highest annual profit if the annual
production is 1000 units and selling price
per unit is Rs.1000?
a. Chandigarh
b. Gurgaon
c. Delhi
d. Both Chandigarh and Gurgaon
169. Which plant location would you select if
you were the authority to make the final
decision?
a. Chandigarh
b. Gurgaon
c. Delhi
d. Any of the above
170. Which of the following is not an
advantage of a good layout?
a. It reduces material handling costs
b. It reduces congestion in the plant
c. It reduces space utilization
d. It increases machine utilization
171. Under which type of layout are similar
machines and equipment grouped to carry
out the production process.
a. Process layout
b. Product layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Hybrid layout
172. What type of machine is used in a process
layout?
a. Specially designed machines
b. General purpose machines
c. Machines that help manufacture
standardized products
d. All of the above
173. Which of the following is an advantage of
process layouts?
a. Increased production time
b. Increased work-in-progress
c. Increased accumulation of work
d. Increased utilization of men and material
174. Which type of layout is designed to
produce standardized products?
a. Process layout
b. Product layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Hybrid layout
Part A
21
175. Which of the following manufacturing
processes requires using a fixed position
layout?
a. Petroleum distillation
b. Beer manufacturing
c. Ship-building
d. Cement manufacturing
176. In a fabrication and assembly plant,
fabrication is done on __________ layout
while assembly is done on
______________ layout.
a. Product, process
b. Process, product
c. Product, fixed position
d. Fixed position, product
177. Managers can use various models like
mathematical models, computer models,
and physical models to develop a process
layout. Which among the following helps
find the best process layout by evaluating
thousands of alternative layouts very
quickly?
a. Graphic and schematic analysis
b. CRAFT model
c. Load distance model
d. Line balancing
178. Different types of products are
manufactured using a process layout. As
workflow differs from product to product,
managers focus on minimizing the
movement of materials as it can hike
material movement costs. Which of the
following models aims at minimizing these
costs?
a. Graphic and schematic analysis
b. CRAFT model
c. Load distance model
d. Line balancing
179. In which of the following countries were
compact production layouts developed due
to space constraints?
a. USA
b. Japan
c. India
d. China
180. Match the following models used to
develop layouts with their respective
features.
i. CRAFT model
ii. Load distance model
iii. Line balancing
iv. Graphic & schematic analysis
p. Used for studying workflow in an
assembly line
q. Evaluates thousands of alternative layouts
in a short period
r. Analyses and minimizes material
movements costs in a plant
s. Two dimensional drawings are used to
determine the best layout
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/q, ii/p, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/r, ii/q, iii/p, iv/s
d. i/q, ii/r, iii/p, iv/s
181. Different types of layout of service
facilities exist based on degrees of
customer contact. In which of the
following layouts is internal work of
employees given secondary importance?
a. Layouts focusing on customer receiving
and servicing
b. Layouts focusing on technology
c. Layouts focusing on physical materials
processing
d. Layouts focusing on production efficiency
182. Which of the following service providers
uses both customer focus layouts and
process focus layouts as part of its service
facility layout?
a. Banks
b. Hospitals
c. Restaurants
d. Call center
183. The following table gives the volume of
quantities to be shipped to four markets.
The X and Y coordinate values of the
location that would help minimize
transportation costs are also given. Use the
center of gravity method to identify
coordinates for the optimal location to set
up a warehouse to service the four markets
with minimal transportation costs.
Operations Management
22
Distribution
Center
X Y VOLUME
(000)
A 4 4 60
B 12 6 90
C 10 14 110
D 5 13 100
a. 10.75, 9.06
b. 10.05, 8.11
c. 9.06. 10.75
d. 8.11, 10.06
184. Which of the following is not a location
evaluation method?
a. Point rate method
b. Center of gravity method
c. Analytic Delphi method
d. Historical analogy method
185. Analytic Delphi Method helps managers
take complex multi-location decisions.
Give the correct sequence of steps to be
taken as part of such location decisions.
a. Form panels - Identify trends and
opportunities - Determine directions and
strategic goals of the organization -
Develop alternatives - Prioritize
alternatives
b. Identify trends and opportunities -
Determine directions and strategic goals of
the organization - Form panels - Develop
alternatives - Prioritize alternatives
c. Identify trends and opportunities - Form
panels - Determine directions and strategic
goals of organization - Prioritize
alternatives - Develop alternatives
d. Form panels - Determine directions and
strategic goals of the organization -
Prioritize alternatives - Develop
alternatives - Identify trends and
opportunities
186. Linear Decision Rules (LDRs) are a set of
equations for calculating the optimal
workforce, aggregate output rate and
inventory level for each time period in a
planning horizon. Which of the following
is not true about LDRs?
a. They provide optimum solutions for the
problems
b. They eliminate trial and error
computations
c. They consider non linear cost relationships
d. They can be generalized to all
organizations
187. ________ is the basis for job analysis, job
description and job specification.
a. Job rotation
b. Job design
c. Job enrichment
d. Job enlargement
188. ________ describes the tasks, duties and
responsibilities of a job.
a. Job analysis
b. Job enrichment
c. Job description
d. Empowerment
189. ___________ investigates job content, the
physical conditions in which the job is
carried out, and qualifications necessary to
carry out job responsibilities.
a. Job description
b. Job analysis
c. Job profile
d. Job specification
190. What does an effective job design ensure?
a. Employees are paid above expectations
b. Jobs are consistent with organizational
goals
c. Proper measurement of work done by each
employee
d. All the above
191. The Job Characteristics Model developed
by Richard Hackman and Greg Oldham
includes five characteristics. They are skill
variety, task identity, task significance,
autonomy and feedback. Match the
following terms with their respective
description.
i. Skill variety
ii. Task significance
iii. Autonomy
iv. Feedback
p. Influence of job on individuals inside &
outside the organization
q. Flexibility, independence, and discretion in
the job
Part A
23
r. Skill sets and abilities needed for the job
s. Extent of information given to employees
on their performance
a. i/q, ii/p, iii/s, iv/r
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/r, ii/q, iii/p, iv/s
d. i/r, ii/p, iii/q, iv/s
192. Which of the following is not a
consequence of a good job design?
a. Improved efficiency
b. Improved productivity
c. Increase in worker inputs
d. Increase in motivation
193. The job design developed should be
feasible for employees as well as the
organization. Feasibility is required in
which of the following areas?
i. Technical feasibility
ii. Economic feasibility
iii. Political feasibility
iv. Behavioral feasibility
a. i, ii, iv
b. i, iii, iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. ii, iii, iv
194. What do you understand by the term job
content?
a. It gives the detailed set of activities to be
performed on the job
b. It describes the physical conditions in
which the job is done and qualifications
for the job.
c. It describes the duties and responsibilities
of a job.
d. All of the above
195. Job content is the key to job design as it
influences other aspects of human resource
management. Job content helps clarify
which of the following aspects?
i. Qualifications
ii. Skill sets
iii. Nature of training programs
iv Level of motivation
a. i and ii
b. iii and iv
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
196. Job specialization at work has many
advantages for the organization. Which of
the following is not an advantage resulting
from this?
a. Ease in recruiting new workers because
fewer skills are required
b. Lower production time and higher
productivity levels
c. Lower flexibility in job rotation
d. Larger scope for mechanization or
automation of processes
197. Which of the following is an advantage of
work specialization for a manager?
a. Lower work satisfaction
b. Ease of supervision and training workers
c. Reduced scope for improvement because
of limited perspective of workers
d. Hidden costs of worker dissatisfaction
resulting from absenteeism and high
employee turnover
198. Which of the following types of
compensation is a basic need and is not a
tool used for employee motivation?
i. Fixed salary
ii. Promotion
iii. Health insurance
iv. Bonus
a. Only i
b. ii, iii and iv
c. i, iii and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
199. Which of the following is a form of
monetary benefit given to employees in an
organization?
a. Rewards
b. Titles
c. Promotions
d. Low interest loans
200. Identify the correct sequence of activities
to be performed by the human resource
manager.
Operations Management
24
i. Job analysis
ii. Job description
iii. Job design
a. i, ii, iii
b. ii, iii, i
c. i, iii, ii
d. iii, i, ii
201. The different techniques used in work
measurement are time study, historical
analysis, standard data, work sampling,
and predetermined motion time data
systems. Each has a different way of
measuring time. How is it done in time
study?
a. Using standard table
b. Using past record
c. Using stop watch
d. Using formula
202. Which of the following are benefits of
setting work standards?
i. It helps improve machine utilization by
reducing idle time
ii. It helps compare efficiency of different
work methods
iii. It helps a manager delegate work to all
employees
iv. It provides benchmarks for evaluating
workers performance
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. i, ii and iv
d. i, ii, and iii
203. Which of the following work measurement
methods does not use historical or stored
data but uses several random observations
in the work environment?
a. Standard data technique
b. Predetermined motion time study
c. Work sampling
d. Historical analysis
204. Which of the following is not a technique
used for setting work standards?
a. Time study
b. Work sampling
c. Delphi method
d. Predetermined motion time systems
205. Which of the following statements gives
an incorrect description of a feature of
time study?
a. The average of observations made always
represents time required to perform each
elemental task
b. Workers behave differently than usual
while conducting a time study
c. Observations are recorded repeatedly
across several workers to arrive at the
standard time
d. Normal time is the product of average
cycle time and worker rating
206. Which of the following is not an
allowance considered under the time study
technique of work measurement?
a. Contingency allowance
b. Interference allowance
c. Dearness allowance
d. Relaxation allowance
(Questions 207 & 208) A time study of a
production worker in a component
manufacturing plant produced the following
results: Cycle time = 3.75 minutes; worker
performance rating = 90 percent. Answer the
following two questions using this information.
207. Calculate the normal time for the job.
a. 3.75 minutes
b. 3.375 minutes
c. 3.455 minutes
d. 3.565 minutes
208. If allowances are 12 per cent of the job
time, calculate the standard time required
for the job.
a. 3.375 minutes
b. 3.775 minutes
c. 3.835 minutes
d. 3.965 minutes
209. Identify the technique of setting work
standards that uses recorded standard time
data for each of the basic motions
associated with performing a task and
summing them up to determine the time
required to perform the whole task.
Part A
25
a. Time study
b. Pre-determined Motion Time Study
c. Standard data
d. Historical analysis
210. Which of the following statements
correctly describes the difference between
Standard Data Technique and Pre-
determined Motion Time Study in work
measurement?
a. PMTS has to be measured by taking
observations while Standard Data provides
standard times for common movements
b. Standard data provides time for basic
movements while PMTS provides time for
job-specific motions
c. PMTS provides time for basic motions
while Standard Data provides time for job-
specific motions
d. PMTS has to be measured by looking at
the standard table while Standard Data
technique uses observations
211. ___________ is a technique of analyzing
work by making several observations,
usually at random, to see the relative
frequency with which various elemental
activities take place.
a. Time study
b. Standard data
c. Historical analysis
d. Work sampling
212. One of the primary applications of work
sampling is to find the percentage of time
an employee or equipment was occupied,
or left idle. What is the name given to this
application of work sampling?
a. Ratio delay
b. Performance measurement
c. Time standards
d. Employee self-timing
213. Which of the following primary
applications of work sampling are used to
identify the standard time for completion
of a task?
a. Ratio delay
b. Performance measurement
c. Time standards
d. None of the above
214. Which of the following are drawbacks of
using employee self-timing, a technique of
work measurement?
i. Low costs
ii. Low accuracy
iii. Does not take allowance into consideration
iv. Less time consuming
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. iv and i
215. Work standards techniques generally find
use in which of the following operations?
a. Operations planning
b. Operations scheduling
c. Operations control
d. All of the above
216. Three of the most widely used
predetermined motion-time data systems
are MTM, MOST and work factors.
Expand MOST.
a. Maynard Operations Sequence Technique
b. Myers Operations Sequence Technique
c. Motion Operations Sequence Technique
d. Maynard Operations Scheduling
Technique
217. Which of the following is not a pure
planning strategy used for developing
aggregate plans?
a. Varying utilization of the workforce
b. Varying workforce size in response to
output requirements
c. Varying size of inventory
d. Varying the compensation method
218. __________ translates the aggregate plan
into a detailed plan that specifies the exact
timing for production of each unit.
a. Master production schedule
b. Total production schedule
c. Primary production schedule
d. Alternative production schedule
219. Which of the following is not an aggregate
planning technique?
Operations Management
26
a. Time series analysis
b. Graphical method
c. Linear programming
d. Heuristic methods
220. Which model is based on historical
aggregate planning data available with an
organization?
a. Heuristic approach
b. Computer search
c. Linear decision rules
d. Linear programming
221. Which of the following is not a pure
planning strategy used as part of aggregate
planning?
a. Back-order strategy
b. Maintaining fixed plant capacity
c. Sub-contracting
d. Varying workforce utilization
222. Which of the following is not a function
under capacity requirement planning?
a. Identifying material requirement
b. Defining how resources can be best
employed to meet market demand
c. Allocating production among plants
d. Determining monthly production
schedules
223. Operations planning activities can be long-
range, medium-range or short-range.
Aggregate planning typically fall under
which category?
a. Long range
b. Medium range
c. Short range
d. Both a & b
224. A production plan does not contain
information about which of the following?
a. Production process
b. Inventory requirements
c. Suppliers
d. Customers
(Questions 225 to 228) The aggregate demand
for product X for the next four months is given
in the following table:
Jun Jul Aug Sept
Demand 2600 2700 2800 2750
Working
Days
26 25 25 26
In addition, the following information is given:
Opening stock of inventory = 500 units,
Inventory holding cost = Rs.20/unit/month,
Worker productivity = 4 units/day, Worker
strength = 25, Shortage cost (due to lost sales)
= Rs.10/unit
Answer the following four questions based on
the above given information
225. What is the change in inventory on hand
after meeting demand for Product X for
the month of June?
a. 300 units
b. 200 units
c. 100 units
d. 0 units
226. Assume that opening stock for the month
of July is 500 units. What is the inventory
carrying cost for that month?
a. Rs.6000
b. Rs.3000
c. Rs.4000
d. Rs.2000
227. Calculate the closing inventory for
August?
a. 300 units
b. 200 units
c. 0 units
d. 100 units
228. What is the shortage cost (due to lost sales)
in the month of September if the opening
inventory for the month is zero units?
a. Rs.3000
b. Rs.2500
c. Rs.2000
d. Rs.1500
229. What is the basic use of the computer
simulation method, a type of optimal
model used in aggregate planning?
Part A
27
a. To develop a master production schedule
b. To identify variables for developing the
plan
c. To evaluate the performance of a specific
plan
d. All of the above
230. A Master Production Schedule (MPS) is
based on which of the following?
a. Amount of inventory needed for the end
product
b. Estimation of overall demand for the end
product
c. Confirmed customer orders for the end
product
d. All of the above
231. Identify the false statement from the
following about Master Production
Schedule and Master Schedule Formation.
a. MPS of make-to-order organizations deals
only with final products
b. MPS for assemble-to-order organizations
concentrates on scheduling major
components assembled to make a product
after orders are received
c. Back orders are common in make-to-stock
organizations
d. There is no finished goods inventory in
make-to-order production
(Questions 232 & 233) The demand forecast
for metal rollers used in manufacturing printing
machines for the next three months is 60, 55,
65. The number of orders booked at the start of
the MPS planning period is 55, 60, 65
respectively. Given, Inventory on hand = 75,
Lead time = 1 month, Production lot size = 100
units. Answer the following two questions.
232. What is the projected inventory at the end
of the second month?
a. 55 units
b. 60 units
c. 65 units
d. 70 units
233. What would be the projected inventory at
the end of the third month if orders for the
month increase to 80 from 65?
a. 90 units
b. 55 units
c. 75 units
d. 80 units
234. What is meant by rolling through time,
associated with implementing aggregate
plans and master schedules?
a. Development of initial aggregate plans
b. Revising and updating aggregate plans
c. Development of the initial master
production schedule
d. Revising and updating master production
schedule
235. It is important to determine adequate
production capacity to meet forecast
demand levels and to determine whether or
not sub-contracting and/or overtime has to
be used. This activity is associated with
which of the following?
a. Capacity planning
b. Aggregate planning
c. Scheduling
d. Demand forecasting
236. Which of the following is not associated
with capacity planning?
a. Identifying available and required capacity
b. Evaluation and summing up of capacities
c. Identifying the right layout design for the
desired capacity
d. Identifying gaps in capacity and plugging
them with sub-contracting, overtime, etc.
237. Identify the correct sequence of steps
associated with capacity planning.
i. Identify current capacity
ii. Forecast future capacity
iii. Identify and evaluate sources to meet
capacity requirements
iv. Select the most appropriate alternative
a. i, ii, iii, iv
b. i, iii, ii, iv
c. iii, i, ii, iv
d. iii, ii, i, iv
238. The capacity utilization rate measures
capacity level at which a production
process is operating. Identify the correct
formula for capacity utilization rate.
Operations Management
28
a. 100
used Capacity
available Capacity
rate n utilizatio Capacity =
b. 100
avaialable Capacity
used Capacity
rate n utilizatio Capacity =
c. 100
avaialable Capacity
n Utilizatio time Available
rate n utilizatio Capacity
=
d. 100
n Utilizatio time Available
available Capacity
rate n utilizatio Capacity
=
239. Which of the following cannot be a reason
for decrease in per unit cost when volume
of production increases?
a. Decrease in fixed costs
b. Adoption of efficient processes
c. Adoption of automation
d. Increased complexity in operations
240. When the scale of production is increased
after a certain point, economies of scale
can become diseconomies of scale. What
can be the possible reasons for
diseconomies of scale?
a. Complexities in operations
b. High cost of modification & replacement
c. Distribution and storage costs
d. All of the above
241. Which of the following statements does
not correctly represent the characteristics
of services?
a. Services cannot be produced in
anticipation of demand
b. Services cannot be stored
c. A service firm with a single office can
efficiently serve customers in another
geographical area
d. Production and consumption of a service
go together
242. The two major sources of inputs that
influence master production schedule are
forecasts and customer orders. Identify the
correct combination from the following.
i. Make-to-stock environment : Takes inputs
from forecasts in deciding the MPS
ii. Make-to-order environment : Takes inputs
from customer demand in deciding the
MPS
iii. Make-to-stock environment : Takes inputs
from customer demand in deciding the
MPS
iv. Make-to-order environment : Takes inputs
from forecasts in deciding the MPS
a. Only iii
b. Only i
c. Both iii & iv
d. Both i & ii
243. Operations planning activities can be long-
range, medium range or short range in
nature. Process planning typically falls
under which category?
a. Long-range planning
b. Medium-range planning
c. Short-range planning
d. Both b & c
244. Carrying costs represent cost incurred
while inventories are stored in warehouses
or stores. Which of the following is not
associated with carrying costs?
a. Insurance costs
b. Maintenance costs
c. Cost of obsolescence
d. Material receiving costs
245. Organizations maintain buffer stocks to
overcome which of the following
conditions?
a. Demand is greater than expected
b. Supply is more than expected
c. Demand is less than expected
d. Supply matches demand
246. On what basis do organizations fix reorder
level for raw material under the EOQ
model?
a. Recommendations of finance managers
b. Estimated demand during lead-time
c. Recommendations of suppliers
d. Estimated sales for a financial year
247. Which of the following is not an
assumption that underlines the EOQ
model?
a. The lead-time for material delivery is
known with certainty and remains constant
b. The total holding cost of inventory is
proportional to the number of inventory
items stored
Part A
29
c. The cost of ordering varies and is
dependent on the quantity ordered
d. The price of the inventory item is
independent of order quantity
248. Opportunity cost is associated with which
basic category of inventory cost?
a. Carrying costs
b. Ordering costs
c. Purchase costs
d. Stock-out costs
249. Which of the following costs are
considered by a firm as part of calculating
inventory costs?
i. Holding costs
ii. Acquisition costs
iii. Ordering costs
iv. Stock out costs
a. i, ii and iii
b. ii, iii and iv
c. i, iii and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
250. What does the EOQ inventory model
primarily attempt to minimize?
a. The number of items ordered
b. The number of orders placed
c. Total inventory costs
d. The safety stock
251. Which of the following is not a primary
cost involved in maintaining inventories?
a. Carrying cost
b. Ordering cost
c. Stock-out cost
d. Purchase cost
252. Which of the following terms refers to the
time lag between the point of order and
receiving the material?
a. Lead-time
b. Slack time
c. Reorder time
d. Order time
253. In a level production plant, if opening
inventory was 500 units, sales forecast was
for 1300 units and closing inventory at the
end of the period was 200 units, how many
units were produced?
a. 500 units
b. 800 units
c. 1000 units
d. 200 units
254. Which of the following are correct reasons
for organizations to hold raw material
inventories?
i. Obtaining raw materials from suppliers
exactly when needed for production
schedules is not always possible
ii. Products can be shown to customers
iii. Quantity discounts can result from larger
purchase quantities
iv. Larger shipments can result in reduced
incoming freight costs and material
handling costs
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i, ii and iv
d. i, iii, and iv
255. Which of the following is not an
assumption of the EOQ model?
a. Demand for a product or its usage rate is
constant over a period of time
b. Supply rate is always greater than or equal
to usage rate
c. The lead-time for material delivery is
known with certainty and it remains
constant
d. The purchase price per unit varies
depending upon quantity ordered
256. Suppose a company consumes a particular
product at an average of 50 units /week. It
costs Rs.200 to order and Rs.0.50 per unit
per week to hold the item in inventory.
Compute the EOQ.
a. 100 units
b. 200 units
c. 150 units
d. 300 units
257. According to which inventory system
inventory is continuously checked and a
new order placed when the level of
inventory reaches the reorder point?
a. Q system
b. P system
Operations Management
30
c. EOQ system
d. Fixed order period system
258. Why do organizations maintain an
inventory of finished goods?
a. To avoid bottlenecks in the production
process
b. To avoid backlogs in customer order
c. To smoothen production flow
d. To reduce material handling costs
259. Semi-finished items stored temporarily and
used to finish production are termed
_________.
a. Raw material inventory
b. Work-in-progress inventory
c. Finished products inventory
d. None of the above
260. Manufacturers maintain buffer stocks of
_________to meet unprecedented increase
in demand.
a. Raw materials
b. Work-in-progress
c. Finished products
d. None of the above
261. A firm decides on quantity of material
ordered to maintain various inventory
costs. Which of the following costs does
not influence quantities ordered by the
firm?
a. Purchase cost
b. Carrying cost
c. Ordering cost
d. Hiring cost
262. Suppliers offer discounts to manufacturers
based on which of the following type of
costs?
a. Purchase costs
b. Carrying costs
c. Ordering costs
d. Stock-out costs
263. Which of the following does not come
under carrying costs?
a. Pilferage
b. Spoilage
c. Maintenance costs
d. Material-receiving costs
264. Match the following inventory costs with
their related descriptions.
i. Purchasing costs
ii. Carrying costs
iii. Ordering costs
iv Stock-out costs
p. These costs arise when inventory is
damaged
q. Loss of customer goodwill is a
consequence of these costs
r. Discounts are given by suppliers on these
costs
s. These costs are fixed and come down with
increase in size of purchase
a. i/r, ii/q, iii/p, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/r, ii/p, iii/q, iv/s
d. i/r, ii/p, iii/s, iv/q
265. Which inventory model is also referred to
as the reorder point system?
a. P system
b. Q system
c. EOQ
d. None of the above
266. What do you understand by the term lead
time associated with inventory
management?
a. Time required for depleting inventory once
replenished
b. Time required for replenishing inventory
after placing an order
c. Time required for inventory to reach the
reorder point
d. Time required for inventory to reach the
safety stock limit
267. In the EOQ model, why is the reorder level
set equal to the number of units estimated
to be used during lead time?
i. To ensure that inventory is just about zero
when the time for replenishment comes
ii. To maintain the lowest possible inventory
costs
iii. To increase carrying costs
iv. To ensure that sufficient inventory is
available before replenishment
Part A
31
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iv
268. If the lead time for replenishing inventory
in a production facility is 7 days and daily
demand is 25 units, calculate the reorder
point at which the firm should order
inventory replenishment.
a. 150 units
b. 175 units
c. 180 units
d. 185 units
269. Which of the following costs are not
considered part of EOQ?
a. Purchasing costs
b. Carrying costs
c. Ordering costs
d. Stock-out costs
(Questions 270 to 273) A production facility
uses a certain type of raw material in its
production process for which details are given
below. Annual Demand = 300000 units,
Quantity per order = 75000 units, Fixed cost
per order = Rs.2000, Holding cost per unit =
Rs.5, Item cost per unit = Rs.10. Using the
EOQ model, answer the following four
questions.
270. Calculate total ordering costs incurred in a
year.
a. Rs.6000
b. Rs.8000
c. Rs.10000
d. Rs.12000
271. Calculate holding costs per order.
a. Rs.37500
b. Rs.75000
c. Rs.150000
d. Rs.300000
272. Calculate total variable cost.
a. Rs.300000
b. Rs.3000000
c. Rs.75000
d. Rs.750000
273. Calculate total cost of maintaining
inventory.
a. Rs.458000
b. Rs.3158000
c. Rs.233000
d. Rs.933000
274. The quantity at which an order is placed
for inventory replenishment is _________.
a. Safety stock
b. Reorder level
c. Buffer stock
d. Cycle stock
275. Lead time is assumed to remain constant.
This is a condition associated with which
of the following inventory systems?
a. Q-System
b. P-System
c. EOQ
d. Fixed Order Quantity system
276. Organizations come up with many reasons
for holding inventory at various stages of
production. Which of the following is not
a suitable reason for holding raw material
inventory?
a. Obtaining raw materials from suppliers
when needed to maintain production
schedules is not always possible
b. Quantity discounts can result from larger
purchase quantities
c. Larger shipments can reduce incoming
freight and material handling costs
d. Producing and transporting in larger
batches reduces material-handling and
production costs
277. In which of the following types of
classification of inventory are items
classified based on annual consumption
value?
a. ABC
b. VED
c. FSND
d. Both b & c
278. Which of the following is the basic
objective of economic order quantity
purchasing?
a. Minimizing total inventory cost
b. Minimizing transport cost
Operations Management
32
c. Minimizing storage cost
d. Minimizing ordering costs
279. Which of the following factors should a
purchase department consider while
purchasing materials and supplies from a
supplier?
i. Low price
ii. High quality
iii. Good after sales service
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iii
d. i, ii, and iii
280. Value analysis is an organized effort to
control cost of _____________.
a. Materials purchased
b. Materials exported
c. New product development
d. Marketing efforts
281. Which of the following is not a primary
responsibility of the purchase department?
a. Vendor development
b. Selection of suppliers
c. Contract negotiation
d. Quality control
282. What are the tasks of a purchase
department in an organization?
a. Processing requisition for materials and
supplies
b. Locating suppliers or vendors
c. Negotiating purchasing contracts
d. All of the above
283. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of traditional purchasing?
a. Delivery schedule is left to the buyer
b. Purchases are in large quantities
c. Multiple sources of supply
d. Standardized packaging for all types of
components
284. For which of the following purchase
activities of a bio-pharmaceutical
company, the purchase manager is more of
a facilitator than a decision-maker?
a. Procurement requests
b. Safety of procured material
c. Contract execution
d. Negotiation process
285. The purchase department is not
responsible for which of the following
activities in a production-centric firm?
a. Vendor relations
b. Procurement
c. Creating goodwill for the company among
vendors
d. Public relations
286. Identify the logical sequence that best
represents a simple purchase process.
a. Purchase indent - Purchase order -
Quotation
b. Purchase indent - Quotation Purchase
order
c. Quotation - Purchase indent Purchase
order
d. Purchase order - Quotation Purchase
indent
287. The review of inputs to get the best kind of
output at the least cost while designing a
product is called ______.
a. Cost reengineering
b. Industrial engineering
c. Value engineering
d. Cost accounting
288. Which of the following does not influence
vendor selection?
a. Cost
b. Delivery and quality
c. Service and reliability
d. None of the above
289. If the material requirement in the various
production facilities of India Metallics
Company differs significantly, which type
of purchasing system is most suitable for
the company?
a. Centralized purchasing
b. Decentralized purchasing
c. A combination system
d. Outsource the purchasing function
Part A
33
290. Which of the following is not an activity
performed by the purchase manager?
a. Vendor analysis and development
b. Supplier selection
c. Value analysis
d. ABC analysis
291. Identify various sources that help purchase
managers obtain information about
potential vendors/suppliers.
i. Yellow pages
ii. Newspapers
iii. Websites
iv. Business journals
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. i and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
292. Which of the following is not part of value
analysis?
a. Study the value of material
b. Review product design
c. Eliminate high-cost parts
d. Negotiate with suppliers
293. From the list of questions given below,
identify the one not considered under
value analysis.
a. Is it possible to run the system without the
item?
b. Can the item be substituted with a standard
part?
c. Can the vendor supply the material at the
right time?
d. How much does the item cost?
294. Purchase indents are also called
__________.
a. Purchase requisitions
b. Purchase quotations
c. Purchase orders
d. Purchase information
295. Who generally issues a purchase indent?
a. User department
b. Purchase department
c. Vendor
d. Top management
296. Which of the following is not mentioned
in a quotation?
a. Price per unit
b. Delivery schedule
c. Terms and conditions
d. Name of the user department
297. Which of the following authorizes
suppliers to supply materials/goods?
a. Purchase indent
b. Quotation
c. Purchase order
d. All of the above
298. In a centralized purchase system, which
department is responsible to the user
department for proper delivery of
components?
a. Supplier
b. Purchase department
c. Top management
d. Quality control department
299. India Rubber Ltd. requires on a continuous
basis a certain rubber component for their
product. When should the firm opt for
buying the component rather than
producing it in-house?
a. When the quantity of the part required is
huge
b. When the fixed cost to make the product is
less than buying costs
c. When the total cost to make the product is
less than buying costs
d. When the quantity of the part required is
small
300. Which of the following is not a reason for
organizations to opt for in-house
production?
a. To gain control over all value chain
activities
b. To put excess plant capacity to productive
use
c. To ensure that the design of a product is
kept secret
d. To take advantage of knowledge and
expertise of suppliers
Operations Management
34
301. Materials managers should pay more
attention to items whose usage value or
consumption value is high and less
attention to items whose usage value is
low. Which inventory classification model
seeks to alter the expenses associated with
controlling materials according to their
usage value?
a. ABC
b. VED
c. FSND
d. FIFO
302. A Kanban system uses different types of
cards to initiate material transactions.
Which of the following type of Kanban
card authorizes a materials handling agent
to move the tray to a specified destination?
a. Conveyance authorization card
b. Production authorization card
c. Vendor authorization card
d. Dual-card Kanban system
303. Which of the following is not a function of
materials management?
a. Vendor analysis
b. Production control
c. Materials handling
d. Inventory control
304. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of the ABC inventory
classification system?
a. It classifies inventory items based on the
size of resources required to control usage
value
b. The greater the usage value, the greater the
resources to be allocated to control usage
of an item
c. The system considers availability of
materials
d. Extent of allocation of resources is based
on value of the inventory
305. The following table gives the unit cost and
annual usage rates for different items.
Classify items based on their rupee volume
using ABC classification and identify them
under A-classification.
Type of item Cost per unit
(Rs)
Annual
usage
1 400 50
2 510 40
3 10 600
4 11 500
5 0.50 1,000
6 0.25 1,500
a. 1 & 2
b. 1 & 3
c. 2 & 3
d. 3 & 4
306. The departments involved in production
control are purchasing, receiving, raw
materials, and production department.
Which of the following tasks does the raw
material inventory department carry out?
i. Repackaging and labeling incoming stock
ii. Storing and protecting raw materials
iii. Auditing existing raw materials
iv. Unpacking incoming materials
a. i and ii
b. ii and iv
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, and iv
307. The shipping department is associated with
the materials handling function. Which of
the following tasks are carried out by this
department?
i. Staging or organizing orders to be shipped
ii. Weighing, labeling, and packing orders to
be shipped
iii. Physically checking orders to make sure
their content is consistent with the order
iv. Storing raw materials safely
a. i and iii
b. ii and iii
c. i and ii
d. i, ii, and iii
308. On what principle is ABC analysis based
upon?
Part A
35
a. An item is critical if its usage is high
b. There are usually a few critical items and
several items that are less critical
c. The safety stock (in terms of volume)
should be higher for A items than for C
items
d. An item is critical if its unit price is high
309. An inventory records file does not contain
__________.
a. Characteristics of products
b. Information on inventory levels
c. Additional information like inventory item
number and description
d. Supplementary information for planning
purposes including vendor names, vendor
addresses, lead times and purchase
quantities
310. Production control is one of the functions
of materials management. Which of the
following is not a function of the
production department associated with
production control function?
a. Monitoring flow of raw materials
b. Determining and adjusting inventory
storage capacity
c. Locating and receiving raw materials
d. Identifying material flow bottlenecks
311. Which of the following tasks are not
performed by the receiving department
under the production control function of
materials management?
a. Unpacking incoming orders
b. Processing requisitions for material
c. Inspecting the quality of incoming material
d. Preparing receiving reports
312. The detailed study of complete material
flow process in a firm is termed ________.
a. Operations management
b. Inventory management
c. Materials management
d. Purchase management
313. How does shortage in materials affect a
firms functioning?
i. It breaks the flow of operations
ii. It delays delivery
iii. It increases operational efficiency
iv. It increases operational expenses
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i, ii, and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
314. Which of the following is not a proper
approach to be followed by materials
managers?
a. Stock large volumes of materials to avoid
shortage
b. Maintain optimum levels of inventory to
avoid shortage
c. Supply materials to the required
workstation quickly to enable smooth
production
d. Procure materials, receive and store safely
for use in operations
315. Spykar Plastics recorded sales of Rs.60
lakhs for the year 2004-05. The profit
recorded is 20% of sales, while material
costs amount to 50% of sales. If the firm
saves Rs. three lakh in material costs,
calculate change in profit?
a. 20% increase
b. 25% increase
c. 20% decrease
d. 25% decrease
316. Which of the following is not an objective
of materials management?
a. To maintain low inventory turnover
b. To maintain cordial relations with
suppliers and supplying firms
c. To help increase effective utilization of
the firms capital
d. To keep searching for new products and
materials that can help the firm run
efficiently
317. Materials management comprises
production control, inventory control and
materials handling. Which of the following
departments is not associated with
production control function?
a. Purchase department
b. Raw material inventory department
c. Finished goods inventory department
d. Production department
Operations Management
36
318. Purchasing can be done through
centralized as well as decentralized
systems. Which of the following is not a
characteristic seen when large firms adopt
centralized purchasing?
a. Huge/voluminous purchases
b. Consistency in buying policies
c. Non-uniformity in maintaining records
d. Higher purchasing power
319. What does a typical materials receiving
report contain?
a. Quantity of material
b. Price of material
c. Technical specifications
d. Information on inventory levels
320. A raw material inventory department helps
production control by arranging for raw
materials to be readily used in the
production process. Which of the
following is not a task of raw material
inventory department?
a. Storing raw materials
b. Maintaining stocks of material at various
stages of production
c. Labeling raw materials to make them
ready for use
d. Arranging for replenishment of stocks in
liaison with purchase department
321. Materials management comprises
production control, inventory control and
materials handling. Which department is
not associated with inventory control
function?
a. Purchase department
b. Raw materials inventory department
c. Production department
d. Finished goods inventory department
322. What is the basic objective of materials
handling function under materials
management?
a. To maintain stock of materials in various
stages of production and in desired
quantities
b. To direct and regulate movement of goods
through the entire manufacturing cycle
from the process of purchasing materials to
making the finished product
c. To move materials to the required location
in a timely and cost-effective way without
affecting the primary objective of
production control and inventory control
d. All of the above
323. The materials management function is also
referred to as a combination of three sub-
functions: traffic, physical distribution and
logistics. Movement of finished goods falls
under which of these sub-functions of
materials management?
a. Traffic
b. Physical distribution
c. Logistics
d. None of the above
324. Which of the following category of robots,
based on the nature of their operations, can
change their sequence of tasks to suit the
operational process?
a. Playback robot
b. NC robot
c. Variable-sequence robot
d. Intelligent robot
325. What does the concept of just-in-time
purchasing highlight?
a. Maintain bulky inventory
b. Maintain safety stock in case of adversity
c. Maintain minimum inventory till the next
replenishment
d. None of the above
326. JIT purchasing has many advantages over
traditional purchasing. Which among these
is not an advantage?
a. Reduction in carrying costs
b. Improved quality
c. Increased responsiveness
d. Reduced flexibility
327. Which company developed the Kanban
System?
a. General Motors
b. Toyota Motor Company
c. Ford Motor Company
d. Suzuki Motor Corporation
Part A
37
328. Which of the following Kanban cards
authorizes a materials handling agent to
move the tray to a specified destination?
a. Vendor authorization card
b. Product authorization card
c. Conveyance authorization card
d. Both a & b
(Questions 329 to 332) Assume that JKL
Industries uses 5 types of materials in its
production process. The quantity of each type
of material used per year and the cost per unit
is given in the table below. Use this data to
answer the following four questions.
Material
type
Quantity used per
year
Cost per
unit
1 2000 20
2 4500 10
3 1500 35
4 3000 20
5 2500 25
329. Use ABC analysis to identify the type of
material that has the most usage value.
a. Type 2
b. Type 4
c. Type 3
d. Type 5
330. What is the least usage value of a material
that requires lowest allocation of
resources?
a. 40000
b. 35000
c. 45000
d. 42500
331. Which type of material can be classified
under A category?
a. Type 1 and 2
b. Type 5
c. Type 2 and 3
d. Type 2
332. Which material falls under the C category
of ABC analysis?
a. Type 4
b. Type 3
c. Type 1
d. Type 2
333. A Kanban system uses different types of
cards to initiate material transactions.
Which of the following type of Kanban
card authorizes the production department
to commence the production process?
a. Conveyance authorization card
b. Production authorization card
c. Vendor authorization card
d. Dual-card Kanban system
334. The primary objective of which of the
following approaches in operations
management is to identify the net
requirement of components needed to
manage the production process and meet
customer expectations?
a. Capacity planning
b. Materials requirement planning
c. Master production schedule
d. Inventory management
335. An MRP system translates the demand for
products into raw material and component
requirements. What type of information is
required for successful operation of an
MRP system?
i. Available inventory at the beginning of the
planning time period
ii. Information on production capacity that
helps anticipate and correct resource
shortage
iii. Number of customer orders pending
iv. Demand forecasts that specify the quantity
of products required
a. i, ii, and iii
b. i, iii, and iv
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
Operations Management
38
336. Which of the following is not an
advantage of an MRP system?
a. Improved customer service
b. Greater investment in inventory
c. Improved operating efficiency
d. Faster response to market changes
337. Which of the following statements about
Bill of Materials (BoM) is incorrect?
i. It lists all the sub-assemblies and
intermediates that go into a parent
assembly
ii. It contains information about whether a
particular item was produced internally or
purchased from external sources
iii. It specifies the purchase or production
lead-time to acquire an item
iv. It shows the hierarchical levels or phases a
product goes through during production
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i and iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
338. Which of the following is not an
advantage of MRP system?
a. Ability to price competitively
b. Better customer service
c. Longer idle time
d. Reduced set-up and tear-down costs
339. What basic information does a master
production schedule contain?
a. Required quantities and delivery dates of
final products
b. Required quantities and delivery dates of
all sub-assemblies
c. Inventory on hand for each final product
d. Scheduled receipts for each final product
340. What is the primary objective of an MRP
system?
i. Manage demand-dependent inventories
ii. Manage demand-independent inventories
iii. Schedule production activities
iv. Initiate purchase activities
a. i and ii
b. iii and iv
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
341. The MRP system helps an operations
manager find the net requirement of a
component. Which of the following have
to be considered by the manager to achieve
this?
a. Material inventory on hand
b. Finished goods inventory on hand
c. Scheduled receipts from the vendors
d. Scheduled order releases for production
342. Improving operating efficiency is one of
the objectives of MRP. What does this
signify?
i. Better control over inventory of raw
material and components
ii. Quick response to production requirements
iii. Speed-up or delay of material supply to
production centers as per requirements
iv. Speed-up or slow-down of the distribution
of finished goods from warehouses
a. Only i
b. Only i and ii
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, iii and iv
(Questions 343 to 348) Given below is the bill
of materials which specifies the quantities of
different items required to product one unit of
end product alpha. Assume that items F, G, H
are purchased from external sources and the
remaining (B, C, D, E and I) are produced in-
house. The given lead times are in hours.
Answer the following six questions using this
information.
343. Find the quantities of F & G respectively,
which are required to produce 5 units of B.
a. 20 and 30
b. 30 and 20
c. 45 and 30
d. 30 and 45
344. What is the total time required to produce
B?
a. 6 hours
b. 5 hours
c. 7 hours
d. 4 hours
Part A
39
345. Find the quantities of G & H respectively,
which are required to produce 8 units of D.
a. 45 and 45
b. 35 and 35
c. 48 and 48
d. 38 and 38
346. What is the total time required to produce
D?
a. 6 hours
b. 7 hours
c. 8 hours
d. 9 hours
347. Find the quantity of G required to produce
10 units of product alpha.
a. 360 units
b. 120 units
c. 240 units
d. 600 units
348. What will be the total time required to
produce product alpha?
a. 9 hours
b. 11 hours
c. 13 hours
d. 21 hours
349. Processing is one of the components of the
MRP system. Here the inputs are
processed and outputs are generated.
Which of the following is not a step
involved in MRP information processing?
a. Explosion
b. Netting
c. Offsetting
d. Order release
350. The first step in MRP information
processing is explosion. Explosion uses
information from which of the following
sources to generate the sequence of
activities in producing the end product?
i. Master production schedule
ii. Inventory records file
iii. Bill of materials
iv. All of the above
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iii
d. Only iv
351. Developing a materials requirement plan
for each item in the bill of materials file
for each time bracket is carried out in
which step of MRP information
processing?
Alpha
LT = 2
D (4)
LT = 4
C (1)
LT = 2
B (4)
LT = 1
E (3)
LT = 2
F (2)
LT = 1
G (3)
LT =2
H (2)
LT =3
I (2)
LT = 3
H (3)
LT = 2
G (3)
LT = 2
Operations Management
40
a. Explosion
b. Netting
c. Offsetting
d. Consolidation of material requirements
352. Planned order releases are determined in
which of the following steps of MRP
information processing?
a. Explosion
b. Netting
c. Offsetting
d. Both a & b
353. The planned order releases for the finished
product or component becomes the gross
product requirement for items at the
___________ level in the product structure
chart.
a. Next lower
b. Next higher
c. Lowest level
d. Highest level
354. The components of an MRP system can be
divided into inputs, processing and
outputs. Match the following outputs of
MRP system with their respective
descriptions.
i. Performance reports
ii. Exception reports
iii. Suspension reports
iv. Planning reports
p. Generated to cancel an order due to
changes in MPS
q. Contain information about material
requirements
r. Contain information about errors and
deviations from planned objectives
s. Helps identify a problem and verify
whether the system can achieve planned
objectives
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/s, ii/q, iii/r, iv/p
c. i/s, ii/r, iii/p, iv/q
d. i/s, ii/r, iii/q, iv/p
355. Which of the following is not an
advantage of MRP system?
a. Low in-process material inventory
b. Better response to market demand
c. Reduced set-up and tear-down costs
d. Longer implementation time
356. Identify the factors that help in effective
implementation of the MRP system.
i. Greater accuracy in all operations
ii. Commitment from top management
iii. Continuous collection of information
regarding the materials used
iv. Training and educating the personnel
a. i, ii, iii
b. i, iii, iv
c. i, ii, iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
357. Which of the following factors can lead to
the failure of MRP system?
a. Highly trained and involved workforce
b. Obsolete data
c. Consistent lead times for purchase of items
d. Both b & c
358. Smith & Smith is a specialty machine
manufacturing company that manufactures
customized machinery for customers. As
part of this manufacturing approach the
company stores the required components
and sub-assemblies and only the final
assembly of the machine is made as per the
customer specifications. Which of the
following types is discussed in this case?
a. Assemble-to-stock
b. Manufacture-to-order
c. Assemble-to-order
d. Fabricate-to-order
359. An MRP system takes the input
information, processes the information and
gives the output in the form of structured
reports. In which step of information
processing in the MRP system, end
product is disassembled into components
required for its production to determine
production process or purchase activity for
each such component?
a. Explosion
b. Netting
c. Offsetting
d. None of these
Part A
41
360. An MRP system takes some inputs,
processes them and gives certain outputs.
Which of the following is not considered
an input?
a. Master production schedule
b. Planning report
c. Bill of materials
d. Inventory records file
361. Jobs A G involve processing on
workstation 1 and 2. The time required at
each workstation for each job is given in
the table below. Use Johnsons rule to
sequence these jobs.
Jobs A B C D E F G
Workstation 1 9 8 7 6 1 2 4
Workstation 2 6 5 7 3 2 6 7
a. A-B-C-D-E-F-G
b. E-F-G-C-A-B-D
c. E-F-G-D-C-B-A
d. E-D-B-A-F-C-G
362. Which of the following scheduling
methods is more suitable for an industry
where jobs are processed in multiple stages
of production?
a. Line balancing
b. Sequencing rules
c. CRAFT
d. Linear programming
363. In which type of scheduling method, are
orders scheduled according to their due
dates?
a. Forward
b. Backward
c. Routing
d. Hybrid
364. Which of the following is not a
disadvantage of varying workforce
strategy?
a. Increased hiring and layoff costs
b. Increased training costs
c. Increased overtime costs
d. Adverse effect on employees morale
365. Which of the following is not true of
backward scheduling?
a. Production activities are scheduled by their
due dates
b. Service delivery schedules are known in
advance
c. Work-in-process inventory level is high
d. Jobs are assigned according to the latest
available time
366. Repetitive operations normally involve
mass production of a product or a service.
Which of the following is not a
characteristic of repetitive operations?
a. Mass production of a product
b. Need to control flow of materials and
application of labor resources to minimize
idle time
c. Focus on synchronizing customer demand
with production activity
d. There are large variations in the production
process and the equipment is designed for
a broad range of applications
367. In which of the following type of labor-
intensive scheduling approach, are
employees given the freedom of choosing
their start time, but have to work for eight
hours each day?
a. Flextime approach
b. Flextour approach
c. Compressed work week
d. Staggered times approach
368. Which of the following is not an
application of Gantt charts?
a. Help sequence jobs in a way that idle time
is minimized
b. Depict work load levels for equipment,
workstations or departments
c. Track job progress as they go through
various departments
d. Help adapt to changes in scheduling
requirement
369. Which of the following statements about
queuing analysis is incorrect?
a. Study of waiting lines and queuing
systems
b. Helps balance the costs of waiting time
with the costs of providing additional
service facilities
Operations Management
42
c. It helps maximize the number of service
workstations required
d. A queue will result if customer arrival rate
is greater than service delivery rate
370. The critical ratio method is a job
sequencing technique that an operations
manager can use to verify whether a job is
being performed on schedule. In this
technique, ________ the critical ratio,
_______ the priority.
a. Lower, lower
b. Higher, higher
c. Lower, higher
d. Higher, lower
(Questions 371 & 372) Jagson Ltd. has started
three jobs and engaged three teams to execute
each job. Today is day 20. The due dates and
scheduled time remaining for each job are
given in the table below. Answer the following
two questions.
Job Due Date Work Days Remaining
1 25 7
2 32 14
3 27 5
371. Calculate the critical ratios for job 1, 2 & 3
respectively?
a. 1.400, 0.714, 0.857
b. 2.8, 1.840, 1.428
c. 0.714, 0.857, 1.400
d. 0.714, 1.400, 0.857
372. Which job should get highest priority?
a. Job 1
b. Job 2
c. Job 3
d. Both job 1 and 3
373. Operations managers generally use several
techniques to schedule jobs in various
departments. Which of the following is
one of them?
a. Routing
b. Loading
c. Scheduling
d. Critical ratio
374. Which of the following is not an effective
criterion for scheduling?
a. Minimizing customer waiting time
b. Minimizing completion time
c. Maximizing flow time
d. Maximizing resource allocation
375. In which scheduling activity is the capacity
limitation of each work center to be
considered while assigning jobs?
a. Loading
b. Sequencing
c. Expediting
d. Routing
376. In which of the following personnel
scheduling approaches are employees
given an option of choosing their work
timings, provided they complete a
specified number of hours a week?
a. Flextime approach
b. Flextour approach
c. Compressed work week
d. Staggered times
(Questions 377 to 382) Use the following table
to answer the following six questions. The
table shows two jobs on two machines and
their respective routing sequences. Both jobs
should be completed in 9 hours.
Job X Route Sheet Job Y Route Sheet
Routing
Sequence
Machine Processing
Time
(Hours)
Routing
Sequence
Machine Processing
Time
(Hours)
1 1 3 1 2 2
2 2 2 2 1 3
3 1 2 2 1
Total 7 Total 6
Part A
43
377. Which of the following gives the correct
representation of forward scheduling for
Jobs X and Y?
a.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 X2 Y3 Y3
b.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 Y3 X2 X2 X2 Y3
c.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1
X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3
M2
Y1 Y1 X2 X2 X2 Y3 Y3
d.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1
X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2
Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3
378. Which of the following gives the correct
representation of backward scheduling for
Jobs X and Y?
a.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3 Y3
b.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3
c.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 X2 Y3 Y3
d.
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3
379. Using forward scheduling what is the
earliest finish time of Job X?
a. 9 hours
b. 8 hours
c. 7 hours
d. 6 hours
380. What is the earliest finish time of Job Y in
forward scheduling?
a. 9 hours
b. 8 hours
c. 7 hours
d. 6 hours
381. What is the latest start time for Job X in
backward scheduling?
a. 1 hour
b. 2 hours
c. 3 hours
d. 4 hours
382. What is the latest start time for Job Y in
backward scheduling?
a. 1 hours
b. 2 hours
c. 3 hours
d. 4 hours
383. Which scheduling activity describes the
specification of work flow in operations
scheduling?
a. Routing
b. Loading
c. Dispatching
d. All of the above
384. Assigning specific jobs to each work
center for the planning period is called
___________.
a. Routing
b. Loading
c. Dispatching
d. None of the above
385. Which of the following dispatching rules
do firms use when they want to maximize
the number of completed jobs and reduce
the number of jobs in waiting?
a. Longest processing time
b. Shortest processing time
c. First in, first serve
d. Slack time remaining
(Questions 386 to 396) Sriram Welders
undertakes customized welding and fabrication
works for different customers across the
country. Jobs A, B, C, D and E are to be taken
up at the beginning of the week. Processing
times and due dates for these jobs are given in
the following table. Use this data to answer the
following eleven questions.
Operations Management
44
Job (In order
of arrival)
Processing
Times (days)
Due date
(Days
hence)
A 4 4
B 5 8
C 4 6
D 2 5
E 3 7
386. What is the order in which jobs are taken
for processing using the earliest due date
rule?
a. C D E A B
b. B A C D E
c. A D C E B
d. A B C D E
387. What is the average time of a job using the
earliest due date rule?
a. 4.2 days
b. 4.4 days
c. 5.4 days
d. 3.2 days
388. The shortest processing time among all
jobs is for job D. What is the total delay
for job D if the longest processing time
rule is used?
a. 9 days
b. 7 days
c. 13 days
d. 11 days
389. What is the average delay using the
longest processing time rule?
a. 5.8 days
b. 6.8 days
c. 5.3 days
d. 6.3 days
390. What is the delay for the last job processed
using the first in-first serve rule?
a. 9 days
b. 10 days
c. 11 days
d. 12 days
391. What is the average delay when the first
in-first serve rule is used?
a. 5.2 days
b. 5.4 days
c. 5.6 days
d. 5.8 days
392. Using the slack time remaining (STR) rule,
the job with the shortest slack time is
dispatched first. Which of the following
jobs have the shortest slack time?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
393. What is the time delay for the last job
processed using the slack time remaining
(STR) rule?
a. 8 days
b. 9 days
c. 10 days
d. 11 days
394. What is the average delay if the STR rule
is used to dispatch jobs?
a. 5.3 days
b. 5.0 days
c. 4.8 days
d. 4.6 days
395. What is the average time if the shortest
processing time rule is used?
a. 4.2 days
b. 4.4 days
c. 4.6 days
d. 4.8 days
396. Which dispatching rule would you suggest
to Sriram Welders if the objective is to
reduce the average delay in the work?
a. Earliest due date
b. First in, first serve
c. Shortest processing time
d. Slack time remaining
397. The scheduling of operations is different
for different types of operations. In which
of the following operations is flow of
material given utmost importance?
a. Job operations
b. Repetitive operations
c. Labor-intensive operations
d. All of the above
Part A
45
(Questions 398 & 399) Given below is a
Workload Gantt chart where X, Y, Z represents
three machines. A, B, and C represent jobs to
be performed on these machines during a
particular week. Answer the following two
questions.
Week Number
Work
Center
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
X A B C
Y
C
A
Z B
C
A
398. Identify the number of weeks required to
complete job A.
a. 2 weeks
b. 4 weeks
c. 7 weeks
d. 5 weeks
399. From the Gantt chart select the machine
most utilized.
a. Machine X
b. Machine Y
c. Machine Z
d. Machines Y & Z
400. Operations managers generally use several
techniques to schedule jobs in various
departments. How does the sequencing of
jobs using Johnsons job sequencing rules
help a firm?
a. It minimizes processing time
b. It maximizes operating efficiency
c. It reduces processing costs
d. All of the above
401. Under Johnsons sequencing rule, a
problem of m machines and n jobs can be
simplified into two fictitious machines and
n jobs. Using this criterion, identify the
correct mathematical representation of
simplifying m machines into two
machines.
a. G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im
H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im
b. G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im
H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im-1
c. G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im-1
H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im
d. G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im-1
H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im-1
402. Which of the following situations leads to
the formation of a queue in a service
organization?
a. Rate of arrival of customers is less than
rate at which service is rendered
b. Rate of arrival of customers is equal to the
rate at which service is rendered
c. Rate of arrival of customers is greater than
the rate at which service is rendered
d. Both b and c
403. Which of the following is not a benefit
associated with queuing analysis?
a. To minimize waiting costs
b. To determine optimum number of
work/service stations
c. To balance waiting costs with the costs of
providing additional service stations
d. To minimize processing time of jobs
404. Critical ratio method is a sequencing
technique used by the operations managers
in scheduling work. Identify the correct
formula for calculating the critical ratio.
a. Total time to complete the job / work
remaining
b. Planned time remaining / work still
remaining
c. Actual work remaining / planned time
remaining
d. Total time remaining / actual time
remaining
(Questions 405 to 407) Crescent SoftDesign, a
designing company, currently has five projects
A, B, C, D, and E on hand which require150
days, 135 days, 180 days, 140 days and 120
days respectively to complete. After 100 days,
the operations manager identifies that these
projects still require 60 days, 30 days, 70 days,
45 days and 30 days respectively for
completion. Based on the given information,
answer the following three questions.
405. Which of these projects has the least
critical ratio?
Operations Management
46
a. A
b. B
c. D
d. E
406. Which of the following projects is ahead
of schedule?
a. A and D
b. A and E
c. B and C
d. B and E
407. Using the critical ratio method, give the
order of priority based on the revised time
of completion after 100 days?
a. A B C D E
b. E D A C B
c. E A D C B
d. E A D B C
408. Which of the following is not a basic
objective of scheduling activities?
a. To meet customer requirements on time
b. To carry out the production process most
efficiently
c. To minimize service delays
d. To minimize inventory costs
409. Which of the following is not true about
ERP?
a. ERP uses multiple databases to store
information
b. It integrates all business functions of an
organization
c. Implementation costs are high
d. It provides smooth information flow
through the organization
410. The implementation of ERP in an
organization has undergone a sea change
over the years primarily due to which of
the following factors?
a. Changes in the ERP concept
b. Changes in organizational structures
c. Advances in software and hardware
technologies
d. None of the above
411. Which of the following is a result of BPR?
a. Customers have become selective due to
availability of wide range of products from
various marketers
b. Marketers have to maintain customer
relationships effectively in a competitive
market
c. Changes in the marketplace have forced
marketers to think about their business
processes
d. Marketers can take speedy decisions in a
dynamic market environment
412. Business modeling is a precursor to
business process reengineering, ERP
implementation, etc. What is the purpose
of business modeling?
a. To provide details of activities performed
and workflow structure
b. To provide an overview of operations
without focusing on processes and systems
c. To provide details of processes and
systems
d. Both a & b
413. A good business model should be
comprehensible, coherent and complete.
Which of the following is not a primary
basis for developing a business model?
a. Goals
b. Objectives
c. Strategic plans
d. Market structure
414. One of the critical steps of ERP
implementation is the development of an
integrated data model. How does this help
an organization?
i. Increases connectivity between
departments
ii. Helps in smooth flow of information
between departments
iii. Increases data redundancy
iv. Ensures availability of right information
a. i, ii, iii
b. i, ii, iv
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
Part A
47
415. To guarantee the success of ERP
implementation, organizations have to
concentrate on three issues functionality,
technology and implementability. Which
of the following statements hold true for
technology issues?
i. Technology used in ERP package should
have low compatibility with other
information systems
ii. Technology used should be flexible and
adapt to any future changes
iii. Technology used should not be too costly
to upgrade in future
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i and iii
d. i, ii, iii
416. Which of the following costs are not
associated with ERP implementation?
a. Cost of consulting
b. Cost of process redesign
c. Cost of training
d. None of the above
417. Which of the following types of
information are required to customize an
ERP package as per an organizations
requirements?
i. Information from mapping of business
processes
ii. Information from gap analysis
iii. Market information
iv. Information about the companys
competitors
a. Only i
b. i and ii
c. ii and iii
d. Only iii
418. The key activity of _____________ is to
monitor the implementation process
continuously in order to identify
deviations, cost overruns, resource
requirements, etc. during implementation.
a. Project member
b. Project leader
c. Project team
d. Steering committee
419. What is the basic objective behind defining
corporate needs of an organization before
ERP implementation?
a. To assess the readiness of the organization
to accept change
b. To identify the gaps in terms of handling
information
c. To facilitate speedy implementation
d. All of the above
420. An organization is required to undergo a
brief business process redesign exercise
before actual ERP implementation. Why?
a. To assess the readiness of the organization
to change
b. To assess the implications of the changes
c. To facilitate speedy implementation
d. To identify the gaps in terms of handling
information
421. Strong leadership is an important success
factor in implementing an ERP system.
Which of the following will enable the
steering committee to produce successful
results in ERP implementation?
i. The committee should understand the
redesign and integration
ii. The committee should be trained in
process mapping
iii. The committee should be fully involved in
process redesign so that it can guide the
team members
a. Only i
b. i and ii
c. ii and iii
d. i, ii, and iii
422. To gain competitive advantage,
organizations should understand what
factors are required to make them a
qualifier for purchase from customers. In
addition, they should know what factors
could enable them to eventually win an
order. Which of the following is a clear
example of an order winner?
a. ISO certification to compete in the global
markets
b. Minimum quality required to enter into a
market
c. Standardized products produced at low
costs
d. Customized products produced at
reasonable costs
Operations Management
48
423. When an ERP marketer uses price as an
order winner, it should focus on certain
areas to reduce the costs involved during
ERP implementation. Which of the
following will not facilitate this objective?
a. Identify the cost centers and devise plans
to reduce production costs
b. Set up tough cost targets
c. Set up tough quality targets
d. Set up a rigorous monitoring system to
make the production process cost efficient
424. Quality encapsulates many dimensions like
performance, features, reliability,
conformance, durability, serviceability and
aesthetics. A measure of a products life in
terms of both its technical and economic
aspects is associated with which of the
following dimensions?
a. Performance
b. Reliability
c. Durability
d. Conformance
425. If HDFC Bank offers a wide range of
products that cover every market segment;
it can be termed as an order winner with
respect to _____________.
a. Price
b. Product range
c. Quality
d. Delivery reliability
426. The logistics-related decisions of an
operations manager focus on which of the
following?
a. Modes of transportation, distribution and
inventory management
b. Selection of suppliers for raw material
supply
c. Layout of warehouse, administrative
facilities and plants
d. Effective management of material flow in
the organization
427. Arrange the following steps in electronic
supply chain management implementation
in the correct sequence.
i. Understand and evaluate the level of
integration within the organization.
ii. Determine the number of suppliers who
have direct influence over the products or
services delivered to customers across the
entire supply chain.
iii. Divide suppliers into different categories:
first tier, second tier and so on.
iv. Define customer base in term of sales,
profitability, size, etc.
v. Improve information infrastructure within
the organization to accommodate ESCM
requirements.
vi. Constitute a team with representation from
various functions within the organization
and representatives from suppliers and
customers to plan and implement.
vii. Identify leaders who are capable of
guiding the implementation process
competently.
a. iv, iii, ii, v, vi, vii. i
b. i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi, vii
c. iv, v, vi, vii, i, ii, iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv, vii, vi, v
428. Which of the following is not considered a
member of a supply chain?
a. Manufacturer
b. Supplier
c. Distributor
d. Customer
429. Which of the following is an intangible
benefit of SCM?
a. Growth in revenue
b. Improved facility utilization
c. Optimum inventory management
d. Improved customer satisfaction
430. What is the relationship between the
location of a facility and the supply chain
performance of the firm?
a. Facilities close to the target market
improve the performance of the supply
chain
b. Facilities away from target markets
improve the performance of the supply
chain
c. Facilities close to target markets worsen
the performance of the supply chain
d. The location of a facility and supply chain
efficiency of a firm are in no way related
431. Which of the following statements about
designing of a logistics network in a
supply chain is incorrect?
Part A
49
a. Firms design a logistic network to meet
average requirements of all customers
b. Firms design a logistic network to meet
even the toughest requirements of a single
customer
c. Firms never custom design a logistic
network to meet the individual
requirements of customers
d. Firms design a logistic network so that
some amount of customization is built in
to meet the requirements of customers
432. If an organization follows the principles of
supply chain management, it can attain a
balance between customers expectations
and growth and profitability objectives.
Which of the following is not a principle
of supply chain management?
a. Quality and performance management
b. Customize the logistics network
c. Enhance ability to meet customer
requirements
d. Have a supply chain-wide technology
strategy
433. Order-to-delivery process is an SCM
component. It can be used to evaluate the
performance of a _________ on the basis
of on-time delivery, costs, defects, etc.
a. Production manager
b. Supplier
c. Purchase manager
d. Distributor
434. Every organization takes steps to maintain
certain standards in terms of quality.
Which of the following components of
SCM is not concerned with these
initiatives?
i. Human resources management
ii. Order-to-delivery process
iii. Business relationship management
iv. Quality and performance management
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, iii
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, iii, iv
435. The health and well-being of suppliers is
critical for organizations, which largely
depend on suppliers for their requirements.
Which of the following hampers
development and maintenance of long-
term relationships with suppliers?
a. Show commitment for long-term
profitability of suppliers
b. Lay down mutually understood rules for
building a long-term relationship
c. Strive for heavy discounts to improve the
organizations short-term profitability
d. All of the above
436. Measurement is an SCM enabler. How
are measurements helpful in supply chain
management?
i. They provide information about inputs,
outputs, performance etc.
ii. They are used to evaluate the performance
of business processes
iii. They provide insights into suppliers
performance in terms of delivery
performance, quality of material supplied
etc
iv. They ensure periodic evaluation of the
performance of processes, programs and
systems that support continuous
improvement
a. i and ii
b. i, ii and iv
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, ii, iii
437. Which of the following supply chain
members traditionally assumed the role of
monitoring consumer preferences?
a. Retailer
b. Wholesaler
c. Distributor
d. Manufacture
438. Which of the following statements
correctly describes the differences between
demand chain and supply chain?
i. Every member in the demand chain has to
collect customer information unlike the
retailer in the supply chain
ii. Any member in the supply chain can
monitor consumer needs and wants, unlike
only retailers in the demand chain
Operations Management
50
iii. In demand chains, any information
regarding relevant consumer trends and
products should be shared by all members
unlike in traditional supply chains
iv. The members in todays emerging demand
chains are different from those in
traditional chains.
a. i, ii, iii
b. ii, iii, iv
c. i and iv
d. Only iv
439. Which of the following is not a method to
collect customer information?
a. Focus groups
b. Quantitative survey
c. Point-of-sale databases
d. Value analysis
440. Which of the following are common
misconceptions about the supply chain
concept?
i. All customers buy from retailers
ii. Industrial marketers should focus on client
preferences and not end users
iii. All members of the supply chain should
work in unison to improve profitability
iv. To improve supply chain efficiency it is
necessary to have a supply chain-wide
technology strategy
a. Only i
b. i and iv
c. i and ii
d. i, iii and iv [c, pg.228]
441. How does electronic supply chain
management cut procurement costs?
a. By transporting goods quickly
b. By enabling customers to directly order
products [c, pg.230]
c. By reducing communication costs
d. By providing suppliers instant access to
information
442. Electronic supply chain management helps
better inventory management. Which of
the following statements support this
benefit?
i. ESCM results in an extended organization
that sums up supplier activities
ii. Inventory level status can be
instantaneously accessed by suppliers
iii. Suppliers can replenish the inventory as
soon as the need arises
iv. ESCM requires the firm to carry high
inventory levels
a. i and iv
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i, iii, and iv
d. iii and iv
443. Electronic supply chain management has
many benefits, but together with the
benefits, there are issues that must be
addressed to improve the efficiency of
ESCM. Which of the following can be
considered the most sensitive issue?
a. Information security
b. Order taking
c. Order delivery
d. Customer information
444. Which of the following are essential
conditions for a JIT system to be
successful?
i. Teamwork
ii. Discipline
iii. Supplier involvement
iv. Employee performance
a. i, ii, and iv
b. i, iii, and iv
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
445. Which of the following statements
correctly depicts the characteristics of a
JIT production system?
a. Producing on need basis
b. No room for surplus or safety stock
c. Doing it right the first time
d. All of the above
446. Which of the following is a feature of the
JIT strategy related to production?
a. Produce in small lots
b. Every worker is responsible to the
immediate customer (worker)
c. Continuous improvement
d. Customer satisfaction
447. Which of the following is not true of a JIT
system?
Part A
51
a. It eliminates all inventory
b. It is a pull system
c. It is a push system
d. Firms place very small and frequent orders
for inventory
448. Which one of the following is not a result
of implementing JIT systems?
a. Small lot sizes
b. Varying workstation loads
c. Quick and economic set-ups
d. Preventive maintenance
449. Identify the Japanese term related to JIT
where a machine is enabled to detect
defects automatically.
a. Andon
b. Soikufu
c. Shojinka
d. Jikoda
450. Nothing is produced until it is required
is a fact practiced in which concept?
a. Make-to-stock process
b. Materials requirement planning
c. Just-in-time manufacturing
d. Inventory management
451. Firms that practice JIT production systems
require reliable suppliers. Therefore, JIT
firms maintain long-term business
relationships with a few selected suppliers.
Which of the following is true about a
supplier relationship under the JIT system?
a. The JIT firm derives more mileage than
the supplier from the relationship in the
long run
b. The supplier derives more mileage from
the relationship
c. The relationship should be profitable to
both the firm and the supplier
d. The supplier need not stick to the terms of
supply under the contract
452. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of JIT system?
a. The JIT firm shares production plans and
schedules with suppliers
b. The JIT firm can provide assistance to
suppliers to improve quality and
productivity
c. The JIT firm invites suppliers to
participate in product design and suggests
changes and/or improvements
d. The JIT firm always maintains only one
supplier for each type of material
453. Building effective partnerships depends on
four elements: trust, communication,
linearity of production and time to make
changes. Under which element do JIT
firms employ special teams or departments
to enhance their relationship with
suppliers?
a. Trust
b. Communication
c. Linearity in production
d. Time to make changes
454. Suppliers require time to respond to
changes in demand. This is one of the four
elements that help build effective
partnerships. Which statement correctly
describes this element?
a. It involves development of production
schedules with uniform workloads
b. Suppliers inform the JIT firm about their
new initiatives to improve quality
c. It focuses on building confidence in each
other that helps further improve the
relationship
d. Suppliers purchase new machinery, hire
and train labor to meet requirements
455. JIT adopts the concept of immediate
customer to increase product quality and
improve customer service. What does the
term immediate customer signify?
a. Every worker in the JIT firm is considered
a customer
b. A person outside the firm who buys its
products for use or consumption
c. Each worker in the firm considers the next
worker in the production line as a
customer
d. Each worker is fully responsible for a task
and inspect his or her own work
456. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of the JIT system?
a. Uniform workstation loads
b. Large lot sizes
c. Quick and economic set-ups
d. Flexible facilities
Operations Management
52
457. Quick and economic set-ups is a
characteristic of a JIT system. What does
this signify?
i. Lesser inventory
ii. Smaller production lot size
iii. Higher number of set-ups
iv. Higher costs
a. i, ii, and iii
b. ii, iii, and iv
c. i, iii, and iv
d. i, ii, iii, and iv
458. How are workers in a JIT firm different
from that of a non-JIT firm?
i. JIT workers are trained continuously
ii. JIT workers are trained to perform
multiple jobs
iii. JIT workers are specialized in a particular
operation
a. Only i
b. i and iii
c. i and ii
d. i, ii and iii
459. Having quick and economic set-ups is a
characteristic of a JIT system. Firms adopt
a procedure to reduce set-up times.
Arrange the steps in the correct sequence.
i. Analyze existing set-up procedures
ii. Separation of internal and external set-up
activities
iii. Convert internal set-up activities into
external set-up activities
a. i, ii, iii
b. ii, iii, i
c. i, iii, ii
d. iii, i, ii
460. JIT does not focus on one of the
following. Identify.
a. Eliminating external demand variations
b. Reducing unreliable delivery of raw
materials
c. Reduction of inventory
d. Reducing excessive set-up times
461. A company can compete on different
quality functions. Which of the following
is not a function of quality?
a. Performance
b. Features
c. Reliability
d. Warranty
462. Control charts do not _________.
a. Display the measurements of every item
being produced
b. Display upper and lower limits for process
variables or attributes and signal when a
process goes out of control
c. Indicate to the process operator the
average outgoing quality of each lot
d. Indicate to the operator the defective
percentage in each lot
463. Control charts are used extensively to
monitor quality. Suppose some individual
parts measured are below the lower control
limit. What does this clearly indicate?
a. The process is out of control and the cause
should be established
b. The process is in control
c. The process is within established control
limits with natural causes of variation
d. The process is outside established control
limits with only natural causes of variation
464. Small boxes of peanuts are labeled net
weight 250 gm. To construct control
charts, random samples of 5 boxes were
weighed. You can assume the value of D
4
as 2.114 for the sample. Based on
observations given in the table below,
determine the upper control limit for the
R-chart.
Sample Mean weight (X) Range (R)
1 240 30
2 260 20
3 250 20
4 270 30
5 240 60
TOTAL 1260 160
Part A
53
a. 60.49
b. 68.53
c. 67.65
d. 69.52
465. Quality in services can be measured in
terms of tangible and intangible aspects in
service delivery. Which among the
following is not an example of intangibles
in service delivery?
a. Promptness
b. Courteousness
c. Ambience
d. Timeliness
466. Quality control is an important function
that helps increase customer satisfaction.
At which of the following stages does
quality control begin?
a. Procurement of raw material
b. Start of production
c. Finished goods inventory
d. Dispatch to customers
467. Productivity is measured as the output
produced with a given set of inputs. Which
of the following is not a measure of
productivity?
a. Number of kilograms of rubber produced
per day
b. Number of toys produced in one hour
c. Average length of the rods in a lot
d. Number of patients treated in day
468. Bottlenecks in the production process can
hamper productivity. Which among the
following cannot be an example of a
bottleneck that can hamper productivity?
a. Layout
b. Slow processing equipment
c. Proper scheduling
d. Inventory shortage
469. How can scheduling help increase
productivity?
a. By decreasing idle time
b. By increasing running time of machinery
c. By decreasing wastage
d. All of the above
470. Which of the following can be a measure
of output associated with productivity in
service organizations?
a. Number of calls made by a telemarketer
b. Number of complaints received by a call
center
c. Amount of time spent in counseling a
student
d. Number of cars serviced in a period
471. How can training employees increase
productivity?
a. It helps acquire new skills
b. It helps improve existing skills
c. It helps motivate employees
d. All of the above
472. Which function of quality focuses on
analyzing the defect rates of a product
during production, and the number of
customer complaints after product sale?
a. Conformity
b. Aesthetics
c. Serviceability
d. Perceived quality
473. Identify the function of quality used by
marketers to target a niche market that is
influenced by individual preferences.
a. Conformity
b. Aesthetics
c. Serviceability
d. Perceived quality
474. At one point cost of inspection and cost of
undetected faults is optimum. What does
this statement signify?
a. The cost of inspection is high
b. The cost of undetected faults is high
c. The total cost of quality control is minimal
d. The average cost of quality control is
minimal
475. At one point, there is an optimal trade-off
between the cost of inspection and the cost
of an undetected fault. At this point, the
cost of total quality control is minimal.
Which of the following is not an
inspection cost?
Operations Management
54
a. Cost of training personnel
b. Loss of goodwill
c. Supervision of inspectors
d. Cost of inspection facilities
476. The cost of quality can be divided into
different categories. Evaluating quality and
performance of products and machinery is
associated with which type of costs?
a. Prevention costs
b. Failure costs
c. Appraisal costs
d. Both a & b
477. Failure costs, which are a type of quality
costs, can be divided into internal and
external failure costs. Which of the
following is not an internal cost?
a. Scrap costs
b. Downtime costs
c. Retesting costs
d. Cost of returned products
478. Control charts are used extensively to
monitor quality. They can be categorized
under control charts for variables and
control charts for attributes. Which of the
following come under the former?
i. X-chart
ii. R-chart
iii. P-chart
iv. C-chart
a. i & ii
b. ii & iii
c. i & iii
d. ii & iv
479. Which of the following control charts is
used to determine the proportion of
defective items in a selected sample?
a. X-chart
b. R-chart
c. P-chart
d. C-chart
480. In which of the following approaches are
continuous improvements in process, skill
sets, systems and operations considered?
a. Kaizen
b. Andon
c. Jikoda
d. Shojinka
481. Universal responsibility is one of the
principles of TQM. Identify the statement
that best represents and underlines the
spirit of this principle.
a. Top management is responsible for the
quality of products entering the market
b. Production department is responsible for
product quality
c. Every employee at every level in the
organization is responsible for quality
d. Emphasis is on continuous improvement in
process, skill sets, systems or operations
(Questions 482 to 487) Use the following data
to answer the following six questions. Given
below is the table that shows the means and
ranges of 8 samples. Every sample contains 5
items. Conversion factors are given as A
2
=
0.373, D
3
= 0.136, D
4
= 1.864.
Sample 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
x
25 36 31 33 27 34 32 25
R 8 9 7 6 6 7 5 8
482. Calculate the mean of means for the given
data.
a. 31.145
b. 31.375
c. 30.375
d. 30.145
483. Calculate the mean of ranges from the
given data.
a. 6.8
b. 7.0
c. 7.3
d. 6.7
484. What is the upper control limit if an X-
chart is developed?
a. 32.986
b. 35.275
c. 35.505
d. 34.275
485. What is the lower control limit if an X-
chart is developed?
Part A
55
a. 27.764
b. 26.135
c. 25.245
d. 25.135
486. If one has to plot an R-chart for the given
data, what would be the lower limit for this
chart?
a. 0.16
b. 0.952
c. 0.93
d. 1.12
487. Calculate the upper limit for the R-chart.
a. 0.93
b. 16.38
c. 13.048
d. 0.16
(Questions 488 & 489) When the quality
control department of Ambuja Rayon inspected
7 carpets manufactured in its plant, it identified
the following number of defects in the process.
Based on the information, answer the following
two questions.
Sample 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Number of
Defects
5 3 4 2 3 1 4
488. Calculate the average number of defects.
a. 3.14
b. 2.34
c. 3.54
d. 3.64
489. If the data in the above question is used to
construct a C-chart, then what would be
the upper and lower control limits for this
chart?
a. 8.456 and -2.176
b. 8.546 and 2.176
c. 8.546 and 0
d. 8.650 and 0
490. What is the condition in which a customer
runs the risk of accepting a lot with minor
defects?
a. Cost of prevention
b. Type I error
c. Type II error
d. Cost of detection
491. Under TQM, every department in an
organization should treat every other
department as its _________.
a. Producer
b. Customer
c. Distributors
d. Supplier
492. What explains how well an acceptance
plan differentiates between good lots and
bad lots?
a. AOQ
b. OC curve
c. Lot Tolerance Percent Defective
d. Acceptable Quality Level
493. The cost of quality can be divided into
three major categories - cost of prevention,
cost of detection/appraisal and cost of
failure. Which of the following is a
prevention cost?
a. Disposition of defective items
b. Equipment maintenance
c. Quality training
d. Warranty charges
494. Which of the following is not an objective
of remedial maintenance?
a. To minimize production losses by getting
equipment back into working condition as
quickly as possible
b. To minimize investments in spare parts
and standby machines used when
equipment is under repair
c. To perform appropriate maintenance based
on the extent of the problem
d. Regular monitoring of vital parameters of
a machine
495. Preventive maintenance can be classified
into periodic maintenance and irregular
maintenance. Irregular preventive
maintenance does not include one of the
following.
a. Repair
b. Overhaul
c. Reducing machine vibration
d. Tasks like cleaning up oil spills
Operations Management
56
496. Which of the following is not an activity
of maintenance management?
a. Improving efficiency of raw material
purchase
b. Minimizing loss of productive time
c. Prolonging asset life
d. Effective utilization of assets
497. Which of the following is not a goal of
maintenance management?
a. Minimizing the availability of the firms
assets for production purposes
b. Improving the quality of products and
increasing the firms productivity
c. Using maintenance personnel and
equipment efficiently
d. Preserving the value of a firms machinery
and reducing deterioration
498. A facilities manager has to consult
different personnel while performing
alterations to facilities or expanding them
for better design. Who among the
following would be the least preferred
choice for the facilities manager?
a. CEO
b. Production manager
c. Architect and designers
d. Marketing manager
499. The process of hiring outside workers or
specialized vendors to accomplish a
particular task is called _________.
a. Outsourcing
b. Out-tasking
c. Overtime
d. Processing
500. Loss of control is one of the costs of
outsourcing certain or all activities to
external service providers. Identify the
possible consequences that may arise from
loss of control.
i. Vendor can take undue advantage of
control
ii. Client may lose the voice in crucial
decisions
iii. Costs reduce over a period of time
iv. Client may not be able to control the
vendors deviation from standards
a. i, ii, iii
b. i, ii, iv
c. iii and iv
d. i and iii
501. Why do vendors prefer to enter into long-
term contracts with firms to undertake
facilities management services?
i. To enable firms retain control over
activities
ii. To cover high initial costs at the beginning
of the contract
iii. Long term contracts fetch more profits to
the vendor
iv. To help firms reduce costs over time
a. ii and iii
b. ii, iii and iv
c. iii, iv and i
d. i, ii and iv
502. Vendors replace skilled workers with
semi-skilled workers in a manufacturing
facility after some time. What could be the
possible reason behind this move?
i. To reduce direct operating costs
ii. To train semi-skilled workers
iii. To use them for new clients
iv. To improve clients profits
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
503. Despite several disadvantages, firms prefer
to outsource facilities management tasks.
Which of the following does not support
this statement?
a. Increases quality of work
b. Helps develop core competence
c. Increases flexibility
d. Increases operational costs
504. Which of the following statements does
not support the importance of maintenance
of machines in a facility?
a. Machine failures do not hinder
productivity
b. Repairing a machine can be expensive
Part A
57
c. Equipment malfunction may reduce
product quality
d. Fixing a broken-down machine can stop
production and may consume time
505. Mr. Suresh Kumar was promoted as
maintenance manager in Unicorn
Manufacturing. He was a design engineer
in the same plant earlier. What benefits can
Kumar offer to Unicorn in his new
position?
i. Focus on regular maintenance to improve
productivity
ii. Help increase the life of assets and
machinery
iii. Help preserve the value of equipment
iv. Minimize the salvage value of machinery
a. i and ii
b. iii and iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
506. Maintenance of air conditioners is an
example of which type of maintenance?
a. Mechanical maintenance
b. Civil maintenance
c. Electrical maintenance
d. All of the above
507. If a 5hp motor is a critical component in
the manufacture of a certain product in a
large organization, its maintenance is
given utmost importance. Who would
appropriately undertake maintenance of
such equipment?
a. Machine mechanic
b. Plumber
c. Electrician
d. Supervisor
508. Match the following personnel with their
respective maintenance responsibilities.
i. Plumbing personnel
ii. Electrical personnel
iii. Housekeeping personnel
iv. Instrumentation personnel
p. Lighting equipment
q. Electronic routers
r. Water supply pipes
s. Buildings
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/q, ii/p, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/r, ii/p, iii/s, iv/q
d. i/r, ii/q, iii/p, iv/s
509. Identify the distinct difference between
preventive and predictive maintenance
a. Predictive maintenance is done after a
machine breaks down while preventive
maintenance is done before a machine
breaks down
b. Preventive maintenance is done after a
machine breaks down while predictive
maintenance is done before a machine
breaks down
c. Preventive maintenance involves regular
servicing of equipment while predictive
maintenance involves monitoring
equipment continuously
d. Preventive maintenance focuses on the
past while predictive maintenance focuses
on the future
510. Krishna, a production worker detected
some minor vibrations in a lathe machine
that is very sensitive to movement. What
does this indicate?
i. The cutting precision will reduce
ii. Rate of production can go up
iii. Quality of product can come down
iv. The equipment needs maintenance
a. i, iii, iv
b. ii, iii, iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
511. Periodic maintenance is associated with
______.
a. Preventive maintenance
b. Predictive maintenance
c. Remedial maintenance
d. Mechanical maintenance
512. What is the term used for the maintenance
activity that attempts to detect problems
while the equipment is still performing at a
satisfactory level?
a. Remedial maintenance
b. Predictive maintenance
Operations Management
58
c. Periodic maintenance
d. None of the above
513. Which of the following is not a cost
associated with preventive maintenance?
a. Cost of replacing materials and parts
b. Cost of replacing the entire machine
c. Cost of instruments used in preventive
maintenance
d. Wages of staff and technicians
514. Condition monitoring is associated with
___________.
a. Predictive maintenance
b. Remedial maintenance
c. Periodic maintenance
d. Irregular preventive maintenance
515. Condition monitoring uses various
instruments to measure machine
parameters like operating temperature,
pressure, vibration, etc. Which of the
following instruments is not associated
with condition monitoring?
a. Amplitude meter
b. Vibration analyzer
c. Audio detector
d. Richter scale
516. Remedial maintenance is termed reactive.
What does this mean?
a. Remedial maintenance is taken up when
machinery breaks down
b. Remedial maintenance is done to avoid
breakdown
c. It occurs before purchase of new
machinery
d. It is carried out regularly
517. Which among the following is not an
objective associated with remedial
maintenance?
a. To minimize investments in spare parts
and standby machines used when
equipment is under repair
b. To minimize production loss by getting
equipment back into working condition as
quickly as possible
c. To perform appropriate repair at
appropriate levels
d. To minimize failures or malfunction to the
lowest possible extent
(Questions 518 to 521) A manufacturing plant
has 25 machines of the same type. The
probability of failure of a machine depending
on time lapsed (in months) after the last
maintenance is given in the following table.
Answer the following four questions based on
the given information.
Elapsed time
after last
maintenance
(in months)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Probability of
failure
0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.15
518. What is the mean time between failures?
a. 7.83 months
b. 6.48 months
c. 7.98 months
d. 6.63 months
519. Calculate the probable number of break-
downs per year for a machine.
a. 1.53
b. 1.50
c. 1.81
d. 1.85
520. What can be the probable number of
break-downs per year for all machines in a
plant?
a. 37.50
b. 38.25
c. 45.25
d. 46.25
521. If the yearly cost of servicing a broken
down machine is Rs.12000, what is the
average cost of repairs per machine per
occasion?
a. Rs.314
b. Rs.265
c. Rs.260
d. Rs.320
Part A
59
(Question 522 to 524) The probability of
failure after maintenance for a machine is given
in the table below. Answer the following three
questions, based on the given information.
Months after
maintenance
1 2 3 4 5
Probability of
break-down
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.1
522. If there are 15 identical machines in the
plant, what is the expected number of
break-downs between maintenance, if the
maintenance is performed every two
months?
a. 3.5
b. 3.65
c. 4.5
d. 4.65
523. What is the expected number of break-
downs between maintenance, if the
maintenance is performed every three
months?
a. 9.5
b. 9.465
c. 9.765
d. 9.565
524. If the average cost of preventive
maintenance is Rs.650 and that of remedial
maintenance per machine is 5500,
calculate the average total cost of
maintenance per month, if the maintenance
is performed every 3 months. Assume the
number of machines as 15.
a. Rs.63457.50
b. Rs.54765.50
c. Rs.45254.50
d. Rs.21152.50
525. Identify the correct sequence of steps
followed in maintenance planning.
a. Develop plan identify problem
estimate work to be done carry out the
sequence of tasks
b. Identify problem develop plan estimate
work to be done carry out the sequence
of tasks
c. Identify problem estimate work to be
done develop plan carry out the
sequence of tasks
d. Develop plan carry out the sequence of
tasks identify problem estimate work
to be done
526. Prioritizing work is very important in
maintenance planning. On what basis are
tasks prioritized when resources are
scarce?
a. Type of tools used to perform each task
b. Significance of tasks in maintaining
production flow
c. Based on personnel who carry out tasks
d. All of the above
527. Which of the following is a precaution
taken by maintenance managers during
maintenance planning?
a. Ensuring sufficient inventory of frequently
used tools and equipment within the plant
b. Reducing inventory costs by cutting
inventory of tools and equipment used
during maintenance
c. Storing frequently used tools and
equipment in a centralized location in case
of multiple plants
d. All of the above
528. What is the difference between a JIT
manufacturing system and a traditional
manufacturing system with respect to
simple preventive maintenance?
i. Simple preventive maintenance is done by
specialized maintenance staff
ii. Simple preventive maintenance is done by
production workers
iii. Simple preventive maintenance is carried
out at the beginning of every shift
iv. Shop floor workers should assist repair
specialists in case of a major break-down
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. i, iii, and iv
529. To provide a clean and conducive work
environment and enable efficient and
effective progress of the core functions of
an organization is an objective of
____________.
a. Quality management
b. Facilities management
c. Maintenance management
d. Inventory management
530. Which of the following is not an example
of a project?
Operations Management
60
a. Developing a new product or service
b. Production of radiator caps
c. Airport expansion
d. Implementing six sigma to bring down
cost overruns by 20%
531. The extent of time by which an activity
can be delayed beyond its earliest start
time without extending the project is called
__________.
a. Slack time
b. Latest start time
c. Optimistic time
d. Expected start time
532. Minimum amount of time that must lapse
before beginning an activity is called
________.
a. Expected start time
b. Earliest start time
c. Latest start time
d. Expected finish time
533. What are the benefits of a project plan?
a. It guides project execution
b. It documents project planning assumptions
c. It provides a baseline for progress
measurement and project control
d. All of the above
534. Which of the following statements is
false?
a. Project management differs from the
management of more traditional activities
due to the limited lifetime of projects
b. In linear programming, dummy activities
are added to paths to make them equal in
length
c. A Gantt chart contains no precedence
relationships, but may be useful for simple
projects
d. Slack time is the extent of time by which
an activity can be delayed without
delaying the entire project, assuming its
preceding activities are completed as early
as possible
535. The process of reducing the duration of the
project by reducing scheduled time of
some activities is called crashing. Which
of the following statements on project
crashing is false?
a. Crashing is not effective when applied to
tasks with zero slack
b. Crashing shortens the length of the critical
path
c. Crashing can be achieved by
subcontracting
d. Crashing can be achieved by employing
more workers
536. The following activities are part of a
project to be scheduled using CPM.
Identify the correct network diagram for
the given data.
Activity Immediate Predecessor
A -
B A
C A
D C
E B, D
F D
G E, F
a.
b.
c.
d.
A
C
G B
D F
E
A
C
G B
D F
E
A
C
G B
D F
E
A
C
G B
D F
E
Part A
61
537. Dummy activities are introduced in
PERT/CPM methods. Which of the
following statements about them is not
true?
a. Dummy activities are used to indicate
zero-length activity duration
b. Dummy activities are used to ensure that
two activities have the same beginning and
end nodes
c. Dummy activities are used to ensure that
the network reflects the project under
consideration
d. Dummy activities are used to represent
activity predecessors
538. Which of the following is not true about
projects?
a. It is a temporary endeavor
b. It is used to create a unique product or
service
c. It is an operation constrained by limited
resources
d. It involves continuous flow of repetitive
work
539. Managers use many terms as part of
networks in project management. In this
context, what is the term used for an
outcome of an activity or group of
activities?
a. Project
b. Event
c. Critical path
d. Node
540. Which of the following statements about
critical path is true?
a. It describes the longest of all paths through
a network
b. Some activities on the critical path may be
slack
c. Every network has exactly one critical path
d. It is the longest path of interrelated
activities in a project with zero slack time
541. Which of the following methods can be
used to identify the best possible schedule
for a project?
a. PERT
d. Routing
c. Dispatching
d. Johnsons rule
542. A project contains critical and non-critical
activities. Which among the following
correctly defines a critical activity?
a. Critical activities are those activities,
which if advanced, extend the project
duration
b. Critical activities are those activities,
which if delayed, reduce the project
duration
c. Critical activities are those activities,
which if delayed, extend the project
duration
d. Critical activities are those activities,
which if advanced, reduce the project
duration
543. Which of the following is an outcome of
an activity in a project?
a. Critical path
b. Event
c. Optimistic time
d. Critical path
544. Which of the following correctly describes
pessimistic time?
a. It indicates the best guess for the
completion of an activity
b. It is amount of time that an activity is
expected to consume
c. It is the maximum time an activity can take
considering obstacles and unfavorable
circumstances
d. It is amount of time that should be
consumed before beginning an activity
545. Which of the following terms, associated
with networks in project management, is
referred to as float?
a. Optimistic time
b. Pessimistic time
c. Most likely time
d. Slack time
546. If in a certain project, the only precedence
relationship is that activity A has to
precede activities B and C, then which of
the following network diagrams correctly
represents this situation?
Operations Management
62
a.
b.
c.
d.
547. Activity A and activity B precede activities
C, D and E. Activities A and B are
independent of each other. Activities D
and E follow activity C. Identify the
correct network diagram for this situation.
a.
b.
c.
d.
548. What is the formula for calculating float
in the critical path method?
a. (Expected time) + (given time)
b. (Expected time) - (earliest start time)
c. (Latest finish time) - (given time)
d. (Latest start time) - (earliest start time)
549. For projects where time values are affected
by chance variations, PERT is used. To
apply it certain conditions have to be
satisfied. Which among the following is
not such a condition?
a. Activities should have identifiable start
and finish times
b. The project must have a large number of
interrelated or overlapping activities
c. The activities should be clearly
distinguishable from each other
d. The project should be flexible and
accommodate different sequences and
timings
(Questions 550 to 554) The following table
gives the optimistic, pessimistic and most
likely times for the network diagram. Use this
data to answer the following five questions.
Activities Optimistic
time t
o
(Weeks)
Pessimistic
time t
p
(Weeks)
Most
likely
time t
m
(Weeks)
1-2 3 5 4
1-4 3 5 4
2-3 2 3 2
2-5 3 5 4
3-6 5 7 5
3-7 7 10 8
4-3 4 6 5
5-3 2 3 2
6-7 6 9 8
[
550. What is the expected time for the activity
5-3 in the project?
a. 5.33 weeks
b. 2.17 weeks
c. 4.0 weeks
d. 7.83 weeks
551. What is the sum of the expected times of
the activities on the critical path?
a. 23.33 weeks
b. 23.0 weeks
c. 22.33 weeks
d. 22.0 weeks
A
B
C
A B C
A B C D E
A B
C
D E
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
A
C
B
C
D
E
A
B
Part A
63
552. What is the sum of the variances of the
activities on the critical path?
a. 0.59
b. 0.632
c. 0.611
d. 0.582
553. What is the probability of completing the
project in 24 weeks?
a. 0.8510
b. 0.8023
c. 0.9217
d. 0.7902
554. What is the probability of finishing the
project in 23 weeks?
a. 0.3336
b. 0.4910
c. 0.4024
d. 0.4332
555. There are both benefits and limitations in
PERT. Which of the following statements
is not a benefit of PERT?
a. Users understand the relationships between
the activities through graphical displays
b. Used in tactical level planning and
operational level control
c. Effective in planning single project
activities in any type of industry
d. Effectively handles situations in which two
or more projects share available resources
556. A certain activity in a project has to be
crashed. Calculate the time-cost ratio for
this activity using the given details: Crash
cost = 25000, Normal cost = 20000, Crash
time = 13 weeks, Normal time = 17 weeks.
a. 5000
b. 2500
c. 1250
d. 625
557. Which of the following formulae correctly
represents the expected time?
a.
=
n
1 i
i
iP
b.
cp
2
E D
Z
=
c.
2
6
o
t
p
t
d.
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t + +
558. What must the prototype of a product
necessarily possess?
a. The final product in a smaller version
b. A model with the basic product
characteristics
c. A model with final physical attributes
d. Blueprint of the product
559. A CAD system incorporates computer
graphics and computer-aided engineering
systems. In what ways can managers make
use it?
i. Creation of a design
ii. Analysis of a design
iii. Modification of a design
iv. Developing a prototype
a. i & ii
b. i, ii, iii
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, iii, iv
560. Communication with which of the
following departments provides maximum
assistance to operations managers in
deciding the quantity, quality and other
specifications of the product or service to
be produced.
a. Finance department
b. Purchase department
c. Marketing department
d. Suppliers
561. Unlike conventional computer systems that
manipulate numbers to solve problems,
systems with artificial intelligence
manipulate _______.
a. Factors
b. Symbols
c. Instructions
d. Signals
Operations Management
64
562. What is the term used for computers that
are capable of performing the tasks of a
human being that require higher
intellectual ability?
a. Automation
b. CNC technology
c. Artificial intelligence
d. Robotics
563. Which of the following is not a benefit
derived by a firm adopting automation?
a. Low level of maintenance
b. Reduced lead-time
c. Improvement in work environment
d. Efficient use of materials
564. _________ refers to a computer
application that integrates various
computerized systems into a single multi-
functional system.
a. Computer integrated manufacturing
b. Artificial intelligence
c. Expert system
d. Flexible manufacturing system
565. ________ is a form of flexible automation
in which several machine tools are linked
to a material-handling system.
a. Computer integrated manufacturing
b. Artificial intelligence
c. Expert system
d. Flexible manufacturing system
566. _____________ is a technology that
includes a set of procedures and guidelines
based on which machines can
automatically execute activities performed
by humans.
a. Automation
b. Artificial intelligence
c. CAD
d. CAM
567. Automation is mostly used by
manufacturers in which of the following
functions of operations management?
a. Staffing
b. Planning
c. Organizing
d. Control
568. Automation is generally not possible in
which of the following?
a. Automobile production
b. Thermal power stations
c. Consultancy activities
d. Tablet manufacturing
569. Which of the following is not an
advantage of automation?
a. Reduction in lead time
b. Reduction in wastage
c. Higher initial investment
d. Higher productivity
570. Which of the following is not a
disadvantage of automation?
a. High initial investment
b. Higher level of maintenance
c. Lower flexibility to different job
requirements
d. Higher product quality
571. Which of the following is a disadvantage
of using Computer Aided Manufacturing?
a. Reliability in labor inputs
b. Reduction in labor costs
c. Improvement in productivity
d. None of the above
572. It involves two or more machining centers
which are automated to process different
kinds of jobs; identify this technology?
a. CAD
b. CAM
c. FMS
d. CNC
573. Which of the following technologies
integrates CAD/CAM, group technology
systems, MRP II, financial reporting
systems, etc and brings in automation in
each of the processes involved?
a. FMS
b. CNC
c. CIM
d. None of the above
574. CIM system integrates various
computerized systems. It is also termed as
_____________ due to the integration
involved.
Part A
65
a. Automated manufacturing system
b. Multi-functional system
c. Flexible system
d. Non-functional system
575. What is the primary difference between
conventional computer systems and
computer systems with artificial
intelligence?
a. Speed
b. Automation
c. Better performance
d. Ability to reason
576. Despite many advantages, CIM has not
been implemented on a large scale.
Identify the reasons for this.
i. Huge costs of installation and
implementation
ii. Standardized interfaces between CIM
components were absent
iii. Lack of integration
iv. Increased operating costs
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. iv and i
577. Expert systems are programs designed to
provide users with the expertise of
professionals in a particular field. Inputs to
this knowledge base and the rules to obtain
a solution are obtained from which of the
following sources?
a. Users
b. Professionals
c. Programmers
d. All of the above
578. Robots are used in different industries like
electronics, automobile, etc. Which area of
manufacture does not use robots
extensively?
a. Material handling
b. Processing operations
c. Assembly and inspection
d. Facility location
579. Which of the following operations are not
done by robots in materials handling?
a. Transfer of material
b. Loading of material
c. Welding activities
d. Unloading of material
580. In manufacturing, robots are used in three
functions material handling, processing
operations, and assembly and inspection.
Which of these operations involve the
handling of a tool by a robot to perform a
particular action?
a. Material handling
b. Processing operations
c. Assembly and inspection
d. Both a & c
581. Employing robots is not justified in which
of the following areas?
a. Tasks that are repetitive and involve the
same basic work motion in every cycle
b. Tasks to be performed under hazardous
conditions and unsafe environment for
humans
c. Tasks that require a part or tool that is
heavy and difficult to handle
d. Tasks where contingency decision making
is needed
582. What are the advantages of EDI in
operations management?
i. Reduces paper work
ii. Helps track orders placed with vendors
iii. Increases inventories
iv Improves coordination across departments
a. Only i
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i, ii, and iv
d. ii, iii, and iv
583. Globalization promotes free and fair trade
among member countries, but sometimes
results in unfair trade. Which among the
following does not support this statement?
a. All member countries of WTO have to
treat every other member nation as their
most favored nation
b. Tariffs and duties with respect to import of
goods have to be liberalized
c. Member countries do not lift existing
quantitative restrictions
d. All member countries have to gradually
open up their markets to foreign
companies
Operations Management
66
584. Some countries have certain competitive
advantages over others. Which of the
following competitive advantage does
India have over America and Western
Europe?
a. Technology
b. Labor
c. Trade surplus
d. Nuclear fuel
585. Many MNCs have established their
production and development centers in
India to reduce operation costs. Which
source of competitive advantage has led to
India becoming a production and
development hub for foreign companies?
a. Comparative advantage
b. Economies of scale
c. Proprietary product knowledge
d. All of the above
586. Chinese companies have become dominant
players in the global manufacturing sector.
They make products in bulk quantities that
allow them lower the costs per unit
produced. What type of competitive
advantage is discussed in this example?
a. Comparative advantage
b. Economies of scale
c. Proprietary product knowledge
d. All of the above
587. Organizations operating globally can
obtain economies of scale not only in
manufacturing but also in purchasing.
Which of the following examples supports
this statement?
a. Toyota's leadership in the low-end truck
market worldwide due to large volume
production
b. GMs strategy to outsource manufacture of
$7.5 billion worth of auto components
c. Satyam Computers strategy to produce
customized software for its clients to suit
their requirements
d. Nokia launching new cell phone models to
maintain market leadership
588. Punj Lloyd is an engineering construction
company involved in construction of
pipelines, oil storage tanks, power plants,
etc, throughout the globe. If it uses the
same salesforce to acquire orders in
different countries, what kind of approach
is the company adopting?
a. Economies of scale in production
b. Economies of scale in purchasing
c. Economies of scale in marketing
d. All of these
589. Which of the following conditions can be a
constraint to achieve economies of scale
globally?
i. Markets across the globe demand the same
kind of product
ii. Every market needs customized products
to meet its requirements
iii. The same product with slight variations is
demanded by different markets
a. Only i
b. i and ii
c. ii and iii
d. i, ii, and iii
590. There are certain impediments to
globalization that can block an
organization in its globalization endeavor.
For instance, MNCs operating in different
markets find it difficult to achieve
economies of scale due to varied
preferences and requirements in each
market. Identify the type of impediment
faced by the MNCs.
a. Economic impediment
b. Managerial impediment
c. Institutional impediment
d. None of the above
591. What is the primary reason for countries to
put in place institutional impediments for
foreign players?
a. To encourage foreign companies to
operate in the country
b. To encourage local companies to
cooperate with foreign companies
c. To encourage exports from local
companies
d. To protect local companies from the threat
of foreign companies
592. Managers cannot simply apply marketing
knowledge gained in one market to another
market due to varying preferences and
cultures. This statement reflects which of
the following impediments for the
marketer?
Part A
67
a. Economic impediment
b. Managerial impediment
c. Institutional impediment
d. Both a & c
593. What are the reasons for global
organizations to look out for more
competent managers across the world?
i. International markets are complex and
require acumen to understand
ii. Managers must be able to look out for
global market opportunities and grab them
as they come
iii. Managers should be capable of providing
insights into developing future products
iv. Companies can get good managers at low
salaries
a. Only iv
b. i and ii
c. ii and iv
d. i, ii, and iii
594. Which of the following is an ideal
interaction approach between headquarters
and a subsidiary of a global company to
develop new products for a certain market
in a certain country?
a. Leave the entire new product development
process to the local subsidiary or division
b. Collective efforts from both headquarters
and the subsidiary
c. Centralize the new product development
process at headquarters
d. Outsource R & D to a third party
595. In the case of global organizations, the
concept of resource allocation is broad in
scope. Which of the following is
considered a scarce resource by global
organizations?
a. Capital
b. Raw material
c. Technology
d. Technologists and managers
596. It is difficult to design organization
structure for a global organization. Most
global organizations prefer which of the
following approaches to organization
structure?
a. Centralized in nature
b. Decentralized in nature
c. Bureaucratic in nature
d. Behavioral in nature
597. Why do global organizations recruit local
people for subsidiaries in each country?
a. Local people can provide information on
the local climate
b. Local people can provide better insights
into the local business environment
c. Local people can use technology more
efficiently than outsiders
d. Local people can provide global
information on products and markets
598. A global company can enter a new market
either through joint ventures or by
establishing a wholly-owned subsidiary.
Identify the possible drawbacks of a
wholly-owned subsidiary?
i. Full control on operations
ii. Low risks
iii. Takes a lot of time to understand the
market
iv. No means to spread the risk
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. iv and i
599. Tornado (an American cellular phone
manufacturer) wants to establish a
manufacturing plant in India to cater
specifically to the Indian market. Which of
the following factors should Tornado
consider while deciding on the location of
a plant in India?
i. Level of demand for the product
ii. Infrastructure availability
iii. Availability of cost-effective labor
iv. Export policy
a. i, ii, iii
b. i, ii
c. iii, iv
d. Only iv
600. In which of the following methods of entry
into foreign markets does a company have
minimal control over the marketing
strategy?
a. Joint venture
b. Alliances
c. Subsidiary
d. Licensing
This section contains answers and explanations for the multiple-choice questions
in part A given earlier in the book
Part A: Answers and Explanations
1. (b) Importance and recognition given to employees
Elton Mayo in 1927 carried out studies at Western Electrics Hawthorne plant. The initial studies
tried to examine the relationship between light intensity on the shop floor and employee
productivity. Finally, Mayo and his team concluded that it was not light or other physical
conditions, but the attention and importance the workers received during the study that was
responsible for their increased productivity.
2. (b) Ford Motors
Henry Ford applied the concepts of scientific management of Taylor in the assembly line
production system of Ford Motors in 1911.
3. (b) Reducing clerical costs
The computerization of operations began when the first computer was installed in General Electric
Appliance Park in 1954. The sole purpose of computerization those days was to reduce manual
labor and the costs involved in tasks like preparing salary statements and accounts statements.
4. (b) Motivating
Motivating is one of the activities of operations managers. It involves encouraging workers
through praise, recognition, and other intangibles.
5. (a) Strategic decisions
Strategic decisions are long-term and broad in nature and usually span five years or more. Long-
term strategic decisions are concerned with production and process design, facility location and
layout, capacity, expansion of existing facilities, etc. These decisions impact the long term
profitability of an organization.
6. (a) Analyzing the firms financial position
Analyzing the firms financial position falls under the basic function of financial management and
not operations management.
7. (c) Scientific management
Division of labor or work specialization is a development of scientific management. According to
Taylor, each worker should be assigned a task based on his or her skill, strength and ability to
learn.
8. (c) Planning
The planning function oversees decisions regarding what products to make and when. It also
includes activities like planning the product-service mix, location and capacity planning,
production methods to use for each item, procurement of equipment, number of shifts and work
hours etc.
9. (b) One or two years
Tactical decisions are medium-term in nature and have a time-frame of one or two years. These
decisions are concerned with identifying manpower requirements, determining the appropriate
inventory level for various materials, determining reordering level and order quantity, identifying
vendors and so on.
10. (d) All of the above
Operations management, as a whole, deals with design of products and processes, acquisition of
resources, transformation of resource inputs into outputs and distribution of goods and services.
Part A: Answers and Explanations
Operations Management
72
11. (b) Organizing
Operations under the organizing function include: decisions to centralize or decentralize
operations; decisions on kind of functions, products, or organization structure; establishing work-
center assignments; assigning responsibility for every activity; arranging supplier and
subcontractor networks and establishing maintenance policies.
12. (a) i, ii, iii
Inclusion of purchasing functions, dispatch, and other allied activities in this field and the
influence of service-related concepts and procedures broadened the scope of this field of study. As
the term Production Management did not cover the entire field, it was replaced with Operations
Management.
13. (a) In the early 1940s during World War II
During World War II (1939-45), the United States and many European nations formed operations
research teams in most of their military branches to find efficient ways to utilize resources like
men, weapons and machinery. The massive deployment of manpower, supplies, planes, ships and
other resources created the need to find the most efficient way to utilize them. At the end of World
War II, the successful operations research techniques were incorporated into decision-making in
many business organizations.
14. (c) Elton Mayo
In 1927 Elton Mayo and his team carried out studies at Western Electrics Hawthorne plant. The
initial studies tried to examine the relationship between light intensity on the shop floor and
employee productivity. Finally, Mayo and his team concluded that it was not light or other
physical conditions, but attention and importance the workers received during the study that was
responsible for their increased productivity.
15. (c) Expert systems
In the 1990s, many new concepts and technologies like artificial intelligence and expert systems
influenced manufacturing systems. Programmable machines (like robots) were introduced in the
production process to perform tasks that were repetitive or hazardous for a human being to
perform.
16. (c) Higher maintenance costs
Higher maintenance costs are a major disadvantage of computerization. Initial establishment and
implementation costs are so huge that they prompt organizations to defer computerization.
Besides, the cost of maintaining these systems is also high.
17. (b) ii & iii
The key objectives of an operations manager are to minimize inventory and maximize resource
utilization. Maximizing customer satisfaction is a primary concern for the top management and the
marketing department. However, customer satisfaction is only a secondary objective for the
operations manager.
18. (a) Quality and on-time delivery
In customized product design, the emphasis is on quality and on ensuring delivery on-time, rather
than on cost. In standardized product design systems, importance is given to cost-control and
quality rather than on the flexibility of the system.
19. (c) Labor costs
Labor costs fall under direct costs while administrative costs, maintenance costs, and rentals fall
under indirect costs.
Part A
73
20. (b) Top-level managers
In an organization, corporate objectives are developed by the top-level managers.
21. (d) All of the above
All the options are considered while formulating corporate objectives.
22. (b) Standardized product design
Standardized production is used when a company manufactures a limited variety of products in
large batches to reduce costs.
23. (c) i & iii
Feasibility studies evaluate whether the idea generated is feasible both technically and
economically. Such studies test whether production is technically feasible and the product
profitable to produce and market.
24. (b) Strategic business units
Strategic business units (SBU) are autonomous operating divisions which have independent
control over their own functions. Every SBU has its own business strategy, objectives and
competitors and these will often be different from those of the parent company.
25. (c) Lower costs
As a result of manufacturing steel by processing steel scrap, costs are substantially lower to the
company than to the large steel plants producing primary steel from iron ore. This lower-cost
process gives Nucor a price advantage over competitors.
26. (a) Designing the production system
Designing the production system is one of the key responsibilities of any operations manager. It
involves selecting the product design, the production system and the inventory policy for finished
goods for each product line.
27. (a) i and ii
Industrial products like boilers and turbines are made based on specific requirements of customers,
while televisions and ceiling fans are produced in large numbers (also termed as standardized
production) where customization of each piece is not possible.
28. (b) Growth stage
During growth stage the sales volume grows exponentially and profits are registered for the firm.
In introduction stage, sales growth is weak, in maturity stage it is stagnant, and in the decline stage
the sales decline.
29. (b) The role of operations department decreases as the product moves up the lifecycle
As the product moves up the lifecycle, the organizations focus shifts towards increasing the
market share and improving the quality of the product. Hence, the role of operations department
decreases.
30. (b) A prototype helps test the product performance under standard conditions
A prototype may not have all the features of the final product however it has all the products basic
characteristics. The prototype is tested under standard conditions and defects are noted. This would
enable the organization to improve the product in terms of quality and performance. Once the final
structure of the prototype is in place, the prototype design is evaluated for profitability.
31. (d) Facility planning
Facility planning deals with location of the facility and its layout. Decisions regarding facility
location are based on the accessibility to raw material and nearness to markets. Allocation of
resource deals with the allotment of existing resources like men, machines, material, etc, to
different strategic alternatives. Technology selection and process development deals with selection
of the most suitable technology for producing products and product design and development is
used to develop new products.
Operations Management
74
32. (a) Organization strategy
The operations strategy should be in accordance with the organization strategy, and the
organization strategy should in turn be in line with the corporate vision and mission. If the
organization strategy is not consistent with the corporate vision and mission, the organization
cannot survive in the competitive marketplace. Further, operations strategies should be consistent
with strategies in other functional areas such as marketing, finance and human resources.
33. (a) Strategic planning is concerned with long-term planning while operational planning
involves short-term day-to-day planning
Strategic planning is different from operational planning in the scope of its application. Strategic
planning is concerned with long-term planning and involves selection of target markets and
distribution channels, whereas operational planning is concerned with short term, day-to-day
planning.
34. (c) It should focus on having short-term operational superiority over competitors
Operational superiority is very important for maintaining the competitive position of
manufacturing and service organizations. The operations strategy should be flexible so that it can
support a product or service through its entire life cycle and accommodate future changes in
market demand or business objectives.
35. (b) Product variety
When an organization focuses on product variety as a competitive advantage it offers a large
number of different products to various customer segments. This is true in the case of HDFC that
offers different financial products to different segments.
36. (a) 5 years
Payback period = Net investment / Expected annual income
= 10,00,000/2,00,000 = 5 years
37. (b) 4.8 years
Payback period = Net investment / Expected annual income
= 12,00,000/2,50,000 = 4.8 years
38. (c) 5.3 years
Payback period = Net investment / Expected annual income
= 8,00,000/1,50,000 = 5.3 years
39. (b) Project B
Of all the investments, Project B is the best option. Though Rs.12, 00,000 are invested in this
project, the payback period is the shortest due to greater expected annual income.
40. (b) Optimize the use of resources for best strategic use
The main objectives behind allocating resources to different alternatives (which are also called
strategic alternatives) include minimizing wastage in the facilities and employing resources to the
best possible use.
41. (d) i, ii, iii and iv
Demand for a product is influenced by conditions like the price of the product, price of substitutes,
price and availability of complementary products, income of consumers, their tastes and
preferences, and their reactions to changes in price.
Part A
75
42. (b) Responsiveness
Forecasted demand may not be equal to actual (true) demand. The organization has to adjust its
operations according to the actual demand on a real-time basis. This characteristic of the
organization is termed as responsiveness. The quicker the organization is in responding to the
changes in the forecasted demand, the more successful it would be in meeting the actual demand.
43. (b) Forecast error
A forecasting error is the difference between the forecasted demand for a particular period and the
actual demand in that period.
44. (b) Decrease the value of
Overreacting to the most recent demand implies that the demand forecasted is very optimistic.
Therefore to reduce the forecasted demand, the value of should be reduced.
45. (a) Low
A high alpha is used to stabilize unstable demand (like that for new products) and a low alpha is
used to even a stable demand.
46. (d) All of the above
Demand forecasting is used to develop marketing plans, facilities plans and financial plans.
47. (b) Delphi Method
Qualitative methods are judgmental and subjective in nature and are based on the estimates and
opinions of individuals like experts in case of Delphi method and consumers in case of market
research method.
48. (d) Exponential smoothing is used to determine independent demand
Exponential smoothing is used to determine dependent demand
49. (d) Forecasts are created using only quantitative data
Forecasts use both qualitative as well as quantitative data to forecast demand.
50. (a) Time-series methods
Time-series methods uses past (historical) data to predict future demand.
51. (d) Plant capacity
Plant capacity is not a factor that is considered to forecast demand. Operations managers may
increase or decrease the running capacity of the plant depending on the demand. Hence, it cannot
be considered a factor that influences demand. Rather plant capacity is influenced by the demand.
52. (d) Mean absolute percentage error
Mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) provides information on the extent of forecast error in
relative terms while the other measures provide information in absolute terms.
53. (c) Spare parts inventory
Spare parts inventory does not generally require long-term forecasts as they are more an
operational issue than strategic issue.
54. (d) Extent of accuracy of demand forecasts
Demand is influenced by conditions like the price of a product, and the price of its substitute and
complementary products; the incomes of customers, their expectations regarding price changes,
and their tastes and preferences; the number of customers and their travel costs to the point of
purchase (PoP). Accurate forecasts of demand help organizations to suitably increase or reduce
production. Therefore accurate forecasts, as such, do not influence the demand for the product.
They instead help the management in decision-making relating to product demand.
Operations Management
76
55. (d) Increased locking up of working capital as inventory
Working capital is locked up as inventory, only when there is excess production. Excess
production happens when demand is overestimated. However, when demand is underestimated,
production will not be sufficient to meet the demand. Hence, there are greater chances of locking-
up of working capital in the form of inventory as a consequence of overestimation of demand
rather than underestimation.
56. (a) Short-term demand
Short-term demand estimates for individual products are generally very detailed, and are used to
plan and schedule production operations. Long-term and medium-term demand forecasts are used
for making location, layout and capacity decisions.
57. (b) Aggregate product demand forecast
On the basis of the aggregate product demand forecast (that is obtained in terms of sales volume)
individual forecasts are made for labor and/or material requirements. Hence, raw material demand
forecast and labor demand forecast (types of short term demand forecasts), are derived from
aggregate product demand forecast.
58. (d) Planning and controlling
Forecasting demand is most important to the planning and control functions of management.
Forecasting is a step in the planning process where plans are developed based on forecasts. Under
the control function, actual results are compared with that of planned standards (based on
forecasts) and deviations are identified and corrected.
59. (b) The geographical distance between the experts
In Delphi method, forecast is made by the coordinator after considering the opinions of a panel of
experts who are geographically apart. Also, as the membership of each expert is concealed from
others, no issue of leadership arises during the process. Thus geographical distance between the
experts cannot be a hindrance to the success, as the experts need not communicate with each other.
The success of this technique depends on the talent of the coordinator and the absence of bias on
the part of the experts. Two main problems inherent in this method are that opinions of members
might be influenced by a socially dominant individual. Members may fear loss of credibility if
they back away from a publicly stated opinion.
60. 87
In the six-month simple moving average technique, the forecast for the seventh month will be the
average of the preceding six months. Thus, the forecast for the month of July is the average
demand of generator sets during Jan, Feb, March, April, May, and June. Similarly, the forecast for
January 2007 would be the average of demand during July, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, and Dec months.
Forecast for January 2007 = (87 + 88 + 86 +89 + 86 + 87) / 6 = 523/6 = 87.1666 (approx 87)
January 78
February 80
March 85
April 82
May 84
June 85
July 87 82.33
August 88 83.83
September 86
October 89
November 86
December 87 86.83
87.17
Part A
77
61. (a) 1
Each element in the weighted moving average method is weighted by a factor and the sum of the
weights should be equal to one.
62. (c) Trial & error
Certain weights are assigned to each element and managers use past experience (not future
forecast) as well as the trial and error method to calculate these weights. The simple moving
average method and exponential smoothing are other types of time series forecasting methods like
the weighted forecasting method.
63. (c) Exponential smoothing
The exponential smoothing method is based on the assumption that the most recent data is a better
indicator of future trends than past data. The method is useful when demand for products exhibit
seasonal tendencies. The simple moving average method is effective only when a product does not
experience fluctuation in demand over a period of time and past demand for the product was not
seasonal. Delphi method is a qualitative forecasting method
64. (c) Larger data storage space
The advantages of the exponential smoothing method are: availability of standard software
packages; relatively little data storage and computational requirements; accuracy of forecasts and
easy understanding of results.
65. (a) Latest time period
In the exponential smoothing method, the demand for the most recent time period is given
maximum weightage. The weights assigned to the preceding periods decrease exponentially.
66. (b) WMA
t+1
=
=
n
1 t
t t
A C
The formula for calculating the weighted moving average is WMA
t+1
=
=
n
1 t
t t
A C
Where,
WMA
t+1
= Weighted moving average at the end of the time period t, A
t
= Actual demand in time
period t, C
t
= Percentage weight given to time period t, 0 C
t
1 and C
1
+ C
2
+ C
3
+... + C
t
= 1
67. (c) i and ii
Smoothing constant shows the effects of past demand on future demand forecasts and helps
smoothen out the effects of any noise. But, is not used to predict future trends in demand.
68. (d) Y intercept or constant value
In linear regression, the relationship between the dependent variable and a single independent
variable is defined by a straight line.
Y = a + bX where, Y = Value of the dependent variable, X = Value of the independent variable, a
= Y intercept (Constant value), and b = Slope of the line, a is the Y-intercept and its value
defines the point at which the regression line crosses the Y-axis.
69. (a) If the slope is positive, then the trend line increases positively
If the slope is positive, then the trend line increases positively. If the slope is negative, then the
trend line decreases negatively.
Operations Management
78
70. (b) 6.67
Slope represents the variation in Y for a unit change in X. Here, Y represents sales and X
represents advertising expenditure. To calculate the slope, change in sales, represented in units,
should be converted into percentage. Hence, slope can be calculated by:
Percentage of change in sales/percentage of change in advertising
{[(20000-15000)/15000] x 100} / 5 = 6.666 = 6.67 (approx)
71. (a) Exponential smoothing
For short-range decisions like purchasing, job scheduling, project assignment and machine
scheduling, time series techniques like moving averages (SMA or WMA) and exponential
smoothing are the most preferred forecasting methods. Regression analysis is used in medium
range forecasting as well as long term forecasting. Linear regression analysis is useful in long term
forecasting of major occurrences and aggregate planning.
72. (b) Delphi method
Delphi method is used when no data is available or if it is too expensive to collect data. The other
three methods primarily require data to forecast demand.
73. (d) None of the above
No forecasting method, either qualitative, time series or causal, gives 100% accurate forecasts.
They can only be highly accurate and 100% accuracy is not possible.
74. (a) Cost is directly proportional to extent of accuracy
Accuracy of forecasts depends on data availability. Forecasts can be more accurate when more
data is available. Also, it is costly to collect huge volumes of data. Hence, to avoid these costs,
some organizations use readily available data at low costs and end up with inaccurate forecasts.
Thus, accurate forecasts come at a dearer price.
75. (b) 6
Demand Forecast
(F)
Actual Demand
(A)
(A - F) |A - F|
500 510 10 10
510 510 0 0
520 515 -5 5
540 550 10 10
550 545 -5 5
Sum 10 30
Solution:
Mean absolute deviation =
=
=
n
t 1
t
F
t
A
n
1
MAD
= 30/5
= 6
Part A
79
76. (c) 50
Demand
Forecast (F)
Actual
Demand (A)
(A - F) (A - F)
2
500 510 10 100
510 510 0 0
520 515 -5 25
540 550 10 100
550 545 -5 25
Sum 10 250
Solution:
Mean Square Error =
=
=
n
1 t
2
t t
) F (A
n
1
MSE
= 250/5
= 50
77. (a) 2
Demand Forecast
(F)
Actual Demand
(A)
(A - F)
500 510 10
510 510 0
520 515 -5
540 550 10
550 545 -5
Sum 10
Solution:
=
=
n
1 t
t t
) F (A
n
1
MFE
= 10/5
= 2
78. (c) 1.14
Demand
Forecast (F)
Actual Demand
(A)
(A - F) |A - F| (|A-D|/2) x 100
500 510 10 10 1.96
510 510 0 0 0
Operations Management
80
520 515 -5 5 0.97
540 550 10 10 1.82
550 545 -5 5 0.92
Sum 10 30 5.67
Solution:
=
n
1 t t
t t
A
F A
n
100
MAPE
MAPE = 5.67/5 = 1.134
79. (a) 1.67
Demand Forecast Actual Demand Deviation
(A-F)
500 510 10
510 510 0
520 515 -5
540 550 10
550 545 -5
Sum 10
=
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
n
i 1
MAD
demand Forecast Demand Actual
TS
TS = 10/6
= 1.67
80. (d) Base demand
Base demand is the average of sales over a given time period. This figure can be taken as the right
forecast if the demand for a product is not impacted by seasonal, trend, cyclic, or promotional
factors.
81. (c) Cyclical component
Cyclic component refers to changes in demand patterns, which exist for more than a year. These
changes could either show an upward or downward movement. A good example is the demand for
luxury products that is linked with the business cycle. Sales usually increase during the boom
phase and slow-down during recession.
82. (b) Promotional component
The sales of LG televisions doubled when LG increased its advertising budget. Here, LG gave
more weightage to the promotional component to arrive at an aggressive estimate.
83. (c) The demand for camera mobile phones in India has increased steeply since 2001
The demand for camera mobile phones has shown a positive trend over a period of time. The long-
term pattern is clearly visible in this example. The prices of gold increased and decreased, leading
to rise and fall in demand. Hence, it is cyclical. The Airtel example highlights the promotional
component, and the demand for wrist watches displays the irregular component.
Part A
81
84. (d) Understand objectives identify influencing factors identify customer segments
select forecasting technique
The forecasting process starts with understanding its objectives. Then, all the major influencing
factors are identified. Next, all possible customer segments in the market are marked out and their
impact on the forecast has to be understood. Finally, a suitable forecasting technique has to be
selected.
85. (b) Time series methods
Time series analysis can be categorized into two broad categories, based on the complexity
involved: static and adaptive. Static methods assume that estimates of trend and seasonal
components do not vary from year to year. Adaptive forecasting is an advanced form of time series
analysis, where trend and seasonal components are adjusted after each demand observation.
86. (b) Static forecasting method
Static forecasting methods assume that estimates of trend and seasonal components do not vary
from year to year. In this method, estimates of trend and seasonal components are determined
based on historical data, which is projected to obtain future demand data.
87. (d) Provides optimal solutions that are always practical
One of the main drawbacks of these models is that the solution obtained may not always be the
optimal one for the real problem. This is because these models do not take into account non-
quantifiable criteria. Sometimes, models may provide a solution that cannot be put into practice.
88. (b) Nature of demand
There are three elements of constrained optimization models: decision variables, objective
functions and constraints.
89. (c) Motivation
Motivational levels are qualitative in nature. Linear programming deals with different variables
that need to be quantified.
90. (c) Feasible solution
A feasible solution satisfies all the restrictions of a linear programming problem.
91. (a) Constraint
Constraints are practical limitations restricting the choice of decision variables. In this case the
practical limitation is the availability of man hours that is restricted to 600 hours.
92. (c) Linear programming
Linear programming is used to allocate resources to strategic alternatives to ensure that they are
utilized optimally. Exponential smoothing and regression analysis are methods to forecast demand
for a product. Decision tree analysis is another operations technique helpful in decision-making
like linear programming.
93. (c) Destination requirements
Destination requirement is a constraint considered while arriving at transportation decisions and
not production plan decisions.
94. (b) Maximize Z = 200x + 150y
As profits have to be maximized, profits from each telephone model have to be considered. Hence,
the objective function would be maximize Z = 200x + 150y, where 200 and 150 represent profit
per unit of each model in rupees.
Operations Management
82
95. (a) 2x + y 650
Total machine hours are 650. The superior quality telephone takes two hours (2x) while the other
takes one hour (y) to be produced. Hence, the total number of telephones produced using available
machine hours has to be less than or equal to 650 hours. Thus, 2x + y 650
96. (d) x + y 600
The total demand is 600 units and production should not exceed demand. Hence, x + y 600.
97. (b) Rs. 70000
Substitute the number of telephones manufactured in the objective function.
Z = 200x + 150y
= 200(200) + 150(200)
= 40000 + 30000
= 70000
98. (d) x = 200, y = 200
Options (a) and (b) are not feasible as they violate the constraint on total machine hours (650
hours). Substituting the number of telephones manufactured in the objective function Z = 200x +
150y for options (c) and (d), option (d) gives a maximum profit of Rs.70000.
99. (b) Optimality
The assumptions that are made while constructing a linear programming problem are
proportionality, additivity, divisibility, and certainty. Using these, problems are solved for
achieving optimality, i.e., achieving an optimum solution. Hence, optimality is not an assumption
but a result.
100. (a) Profits
Profits can be maximized while inventory, advertising expenditure and production costs have to be
minimized. Hence, profits can be considered for a maximizing function.
101. (c) 3x + 2y = 120
The coordinates of the line are (40, 0) and (0, 60). When these coordinates are substituted in each
of the above options, we get LHS = RHS only in option (c). Hence, the constraint is 3x + 2y = 120.
102. (d) (0,60), (40,0), (80,0), (80,60)
ABCS is the feasible region.
Coordinates of A (0,60), Coordinates of B (40,0), Coordinates of C (80,0), and Coordinates
of S (80,60).
103. (a) x = 80
The line passes through the coordinates (80,0) At that point, the value of x=80 and y=0. Thus, x =
80 would be the equation of the line.
104. (c) 800
The coordinates are (0,60), (40,0), (80,0), (80,60)
At A(0,60), Z = 20(0) + 35(60) = 2100
At B(40,0), Z = 20(40) + 35(0) = 800
At C(80,0), Z = 20(80) + 35(0) = 1600
At S(80,60), Z = 20(80) + 35(60) = 3700
Part A
83
105. (d) The resources considered in the linear programming problem should have unlimited
supply
The resources in any linear programming problem are scarce and the objective is to use them
optimally.
106. (a) ii, i, and iii
The first and foremost step in formulating a linear programming problem is to identify the decision
variables. Next is to identify the objective function, and finally comes identifying constraints
present in the problem.
107. (c) In the feasible region
A feasible region is obtained when constraints are plotted on the graph. The optimum solution
always lies in the feasible region.
108. (a) Adding a slack variable
A slack variable is always added to the left-hand side of the lesser than or equal to inequality
(constraint) to convert it to an equation.
109. (b) Iteration
An iteration of the simplex method forms the sequence of steps in moving from one basic feasible
solution to another.
110. (c) To minimize the sum of all transportation costs
The objective of any transportation problem is to minimize the transportation costs.
111. (d) Stepping stone method
While methods mentioned in options (a), (b), and (c) can be used to develop the initial feasible
solution, the stepping stone method is used to test the solution for optimality.
112. (c) Vogels approximation method
Vogels Approximation Method is most effective and preferred over other methods as it usually
results in an optimal or a near-optimal solution.
113. (b) Additivity
The objective function and constraints include several decision variables. Here, it is assumed that
the total value of the objective function and each constraint is equal to the sum of individual
contributions from each decision variable. It means that the model does not consider any
synergistic or anti-synergistic effects among decision variables while calculating the total value for
the objective function.
114. (d) Customized service
Industrial design services vary from company to company and depend upon their products and
target markets. Hence they are categorized as customized services.
115. (d) All of the above
The term structure has a broad meaning and includes issues like the number of plants, size of
plants and their location, plant capacity, choice of equipment and process technology, production
control, workforce management, etc.
116. (c) Increases to a certain level
As the price of a commodity decreases, demand increases as consumers buy more of the
commodity. However, this is observed only until a certain point. Beyond this there will not be a
proportionate increase in demand when prices are decreased.
Operations Management
84
117. (c) Backward integration
Backward integration refers to gaining ownership over the source of raw material supplies and
other materials required for production. Forward integration refers to gaining ownership of front-
end activities (distribution networks through which products are distributed to the customers).
118. (a) Level of training for distributor employees
Option (a) is not a factor while making decisions on backward integration. It is among forward
integration issues. Backward integration decisions are concerned with make or buy decisions,
availability of funds, return on investments, and long-term relationships with the suppliers of raw
materials.
119. (d) i, ii, and iii
The basic objectives of process planning and design in an organization are to produce products
with desired quality, at the right time, and in required quantities. To produce products below
competitor prices is not a basic objective; rather it is dependant on the strategy of the company.
120. (a) Product flexibility
Product flexibility is the ability of the production system to shift quickly from producing one
product to another. Some business strategies call for the production of many custom-designed
products/services, in small lots. Product/service flexibility is required in such cases.
121. (a) Square
In an assembly chart, operations are represented by circles and inspections by squares.
122. (b) Less manufacturing cycle time
The process-focused production system may lead to loss of time, especially when a major portion
of production time includes the time in which jobs are waiting to be processed in different
departments. Also, process-focused production systems require greater employee skill, more
employee training, supervision, and complex production control.
123. (b) Lower initial investments
Product focused production systems entail high investments initially in terms of capital equipment
and machinery.
124. (c) Discrete unit processing
Discrete unit manufacturing refers to the production of distinct products like radio or television
sets. These products can be made in batches, and the system can be shifted to produce other
products in similar batches. However, assembly lines and continuous processing do not help in
changing jobs. Job shop process is used to produce highly customized products where one job can
be carried out at one point of time on one machine. The flexibility is minimal here. Hence, ABC
must use discrete unit processing.
125. (c) Process planning
Process planning forms the basis for designing factory buildings and facility layouts, and selecting
production equipment. It also has a bearing on quality control, job design and capacity in different
facilities of the organization.
126. (c) Employee skill level requirements
Operations managers generally make process-design decisions after taking into consideration
several factors like nature of demand, degree of vertical integration, flexibility, degree of
automation, quality level, and degree of customer contact. However, employee skill level
requirements are dependent on the type of process plan decided and are considered only after
developing the process plans.
Part A
85
127. (a) As demand is seasonal Pepsi cola should not be produced in winter season
Seasonality of demand is not directly linked to the production because companies focus on
meeting annual demand. A company may bring down production capacity in the lean season and
increase it to peak capacity during high demand. Also, production can be beefed up just before the
season begins and inventory can be stocked to meet the excess demand.
128. (d) Ability of the organization to market its products
Ability of the organization to market its products is a factor that affects the forward integration
process of the organization, while the remaining options refer to the factors affecting the backward
integration in an organization.
129. (b) It helps decentralize the overheads
Vertical integration relieves an organization from excessive dependence on the purchasing
function and provides flexibility in manufacturing. This can result in an increase in profits due to
centralized overheads, pooling of R&D and design efforts, and economies of scale.
130. (b) Backward integration
The raw material for a readymade garment retailer is fabrics. Hence, when Eastside acquired a
textile mill, it gained ownership of a supplier leading to greater control over fabric production and
supply. This is a backward integration strategy.
131. (a) Product-focused systems
In this type of process design, products or services tend to flow along linear paths without
backtracking or sidetracking. Items follow a similar production sequence, which can be anything
from a pipeline (for oil) to an assembly line (for televisions or radios).
132. (b) Process manufacturing
Process manufacturing involves the movement of materials between different operations such as
screening, crushing, storing, mixing, milling, blending, cooking, fermenting, evaporating and
distilling. It is widely applied in the cement, plastic, paper, chemical, steel and brewing industries.
133. (a) Product-focused systems
Product-focused systems require higher initial investments because of the use of specialized and
expensive fixed position processing equipment in the production process.
134. (c) i, ii, and iii
In process-focused production systems, all operations are grouped according to the type of process.
The system is also referred to as an intermittent production system because production is
performed on products intermittently (that is on a start and stop basis). In this system, the products
move from department to department in batches (jobs) that are usually determined by customers
orders. The diversity of customer orders is a primary criterion for adopting a process-focused
production system.
135. (d) It requires high employee skills
Organizations draw the following benefits by implementing a coding system. Coding gives a clear
picture of the steps that are involved in producing a part. Hence, it is easy to route the parts during
production. Coding results in standardization of part designs. A database can be maintained with
the design details of old parts. Whenever a new product is to be designed, the codes of existing
products can be accessed to identify similar parts present. This simplifies the process of
manufacturing new products. Parts with similar characteristics can be grouped into families as
similar products are generally produced in similar ways.
136. (d) Increase in the in-process inventory
In cellular manufacturing, parts spend less time in waiting before they are processed. Hence, the
in-process inventory levels get reduced.
Operations Management
86
137. (a) Assembly charts
In assembly charts it is standard practice to indicate operations by circles and inspections by
squares. Gantt charts and flow charts are entirely different in the sense that they are used for
scheduling of operations in a manufacturing plant. Assembly and process charts are used for
process planning.
138. (a) Job shop production systems
Job shop production systems involve production of customized products. As a result, product
designs vary between different customer orders. Since the customization is high, number of
products produced in a given time period is very low.
139. (c) The total cost of production increases as the output volume increases
The product-focused systems require initial investments in the form of expensive machinery and
this result in high initial fixed costs. But, as the product-focused systems produce a single or few
varieties of products, the variable costs remain low. Product-focused systems are used to produce
bulk volumes and as the volume of output increases, the total cost of production decreases.
140. (b) Higher fixed costs and lower variable costs
Product focused systems need high initial costs (fixed costs); however operating variable costs
remain low due to limited scope for product variety.
141. (c) i, ii, iii
Except alternative iv, all others are reasons for companies to set up facilities in select zones. Low
cost of manpower is a country-specific factor and does not significantly differ within and outside
exclusive zones.
142. (b) Proximity to input sources
A manufacturing facility that uses bulk raw materials has to be in proximity to raw material source.
In this case, bauxite is the basic raw material for aluminum production and it is available from
mines.
143. (c) Healthcare industry
Hospitals are service organizations where location plays a major factor. People prefer to go to a
hospital close to their homes. Since services cannot be stored, they have to be developed and
delivered in close contact with customers. Hence, proximity to customers is necessary.
144. (b) The physical distribution of various departments for ease in production
A facility layout represents the physical spread of all the equipment, machinery, parts, etc. in a
plant/facility. They are distributed so as to ensure smooth work flow and maximum efficiency.
145. (a) Equipment is dedicated to the manufacture of a narrow product line
Product layout is used to produce a narrow product line and all machinery and equipment is
dedicated for this. Material handling costs are low as there is less scope for product change over.
Product layouts are extensively used to produce standard products and not customized products.
146. (a) Graphic and schematic analysis
In Graphic and schematic analysis templates, two-dimensional cutouts of equipment drawn to scale
are the most common layout-planning tools. Templates are moved about within a scaled model of
the walls and columns of a facility to identify the best layout through trial and error. These
templates are also used for developing product and fixed-position layouts. Managers can use
various models like load distance and computer models. CRAFT is a type of computer model.
147. (c) Suitability of climate
Cotton yarn manufacturing units require a certain level of humidity in the atmosphere throughout
the year which is present in only certain places. This is because cotton is affected by high humidity
levels. Hence, many companies are set up in low humidity locations.
Part A
87
148. (b) To serve the customer better
Better customer service is a primary objective of the marketing department and not the operations
department.
149. (d) Cost of technology
Plant location decisions fall within the internal environment of the organization while technology
is part of the macro environment. The cost of acquiring technology is not a direct function of plant
location.
150. (c) Fixed position layout
Fixed position layout involves movement of men, machines and equipment to the product, which
remains stationary. The product here may be bulky, large, heavy or fragile. Layout adopted in ship
building is an example of fixed position layout.
151. (d) CRAFT analysis
CRAFT analysis is used for developing a process layout and not for determining plant location.
152. (a) A retailer
The success of a retail organization primarily depends on the number of customers visiting the
facility. Here, the location is more market/customer oriented than supply oriented. For example,
discount stores are present in downtown areas of most cities in America where the low income
population resides.
153. (c) Employee layout
Employee layout is not a type of facility layout. The various types of layouts are process layout,
product layout, hybrid layout and fixed position layout.
154. (b) Grouping technology layout
In a grouping technology layout (also called cellular manufacturing layout), dissimilar machines
are grouped into cells and each cell functions like a product layout within a larger job shop or
process layout.
155. (b) When expansion of the existing plant is possible
A new location is necessary under all conditions except option b. The need for selection of
facility location also arises when there is no possibility of expanding the existing plant and the firm
is compelled to search for a new location.
156. (c) iii, ii, i, iv
A firm first looks out for a location and identifies two or more possible locations. It then selects the
best location from available choices. After selecting the location, it designs a layout. Firms can
then revise or redesign the layout in the future depending on its strategies (expansion etc,).
157. (b) In a town/city
The location of the facility affects the companys ability to serve its customers quickly and
conveniently. Rahul must set up the printing press within reach of target markets. In this case, a
town or city is an ideal location as people who wish to publish their work live largely in cities.
158. (b) High transportation costs
If selection of a location leads to high transportation costs, it would reduce profitability of the firm.
Low labor costs, availability of public utility services and tax holidays are factors that would
encourage firms to choose a particular location.
Operations Management
88
159. (c) Close to the raw material source
Cement plants are generally located near limestone quarries. This is because raw material required
is huge and transportation cost over long distances cannot offset the benefits accrued from other
options mentioned in the question.
160. (a) Functional layouts
Process layouts, also known as functional layouts or job-shop layouts, involve grouping of similar
equipment or functions (for instance, lathe machines in one section, drilling machines in another
section and all activities related to assembling the product in another area, etc.).
161. (b) Proximity to markets
The major markets for auto-ancillary units are auto makers like Hyundai and Ford. Proximity to
these plants enables them to service clients more effectively.
162. (d) Availability of real estate
Government provides many benefits to industries that set up operations in special export zones. In
addition to tax holidays, infrastructure support and low interest loans from banks, etc, companies
are provided land at low costs. The land provided is not prime real estate as SEZs are located away
from cities or towns.
163. (c) Define location objectives identify relevant decision criteria relate objectives to
the criteria evaluate alternative locations select the best location
Though there is no standard procedure, the following steps serve as a guideline for location
decisions. The correct sequence includes: define location objectives and associated constraints,
identify relevant decision criteria, relate objectives to the criteria using appropriate models, do
field research to relevant data and use models to evaluate alternative locations and select the
location that best satisfies the criteria.
164. (d) Competitors
Location objectives and associated constraints are defined on the basis of the views and
requirements of promoters, owners, employees, suppliers and customers of the firm. Competitor
views are not an important factor.
165. (a) Revenue
From the figure it is evident that there is only one line representing revenue for the two locations,
while fixed costs, variable costs (difference between total and fixed costs) and total costs are
different for the two locations. Hence, revenue can be considered the same for both locations.
166. (c) 25000
Solution:
Price per unit = variable cost + contribution
50 = 30 + contribution
Hence, contribution per unit = (Rs50 - Rs30) = Rs.20
Break-even point = fixed cost / contribution per unit
= 500000/20
= 25000 units
Hence, 25000 units are required for the firm to break even.
167. (c) Delhi
Solution:
Total costs = total variable cost + fixed cost
Chandigarh = (300 x 1000) + 400000 = 700000
Part A
89
Gurgaon = (285 x 1000) + 450000 = 735000
Delhi = (275 x 1000) + 500000 = 775000
Delhi would have the highest total cost per year if annual output of a firm located there is 1000
units.
168. (a) Chandigarh
Solution:
Total revenue when annual ouput is 1000 units = 1000 x 1000 = Rs.10,00,000
Profit = Total revenue Total costs
Profit at Chandigarh = 1000000 700000 = 300000
Profit at Gurgaon = 1000000 735000 = 265000
Profit at Gurgaon = 1000000 775000 = 225000
Chandigarh would have the highest annual profit if annual production is 1000 units and selling
price per unit is Rs.1000.
169. (a) Chandigarh
Though variable costs are higher, annual profits are highest at Chandigarh. Hence, in terms of
profit, it is a better choice over Delhi and Gurgaon.
170. (c) It reduces space utilization
A good layout always helps increase space and machine utilization.
171. (a) Process layout
Process layouts, which are also known as functional layouts or job-shop layouts, involve grouping
of similar equipment or functions (all lathe machines in one area, all drilling machines in another
area and all assembling works in some other area).
172. (b) General purpose machines
Process layouts mostly use general purpose machines that can change rapidly to new operations for
different product designs.
173. (d) Increased utilization of men and material
In process layouts, men and machines are utilized most efficiently, owing to use of general purpose
equipment. The other options are not advantages. Production requires more time as work-in-
progress has to travel from one place to another. This increases accumulation of work at different
stages of production.
174. (b) Product layout
Product layouts are designed to accommodate only a few, mostly one or two, standardized
products and process designs. Process, hybrid and fixed position layouts allow production of
customized products.
175. (c) Ship-building
Ship-building is an example of fixed position layout where all the men, material and equipment are
brought to the ship that is stationary.
176. (b) Process, product
In a fabrication and assembly plant, fabrication is done on process layout while assembly is done
on product layout. Fabrication involves different processes like drilling, grinding, etc. Hence, it
requires a process layout. In the assembly section, each part is assembled one after the other and
does not require any deviations. Thus, a product layout can be used for assembly.
Operations Management
90
177. (b) CRAFT model
Except line balancing, all other options are models used in process layout development. CRAFT
model finds a layout by evaluating thousands of alternatives quickly. CRAFT has the capacity to
handle plants comprising up to 40 work centers of different shapes and sizes. It can account for
mobile and immobile process centers. The model considers various types of layouts and different
materials-handling methods that a firm can use in its work centers.
178. (c) Load distance model
The load distance model is an important model used to minimize material flow in a layout. In this
model, the number of loads (standardized amount of material) moved between each pair of process
centers over a period of time and distances between them are considered. Line balancing is used to
determine product layouts.
179. (b) Japan
In Japan, space availability is a major constraint as it is a very small nation in terms of geographic
area. Hence, layouts were designed to use minimal available space. In contrast, in USA, India and
China, as space is not a problem, comparatively larger layouts are designed.
180. (d) i/q, ii/r, iii/p, iv/s
CRAFT is used to analyze and evaluate thousands of alternative layouts very quickly. Load
distance model is used to reduce material movement costs in a production plant. Line balancing is
used to study workflow in an assembly line. Graphic and schematic analysis is used to study two-
dimensional scaled drawings of equipment and machinery to arrive at the best possible layout.
181. (a) Layouts focusing on customer receiving and servicing
Two extremely different types of layout of service facilities exist based on degrees of customer
contact. At one extreme is the layout totally designed around customer-receiving service functions.
The other is the layout designed around technology, processing of physical materials and
production efficiency.
182. (c) Restaurants
In a restaurant, the service layout has to cater to activities of receiving and servicing customers
(customer focus) as well as processing and preparation of food items (process layout).
183. (d) 8.11, 10.06
Solution:
The coordinates of the center of gravity can be identified by
Where,
X
c
= X coordinate of the center of gravity, Y
c
= Y coordinate of the center of gravity, V
i
= Volume
of items transported to and from location i, X
i
= X coordinate of location i, Yi= Y coordinate of the
location i
( )
=
i
i i
c
V
V X
X
( )
=
i
i i
c
V
V Y
Y
Part A
91
Distribution
Center
X Y Volume
(V
i
)
V
i
X
i
V
i
Y
i
A 4 4 60 240 240
B 12 6 90 1080 540
C 10 14 110 1100 1540
D 5 13 100 500 1300
Total
360 V
i
=
2920 X V
i i
=
3620 Y V
i i
=
Substituting these values in the equation for
Volume-weighted X coordinate = X
c
=
( )
i
i i
V
V X
X
c
= 2920/360 = 8.11
Volume-weighted Y coordinate = Y
c
=
i
i i
V
Y V
Y
c
= 3620/360 = 10.06
The X and Y coordinates of the point of center of gravity are 8.11 and 10.06.
184. (d) Historical analogy method
The historical analogy method is a forecasting method. The other options point rate method,
center of gravity method and analytical Delphi method are standard methods to locate the optimal
location for a firm.
185. (a) Form panels - Identify trends and opportunities - Determine directions and strategic
goals of the organization - Develop alternatives - Prioritize alternatives
Analytic Delphi Method helps managers take complex multi-location decisions. This method
requires the participation of a coordinating panel, forecasting panel and strategic panel. The
coordinating team selects two teams from within the organization, the forecasting and strategic
panels. These two panels participate in two Delphi inquiries. In the first, the coordinating panel
uses a questionnaire to elicit information from the forecasting panel regarding future trends, threats
and opportunities. In most cases, the process is repeated several times till consensus is reached. In
the next step, information collected through the first Delphi inquiry is given to the strategic panel.
This information is used by the strategic panel in the second Delphi inquiry to identify the
organization's direction and goals. After strategic goals have been identified, the strategic panel
develops various alternatives. Finally, all alternatives generated in the previous step are presented
to members of the strategic panel to obtain their subjective value judgments.
186. (d) They can be generalized to all organizations
LDRs cannot be generalized to all the organizations. They are organization-specific and must be
tailor-made to fit each organizations requirements. Extensive mathematical analysis is required to
arrive at the LDRs for a specific organization.
187. (b) Job design
Job design is the basis for job analysis.
Operations Management
92
188. (c) Job description
Job description describes the tasks, duties and responsibilities of a job. It includes information
regarding job content, job requirements in terms of necessary and desirable qualifications, work
experience, mental and physical effort involved, scope of responsibilities, nature of reporting
relationships and so on.
189. (b) Job analysis
Job analysis investigates job content, physical conditions in which the job is done, and
qualifications necessary to carry out job responsibilities.
190. (b) Jobs are consistent with organizational goals
An effective job design ensures that jobs are consistent with the organizations goals. It also
ensures that employees are sufficiently paid and not over-paid. Measuring work done by
employees falls under work measurement and does not include job design.
191. (d) i/r, ii/p, iii/q, iv/s
Skill varieties mean the various abilities and skill sets required for a particular job. Task identity
defines identifiable tasks to complete a job. Task significance is the influence the job has on
individuals inside and outside the organization. Autonomy is the flexibility and discretion available
in carrying out the job. Feedback is the level of information provided to employees on their
performance.
192. (c) Increase in worker inputs
One of the objectives of a good job design is to reduce (not increase) worker inputs like time and
physical effort.
193. (a) i, ii, iv
Job design should be technically, behaviorally, and economically feasible for workers as well as
the organization. Political issues are external and not internal to the organization.
194. (a) It gives the detailed set of activities to be performed on the job
Job content is the central aspect of job design. It defines the set of activities to be performed in the
job. These include duties, tasks and job responsibilities to be carried out by the jobholder,
equipment, machines and tools to be used and the required formal interaction with others.
195. (c) i, ii, and iii
Job content determines the qualifications and skills an organization should seek when selecting
personnel. Job content also determines the nature of training programs to be conducted and level of
compensation that is to be given.
196. (c) Lower flexibility in job rotation
Lower flexibility in job rotation is not an advantage of work specialization. This is because in the
absence of a worker, it is difficult to shift workload to other available workers as they may not
possess the required variety of skills or expertise.
197. (b) Ease of supervision and training workers
Ease of supervision and training workers is an advantage of work specialization while the other
options are probable problems that might arise as a result of work specialization.
198. (a) Only i
Salary is the basic compensation for work done. A fixed salary fulfils basic needs. A bonus can act
as a source of employee motivation. Promotion fulfils self esteem needs and health insurance
fulfils security needs.
Part A
93
199. (d) Low interest loans
Monetary benefits are tangible benefits other than salary. Monetary benefits may include company
shares, retirement benefits, health insurance, low interest loans, bonuses, etc. Low interest loans
come under monetary benefits as employee saves some amount of money due to low interest rates.
The other three options are types of non-monetary benefits.
200. (d) iii, i, ii
The correct sequence is Job design, followed by Job analysis and Job description.
201. (c) Using stop watch
In time study, work measurement is done through time using a stop watch
202. (c) i, ii, and iv
Setting work standards helps work measurement by providing benchmarks for evaluating workers
performance leading to comparison of efficiency of different work methods and improved machine
utilization by reducing idle time. Delegation is based on the experience and skill levels of
employees and the authority of the superior.
203. (c) Work sampling
Work sampling uses several random observations made during everyday work in the organization
instead of historical or stored data.
204. (c) Delphi method
Delphi method is not a technique of work measurement but is used in forecasting and decision-
making.
205. (a) The average of observations made always represents time required to perform each
elemental task
The averages of observations made in a time study need not always represent the standard time
required to perform each elemental task. Workers tend to behave differently while conducting a
time study. Some may become nervous and perform poorly while others may produce more output
than in usual circumstances. Hence, the readings have to be recorded several times to smooth out
such behavior. Apart from this, certain other allowances have to be considered like working
conditions, environmental disturbances, etc. while computing the standard time.
206. (c) Dearness allowance
Dearness allowance is associated with compensation. It is calculated as a percentage of the basic
pay of the employee. Contingency, interference and relaxation allowance are considered in the
time study to calculate standard time.
207. (b) 3.375 minutes
Normal time = average cycle time x worker rating
= 3.75 x 0.90
= 3.375 minutes
208. (c) 3.835 minutes
Standard time = normal time/available fraction time
= 3.375/(1- 0.12)
= 3.375/0.88
= 3.835 minutes
Operations Management
94
209. (b) Pre-determined Motion Time Study
Pre-determined Motion Time Study (PMTS) is the technique of setting work standards that use
recorded standard time data for each of the basic motions associated with performing a task and
summing them up to determine time required to perform the whole task.
210. (c) PMTS provides time for basic motions while Standard Data provide time for job
specific motions
PMTS differs from standard data in that PMTS provides time for basic motions (which are generic
in nature) rather than job-specific work elements.
211. (d) Work sampling
Work sampling is a technique of analyzing work by taking several observations, usually at
random, to see the relative frequency with which various elemental activities take place.
212. (a) Ratio delay
Ratio delay, performance measurement and time standards are primary applications of work
sampling. Ratio delay refers to the activity time percentage for an employee or equipment. Ratio
delay shows the percentage of time an employee or equipment was occupied or idle.
213. (c) Time standards
Time standards refer to identification of the standard time for completion of a task. Companies use
time standards to generate time schedules and assign tasks.
214. (b) ii and iii
The employee self-timing technique is cost effective and simple to use, but not that accurate as
other work measurement techniques. Also, it does not take allowances into consideration while
measuring work.
215. (d) All of the above
The time consumed by an average worker, working at average speed, to perform a specific task
under normal operating conditions is generally referred to as time standard, work standard, or just
standard. It is expressed in terms of time elapsed per unit of output, or units of output per unit of
time. Managers use these standards in planning, controlling and scheduling operations.
216. (a) Maynard Operations Sequence Technique
MOST stands for Maynard Operations Sequence Technique.
217. (d) Varying the compensation method
Strategies for aggregate planning include varying utilization of the workforce, varying workforce
size in response to output requirements, varying size of inventory, back orders, sub-contracting and
plant capacity. Varying the compensation method is part of human resource management function.
218. (a) Master production schedule
Master production schedule translates the aggregate plan into production schedules. The Master
Production Schedule (MPS) defines the type and volume of each product to be produced within the
planning horizon. The MPS is a detailed plan that specifies the exact timing for production of each
unit.
219. (a) Time series analysis
Time series analysis is not an aggregate planning technique. It is associated with forecasting.
220. (a) Heuristic approach
Heuristic models are based on historical aggregate planning data available with organizations.
Part A
95
221. (b) Maintaining fixed plant capacity
Varying workforce utilization is a strategy where the firm maintains a stable workforce and varies
workforce utilization in accordance with demand or required output. Other pure planning strategies
are back-orders, sub-contracting and varying plant capacity. Adjusting or varying plant capacity by
changing equipment capacity over short-term or long-term is a pure strategy to absorb demand
fluctuations.
222. (b) Defining how resources can be best employed to meet market demand
Except b all other options are part of capacity planning. Aggregate plans define how resources
can be best employed to meet market demand for given products. The objective of an aggregate
plan is to minimize production costs, make appropriate changes in production rates and workforce
levels. It is also to improve profits, customer service and utilize resources. Capacity requirement
planning is primarily concerned with ensuring sufficient capacity available to meet market
demand.
223. (b) Medium range
Medium-range planning focuses on a period of six to 18 months. Examples of medium range
planning are aggregate planning, master production scheduling and materials requirement
planning.
224. (d) Customers
A production plan contains information about the production process, manufacturing facilities,
inventory requirements, suppliers, etc. Such a plan is usually made based on sales estimates.
225. (d) 0 units
25 workers in 26 days can produce 2600 units. This is exactly equal to the demand for the month
of June, as given in the table. Hence, existing inventory will remain untouched as there is no
necessity to use it to meet demand. The available inventory at the end of June is the same i.e. 500
units.
226. (a) Rs.6000
In July, 25 people working for 25 days with a daily output of 4 units can produce 2500 units for the
month. As the demand is 2700 units, the additional 200 units are taken from the inventory on hand
of 500 units. Hence, the inventory left is 300 units. Thus, inventory carrying cost will be Rs. 20 x
300 units = Rs.6000.
227. (c) 0 units
In August, 25 people working for 25 days with daily output of 4 units can produce 2500 units for
the month. As demand is 2800 units, additional 300 units are taken from the inventory. Hence,
there will be no inventory available.
228. (d) Rs.1500
In September, 25 people working for 26 days with a daily output of 4 units can produce 2600 units
for the month. As the demand is 2750 units, there is shortage in supply of 150 units. Thus, the
shortage cost in September will be 150 units x Rs. 10 = Rs.1500.
229. (c) To evaluate the performance of a specific plan
Computer simulation is used to evaluate the performance of a specific plan, based on real-world
variables and situations. Simulation provides what-if analysis of different situations, using
different variables with alternative values attached, to judge the system performance under
different conditions.
Operations Management
96
230. (b) Estimation of overall demand for the end product
MPS is based on an estimation of overall demand for the end product. A final assembly schedule is
developed only when customer orders are received.
231. (c) Back orders are common in make-to-stock organizations
Back orders are common in make-to-order (not make-to-stock) organizations. This is because
actual production does not begin until customer orders are placed.
232. (a) 55 units
In the first month, demand is 60 units, which can be met from inventory on hand. Hence, at the end
of the first month inventory available = inventory on hand + MPS quantity projected
requirements for the month. That is = 75 + 0 - 60 = 15. For the second month, customer orders are
60 and inventory on hand is 15. There is a deficit of 45. To meet demand for the second month,
production has to start in the first month as production lot size = 100 units. Then, inventory at the
end of the second month = 15 + 100 - 60 = 55 units. (See the following table)
1 2 3
Forecast 60 55 65
Orders 55 60 65
MPS quantity 0 100 100
Projected on-hand inventory 15 55 90
MPS start 100 100
233. (c) 75 units
The inventory at the end of the second month is 55 units. The order for the third month is 80 units.
The inventory on hand at the end of the third month = 55 + 100 - 80 = 75 units. (See the following
table)
1 2 3
Forecast 60 55 65
Orders 55 60 80
MPS quantity 0 100 100
Projected on-hand inventory 15 55 75
MPS start 100 100
234. (d) Revising and updating master production schedule
Forecasted demand and actual demand for a product may differ significantly due to unexpected
events. Transactions, records, and reports developed as part of MPS are updated and reviewed
continuously to accommodate these differences. This process of continuous reviewing and
updating is called rolling through time
235. (a) Capacity planning
Capacity planning is important to determine adequate production capacity to meet forecast demand
levels. Capacity planning is also used by organizations when deciding on issues like whether or not
to use sub-contracting or overtime to achieve production goals.
Part A
97
236. (c) Identifying the right layout design for the desired capacity
The capacity planning process involves identifying available capacity and additional capacity
requirements and evaluating and summing up capacity required at each work center. If there is any
gap between planned and available capacity, it is increased by overtime, sub-contracting, etc. or
the master production schedule is revised. Designing a plant layout precedes capacity planning and
is part of plant layout.
237. (a) i, ii, iii, iv
The correct sequence of activities in a capacity plan is to identify current capacity, forecast future
capacity, identify and evaluate sources to meet capacity requirements and select the most
appropriate alternative.
238. (b) 100
available Capacity
used Capacity
rate n utilizatio Capacity =
Capacity utilization rate measures the rate at which available capacity is used in production. It is
obtained by dividing used capacity by available capacity. To measure in terms of percentage,
multiply the obtained value with 100.
239. (d) Increased complexity in operations
The complexity in operations can lead to diseconomies of scale or increase in per unit cost.
Efficient processes decrease fixed costs, while automation reduces per unit cost considerably.
240. (d) All of the above
All the stated options can be reasons for diseconomies of scale. Complexities in operations can
lead to high cost due to production bottlenecks. When modifications in machinery or replacements
take place frequently, it may prove costly. Further, when scale of production increases, distribution
and storage costs also increase.
241. (c) A service firm with a single office cannot efficiently serve customers in another
geographical area
Unlike manufacturing organizations, a service organization based in one geographical location
cannot usually serve customers efficiently in other geographical areas. The service capacity should
be located near customers because most service delivery processes involve customers. As a result,
service organizations generally operate through branches or franchises in different locations.
242. (d) Both i & ii
The two major sources of inputs that influence the MPS are forecasts and customer orders. Make-
to-stock environment takes inputs from forecasts in deciding the MPS. On the other hand, make-
to-order environment takes inputs from customer demand and generates an MPS based on that.
243. (a) Long range planning
Long-range planning focuses on a period of over one year and is generally carried out annually.
Process planning and strategic capacity planning are examples of long-range planning. Medium-
range planning focuses on a period of six to 18 months. Examples of medium range planning are
aggregate planning, master production scheduling and materials requirement planning. Short-range
planning focuses on a period less than six months. Order and workforce scheduling are examples
of such planning.
244. (d) Material receiving costs
Carrying costs include opportunity costs besides storage costs, staffing costs, equipment and
maintenance costs, insurance costs, loss of inventory due to pilferage, spoilage or breakage in
warehouses and the cost of obsolescence.
Operations Management
98
245. (a) Demand is greater than expected
Buffer stocks come in handy when demand for a product suddenly increases. In such situations
buffer stocks help meet the excess demand.
246. (b) Estimated demand during lead-time
The calculation of the reorder point should ensure that inventory level reaches zero at the end of
each reordering cycle. This is because a positive inventory level at the end of the cycle raises
average inventory and associated costs. To ensure this condition is satisfied, reorder level is set
equal to the number of units estimated to be used during lead-time.
247. (c) The cost of ordering varies and is dependent on the quantity ordered
Under the EOQ model, the cost of ordering (C
o
) is fixed and independent of quantity ordered (Q).
The model makes the following assumptions: The price of the inventory item (p) is independent of
the order quantity. It means that the benefits of economies of scale are not taken into consideration
while purchasing. The total holding cost of inventories is proportional to the number of inventory
items stored. Demand for a product or its usage rate is constant over time. Materials are always
issued in equal quantities to the indenting departments and the inventory supply rate is always
greater than or equal to the usage rate (i.e. there is no scope for shortage of inventory). The lead-
time for material delivery is known with certainty and it remains constant. The quantity of
inventory ordered is delivered in a single lot and there is no scope for splitting of deliveries.
248. (a) Carrying costs
Carrying costs include opportunity costs, storage costs, staffing costs, equipment and maintenance
costs, insurance costs, interest charges for financing inventories, taxes, security and other expenses
associated with holding materials in warehouses.
249. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
Acquisition (purchase) costs, holding costs, ordering costs and stock-out costs are considered in
calculating inventory costs.
250. (c) Total inventory costs
EOQ model always aims to reduce total inventory costs, which include ordering costs, purchasing
costs, carrying costs and stock-out costs.
251. (c) Stock-out cost
Stock-out costs arise only when the inventory is exhausted and the firm is unable to meet demand.
Such costs are penalty costs and come into the picture only when there is no inventory to meet
demand. Hence, it is a secondary inventory cost.
252. (a) Lead-time
Lead time refers to the time between placing the order for the material and receiving it.
253. (c) 1000 units
Opening inventory = 500 units, Closing inventory = 200 units, Sales forecast = 1300 units
Assuming actual sales is equal to forecast (1300 units), Sales = 500 units (inventory) + 800 units
(produced). But, closing inventory is 200 units, which means that it is part of the total lot produced
(as the opening inventory of 500 units was sold). Hence, total units produced = 800 units (sold) +
200 units (inventory) = 1000 units.
254. (d) i, iii and iv
Finished product inventories offer organizations the ability to show products to customers, not raw
material inventories.
Part A
99
255. (d) The purchase price per unit varies depending upon quantity ordered
One of the assumptions of the EOQ model is that purchase price per unit is fixed and is
independent of order quantity. It means that benefits of economies of scale, if any, are not taken
into consideration.
256. (b) 200 units
Assuming 50 units /week as weekly demand, EOQ can be calculated using the formula:
EOQ =
h
C
D
o
2C
Where, C
o
is the ordering cost (Rs. 200), D is the demand in units per unit time (50 units), C
h
is the
holding cost per unit per unit time (Rs. 0.50). Hence, EOQ = ((2 x 200 x 50)/ 0.5) = 200 units.
257. (a) Q system
Under the Q system (also called Fixed Order Quantity System), inventory is continuously checked
and a new order is placed when the inventory level reaches the reorder point.
258. (b) To avoid backlogs in customer order
Organizations maintain finished goods inventory to avoid backlogs in customer orders. Finished
goods inventory helps during sudden increase in customer demand.
259. (b) Work-in-progress inventory
Work-in-progress goods are semi-finished items stored temporarily during the production process.
260. (c) Finished products
Firms maintain adequate levels of inventory to successfully operate in an uncertain environment.
Inventories help firms take advantage of unexpected opportunities. For instance, a sudden and
unexpected increase in demand can be met with larger finished goods inventory.
261. (d) Hiring cost
Hiring costs are those incurred by an organization as part of recruitment. It is not a factor that
influences the quantity of material ordered. Purchase, carrying and ordering costs influence the
quantity ordered.
262. (a) Purchase costs
The cost of purchasing a unit of a particular item is its purchase cost. Suppliers sometimes provide
discounts to customers (manufacturers) based on purchase costs (quantity of purchase). Discounts
are usually given while purchasing quantities in bulk.
263. (d) Material-receiving costs
While pilferage, spillage and maintenance costs come under carrying costs, material-receiving
costs fall under ordering costs.
264. (d) i/r, ii/p, iii/s, iv/q
Discounts are given by suppliers on the basis of total cost of purchase when material is purchased
in bulk. Damage to inventory either in the warehouse or in production facilities can increase
carrying costs. Ordering costs are considered fixed and so decrease with increase in order size.
Marketers may lose customer goodwill if they cannot supply goods on time due to non-availability
of finished goods in the inventory.
Operations Management
100
265. (b) Q system
In Q system, order quantity (Q) is always constant and the order is placed when the level of
inventory reaches the reorder point. This system is also referred to as the reorder point system.
266. (b) Time required for replenishing inventory after placing an order
Lead time gives the time required to replenish inventory once the order is placed. Lead time is an
important consideration in inventory management.
267. (a) i and ii
The calculation of the reorder point should ensure that inventory level reaches zero at the end of
each reordering cycle. This is because a positive inventory level at the end of the cycle results in a
rise in average inventory and associated costs. To ensure this condition is satisfied, reorder level is
set equal to the number of units estimated to be used during the lead-time.
268. (b) 175 units
Reorder point = average daily demand x lead time
= 25 x 7
= 175 units
269. (d) Stock-out costs
One of the assumptions of EOQ concept is that stock-outs are not allowed. It implies that inventory
is replenished just before the time when it becomes zero. Hence, the total cost of maintaining
inventory can be assumed to have only three components: ordering costs, holding costs and
variable item costs.
270. (b) Rs.8000
Total order cost (A) = fixed cost per order x (demand / quantity per order)
= 2000 x (300000/75000)
= 2000 x 4
= 8000
271. (c) Rs.150000
Holding costs per order (B) = holding costs per unit x (quantity per order /2)
= 5 x (75000/2)
= 5 x 37500
= 150000
272. (b) Rs.3000000
Total Variable cost (C) = item cost x demand
= 10 x 300000
= 3000000
273. (b) Rs.3158000
Total cost of maintaining inventory = Total order cost (A) + Holding cost per order (B) +
variable cost (C)
= 8000 + 150000 + 3000000
= 3158000
274. (b) Reorder level
Reorder level is the quantity of inventory where a new order is placed for replenishment. In the Q
system, the reorder level is equal to quantity used in lead time plus safety stock. But in EOQ
model, it is equal only to the quantity used in the lead time.
Part A
101
275. (c) EOQ
In the EOQ system, lead time is known and is assumed to remain constant.
276. (d) Producing and transporting in larger batches reduces material-handling and
production costs
The first three options are reasons for holding raw material inventory while option (d) is a reason
to hold semi-finished goods inventory. Producing and transporting in larger batches reduces
material-handling and production costs of semi-finished goods for a firm.
277. (a) ABC
ABC is one of the most widely used inventory classification models. It is also known as Always
Better Control model. As per ABC classification, items are classified on the basis of their annual
consumption value. Items with highest value are classified as A, next lower value items are
classified as B and the lowest value items are classified as C.
278. (a) Minimizing total inventory cost
EOQ method is used to identify order quantity to minimize total cost i.e. the sum of ordering and
carrying costs.
279. (d) i, ii and iii
All the above factors must be taken into consideration by the purchase department while buying
material and supplies from a supplier.
280. (a) Materials purchased
Value analysis aims at reviewing design of materials to be procured and attempts to modify the
design to replace high cost and obsolete parts with cost effective parts and designs. Value analysis
mainly aims at controlling costs of purchasing material.
281. (d) Quality control
Quality control is part of raw material purchase. It is an activity taken up by the production/ quality
control department, sometimes in conjunction with the purchase department.
282. (d) All of the above
Processing requisition for materials and supplies, locating suppliers or vendors, and negotiating
purchasing contracts are tasks carried out by the purchase department.
283. (d) Standardized packaging for all types of components
Standardized packaging for all kinds of parts is a characteristic of modern purchasing. Earlier, the
type of packaging depended on the type of components.
284. (a) Procurement requests
Procurement requests are placed by individual departments, which require materials and the
purchase manager only facilitates requests. This is more so in a bio-pharmaceutical company
where the R&D department requests for specialty chemicals and instruments.
285. (d) Public relations
Maintaining public relations does not fall under the purview of the purchase department in a
production-centric firm. It is the responsibility of the marketing or corporate communications/PR
department.
286. (b) Purchase indent -Quotation - Purchase order
A purchase indent from a department within the firm initiates the purchase process. This is
followed by request for quotations from suppliers by the purchase department.. After selecting a
supplier, the purchase order is placed by the purchase department.
Operations Management
102
287. (c) Value engineering
Value engineering is related to product review and components in terms of design and other
features so as to retain all properties of the item while reducing cost as much as possible.
288. (d) None of the above
All three options are factors that influence vendor selection. The cost, quality and reliability of a
product along with the delivery and service determine the preference for a particular vendor.
289. (b) Decentralized purchasing
When specific material requirements vary between production facilities, a firm must adopt a
decentralized purchasing system. Centralized purchasing reduces flexibility and outsourcing
reduces control of the firm over the purchasing function.
290. (d) ABC analysis
ABC analysis is used in materials management and is not performed by the purchase manager.
291. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
All the options provide information about vendors and suppliers.
292. (d) Negotiate with suppliers
Value analysis deals with measuring and enhancing the value of a material/product. It reviews the
design of products and identifies costly components in the product. Attempts are made to replace
high-cost parts with economical ones. Negotiating with suppliers is not an activity under value
analysis, though it is part of the purchase function.
293. (c) Can the vendor supply the material at the right time?
Value analysis is concerned about increasing product value by reviewing design and modifying the
product without affecting its usability. Option (d) relates to vendor supply and does not come
under value analysis.
294. (a) Purchase requisitions
Purchase indents are also called requisitions, which include a clear specification of materials
required.
295. (a) User department
The user department that utilizes material or goods issues purchase indents. They are issued to the
purchase department, which requests for quotations from vendors for the materials.
296. (d) Name of the user department
The name of the user department is present in the purchase indent or requisition and not in the
suppliers quotation. The latter usually contains price per unit, delivery schedule, mode of
transportation, special terms and conditions, etc.
297. (c) Purchase order
The purchase order is the legal document authorizing the supplier to supply goods. It represents the
buyers obligation to buy materials against specified terms.
298. (b) Purchase department
The purchase department is responsible for proper delivery of goods purchased. As this department
acts as an interface between the user department and suppliers, it is answerable to the user
department for delays in delivery of material.
Part A
103
299. (d) When the quantity of the part required is small
India Rubber can buy the part when the quantity required is small or when total costs to make it
are more than buying costs.
300. (d) To take advantage of knowledge and expertise of suppliers
Organizations opt for in-house production when they want to control all value chain activities, to
use excess plant capacity productively, or when they do not want competitors to get to know the
product design. Suppliers knowledge and expertise is a factor when the organization decides to
outsource rather than produce in-house.
301. (a) ABC
The ABC classification system is also referred to as ABC (Always Better Control) analysis. The
purpose is to alter expenses associated with controlling materials according to their usage value
302. (a) Conveyance authorization card
A Kanban system uses three types of cards to initiate material transactions: production
authorization card, vendor authorization card and conveyance authorization card. A conveyance
authorization card authorizes a materials handling agent to move the tray to a specified destination.
This specifies the products name, its identification number and delivery destination. The dual-card
Kanban system makes use of two Kanban cards, a conveyance card and a vendor card.
303. (a) Vendor analysis
The functions of materials management are production control, materials handling and inventory
control. Vendor analysis is associated with purchase management (purchase department).
304. (c) The system considers availability of materials
Resource allocation is made based on value of the inventory. The more valuable the inventory is,
the more the resources allocated. Even though the method facilitates selective control of materials,
the method suffers from several limitations. One limitation is that ABC analysis does not consider
the aspect of availability of materials.
305. (a) 1 & 2
Calculate usage value of each material and arrange them in the descending order of their usage
values.
Type of material Usage Value
(cost per unit x annual usage)
% of usage value Cumulative value
1 20000 37.90 37.90
2 20400 38.65 76.55
3 6000 11.37 87.92
4 5500 10.42 98.34
5 500 0.95 99.29
6 375 0.71 100
Total 52775 100
Here, we can see that two materials (materials 1 and 2) out of 6 materials account for 76.55% of
total costs. That means 76.55% of total resources are to be assigned to control 33.33% of the
materials (two out of six materials). So, materials 1 and 2 are categorized A type materials.
Operations Management
104
306. (c) i, ii and iii
Alternatives i, ii and iii are tasks carried out by the raw material inventory department. Alternative
iv is associated with the receiving department. The tasks of the receiving department include
unpacking incoming materials, checking quantity and inspecting quality and then generating
receiving reports.
307. (d) i, ii and iii
Storing raw materials safely is a task of the raw material department. All other tasks are carried out
by the shipping department.
308. (a) An item is critical if its usage is high
In ABC analysis, an item is said to be critical if its usage is high. The purpose of this analysis is to
alter expenses associated with controlling materials according to their usage value.
309. (a) Characteristics of products
The details of product characteristics need not be entered in inventory records file as the inventory
department has nothing to do with product attributes.
310. (c) Locating and receiving raw materials
Locating and receiving raw materials is the function of the raw materials inventory department. All
the other options are functions of the production department. The function of production control
aims at directing and regulating goods movement through the entire manufacturing cycle from the
process of purchasing materials to making the finished product. The departments involved in this
function are purchasing department, receiving department, raw materials inventory department and
production department.
311. (b) Processing requisitions for materials
Processing requisitions for material is done by the purchase department and not by the receiving
department. The main task of the former is to acquire the required materials in the right quantity,
of the right quality, from the right source, at the right time and at the least possible cost. The
primary responsibility of the receiving department is to process incoming shipments of materials.
312. (c) Materials management
Materials management is the study of flow of materials through various operations in a production
facility. Inventory management deals with managing inventory and maintaining it at optimum
levels. Operations management encompasses both materials management and inventory
management. Purchase management is a separate sub-function under materials management.
313. (b) i, ii and iv
Shortage in materials supply affects the firm in many ways. They include stoppage or breakage in
production, delay in delivery to customers, increase in operational expenses, etc. On the other
hand, the efficiency of the production process actually decreases rather than rising.
314. (a) Stock large volumes of materials to avoid shortage
To reduce shortages it is not advisable for a materials manager to stock huge volumes of inventory.
This will lead to heavy carrying costs, which will eat into the firms profitability.
315. (b) 25% increase
Solution:
Sales = Rs.60 lakhs, Profit = Rs.12 lakhs (20% of sales), Material cost = 30 lakhs (50% of sales). If
3 lakhs are saved in material costs, the amount is passed onto profits. The percentage change in
profit = (3/12) x 100 = 25%. The profit now is 15 lakhs. Hence, profit increases by 25%
Part A
105
316. (a) To maintain low inventory turnover
One of the objectives of materials management is to maintain high inventory turnover (not low) so
that less capital is tied up in inventory.
317. (c) Finished goods inventory department
Purchase department, raw material inventory department, receiving department and production
department are associated with production control. The finished goods inventory department is
associated with inventory control function.
318. (c) Non-uniformity in maintaining records
Under centralized purchasing, purchase records are uniformly maintained. This is not the case
under decentralized purchasing where there is a great deal of difference in record maintenance
across purchase departments in different units of the firm.
319. (d) Information on inventory levels
A materials receiving report contains quantity of material, price, description and other technical
specifications. Information on inventory levels is associated with an inventory records file.
320. (b) Maintaining stocks of material at various stages of production
The tasks of raw material inventory department include labeling raw materials to make them ready
for use in the production process, storing raw materials safely and protecting them from damage
and pilferage, updating and maintaining records of quantities of various raw materials, arranging
for replenishment of stocks in liaison with the purchase department and auditing raw materials
periodically. Maintaining stocks of material at various stages of production is the task of the
inventory control department.
321. (a) Purchase department
The inventory control function is represented in three departments - Raw materials inventory
department, production department and finished goods inventory department. Purchase department
is associated with the inventory control function of materials management.
322. (c) To move materials to the required location in a timely and cost-effective way without
affecting the primary objective of production control and inventory control
Materials handling refers to managing the physical movement of materials into, through, and out
of the firm. The primary objective of materials management is to move materials to the required
location in a timely and cost-effective way without affecting the primary objective of production
control and inventory control functions.
323. (b) Physical distribution
The sub-function physical distribution is associated with the movement of finished products and
other materials. The sub-function traffic deals with arranging the most economic transportation
method for both incoming and outgoing materials. Finally, the sub-function logistics deals with
obtaining, producing and distributing materials and products at/to the desired place, at the right
time.
324. (c) Variable-sequence robot
The function of variable-sequence robots is similar to that of fixed-sequence robots, but the
sequence of tasks can be changed depending on the nature of operations to be performed.
325. (c) Maintain minimum inventory till the next replenishment
JIT purchasing implies that inventory can be replenished just-in-time for manufacture. The method
advocates reduction in size of purchased quantities to the extent that materials reach the production
point directly. Hence, safety stocks need not be maintained.
Operations Management
106
326. (d) Reduced flexibility
In JIT purchasing, flexibility is higher in terms of ability to change materials required at the last
minute depending on changes in customer/client preferences, etc. Thus, flexibility is not reduced.
It rather increases.
327. (b) Toyota Motor Company
The Kanban system was developed by Toyota Motor Company, Japan.
328. (c) Conveyance authorization card
A conveyance authorization card authorizes a materials handling agent to move the tray containing
material or component parts to a specified workstation. Here, this material is used in the
production process.
329. (d) Type 5
Material type Quantity used per year Cost per unit Usage value
(quantity used x cost per unit)
1 2000 20 40000
2 4500 10 45000
3 1500 35 52500
4 3000 20 60000
5 2500 25 62500
330. (a) 40000
Material type Quantity used per year Cost per unit Usage value
1 2000 20 40000
2 4500 10 45000
3 1500 35 52500
4 3000 20 60000
5 2500 25 62500
331. (b) Type 5
From the above table it is evident that Type 5 material have the highest usage values of Rs.60000
and Rs.62500 respectively. Hence, it falls under A category.
332. (c) Type 1
Type 1 material has the least usage value of Rs.40000. Hence, this material is under C category.
333. (b) Production authorization card
A Kanban system uses three types of cards to initiate material transactions: production
authorization card, vendor authorization card and conveyance authorization card. The production
authorization card authorizes the production department to start the production process. This card
describes the products name, identification number and description and the list of materials
needed for continuing the production process.
334. (b) Materials requirement planning
The primary objective of an MRP system is to manage the inventories of parts which are demand-
dependent and schedule production activities. MRP system helps an operations manager compute
the net requirement of a component after taking into consideration inventory on hand, scheduled
receipts and order releases.
Part A
107
335. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
An MRP system requires a host of information that includes: customer orders pending for future
deliveries; unfinished orders that must be completed in the planned production period; demand
forecasts that specify the quantity of products demanded and the time period in which these
demands are to be satisfied; capacity information that helps anticipate and correct resource
shortage; details of dependent demand inventory items at various stages of the transformation
process and the stages through which these items traverse to make an end product; changes in
inventory requirements due to product design changes expected during the planning time period;
available inventory at the beginning of the planning time period; quantities of ordered, purchased
or contracted inventory items that an organization expects to receive during the planning time
period
336. (b) Greater investment in inventory
The primary purpose of MRP is to provide adequate supply of demand-dependent inventory as and
when required. By doing so it helps an organization improve customer service, reduce (not
increase) investment in inventory, improve operating efficiency and speed up response to market
changes
337. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
All the statements are true. The Bills of Material contain the list of materials along with the
quantity required to produce one unit of a product. It shows the hierarchical levels or phases a
product goes through during production (from raw material to end product). It consists of the
complete list of all end products, the structure (subassemblies, parts, and raw materials which
constitute the product assembly) of the products, and the quantity of each item required for
producing each higher-level product in the hierarchy. It also contains information about whether a
particular item was produced internally or purchased from external sources. The purchase or
production lead-time to acquire the item is also specified.
338. (c) Longer idle time
Ability to price competitively, better customer service, and reduced set-up and tear-down costs are
advantages. In addition, comprehensive material tracking and optimized production scheduling are
also advantages of MRP system. They help in better response to market demand and lower the lead
time.
339. (a) Required quantities and delivery dates of final products
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) file contains information about when and how many units
of finished products are required. It also gives the available cumulative lead-time for purchasing,
receiving, fabricating, and assembling.
340. (c) i and iii
The primary objective of an MRP system is to manage demand-dependent inventories and
schedule production activities.
341. (b) Finished goods inventory on hand
MRP system helps an operations manager find the net requirement of a component after taking
into consideration inventory on hand, scheduled receipts and order releases. Finished goods
inventory is not considered under MRP as it is the final output of production and MRP system is
part of the production process.
342. (c) i, ii and iii
The operating efficiency can be improved by controlling the raw material inventory, and by
responding quickly to production requirements by speeding up or delaying the material supply.
Controlling the movement of finished products is not under the scope of MRP.
Operations Management
108
343. (d) 30 and 45
One unit of B requires 3 units of E. One unit of E requires 2 units of F. Therefore, total quantity of
F required = (3 x 2 x 5) = 30 units.
One unit of E requires 3 units of G. One unit of B requires 3 units of E. Therefore, total quantity of
G required = (3 x 3 x 5) = 45 units.
344. (b) 5 hours
F & G are required to produce E. Lead times of F & G are 1 hour and 2 hours respectively.
Therefore, production of E will start only after 2 hours when both F & G are ready. The lead time
to produce E is 2 hours. Hence, to produce E the total time required is 4 hours. After E is
produced, it takes one hour before production of B can commence. Therefore, the total time to
produce B is (2 + 2 + 1) = 5 hours.
345. (c) 48 and 48
One unit of I requires 3 units of G. One unit of D requires 2 units of I. Therefore, total quantity of
G required = (3 x 2 x 8) = 48 units
One unit of I requires 3 units of H. One unit of D requires 2 units of I. Total quantity of H required
= (3 x 2 x 8) = 48 units
346. (d) 9 hours
G & H are required to produce D. Lead times of G & H is 2 hours each. Hence, production of I
will start only after 2 hours. The lead time to produce I is 3 hours. To produce I the total time
required is 5 hours. After I is produced, it takes 4 hours to produce D. Therefore, the total time to
produce D is (2 + 3 + 4) = 9 hours
347. (d) 600 units
One unit of E requires 3 units of G. One unit of B requires 3 units of E. One unit of alpha requires
four units of B. Therefore, total quantity of G required = (3 x 3 x 4 x 10) = 360 units.
One unit of I requires 3 units of G. One unit of D requires 2 units of I. One unit of alpha requires 4
units of D. Therefore, total quantity of G required = (3 x 2 x 4 x 10) = 240 units
Total units of G required are 360 + 240 = 600 units.
348. (b) 11 hours
B, C, & D are required to produce alpha. Time required to produce B is 5 hours, for C it is 5 hours
and for D it is 9 hours. Hence one must wait for 4 hours for D to be ready. Once D is ready, it takes
2 hours to produce alpha. Hence, total time required to produce alpha is 9+2 = 11 hours.
349. (d) Order release
Order release is part of the primary reports, which is an output component of the MRP system. The
steps in information processing include explosion, netting, offsetting and finally consolidation of
material requirements.
350. (b) i and iii
Explosion uses the information from MPS and BOM to develop the sequence to be followed to
produce the end product.
351. (b) Netting
Netting is the step in MRP information processing that is used to develop a materials requirement
plan for each item in the BOM file for each time bracket.
352. (c) Offsetting
Offsetting uses the information obtained from explosion and netting to determine planned order
releases i.e. the quantities to be ordered (either internally through production or from an external
supplier) so that the materials arrive as and when they are needed.
Part A
109
353. (a) Next lower
The planned order releases for the finished product or component become the gross product
requirement for items at the next lower level in the product structure chart.
354. (c) i/s, ii/r, iii/p, iv/q
Performance reports contain information about the performance of an MRP system. They also help
identify a problem and verify whether the system can achieve planned objectives. Exception
reports contain information about errors and deviations from planned objectives. Suspension
reports are generated to cancel an order due to changes in MPS. Planning reports contain
information about material requirements.
355. (d) Longer implementation time
The implementation of an MRP system involves huge costs and takes long time for installation.
Hence, longer implementation time is a disadvantage of the MRP system
356. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
The factors that ensure the effective implementation of MRP systems include commitment from
top management, educating and training the employees about the system, continuous collection of
information regarding the materials used and a high degree of accuracy in all operations.
357. (b) Obsolete data
Obsolete data like an outdated BOM can badly affect the success of an MRP system. Hence, all the
data pertaining to materials should be accurate and up-to-date.
358. (c) Assemble-to-order
In assemble-to-order approach in materials requirement planning, only the final assembly of the
machine is made based on the customer order specifications. Smith & Smith also does the same. In
assemble-to-stock approach, the firm combines multiple component parts into a finished product,
which is then stocked in inventory to satisfy customer demand. In manufacture-to-order approach
the items are either fabricated or assembled completely in adherence to customer specifications.
Items are manufactured by machines to customer orders and do not involve any assembly in
fabricate-to-order approach.
359. (a) Explosion
The first step in the MRP information processing is that of explosion in which end product is
disassembled into components required for its production. It starts with the time when the product
is required and then proceeds backward to determine each production or purchasing activity that is
necessary to make each higher-level item in the product structure chart.
360. (b) Planning report
While master production schedule, bill of materials and inventory records file are inputs to a MRP
system, planning report is an output.
361. (b) E-F-G-C-A-B-D
The least time on workstation 1 is for job E. Place E at the beginning of the sequence. Least time
on workstation 2 is again job E, which is already placed. The next least time is for job D on
workstation 2. Place D at the end of the sequence. Continue this process to arrive at the sequence:
E-F-G-C-A-B-D.
362. (b) Sequencing rules
When jobs are processed in a single stage of production, they can be scheduled one after another.
If two or more stages of production are required, firms should ensure that jobs are sequenced in a
way that idle time is minimized. Operations managers can use job sequencing rules and develop a
job sequence that minimizes total time required to complete a given job.
Operations Management
110
363. (b) Backward
The backward scheduling method schedules orders as per their due dates. The operations manager
schedules production activity based on due dates for job orders so that the production activity can
be timed to complete the order on time. Forward and hybrid scheduling are also types of
scheduling methods. Routing is a scheduling activity.
364. (c) Increased overtime costs
An increased overtime cost is a disadvantage of a fixed workforce strategy. In this strategy, regular
workers are made to work overtime as part-time workers are not employed to meet additional
demand.
365. (c) Work-in-process inventory level is high
Work-in-process inventory will be high in forward scheduling because jobs are assigned based on
earliest available time slots. As the jobs start at the earliest possible time, they are completed
before they are required at subsequent work centers.
366. (d) There are large variations in the production process and the equipment is designed
for a broad range of applications
There are few variations in the production process for repetitive operations. In these operations,
labor is trained and the equipment designed for a narrow range of applications.
367. (b) Flextour approach
Under Flextour, employees are given some freedom in choosing their start time, but they must
work eight hours a day.
368. (a) Help sequence jobs in a way that idle time is minimized
Gantt charts do not help sequence jobs in a way that idle time is minimized. This is possible
through the use of Johnsons sequencing rules.
369. (c) It helps maximize the number of service workstations required
Queuing analysis helps determine the optimum (not maximum) number of workstations required to
meet demand.
370. (c) Lower, higher
The lower the critical ratio, the higher the priority in sequencing the job in the next days
production activities.
371. (c) 0.714, 0.857, 1.400
Critical ratio = Planned time remaining / actual work remaining
Job Due
Date
Actual work
remaining
Planned time
remaining
Critical ratio
1 25 7 25-20 = 5 0.714
2 32 14 32-20 = 12 0.857
3 27 5 27-20 = 7 1.400
372. (a) Job 1
The critical ratio for job 1 is the least at 0.714. Hence, it is given first priority over job 2. Job 3 is
already ahead of schedule.
Part A
111
373. (d) Critical ratio
The critical ratio method is a job sequencing technique an operations manager can use to verify
whether a job is on schedule. Whatever the method employed, the process of scheduling involves
three activities: routing, loading and dispatching.
374. (d) Maximizing resource allocation
One of the basic objectives of scheduling jobs is to optimize the resources allocated to meet
customer requirements.
375. (a) Loading
When assigning specific jobs to each work center, loading decides capacity limitations of centers
as well.
376. (a) Flextime approach
Under flextime, employees are given the option of choosing their work timings provided they work
for a specified number of hours in a given time period, say a week.
377. (d)
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M 1 X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M 2 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3
In forward scheduling, both jobs start immediately after job orders are received. Job X starts on
machine 1 (M1) and job Y on machine 2 (M2). X runs on M1 for 3 hours and Y runs on M2 for 2
hours. Y remains idle for the third hour as X is under process on M1. In the fourth hour Y goes to
M1 for 3 hours and X goes to M2 for 2 hours. Hence in the sixth hour X has to wait to be
processed on M1 as Y is still on M1. In the seventh hour, X goes to M1 for 2 hours and Y goes to
M2 for 1hour. Hence, Job Y gets completed at the end of seventh hour and Job X gets completed at
the end of eight hour.
378. (b)
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
M1 X1 X1 X1 Y2 Y2 Y2 X3 X3
M2 Y1 Y1 X2 X2 Y3
In backward scheduling, the schedule is calculated backwards from the due date of completion. As
this is nine hours, scheduling starts at the ninth hour and works backwards. Here the last sequence
for jobs X and Y are placed at the ninth hour. X3 needs 2 hours and Y needs 1 hour. M1 is
occupied up to the eighth hour. In the seventh hour Y2 is processed on M1 and X2 on M2. Y2
requires 3 hours and X2 requires 2hours. Y2 would be on M1 until fifth hour and X2 would be
completed in the sixth hour itself. In the fourth hour, X1 must be completed on M1 and Y1 on M2
in the third hour. Hence, X1 starts in the second hour and Y1 in the third hour.
379. (b) 8 hours
In forward scheduling, both jobs start immediately after job orders are received. Job X starts on
machine 1 (M1) and job Y on machine 2 (M2). X runs on M1 for 3hours and Y runs on M2 for
2hours. Y remains idle for the third hour as X is under process on M1. In the fourth hour Y goes to
M1 for 3 hours and X goes to M2 for 2 hours. Hence in the sixth hour X has to wait to be
processed on M1 as Y is still on M1. In the seventh hour, X goes to M1 for 2hours and Y goes to
M2 for 1hour. Hence, Job Y gets completed at the end of seventh hour and Job X gets completed at
the end of the eighth hour.
Operations Management
112
380. (c) 7 hours
In forward scheduling, both jobs start immediately after job orders are received. Job X starts on
machine 1 (M1) and job Y on machine 2 (M2). X runs on M1 for 3hours and Y runs on M2 for
2hours. Y remains idle for the third hour as X is under process on M1. In the fourth hour Y goes to
M1 for 3 hours and X goes to M2 for 2 hours. Hence in the sixth hour X has to wait to be
processed on M1 as Y is still on M1. In the seventh hour, X goes to M1 for 2hours and Y goes to
M2 for 1hour. Hence, Job Y gets completed at the end of the seventh hour and Job X gets
completed at the end of eighth hour.
381. (b) 2 hours
In backward scheduling, the schedule is calculated backwards from the due date of completion. As
this is nine hours, scheduling starts at the ninth hour and works backwards. Here the last sequence
for jobs X and Y are placed at the ninth hour. X3 needs 2 hours and Y needs 1 hour. M1 is
occupied up to the eighth hour. In the seventh hour Y2 is processed on M1 and X2 on M2. Y2
requires 3 hours and X2 requires 2 hours. Y2 would be on M1 until the fifth hour and X2 would be
completed in the sixth hour itself. In the fourth hour, X1 must be completed on M1 and Y1 on M2
in the third hour. Hence, X1 starts in the second hour and Y1 in the third hour.
382. (c) 3 hours
In backward scheduling, the schedule is calculated backwards from the due date of completion. As
this is nine hours, scheduling starts at the ninth hour and works backwards. Here the last sequence
for jobs X and Y are placed at the ninth hour. X3 needs 2 hours and Y needs 1 hour. M1 is
occupied up to the eighth hour. In the seventh hour Y2 is processed on M1 and X2 on M2. Y2
requires 3 hours and X2 requires 2hours. Y2 would be on M1 until the fifth hour and X2 would be
completed in the sixth hour. In the fourth hour, X1 must be completed on M1 and Y1 on M2 in the
third hour. Hence, X1 starts in the second hour and Y1 in the third hour.
383. (a) Routing
It explains the sequence of operations and processes to be followed to produce a particular product.
Routing determines what work is to be done and where and how it is to be done. Hence, routing
describes the specification of workflow.
384. (b) Loading
Loading is defined as assigning specific jobs to each work center for the planning period. Loading
of jobs is done upto the standard capacity of the workstation.
385. (b) Shortest processing time
Here, jobs are processed in the shortest time. Under this rule, jobs with shorter processing times
get completed earlier than jobs with longer processing times. This rule ensures that minimum
number of jobs are left for processing.
386. (c) A D C E B
From the given data, the earliest due dates are given below:
A 4 days, B 8 days, C 6 days, D 5 days, and E 7 days. Therefore, the order of jobs is A
D C E B.
387. (a) 4.2 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Flow Time Delay
A 4 4 0 + 4 = 4 4 - 4 = 0
D 2 5 4 + 2 = 6 6 5 = 1
C 4 6 6 + 4 = 10 10 6 = 4
E 3 7 10 + 3 = 13 13 7 = 6
B 5 8 13 + 5 =18 18 8 = 10
Average time = (0+1+4+6+10)/5 = 21/5 = 4.2 days
Part A
113
388. (c) 13 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Flow Time Delay
B 5 7 0 + 5 = 5 5 5 = 0
A 4 4 5 + 4 = 9 9 5 = 5
C 4 6 9 + 4 = 13 13 6 = 7
E 3 7 13 + 3 = 16 16 7 = 9
D 2 5 16 + 2 = 18 18 5 = 13
Hence, the total delay for job D is 13 days.
389. (b) 6.8 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Flow Time Delay
B 5 7 0+5 = 5 5 5 = 0
A 4 4 5+4 = 9 9 5 = 5
C 4 6 9+4 = 13 13 6 = 7
E 3 7 13+3=16 16 7 = 9
D 2 5 16+2 = 18 18 5 = 13
Average delay = (0+5+7+9+13) /5 = 34/5 = 6.8 days
390. (c) 11 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Time Flow Delay
A 4 4 0 + 4 = 4 4 4 = 0
B 5 8 4 + 5 = 9 9 8 = 1
C 4 6 9 + 4 = 13 13 6 = 7
D 2 5 13 + 2 = 15 15 5 = 10
E 3 7 15 + 3 =18 18 7 = 11
The last job performed using this rule is E and the delay for job E is 11 days.
391. (d) 5.8 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Time Flow Delay
A 4 4 0+4 = 4 4 4 = 0
B 5 8 4+5 = 9 9 8 = 1
C 4 6 9+4 = 13 13 6 = 7
D 2 5 13+2 =15 15 5 = 10
E 3 7 15+3=18 18 7 = 11
Average delay = (0+1+7+10+11)/5 = 29/5 = 5.8 days
Operations Management
114
392. (a) A
Job A has the shortest slack time as the difference between due date and processing time for job A
is (4 4) = 0 days.
393. (d) 11 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Time Flow Delay
A 4 4 0+4 = 4 4 4 = 0
C 4 6 4+4 = 8 8 6 = 2
D 2 5 8+2 =10 10 5 = 5
B 5 8 10+5 =15 15 8 = 7
E 3 7 15+3=18 18 7 = 11
Jobs D and B are having the same slack time of three (5 2) & (8 5) days respectively. But job D
has a processing time of 2 days, which is less than for job B (5 days). Here D is dispatched before
B. But the last job to be processed using this rule is E, which has a maximum slack time of 4 (7 3)
days. The time delay for job E is 11 days.
394. (b) 5.0 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Time Flow Delay
A 4 4 0+4 = 4 4 4 = 0
C 4 6 4+4 = 8 8 6 = 2
D 2 5 8+2 =10 10 5 = 5
B 5 8 10+5 =15 15 8 = 7
E 3 7 15+3=18 18 7 = 11
Average delay = (0+2+5+7+11)/5 = 25/5 = 5 days
395. (b) 4.4 days
Job Sequence Processing Time Due Date Time Flow Delay
D 2 5 0+2 =2 0
E 3 7 2+3=5 0
A 4 4 5+4 = 9 9 4 = 5
C 4 6 9+4 = 13 13 6 = 7
B 5 8 13+5 =18 18 8 = 10
Average time delay = (0+0+5+7+10)/5 = 22/5= 4.4 days
396. (a) Earliest due date
Average delay using each of these rules (calculated earlier) is as follows:
Earliest due date = 4.2 days, First in, first serve = 5.8 days, Shortest processing time = 4.4 days,
and Slack time remaining = 5.0 days. Hence, to reduce the average delay to a minimum, earliest
due date rule can be suggested for the job A, B, C. D, and E.
397. (b) Repetitive operations
Repetitive operations are also called continuous operations as they are performed continuously to
produce goods in bulk. Here, stock-outs can hinder the production process and lead to high costs
for the firm.
Part A
115
398. (d) 5 weeks
Job A was processed on machine X in the first two weeks and on machine Y in the 6
th
and 7
th
weeks. Finally, it is processed on machine Z in week 8. The total time is 5 weeks.
399. (a) Machine X
Machine X was the most utilized. From the Gantt chart, it is clear it was used for 6 weeks.
Machines Y and Z were utilized for 4 weeks each.
400. (d) All of the above
Johnsons job sequencing rules help the operations managers in minimizing processing time,
maximizing the operating efficiency, and reducing the operating costs.
401. (c) G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im-1
H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im
A problem of n jobs and m machines can be simplified to n jobs and two machines to use
Johnsons sequencing rule. Two fictitious machines (G
i
and H
i
) are introduced where
G
i
= A
i1
+A
i2
+A
i3
++A
im-1
and H
i
= A
i2
+A
i3
+A
i4
++A
im
402. (c) Rate of arrival of customers is greater than the rate at which service is rendered
In a service organization, when the arrival rate of customers is greater than the rate at which
service is rendered to each customer a queue forms.
403. (d) To minimize processing time of jobs
Waiting time in a queue often proves costly to service firms and so they use queuing analysis to
minimize this as far as possible. Queuing also helps operations managers to determine the
optimum number of service stations required, which can lead them to striking a balance between
waiting costs and cost of providing additional service stations. Johnsons job sequencing rules is
useful for proper scheduling of jobs. It helps firms minimize the processing time of jobs
404. (b) Planned time remaining / work still remaining
Critical ratio is calculated by dividing the actual time remaining to complete work by work
remaining (in time units). If the critical ratio of an operation is less than one, the operation is
behind schedule. If the critical ratio is more than one the operation is being processed ahead of
schedule.
405. (d) E
Critical ratio is calculated by dividing the planned time remaining to complete the work by actual
work remaining (in time units). Critical ratio for Project A = (150 -100)/60 = 0.833, Critical ratio
for Project B = (135 - 00)/30 = 1.167, Critical ratio for Project C = (180 -100)/70 = 1.143, Critical
ratio for Project D = (140 -100)/45 = 0.889, Critical ratio for Project E = (120 -100)/30 = 0.667.
Projects A, D and E have critical ratio less than one. Hence they are on priority as they are behind
schedule. Among them Project E has the least critical ratio of 0.667 and therefore is of highest
priority.
406. (c) B and C
If the critical ratio of an operation is less than one, it can be said the operation is behind schedule.
If the critical ratio is more than one, the operation is being processed ahead of schedule. Of the five
projects, only B and C have a critical ratio more than one. Hence, B and C are ahead of schedule.
407. (c) E A D C B
The lower the critical ratio, the higher the priority for sequencing that job during further
production. Hence, by arranging the five projects in order from least critical ratio to highest critical
ratio, we get, E A D C B.
Operations Management
116
408. (d) To minimize inventory costs
Minimizing inventory costs is the objective of inventory management. Scheduling is concerned
with meeting customer requirements on time by carrying out the production process efficiently and
by reducing service delays.
409. (a) ERP uses multiple databases to store information
ERP uses a centralized database to integrate the diverse business functions like marketing,
production, finance, etc. This facilitates information flow between departments. The disadvantage
of ERP implementation is that it takes a long time and involves huge costs.
410. (c) Advances in software and hardware technologies
Since the 1970s, advancements in computer and communication hardware have changed the entire
ERP implementation process and have made it highly complex.
411. (d) Marketers can take speedy decisions in a dynamic market environment
Options (a), (b) and (c) are factors that have led to the need for business process reengineering.
Option (d) is a consequence of BPR implementation. Corporate restructuring can help marketers
take speedy decisions in a dynamic market environment.
412. (b) To provide an overview of operations without focusing on processes and systems
The purpose of business modeling is to provide a general overview of the operations of a business
without going into the technical details of processes and systems. It defines the activities
performed and workflow structure in a broad manner.
413. (d) Market structure
A good business model should be comprehensible, coherent and complete. It should define clearly
the different systems and subsystems of a business. A business model is developed on the basis of
the organization's goals, objectives and strategic plans. The market structure is external to the
organization and is one of the many factors that helps decide on the organization's goals, objectives
and strategic plans.
414. (b) i, ii, iv
Integration of data across departments helps in better connectivity and smooth flow of information.
It reduces data redundancy and ensures availability of right information to the concerned
department or personnel.
415. (b) ii and iii
The technology used should be scalable and should support open and non-proprietary technology
standards. These characteristics reduce risk and ensure the compatibility of the systems with other
IT solutions. The technology should be adaptable to any future changes in business processes
without excessively incurring large investment in up gradation.
416. (d) None of the above
Cost of consulting, process redesign and training are incurred in various stages of ERP
implementation.
417. (b) i and ii
Information gathered from mapping and gap analysis is used for customization of the ERP
package. The other two options are not basic requirements for customizing an ERP package.
418. (d) Steering committee
The key activity of the steering committee is to monitor the ERP implementation process
continuously in order to identify deviations, cost overruns, resource requirements etc, during ERP
implementation.
Part A
117
419. (a) To assess the readiness of the organization to accept change
Defining corporate needs before ERP implementation helps the organization to assess its readiness
to change. Implementing an ERP system involves the redefinition of the roles of different
functional departments and the authority and responsibility of individuals throughout the
organization. Hence, organizations have to adapt to these changes as quickly as possible.
420. (b) To assess the implications of the changes
Even though an organization may be willing to adapt to changes, it may not be able to assess the
implications of the changes. Hence, it must undergo a brief business process redesign exercise
before actual implementation.
421. (d) i, ii and iii
To carryout successful ERP implementation, the members of the steering committee should be
able to understand business redesign and integration. The steering team should be trained in
process mapping and reengineering methodology and it should be fully involved in the process
redesign so that it can guide the team members (implementation team) properly.
422. (d) Customized products produced at reasonable costs
Customized products produced at reasonable costs is an example of an order winner.
The remaining are examples of qualifiers that is a basic requirement for any ERP marketer.
423. (c) Set up tough quality targets
Tough quality targets can be set up if the organization uses quality as the order winner. Further,
when quality is given more importance, price of the product shoots up as quality never comes
cheap.
424. (c) Durability
Durability of a product is defined as the measure of the products life in terms of both its technical
and economic dimensions.
425. (b) Product range
Product range implies all the products that are offered by an organization. HDFC Bank offers a
wide range of products like deposits, loans, bank accounts, NRI products, insurance products,
investment products like mutual funds, pension plans, etc.
426. (a) Modes of transportation, distribution and inventory management
Logistics is concerned with transportation of materials, distribution of finished products, inventory
of materials and finished products in warehouses, etc. Selection of suppliers for supply of raw
materials is a function of inventory management. Layout of warehouses, administrative facilities
and plants is associated with facilities location and layout decisions. Effective management of
material flow in the organization is associated with materials management.
427. (b) i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi, vii
To improve ESCM implementation, the following activities should be undertaken:
1) Understand and evaluate the level of integration within the organization, 2) Determine the
number of suppliers with direct influence over products or services delivered to customers across
the entire supply chain, 3) Divide suppliers into different categories: first tier, second tier and so
on, 4) Define customer base in term of sales, profitability, size, etc., 5) Improve information
infrastructure within the organization to accommodate ESCM requirements, 6) Constitute a team
with representation from various functions within the organization and representatives from
suppliers and customers to plan and carry out implementation, 7) Identify leaders capable of
guiding the implementation process competently.
Operations Management
118
428. (d) Customer
Supply chain members include manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, wholesalers, retailers,
logistic service providers, etc. Customers are the basis for all supply chain activities. Supply chain
members strive hard to meet customer demand for products they deal with.
429. (d) Improved customer satisfaction
Tangible benefits include revenue growth, improved facility utilization, optimized inventory
management, etc. Intangible benefits include improvement in quality, improvement in customer
satisfaction and enhanced customer and supplier relationships.
430. (a) Facilities close to the target market improve the performance of the supply chain
The capacity and location of a facility has a significant effect on the performance of the supply
chain. More facilities close to the customer may improve supply chain effectiveness although cost
of maintenance of so many facilities will be high.
431. (c) Firms never custom design a logistic network to meet the individual requirements of
customers
Companies usually design logistics systems either to meet average service requirements of all
customers or to satisfy the toughest requirements of a single customer. However, both these
approaches lead to poor resource utilization. Hence, a certain amount of customization is built into
the network to meet specific requirements of customers.
432. (a) Quality and performance management
Quality and performance management is a component of SCM and not considered a principle of
SCM. All other options mentioned are principles of supply chain management.
433. (b) Supplier
The order-to-delivery process can be used to evaluate suppliers performance on the basis of
criteria like on-time delivery, cost, defects, lead time, flexibility in scheduled time, etc.
434. (b) i, ii, iii
The quality and performance component is related to initiatives that organizations and suppliers
take towards improving and maintaining quality standards. It helps identify quality defects in
supplier products and facilitates cooperation between suppliers and the manufacturer to improve
the quality of items supplied.
435. (c) Strive for heavy discounts to improve the organizations short-term profitability
To improve supplier satisfaction, organizations should have clear and mutually understood rules of
relationship. Organizations should show commitment for long-term profitability and success of
suppliers. This commitment would require suppliers involvement in new product development
and improvements in current products or services. But focus on discounts to increase short-term
profits will hamper development and maintenance of long-term relationships with suppliers.
436. (d) i, ii, iii
Measurements provide information on inputs, outputs, performance of business processes,
suppliers performance, etc. The latter can be measured using metrics like on-time delivery
performance, quality, etc. Periodic evaluation of performance of processes, programs and systems
is associated with periodic review, another SCM enabler.
437. (a) Retailer
Traditionally, retailers have been the closest to consumers. Owing to this proximity, retailers
assume the role of monitoring consumer preferences. But the use of the Internet and direct sales
are changing all that. Consumers are now interacting with different entities in the purchasing
process.
Part A
119
438. (a) i, ii, iii
The most essential pre-requisite for a supply chain to become a demand chain is to share
information collected by various members. Information sharing allows all members to identify the
product and packaging requirements, marketing opportunities, etc. and can plan activities
accordingly. Every member of the demand chain, whether they design, manufacture, market, sell
or transport a specific product, needs to monitor consumer needs and wants. The members in
todays emerging demand chains are the same as those in traditional chains, but their respective
roles and responsibilities have changed.
439. (d) Value analysis
Value analysis is not a method for collecting customer information. It deals with the process of
identifying components with the most value in the production process. Some methods used to
collect customer information include point-of-sale databases, focus groups, quantitative surveys,
shadowing of consumers, in-house research, etc.
440. (c) i and ii
There are two common misconceptions in the supply chain concept. One is that all consumers buy
from retailers. This can be true in most cases but many consumers are shifting to other channel
members who deliver products at the right time and at reasonable prices. The second
misconception is that industrial marketers should monitor only their customers and need not bother
about end-users. They should not ignore the fact that demand for their products is based on end-
users.
441. (c) By reducing communication costs
ESCM helps supply chain partners communicate through the Internet. Communication through
Internet is quicker and cost effective. As the supplier can access information regarding inventory
and procurement automatically, the purchasing department can lessen its involvement in minor
transactions and focus on high value activities like vendor selection and sourcing. The other two
options are not related to procurement.
442. (b) i, ii and iii
ESCM results in an extended organization with suppliers being electronically linked. Hence, it
provides instant information about the status of inventory levels to suppliers. As and when the
inventory is depleted, suppliers replenish with just adequate levels to carry out production. Thus,
there is no need to maintain a large inventory in the organization.
443. (a) Information security
Security of information is the most sensitive issue when information is shared or exchanged over
the Internet. An organization has to ensure that the rightful recipient views the information. All
other options are some types of information shared over the Internet between supply chain
partners.
444. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
Teamwork, discipline, employee performance, and supplier involvement are considered important
elements for successful implementation of the JIT system in an organization.
445. (d) All of the above
All options correctly depict the characteristics of a JIT production system.
446. (a) Produce in small lots
Traditionally, firms manufacture products in large lots, resulting in a lower number of machine set-
ups. But JIT manufacturing firms undergo a larger number of set-ups as they produce in small lots.
Operations Management
120
447. (c) It is a push system
JIT system is a pull system rather than a push system.
448. (b) Varying workstation loads
Just-in-time manufacturing helps firms maintain uniform loads at workstations. Some of the
characteristics of a JIT system are uniform workstation loads, small lot sizes, closer supplier ties,
maintenance of high quality, quick and economic setups, flexible facilities and multi-skilled
workforce, preventive maintenance, and continuous improvement.
449. (d) Jikoda
Jikoda means autonomation. This approach enables machines to be autonomous and automatically
detect defects.
450. (c) Just-in-time manufacturing
The Just-in-time concept states that 'nothing is produced until it is required.' The practice of JIT
aims at assembling finished products just before they are sold, sub-assembling just before products
are assembled and fabricating components just before sub-assemblies are done.
451. (c) The relationship should be profitable to both the firm and the supplier
Under the JIT system, the relationship should be profitable to both the supplier and the JIT firm in
the long run. Hence, the JIT firm and the supplier should work towards the betterment of each
other by abiding to the terms of the contract.
452. (d) The JIT firm always maintains only one supplier for each type of material
JIT firms maintain fewer suppliers, but they are more than one. JIT firms normally share their
production plans and schedules with suppliers to enhance their understanding of the production
and supply the material at the right time. They also help suppliers with their expertise and suggest
ways to improve quality and productivity. This will help firms improve the quality of end products.
When the firms plan to introduce new products, they also take suggestions from suppliers
regarding product design and types of materials that can be used to improve quality as well as
profitability.
453. (b) Communication
Communications play an important role in establishing a good partnership. The JIT firms can
establish a buyer - quality engineering team that stays in constant touch with suppliers. This
reduces potential miscommunication with suppliers. They should also inform the JIT firm about
new programs undertaken by them to improve quality and ensure timely delivery of supplies.
454. (d) Suppliers purchase new machinery, hire and train labor to meet requirements
Option (d) talks about time to make changes to meet demand. Option (a) talks about linearity in
production, option (b) talks about communication, and option (c) talks about trust.
455. (c) Each worker in the firm considers the next worker in the production line as a
customer
In a JIT firm each worker considers his/her next worker in a production line as his/her customer.
This is because the work done by him/her passes to the next worker for further processing.
456. (b) Large lot sizes
Firms that follow JIT type of manufacturing system maintain inventory in the smallest possible lot
sizes. This is required as small lot sizes reduce cycle inventory (the excess of inventory, above the
safety stock, that is carried between two orders), cut lead times and also help in achieving a
uniform workload. JIT manufacturing systems follow uniform workstation loads where material is
fed to the workstation uniformly and uniform output is produced across different workstations.
Besides, these firms have flexible facilities and quick and economic set-ups.
Part A
121
457. (a) i, ii and iii
Traditionally, firms manufacture products in large lots, resulting in a lower number of machine set-
ups. But JIT manufacturing firms undergo a larger number of set-ups as they produce in small lots.
Therefore, JIT manufacturing firms require quick and inexpensive setups to minimize the
disadvantages of having more number of set-ups and higher costs.
458. (c) i and ii
In a JIT production system, workers must be capable of performing more than one operation.
Hence, the entire workforce is trained continuously (at regular intervals) to develop a variety of
skills to perform any function the firm requires. A worker is trained to perform several operations
rather than being limited to a single assigned operation.
459. (a) i, ii, iii
The successful implementation of a JIT system is greatly dependent on its ability to reduce set-up
times. JIT firms engage specialists and consultants to train workers to reduce set-up times. Firms
adopt the following steps to reduce set-up times: 1) Analyze existing set-up procedures, 2)
Separation of internal and external set-up activities and 3) Convert internal set-up activities into
external set-up activities.
460. (a) Eliminating external demand variations
External demand variations cannot be eliminated by using the JIT system. By using JIT principles,
firms can reduce wastage that arises during the production process such as the waste of
overproduction, of time spent in waiting, in transportation and movement, in processing, in
keeping excess inventory and in defective parts.
461. (d) Warranty
All the options are functions of quality except warranty, which is an external failure cost, due to
poor quality of product.
462. (a) Display the measurements of every item being produced
Control charts do not give the measurement of every item being produced. They only display the
upper and lower limits for process variables or attributes and signal when a process is no longer in
control, when the variable is outside the upper or lower limit. Control charts for variables are used
to evaluate the mean and variability of the process distribution i.e. the average outgoing quality of
each lot. Control charts for attributes ensure that the items after inspection are identified either as
defective or non-defective.
463. (a) The process is out of control and the cause should be established
If the values fall outside the control limits then the process is considered out of control. Remedial
action has to be taken to rectify these discrepancies.
464. (c) 67.65
Upper Control Limit =D
4
R
, Lower Control Limit = D
3
R
.
D
3
and D
4
are constants whose values are based on the sample size.
R = R/n = 160/5 =32
UCL = D
3
R = 2.114 32 = 67.65
465. (c) Ambience
Ambience generally is associated with physical evidence, i.e., infrastructure, layout, furniture,
dcor, etc.
Operations Management
122
466. (a) Procurement of raw material
Quality control begins as early as procurement of raw materials. Raw materials have to be
procured with the right specifications and in the right quantity. This is part of preventive control.
467. (c) Average length of the rods in a lot
Average length of the rods in a lot is an example of the quality of rods and not productivity.
468. (c) Proper scheduling
Layout, slow processing equipment and inventory shortages can reduce productivity. But, proper
scheduling helps the operations mangers increase productivity.
469. (d) All of the above
Through proper scheduling, one can decrease the idle time of the material spent in waiting,
increase the running time of machinery and also decrease extent of wastage in the plant.
470. (d) Number of cars serviced in a period
Options - (a), (b), and (c) are inputs to calculate productivity in service organizations, while option
(d) is an output.
471. (d) All of the above
Training helps increase productivity through all these ways.
472. (a) Conformity
A products conformity to specifications can be identified by analyzing their defect rates during
production and the number of customer complaints after sale.
473. (b) Aesthetics
The aesthetics value of a product or service is influenced by individual preferences. While one
group of customers may regard a product as aesthetic, another may feel it is not tastefully
designed. So companies can use this quality dimension to cater to a niche market.
474. (c) The total cost of quality control is minimal
An optimal trade-off between the cost of inspection and the cost of undetected faults exists when
the cost of total quality control is minimal.
475. (b) Loss of goodwill
The cost of undetected faults includes customer complaints, loss of goodwill, product replacement
cost, product liability suits, product recall programs and returned products.
476. (c) Appraisal costs
Detection or appraisal costs are costs associated with evaluating the quality and performance of
products and machines. These include inward materials inspection, tests and inspection throughout
the transformation process, equipment maintenance, etc.
477. (d) Cost of returned products
Cost of returned products is an example of external costs. Internal costs include scrap, repair,
retesting of repaired products, downtime, loss due to process variability and disposition of
defective items.
478. (a) i and ii
Quality control charts can be broadly classified into control charts for variables and control charts
for attributes. Control charts for variables include X-Chart and R-Chart.
Part A
123
479. (c) P-chart
P-chart and C-chart fall under control charts for attributes. P-chart determines the proportion of
defects in a given sample while C-chart is used to determine the total number of defects in a
product.
480. (a) Kaizen
Kaizen is a concept under Total Quality Management (TQM). It emphasizes continuous
improvement in process, skill sets, systems or operations. All the other terms are associated with
just-in-time approach.
481. (c) Every employee at every level in the organization is responsible for quality
Maintaining quality is not just a prerogative of top management or the quality inspection
department but every employee at every level. Quality responsibilities result in employees being
more committed, motivated and creative in performing assigned tasks.
482. (c) 30.375
Sample
x
R
1 25 8
2 36 9
3 31 7
4 33 6
5 27 6
6 34 7
7 32 5
8 25 8
Total 243 56
Mean of means
375 . 0 3
8
243
n
x
x = =
=
483. (b) 7.0
Sample
x
R
1 25 8
2 36 9
3 31 7
4 33 6
5 27 6
6 34 7
7 32 5
8 25 8
Total 243 56
7
8
56
n
R
R = =
=
484. (a) 32.986
Upper control limit is given by the formula UCL = x + A
2
R
= 30.375 + (0.373 7) = 32.986
485. (a) 27.764
The formula to calculate lower control limit is LCL = x - A
2
R
= 30.375 (0.373 7) = 27.764
Operations Management
124
486. (b) 0.952
The formula for lower control limit in an R-chart is LCL = D
3
R
= 0.136
7 = 0.952
487. (c) 13.048
The formula for upper control limit in an R-chart is UCL = D
4
R
= 1.864
7 = 13.048
488. (a) 3.14
Sample Number of Defects
1 5
2 3
3 4
4 2
5 3
6 1
7 4
Total 22
Average number of defects, c = 22/7 = 3.14
489. (c) 8.546 and 0
Control limits for a c-chart is given by the equations
UCL = c + 3 c
LCL = c - 3 c
where, c is the average number of defects produced by a process.
UCL = 3.14 + 3
14 . 3
= 8.456
LCL = 3.14 3
14 . 3
= -2.176
As LCL is negative it can be taken as zero.
490. (c) Type II error
The probability of accepting a lot with some percent of defective items is termed as consumers
risk or Type II error.
491. (b) Customer
TQM believes that each department should treat other departments as its customers.
492. (b) OC curve
The operating characteristics (OC) curve is an important feature of acceptance plans. It shows how
well an acceptance plan differentiates between good and bad lots. The OC curve is used to
determine the limit of average outgoing quality.
Part A
125
493. (c) Quality training
Prevention costs include investments made in machinery, technology and education/training
programs to reduce defects. It also includes costs to administer the firms quality program, data
collection and analysis and vendor certification. Equipment maintenance is a detection or appraisal
cost. Disposition of defective items is an internal failure cost and warranty charges are an external
failure cost.
494. (d) Regular monitoring of vital parameters of a machine
Predictive maintenance is concerned with inspecting vital signs of the machine regularly to
identify the health of the system. Some objectives of remedial maintenance are to minimize
production losses by getting the equipment back into working condition as quickly as possible, to
minimize investments in spare parts and standby machines used when equipment is under repair,
and to perform appropriate maintenance based on the extent of problem.
495. (c) Reducing machine vibration
Reduction of machine vibrations does not come under irregular preventive maintenance. It is a
form of remedial maintenance.
496. (a) Improving efficiency of raw materials purchase
Improving the efficiency of raw materials purchase in an organization is not associated with
maintenance management. It is more related to materials management.
497. (a) Minimizing the availability of the firms assets for production purposes
One of the goals of maintenance management is to maximize (not minimize) the availability of the
firms assets for production.
498. (d) Marketing manager
A facilities manager has to plan activities in facilities in consultation with top management,
production managers, architects, designers, etc., who are directly related to the management of
facilities. Marketing managers are seldom consulted for planning a facility.
499. (b) Out-tasking
Out-tasking involves hiring outside workers or specialized vendors to carry out a particular task.
Out-tasking (i.e. hiring individuals, specialized vendors) is done more frequently than outsourcing
(i.e., hiring of full-service, single source vendors).
500. (b) i, ii, iv
If the client organization gives control of its facilities to an external agency, it is virtually like
inviting the agency to gain monopoly over its facilities. This can lead to loss of control over crucial
decisions like alterations, expansion of facilities or cost savings. The client may also lose the
power to control any deviations in vendor performance. Loss of control can lead to strained
relationships between client and vendors and become the cause for serious conflicts. The service
providers need to raise profits can lead to exploitation of client resources or reduction in quality of
work.
501. (a) ii and iii
In a long term contract, vendors can easily cover initial costs and have scope to make more profits
by revising prices. Firms lose control over activities if they are in the hands of the vendor.
502. (c) i and iii
Usually vendors replace skilled workers with semi-skilled workers in a clients organization either
to decrease direct operating costs or to use them for a new client.
Operations Management
126
503. (d) Increases operational costs
Advantages of outsourcing include increase in quality of work and flexibility of operations,
reduced operation costs and more focus on core competencies.
504. (a) Machine failures do not hinder productivity
Machine failures can actually reduce productivity halting the production process. Equipment
malfunction can reduce product quality and it may prove expensive to repair them
505. (c) i, ii, iii
Mr. Kumar can help improve productivity, increase the life of assets and machinery, preserve
equipment value and maximize the salvage value of machinery.
506. (b) Civil maintenance
Civil maintenance includes building construction and maintenance, maintenance of service
facilities like water filters, air conditioning, plumbing, etc. Other activities include maintaining
drainage systems, fire fighting equipment, security systems, waste disposal, etc.
507. (c) Electrician
As the 5hp motor is an electrical component, it has to be maintained and serviced by a qualified
electrician.
508. (c) i/r, ii/p, iii/s, iv/q
A plumber maintains water supply pipes, an electrician takes care of lighting equipment,
housekeepers are responsible for cleanliness of buildings and instrumentation personnel maintain
and service routers.
509. (c) Preventive maintenance involves regular servicing of equipment while predictive
maintenance involves monitoring of equipment continuously
The objective of preventive maintenance is to service machines regularly so that equipment
functions satisfactorily under optimum load conditions without breakdown or reduction in
efficiency. Predictive maintenance involves identification of possible problems before they occur.
Options a & b are similar for both types of maintenance operations.
510. (a) i, iii, iv
Any abnormal vibration in equipment indicates that it is not functioning properly in terms of
precision cutting. Quality and productivity can come down drastically. The vibration also indicates
that the equipment needs maintenance.
511. (a) Preventive maintenance
Periodic maintenance and irregular preventive maintenance fall under preventive maintenance.
Periodic maintenance activities are conducted at regular intervals, i.e. weekly, monthly etc.
512. (b) Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is taken up when problems or indications of problems are detected in
machinery and equipment. Problems do not mean that the equipment is not functioning properly.
But it indicates that such problems or indications can cause breakdown of machinery in future if
they are neglected.
513. (b) Cost of replacing the entire machine
Cost of replacing the entire machine is associated with remedial maintenance where the entire
machine has to be replaced with a new machine due to breakdown or failure.
514. (a) Predictive maintenance
Condition Monitoring refers to monitoring the performance of machinery to spot indications that
may lead to failure or breakdown. It is associated with predictive maintenance.
Part A
127
515. (d) Richter scale
The first three options are examples of instruments used in condition monitoring. Option (d) is
used to measure earthquake intensity.
516. (a) Remedial maintenance is taken up when machinery breaks down
Remedial maintenance is performed only when there is breakdown or failure of machinery. So, it
is reactive in nature. Preventive and predictive maintenance are proactive in nature.
517. (d) To minimize failure or malfunction to the lowest possible extent
The objective of preventive maintenance is to minimize failure or malfunction to the lowest
possible extent. Remedial maintenance, on the other hand, is reactive in nature and is done after a
machine breaks down.
518. (c) 7.98 months
Mean time between failure = i.P
i
= (1x0.04) + (2x0.04) + (3x0.05) + (4x0.05) + (5x0.06) + (6x0.06) + (7x0.10) + (8x0.1) + (9x0.1)
+ (10x0.1) + (11x0.15) + (12x0.15)
= 0.04 + 0.08 + 0.15 + 0.20 + 0.30 + 0.36 + 0.7 + 0.8 + 0.9 + 1.0 + 1.65 + 1.80
= 7.98 months
519. (b) 1.50
Number of break-downs per year = Number of months / mean time between failures
= 12/7.98 = 1.50
520. (a) 37.50
There are 25 machines in the plant.
Hence, the number of break-downs per year for 25 machines = 25 x 1.50 (number of break-downs
per year for a machine). This is equal to 37.50
521. (d) Rs.320
Average cost of repairs per machine per occasion = 12000/37.5 = Rs.320
522. (d) 4.65
Given
N=15, t=2, P
1
=0.1, P
2
=0.2
B
1
= NP
1
where B
1
= number of break downs during the first month after service
= 15 x 0.1 = 1.5
B
2
= N(P
1
+ P
2
) + B
1
P
1
where B
2
= the number of break-downs expected between servicing if the
service is performed every two periods
= 15(0.1 + 0.2) + 1.5 x 0.1
= 4.5 + 0.15
= 4.65
Thus, the expected number of break-downs between servicing is 4.65
523. (c) 9.765
Given N=15, t=3, P
1
=0.1, P
2
=0.2, P
3
=0.3
From the previous question, we know that B1=1.5 and B2=4.65
B
3
= N(P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
) + B
2
P
1
+ B
1
P
2
Operations Management
128
= 15(0.1 + 0.2 + 0.3) + (4.65 x 0.1) + (1.5 x 0.2)
= 9 + 0.465 + 0.3
= 9.765
Thus, the expected number of breakdowns between servicing is 9.765
524. (d) Rs.21152.50
Total cost of maintenance for every 3 months = C
P
x N + C
R
x B
t
Where C
P
is the cost of preventive maintenance and C
R
is the cost of remedial maintenance.
TC = (650 x 15) + (5500 x 9.765)
= 9750 + 53707.5
= 63457.5
Average total cost of maintenance per month = TC/3 = 63457.5/3 = Rs.21152.5
525. (c) Identify problem estimate work to be done develop plan carry out sequence of
tasks
In maintenance planning, problems (if any) in machinery and equipment are identified first. Then,
an estimation of the amount and type of work to be performed is made. Based on the estimate,
plans are developed followed by implementing the sequence of tasks to be carried by different
personnel.
526. (b) Significance of tasks in maintaining production flow
Maintenance tasks are prioritized on the basis of their importance in maintaining a continuous
production process when maintenance resources are scarce.
527. (a) Ensuring sufficient inventory of frequently used tools and equipment within the plant
Maintenance managers often maintain inventories of equipment and materials required for
maintenance activities within the plant to reduce lead-time before repair can begin. Organizations
with production facilities in more than one location reduce inventory costs by storing basic and
frequently-used maintenance materials at each location, and occasionally-used materials at a
central location.
528. (c) ii, iii and iv
Breakdown in a manufacturing plant adopting JIT system can create a shortage of inputs for all
workstations and can hamper the productivity seriously. Hence, production workers are required to
do simple preventive maintenance at the beginning of every shift. And in case of major preventive
maintenance, they should assist maintenance specialists in the process.
529. (b) Facilities management
The primary objective of facilities management is to provide a clean and conducive work
environment and enable efficient and effective progress of the core functions of an organization, be
it manufacturing, distribution or research. Maintenance management is a primary function
associated with facilities management.
530. (b) Production of radiator caps
Production of radiator caps is a repetitive and regular process that cannot be classified as a project.
It is a process. A project is generally undertaken to solve a problem or take advantage of an
opportunity. It is short-term in nature. Examples of projects include new product development,
buying a new plant, or solving a production problem. Setting up a plant to manufacture radiator
caps is an example of a project.
531. (a) Slack time
Slack time refers to the amount of time that an activity can be delayed beyond its earliest start time
without extending the duration of a project.
Part A
129
532. (b) Earliest start time
The earliest start time is the minimum amount of time that must lapse before beginning an activity.
533. (d) All of the above
The benefits of a project plan are: it guides in project execution, help document project planning
assumptions and provides a baseline for progress measurement and project control.
534. (b) In linear programming dummy activities are added to paths to make them equal in
length
In linear programming, addition of dummy activities ensures that two activities do not have the
same beginning and end nodes. As a result the paths are not equal in length.
535. (a) Crashing is not effective when applied to tasks with zero slack
Crashing is also effective when applied to tasks with zero slack time. One of the steps in crashing
is to highlight the activities on the critical path with the smallest time-cost ratio and crash those
activities by ensuring that the reduced time is equal to the smallest slack value of the non-critical
activities.
536. (a)
From the table we can infer that activity A precedes B and C, activity B and D must precede E,
activity C precedes D, activity D precedes F, and activities E & F precede G.
537. (b) Dummy activities are used to ensure that two activities have the same beginning and
end nodes
Dummy activities ensure that two activities do not have the same beginning and end nodes. They
are the activities that do not utilize any time or resource but are introduced to indicate the
precedence relationship.
538. (d) It involves continuous flow of repetitive work
A project is a non-repetitive task that runs for a limited time to achieve the set objective.
539. (b) Event
An event is the outcome of an activity or group of activities. It represents the completion of some
activities and the beginning of some others in the network.
540. (d) It is the longest path of interrelated activities in a project with zero slack time
CPM is a networking methodology which is employed to compute the minimum time required to
complete a project and at the same time identify the sequence of tasks to be performed. The critical
path depicts the longest path of interrelated activities in a project with zero slack time.
541. (a) PERT
PERT and CPM are two important tools that are used to identify the best possible schedules in
project management. The other three options are used to schedule routine tasks to different
machines in a production process.
A
C
G B
D F
E
Operations Management
130
542. (c) Critical activities are those activities, which if delayed, extend the project duration
Critical activities are those activities which if delayed can extend the project duration. Therefore,
identifying critical and non-critical activities helps project managers determine which activities can
be delayed without affecting the project duration.
543. (b) Event
An event is the outcome of an activity or group of activities. It represents the completion of some
activities and the beginning of some others in the network.
544. (c) It is the maximum time an activity can take considering obstacles and unfavorable
circumstances
Pessimistic time for an activity is the maximum amount of time required to complete the activity
under unfavorable circumstances.
545. (d) Slack time
Also called float, slack time is a measure to determine the criticality of an activity. An activity
with more float is less critical and can be delayed in case of resource scarcity.
546. (b)
Only option A is the appropriate network diagram for the given situation. In option b, c and d,
there is an additional precedence relationship that activity B should precede activity C.
547. (c)
Activity A and activity B precede activities C, D and E, and activities D and E follow activity C.
Only option C fulfils this condition.
548. (d) (Latest start time) - (earliest start time)
Float or slack time is the difference between the latest start time and the earliest start time. It is a
measure for determining the criticality of an activity. An activity with more float is less critical and
can be delayed in case of resource scarcity.
549. (b) The project must have a large number of interrelated or overlapping activities
A project should not have too many interrelated or overlapping activities. Such activities make
application of PERT difficult.
550. (b) 2.17 weeks
Activities Optimistic
time t
o
Pessimistic
time t
p
Most likely
time t
m
t
e
( )
6
t 4t t
p m o
+ +
Variance
2
o p
6
t t
)
`
1-2 3 5 4 4 0.111
1-4 3 5 4 4 0.111
2-3 2 3 2 2.167 0.028
A
B
C
A
B
C
D
E
Part A
131
2-5 3 5 4 4 0.111
3-6 5 7 5 5.333 0.111
3-7 7 10 8 8.167 0.25
4-3 4 6 5 5 0.111
5-3 2 3 2 2.167 0.028
6-7 6 9 8 7.833 0.25
Total (Only
Critical Path
Activities)
23.333 0.611
[
Using the formula
( )
6
t 4t t
p m o
+ +
the expected time for the activity 5-3 is 2.17 weeks (approx.).
551. (a) 23.33
Refer table above
The expected time for the activities on the critical path 1-2-5-3-6-7 is
4 + 4 + 5.333 + 2.167 + 7.833 = (23.33 weeks)
552. (c) 0.611
Refer table above
The sum of the variances of the activities on the critical path 1-2-5-3-6-7 is
0.111 + 0.111 + 0.111 + 0.028 + 0.25 = 0.611
553. (b) 0.8023
cp
2
E D
Z
=
Where, D = desired project completion date = 24, E
= earliest expected project completion time =
23.333,
2
cp
= Sum of variance of critical path activities = 0.61.
From the formula, Z = (24 23.333) / 0.611= 0.85
P(z 0.85)
(From the standardized normal distribution function, F(z) table, the area under the normal curve
corresponding to z = 0.85 is 0.3023.)
Probability of completing in 24 weeks = 0.5 + P(0 z 0.85) = 0.5 + 0.3023 = 0.8023.
554. (a) 0.3336
cp
2
E D
Z
=
Where, D = desired project completion date = 23, E
= earliest expected project completion time =
23.333,
2
cp
= Sum of variance of critical path activities = 0.61.
From the formula, Z = (23 23.333)/ 0.611 = -0.43
P(z 0.43)
P(z 0.43)
(From the standardized normal distribution function, F(z) table, the area under the normal curve
corresponding to z = 0.43 is 0.1664.)
Probability of completing in 23 weeks = 0.5 P(0 z 0.43) = 0.5 0.1664 = 0.3336.
555. (d) Effectively handles situations in which two or more projects share available resources
PERT is effective in handling single project activities. But it is not useful in situations in which two
or more projects share available resources.
Operations Management
132
556. (c) 1250
Time-cost ratio
( )
( ) Crash time time Normal
cost Normal cost Crash
= (25000 20000) / (17 13)
= 5000/4 = 1250
557. (d)
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t
e
t
+ +
=
Expected time represents the mean of the optimistic, pessimistic and most likely times. Expected
time is calculated by using the equation
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t
e
t
+ +
=
Option a gives the formula for mean time between failures. Option b gives the formula for the
probability of completing the project within the desired completion period. Option c represents
activity time variances.
558. (b) A model with the basic product characteristics
The prototype of a product is a model with basic characteristics. However, it does not exhibit such
features like shape, final finishing, color, casing, etc.
559. (b) i, ii, iii
Computer Aided Design (CAD) is a technique used for designing the product and the process on a
computer. Computer systems assist in the creation, modification, analysis and optimization of a
design, but they cannot develop a prototype.
560. (c) Marketing department
Marketing department has direct contact with the customers and know their preferences. Hence
operations managers should communicate with the marketing department regarding the quantity
and quality of the products to be produced.
561. (b) Symbols
Unlike conventional systems that manipulate numbers to solve problems, artificial intelligence
systems manipulate symbols. Symbols are patterns and processes that can be combined into
expressions.
562. (c) Artificial intelligence
Computers, equipped with artificial intelligence (AI), have the capacity to perform tasks
commonly associated with the higher intellectual process characteristics of human beings such as
the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize or learn from past experience.
563. (a) Low level of maintenance
As automated systems are complex, they require higher levels of maintenance and the cost of
maintenance can be substantial.
564. (a) Computer integrated manufacturing
CIM refers to a computer application that integrates various computerized systems into a single
multi-functional system. For instance, budgeting, CAD/CAM, process controls, group technology
systems, MRP II, financial reporting systems, etc, are linked together. In many ways, CIM
represents the highest level of integration in manufacturing
565. (d) Flexible manufacturing system
FMS is a form of flexible automation in which several machine tools are linked to material-
handling system. A central computer controls all aspects of this, which is effective in producing
different items that have similar processing requirements.
Part A
133
566. (a) Automation
Automation is used to perform tasks without human intervention based on certain programmed
commands.
567. (d) Control
Automation is regularly used to control, monitor and execute manufacturing activities
568. (c) Consultancy activities
Automation can be conveniently implemented in jobs where repetitive and monotonous tasks are
done. It is also widely used for tasks that involve hazardous working conditions. Consultation is
more client-specific and varies across customers.
569. (c) Higher initial investment
Organizations have realized the potential of automating their operations in terms of lower wastage,
lower lead-times and higher productivity. However, the cost of automating can be very high.
570. (d) Higher product quality
Higher product quality is an advantage of automation. Besides, organizations have realized the
potential of automating their operations in terms of lower wastage, lower lead-times and higher
productivity.
571. (d) None of the above
Some of the benefits of using CAM are reliable information inputs, consistent product quality,
reduction in labor costs, better control and management of equipment and materials, improvement
in production rate, etc.
572. (c) FMS
A flexible manufacturing system contains different machining centers where several kinds of jobs
are processed. They are also enabled with automatic tools changing which allows them to change
the tools for the next job.
573. (c) CIM
CIM refers to a computer application that unites various computerized systems into a single multi-
functional system. For instance, budgeting, CAD/CAM, process controls, group technology
systems, MRP II, financial reporting systems, etc, are linked together in CIM.
574. (b) Multi-functional system
CIM integrates many functions into a single system and is capable of performing tasks associated
with all those integrated functions. Hence, it can be termed as a multi-functional system.
575. (d) Ability to reason
Computers equipped with artificial intelligence have the capacity to perform tasks that involve
reasoning and decision making.
576. (a) i and ii
CIM systems have so many advantages like reduced operating costs, improved quality, highly
reliable delivery performance, etc. However, the proliferation of CIM systems was extremely slow
due to huge implementation costs, lack of standardized interfaces between components of CIM and
slow acceptance of standardized communication protocols to support the integration.
Operations Management
134
577. (b) Professionals
Professionals or experts give information inputs to the expert systems. Their methods, logic and
analyses used in different situations are framed into rules that guide expert systems to provide
solutions to problems posed by the users.
578. (d) Facility location
Facility location is primarily concerned with deciding the location of a manufacturing plant.
Robots are rarely used in this process.
579. (c) Welding activities
In materials handling, the applications of robots include transfer of materials, material loading and
unloading. Spot welding is done under processing.
580. (b) Processing operations
Processing operations involve the manipulation of a tool by a robot to perform a particular action.
For instance, spray painting involves pre-programmed movements of the spray painting gun over
the area to be painted.
581. (d) Tasks where contingency decision making is needed
Robots must not be used in the areas where human presence is a must, especially in non-repetitive
or contingency situations.
582. (c) i, ii, and iv
Due to the increased coordination between the departments as well as with the suppliers, the
inventory can be reduced to a minimum. Customers can also track their own orders within the
vendors system to determine the status of their orders. EDI allows organizations to cut down their
inventory levels by planning for better production and shipment schedules.
583. (c) Member countries do not lift existing quantitative restrictions
Option (c) contradicts the spirit of globalization. Quantitative restrictions imply import tariffs,
quotas, duties, etc. against foreign countries from whom goods are imported. Under the WTO
agreement, by the year 2002, all member countries had to lift quantitative restrictions imposed on
foreign countries.
584. (b) Labor
India, like other Asian countries, has low-cost skilled manpower compared to the US and Western
Europe.
585. (a) Comparative advantage
The comparative advantage of a country can be defined as its ability to produce goods and services
cheaper than other countries. Organizations generally globalize their operations to take advantage
of such opportunities.
586. (b) Economies of scale
Economies of scale implies producing in huge quantities. It is known that as the volume of
production increases, cost of operations comes down, lowering the per unit cost. When the cost of
production decreases, lower price can be charged in the market.
587. (b) GMs strategy to outsource manufacture of $7.5 billion worth of auto components
Organizations operating globally can also obtain economies of scale in purchasing. Purchasing in
bulk can reduce costs. GM outsourced a huge volume worth $7.5 billion of components.
Part A
135
588. (c) Economies of scale in marketing
Organizations can also obtain economies of scale in their marketing function. They either use the
same salespeople or same promotion strategy or both for promoting their products in different
markets.
589. (c) ii and iii
Economies of scale can be achieved by making a product with minimum modifications. However,
modifications whether major or minor, are hurdles to achieve economies of scale.
590. (a) Economic impediment
When customer requirements in different national markets are vastly different, an organizations
global activities become uneconomical due to the need for customization. Differing requirements
necessitate variations in cost, quality, performance, style and size of the product/service. Logistic
problems and difficulties such as availability of transportation and distribution channels may also
make global presence uneconomical.
591. (d) To protect local companies from the threat of foreign companies
These impediments are put in place to protect local organizations from global competition. They
are framed keeping in mind a particular nations interests with regard to employment, defense and
regional development.
592. (b) Managerial impediment
It can be difficult for managers to apply the same strategies and tactics to market products in
different markets. This is termed as managerial impediment for companies that are interested in
becoming global players.
593. (d) i, ii and iii
Global organizations require competent managers because issues and operations in international
markets are much more complex and demanding than those in the domestic market. They need to
look not only for market opportunities or resource availabilities, but also for talent to design future
products. In other words, global managers should strive to leverage local assets of their
organizations for global advantage. Option d is not a reason to scout for competent managers.
594. (b) Collective efforts from both headquarters and subsidiary
Managers at headquarters should not dictate product development and technology choice to their
subsidiaries nor should they leave it entirely to the subsidiary. They should help the subsidiary in
using the pool of knowledge and expertise gained by headquarters by operating in other markets,
to develop a new product. Thus, a collective and cooperative effort will yield a product that will be
in line with organizational goals as well as be successful in the local market.
595. (d) Technologists and managers
In the case of global organizations, the concept of resource allocation has a broad scope. The
most scarce and precious resource in many global organizations are their technologists and
international managers who can coordinate work for continuous improvement.
596. (b) Decentralized in nature
The organizational structure adopted by most global organizations is characterized by the presence
of authority at the lower levels of the hierarchy. Presence of power in the lower levels of the
organizational hierarchy is a sign of decentralization.
Operations Management
136
597. (b) Local people can provide better insights into the local business environment
Organizations can select managers from the host country or from other parts of the world. But
local candidates bring significant knowledge about the local business environment, whereas global
managers provide considerable inputs due to their international experience.
598. (c) iii and iv
Though wholly-owned subsidiaries give organizations full control over the operations of their new
establishments, they have to start from scratch in every aspect of the business to set up such
subsidiaries. Unlike joint ventures, they cannot spread their risk as they have no partners. Further,
the time taken to understand the market is greater in subsidiaries than in joint venture or through an
alliance.
599. (a) i, ii, iii
Option a covers most of the alternatives in comparison to other options. As Tornado wants to
establish a manufacturing base in India with the aim to cater to the Indian market, the export policy
is not a major requisite.
600. (d) Licensing
When a company licenses its product to a partner in a foreign market, it has limited control over
the way the partner markets the product.
The model tests are intended to test the conceptual understanding of the students. Each
model test contains multiple-choice questions for a total of 100 points. Students should
note that the format of the question paper may be change from time to time.
Paper I
Part B: Model Tests
Paper I - Model Test 1
Time: 3 Hours Total Points: 100
1. Which of the following is not an
advantage of computerizing production
systems?
a. Increased productivity
b. Better quality
c. Lower initial investment
d. Improved worker safety
2. Scientific rules govern worker productivity
and it is the prerogative of the
management to study and apply these rules
in their operations. Who introduced the
concept of scientific management in the
field of operations management?
a. Adam Smith
b. Frederick W. Taylor
c. Henry Ford
d. Elton Mayo
3. Identify the systematic approach to
improve labor efficiency proposed by
Frederick Taylor.
a. Shop system
b. Reward system
c. Workplace efficiency system
d. Assembly line system
4. Name the production policy where
products are produced well in advance and
stored in a warehouse from where they are
distributed in accordance with customer
orders.
a. Produce-to-stock policy
b. Produce-to-order policy
c. Assemble-to-order policy
d. Custom-to-Order policy
5. Match the following competitive
advantages with their correct explanations.
i. Production flexibility
ii. Low cost process
iii. Product variety
iv. Quality
p. Producing products at lower costs when
compared to competitors
q. Offering a variety of products under one
roof
r. Offering products of higher quality when
compared to competitors
s. Capability to produce different products
within a short span of time
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/r, iii/q, iv/s
c. i/s, ii/p, iii/r, iv/q
d. i/s, ii/p, iii/q, iv/r
6. In this stage of the product life cycle,
organizations focus on improving
efficiency of the processes, minimizing
costs, etc. Identify the stage of the product
life cycle.
a. Introduction stage
b. Growth stage
c. Maturity stage
d. Decline stage
7. Asahi Glass has superior technical
expertise and production methodology that
allow it to produce high quality float glass
products that other companies cannot
produce. What is this distinct advantage
called?
a. Core competence
b. Unique selling proposition
c. Production flexibility
d. Cost advantage
8. The systems which are highly flexible and
can easily be modified to support other
product designs are termed as
_________________.
a. Product-focused systems
b. Process-focused systems
c. Standardized systems
d. None of the above
Answer all the questions.
Each question carries one point, unless specified otherwise.
Operations Management
140
9. A forecast made by using exponential
smoothing was found to be over-optimistic
to the most recent trends in demand.
Which of the following is the most suitable
corrective action possible to make the
forecast more realistic?
a. Increase the value of
b. Decrease the value of
c. Shift to some other forecasting method
d. Ensure that remains constant
10. In the first order exponential smoothing
forecast method, demand forecast for the
next period is given by the equation
_____________.
a. F
t
= D
t-1
+(1-) F
t-1
b. F
t
= D
t
+ (1-)F
t-1
c. F
t
= D
t-1
+ F
t-1
d. F
t+1
= D
t-1
+ (1-) F
t-1
11. What is the value of exponential
smoothing constant alpha ()?
a. It is always 0.2
b. It is always less than unity
c. It always lies between 0 and 1
d. It can take any positive value
12. Which of the following helps measure the
accuracy with which forecasting methods
are able to predict demand?
i. Nominal group technique
ii. Mean forecast error
iii. Tracking signal
iv. Least square method
a. Only i
b. ii and iv
c. iii and iv
d. ii and iii
13. Which of the following forecasting
methods is not effective when there are
fluctuations in demand or when the
demand is seasonal?
a. Simple moving average method
b. Weighted moving average method
c. Regression analysis
d. Historical analogy
14. To determine how well forecasts from a
forecasting model fit the actual demand
pattern, the average error of the model is
calculated. Which of the following
statements about the various measures of
forecasting error are not true?
a. MAPE indicates relative error
b. MSE is used to identify and penalize larger
errors
c. Tracking signal value nearer to zero
indicates low forecast accuracy
d. MFE for an accurate forecast will be closer
to zero
15. Graphical method can be applied for
solving linear programming problems in
which _____________are involved.
a. More than three decision variables
b. A maximum of three decision variables
c. A maximum of two decision variables
d. A minimum of three constraints
16. The concept of linear programming does
not consider any synergetic effects among
decision variables while calculating their
total value for the objective function or the
constraints they are associated with. This
is part of which assumption of linear
programming?
a. Proportionality
b. Additivity
c. Divisibility
d. Certainty
17. In the graphical method of solving a linear
programming problem, what is the right
way of plotting constraints on the graph?
a. The constraints are plotted as curves
b. Constraints parallel to the axes are not
considered while plotting.
c. The constraints are plotted and moved
either to the right or left to achieve an
optimal solution
d. Constraint inequalities are taken as
equations and are plotted on the graph
18. In which method used to develop an initial
feasible solution in transportation
problems, is the difference between the
least cost and the next least cost calculated
in a row or column before assigning
quantities to any cell?
a. North-West corner method
b. Least cost method
Part B
141
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Both a & b
19. The transportation problem is a special
case of linear programming. In which of
the following methods are allocations
made based on quantity, demand, and
supply numbers, as part of determining an
initial feasible solution?
a. North-West corner method
b. Least cost method
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Stepping stone method
20. The assumptions made in linear
programming models are proportionality,
additivity, divisibility and certainty. What
does the assumption certainty state?
a. An optimal solution is possible only when
coefficients of variables have certain or
definite problems
b. Integer programming is used to avoid
fractional values for decision variables
c. The total value of the objective function
and each constraint is equal to the sum of
the individual contributions from each
decision variable
d. Economy of scale does not play a role in
linear programming problems
21. Which of the following provides an overall
macro view of the movement of
components and sub-assemblies in the
production process?
a. Assembly chart
b. Process chart
c. Gantt chart
d. Flow chart
22. In what way is a typical product focused
system distinct when compared to a
process focused system?
a. Lower fixed costs and higher variable
costs
b. Higher fixed costs and lower variable costs
c. Higher fixed costs and higher variable
costs
d. Lower fixed costs and lower variable costs
23. Many inputs are required to develop a
process plan. Which of the following is
not an input used in process planning?
a. Demand
b. Resource availability
c. Allocation of resources
d. Facility layout
24. Which of the following types of
integration determines the extent to which
a product and its components are produced
internally?
a. Horizontal integration
b. Vertical integration
c. Diagonal integration
d. Lateral integration
25. Which of the following is not a synonym
for process-focused production?
a. Intermittent production system
b. Stop-and-go production
c. Job shops
d. Line flow production system
26. A certain product is made of parts which
are produced under standardized
production. But, the product as a whole is
produced in moderate numbers in batches.
What kind of production system would be
appropriate to produce this product?
a. Job shop production
b. Group technology
c. Product-focused production
d. Process focused production
27. What is the overall objective of facility
layout decision in a manufacturing unit?
a. To provide smooth workflow of materials
and ensure operational efficiency
b. To give workers a pleasant work
environment
c. To arrange various facilities at the plant to
improve aesthetics
d. To utilize available space within the plant
location to the fullest
28. A multinational company prefers to use
labor intensive production processes. The
company plans to expand its global
presence by entering a new country.
Which of the following countries should it
prefer as a choice location?
a. Japan
b. Germany
c. China
d. Australia
Operations Management
142
29. Break-even analysis is a graphical and
algebraic representation of relationships
among volume of output, costs and
revenues. What is the other commonly
used term for break-even analysis?
a. Quality factor analysis
b. Cost-volume - profit analysis
c. ABC analysis
b. Value analysis
30. Layouts are differentiated by the types of
work flow they entail and the work flow in
turn is dictated by the nature of the
product. Which type of layout is also
called flow-shop layout?
a. Process layout
b. Product layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Hybrid layout
31. Which of the following layout formats
involves grouping similar equipment or
functions in an area?
a. Product layout
b. Process layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Grouping technology layout
32. Which of the following conditions would
arise if a steel manufacturer selects a
location close to the sea port?
a. Higher transportation costs of raw
materials
b. Better inventory management
c. Greater possibility of just-in-time delivery
of finished goods
d. Greater ability to respond to changes in
demand
33. Managers have to balance job
specialization and skill variety, while
designing jobs for employees. Which of
the following is not an advantage of job
specialization for workers in an
organization?
a. Ease in recruiting new workers
b. Lower production time or higher
productivity due to the learning curve
effect
c. Higher flexibility in job rotation
d. Ease of supervision and training worker
34. Match the following terms associated with
the process of job design.
i. Job identification
ii. Job title
iii. Job duties
iv. Job specification
p. Describes the duties and responsibilities
associated with the job in a summarized
form
q. Reflects the number of workers needed
and the reporting authority in a job
r. Describes the required skills and
qualifications for a job
s. Describes the purpose and responsibilities
of a job
a. i/r, ii/q, iii/p, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/q, ii/s, iii/p, iv/r
d. i/q, ii/s, iii/r, iv/p
35. The Job Characteristics Model developed
by Richard Hackman and Greg Oldham
includes five characteristics. They are skill
variety, task identity, task significance,
autonomy and feedback. Which of the
following defines details of tasks needed to
complete/perform a job?
a. Task identity
b. Task significance
c. Autonomy
d. Feedback
36. The extent to which tasks can be defined
differs from job to job. Defining tasks is
most difficult for which of the following
organizational levels?
a. Assembly line workers
b. Supervisors
c. Middle managers
d. Top management
37. Job design refers to the process through
which tasks are structured to improve the
efficiency and productivity of workers.
Which of the following is not an objective
of job design for a manager?
a. To enhance self-esteem and motivate
employees
b. To maximize worker inputs in terms of
time and physical effort
Part B
143
c. To improve efficiency and productivity of
workers
d. To keep workload at a convenient level
38. Job design includes skill varieties, task
identity, task significance, autonomy and
feedback. Which of the following is not
considered a part of skill varieties of
workers?
a. Range of skills
b. Extent of motivation needed
c. Abilities and talent needed
d. Level of skills
39. Name the work measurement technique
that analyzes work by taking a number of
random observations to see the relative
frequency with which various activities are
carried out.
a. Standard data technique
b. Predetermined motion time study
c. Time study
d. Work sampling
40. Identify the correct definition of time
standard.
a. The time consumed by an average worker,
working at average speed, to perform a
specific task under normal operating
conditions
b. The time consumed by the most productive
worker, working at top speed, to perform a
specific task under special operating
conditions
c. The time consumed by the most productive
worker, working at top speed, to perform a
specific task under normal operating
conditions
d. The time consumed by the most
unproductive worker, working at the
lowest possible speed, to perform a
specific task under normal operating
conditions
41. Identify the correct sequence of steps
followed as part of time study technique.
a. Observation job identification pace
rating computing normal time &
allowances observation computing
standard time
b. Job identification observation pace
rating computing standard time
computing normal time & allowances
c. Job identification observation pace
rating computing normal time &
allowances computing standard time
d. Job identification pace rating
observation computing normal time &
allowances computing standard time
42. What is referred to as the time that is
generally consumed by an average worker,
working at an average speed, to perform a
specific task under normal operating
conditions?
a. Work rate
b. Work record
c. Work standard
d. Observation time
43. Zentech Engineering establishes work
standards as part of work measurement in
its plant. Which of the following cannot
be a possible benefit of using work
standards?
a. They help schedule operations
b. They help reduce machine utilization
c. They provide benchmarks for evaluating
workers performance
d. They help compare efficiency of different
work methods
44. Which of the following is not an optimal
model used to formulate the aggregate
plan?
a. Linear programming
b. Linear Decision Rules
c. Pre-determined Motion Time Study
d. Heuristic models
45. Operations planning activities can be long-
range, medium-range, or short-range in
nature. Process planning typically falls
under which category?
a. Long-range planning
b. Medium-range planning
c. Short-range planning
d. Both b & c
46. As the Master Production Schedule (MPS)
is based on an estimation of overall
demand for the end product, the actual
production output is not always equal to
the actual demand. Operations managers
can modify the MPS to adjust to these
deviations. Which of the following is not
the correct approach to adjust deviations?
Operations Management
144
a. Allowing inventory level to increase when
demand is low and vice-versa
b. Modifying the size or composition of the
product temporarily
c. Sub-contracting additional capacity
requirements
d. Maintaining product prices to influence the
demand level
47. When a firm achieves economies of scale,
production costs reduce considerably. This
results due to which of the following?
i. Decrease in per unit cost
ii. Decrease in fixed costs
iii. Decrease in variable costs
iv. Decrease in inventory costs
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
b. ii and iii
c. i, ii and iii
48. A master production schedule of make-to-
order organizations contains information
about which of the following?
a. Quantities and required delivery dates of
the final product
b. Quantities and required delivery dates of
all sub-assemblies
c. Inventory on hand for each component
d. Scheduled receipts for all components
49. Operations planning activities can be long-
range, medium range or short range in
nature. Under which category do order
scheduling and workforce scheduling
typically fall?
a. Long-range
b. Medium-range
c. Short-range
d. Both a & b
50. Which of the following is the basic
objective of economic order quantity
purchasing?
a. Minimizing total inventory cost
b. Minimizing transport cost
c. Minimizing storage cost
d. Minimizing ordering costs
51. Large shipments can result in reduced
incoming freight costs and material
handling costs. This statement, given by
manufacturing firms, refers to which type
of inventory?
a. Raw material inventory
b. Work-in-progress inventory
c. Finished products inventory
d. None of the above
52. Which of the following statements
correctly describe the P-System?
a. Orders are placed at equal intervals of time
b. Inventory is monitored continuously
c. The order is placed so that total cost of
maintaining inventory is less
d. Lead time for replenishment is zero
53. Which type of cost does a firm incur if the
rate of inventory replenishment is less than
demand rate?
a. Stock-out costs
b. Replenishment costs
c. Production costs
d. Direct costs
54. Which inventory model is also referred to
as the reorder point system?
a. P system
b Q system
c. EOQ
d. None of the above
55. Before taking make-or-buy decisions,
organizations take into account factors like
availability of raw materials in the long-
run, ability to monitor and control quality,
etc. Which of the following is not an
argument in favor of buy decisions
(outsourcing production)?
a. Take advantage of suppliers know-how
and expertise
b. Quantity required is too low to justify in-
house production
c. Helps maintain multiple supply sources
d. Maintain control over supply chain
activities
56. What precedes a typical make-or-buy
decision?
Part B
145
a. Value analysis
b. ABC analysis
c. Break-even analysis
d. Vendor analysis
57. The purchase department acts on behalf of
the user departments and interacts with the
suppliers to purchase materials at
economic prices. This is associated with
which activity of the purchase department?
a. Vendor analysis and development
b. Supplier selection
c. Value analysis
d. Contract negotiation and communication
interface
58. Which of the following purchasing
instruments authorizes suppliers to supply
goods for a firm?
a. Organizational document
b. Purchase quotation
c. Purchase requisition
d. Purchase order
59. Identify conditions that influence a firm
for a buy decision.
i. The cost of purchasing the item is less than
for manufacturing it
ii. The company does not have required
manpower to make the item
iii. Expected returns on investment in
manufacturing items are attractive
iv. The demand for the item (to be
manufactured) is seasonal and there is risk
in storing and maintaining it.
a. i, ii, iv
b. ii, iii, iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. i, ii, iii, iv
60. Which of the following studies prompted
management thinkers and organizations to
take up in-depth research into human
behavioral aspects at work?
a. Moving assembly lines
b. Hawthorne studies
c. Operations research
d. Scientific management
61. Ingersoll Rand manufactures a limited
variety of horizontal compressors and the
customer has to select from the available
models. What type of production policy is
the company following?
a. Varying workforce production
b. Standardized production
c. Employee focused production
d. Customized production
62. A tires supplier to the Maruti assembly
line prides itself on providing the required
quantity and types needed for every day
production. What type of competitive
advantage strategy is described here?
a. Differentiation strategy
b. Straddling strategy
c. Response strategy
d. Level production strategy
63. Which of the following forecasting
methods is an example for causal models?
a. Simple moving average
b. Weighted moving average
c. Exponential smoothing
d. Regression analysis
64. What is the value of the mean forecast
error for an accurate forecast model that is
unbiased?
a. Close to unity
b. Close to zero
c. Negative
d. Equal to one
65. What happens to the demand of the
commodity when the price of the
commodity is reduced, keeping other
things constant?
a. Increases continuously
b. Decreases continuously
c. Increases to a certain point
d. Does not change
66. Proportionality is an assumption made in
linear programming. It indicates that
contribution of individual decision
variables in the objective function is
proportional to their numeric value. Which
of the following can be derived from this
assumption?
Operations Management
146
a. Economies of scale play an important role
in linear programming
b. Economies of scale do not play any role in
linear programming
c. Finished products are not proportional to
the amount of raw material consumed
d. Does not consider any synergistic or anti-
synergistic effects among decision
variables
67. The generalized objective function of a
linear programming problem is minimize
Z = C
1
x
1
+ C
2
x
2
+ + C
n
x
n.
If X
2
is
decreased by one unit, what will the value
of objective function be?
a. The value will increase by C
2
b. The value will decrease by C
2
c. The value will increase by one unit
d. The value will decrease by one unit
68. Which of the following systems is the
most appropriate for a production
organization producing large volumes with
very little scope for product variety?
a. Process focused system
b. Process focused batch production system
c. Product-focused production system
d. Cellular manufacturing system
69. A manufacturer decides to buy its
marketing and distribution channels. What
type of integration strategy is the
manufacturer adopting?
a. Product expansion
b. Forward integration
c. Backward integration
d. Diversification
70. The cost incurred in transporting raw
materials and other components from
different places must be considered while
deciding on the location of a facility.
Which among the following methods helps
analyze these costs?
a. Break-even analysis
b. Point-rate method
c. Transportation method
d. All of the above
71. Identify the statement that does not
correctly describe plant layouts.
a. Layouts are permanent and do not change
over time
b. Layouts differ from plant to plant, location
to location, and industry to industry
c. Layout decisions have long-term
consequences for the firm
d. A good layout always attempts to reduce
material-handling costs
72. Identify the layout using a product layout
within a group of machines and a process
layout between such groups of machines?
a. Hybrid layout
b. Functional layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Grouping technology layout
73. Skills, knowledge, and abilities required to
satisfy the requirements of a job are
associated with which function of job
design?
a. Job specification
b. Job specialization
c. Job content
d. Job specialization
74. What does job identification describe?
a. The number of workers and reporting
authority in a job
b. Purpose and responsibilities of a job
c. Duties and responsibilities
d. Skills and qualifications required
75. Which of the following is not a type of
pre-determined motion time data system?
a. Methods time measurement
b. Work sampling
c. Work factors
d. Maynard Operations Sequence Technique
(MOST)
76. Some organizations may not be in a
position to fulfill customer orders. They
may fulfill them in the future. What is the
practice of fulfilling current orders of
customers at a future date called?
a. Back-order strategy
b. Sub-contracting
c. Aggregate planning
d. Capacity planning
Part B
147
77. The graphical method for aggregate output
planning is a technique used in developing
and evaluating various alternative plans or
a combination of alternatives. This method
focuses on which of the following
relationships?
a. Absolute demand and absolute output
capacity
b. Cumulative demand and cumulative output
capacity
c. Absolute demand and cumulative output
capacity
d. Cumulative demand and absolute output
capacity
78. Jumbo Auto Ltd achieved sales of 20,000
units in 2006 when the sales forecast was
for 19,500 units. Estimate the sales for
2007 using a first order exponential
smoothing method. The smoothing
constant is 0.1. (1 point)
a. 17,550 units
b. 19,500 units
c. 19,550 units
d. 21,500 units
Questions (79 & 80) Answer the following two
questions from the given transportation
problem.
Factory/
Warehouse
W
1
W
2
W
3
Supply
14 20 11
F
1
250
17 11 16
F
2
350
8 9 13
F
3
300
Demand 200 250 450
79. Which will be the first cell to which
quantity should be allocated, if Vogels
approximation method is used? (1 point)
a. F
1
W
1
b. F2 W3
c. F
2
W
1
d. F
3
W
1
80. What is the initial feasible solution using
the least cost method? (4 points)
a. 10,100
b. 8,400
c. 8,300
d. 9,400
81. What is the annual ordering cost if the
fixed cost per order is Rs.5000, yearly
demand is one million units and 200,000
units are ordered per order? (2 points)
a. Rs.15, 000
b. Rs.20, 000
c. Rs.25, 000
d. Rs.30, 000
82. Using EOQ model, calculate the holding
cost per order if the holding cost per unit is
Rs.10 and order quantity is 10000 units?
(2 points)
a. Rs.100,000
b. Rs.75,000
c. Rs.25,000
d. Rs.50,000
(Questions 83 to 85) Cutting Tools India Ltd.
(CTIL) produces different drilling tools
including pneumatic power tools. The company
decides to launch a new product that requires a
new component. The price of this component is
Rs.50 per unit and CTIL estimates the annual
demand at 2,000 units. If the component has to
be manufactured in-house, one-time fixed costs
would be Rs.200,000 and variable cost per unit
would be Rs.25. Based on this information,
answer the following three questions.
83. What will be the total cost of producing
the component in-house as well as the cost
to buy it from vendors? (2 points)
a. Rs.100,000 and Rs.250,000
b. Rs.250,000 and Rs.100,000
c. Rs.150,000 and Rs.200,000
d. Rs.200,000 and Rs.150,000
84. If it is estimated that the demand for the
component will double annually, what will
be the total cost to make and total cost to
buy for the next three years? (3 points)
a. Rs.550,000 and Rs.700,000
b. Rs.850,000 and Rs.800,000
c. Rs.800,000 and Rs.850,000
d. Rs.700,000 and Rs.550,000
Operations Management
148
85. If the variable cost of in-house production
increases to Rs.30 per unit, what decision
would you take if the firm requires 25,000
units in five years? (5 points)
a. Buy
b. Make
c. Buy for first two years and make for the
remaining three years
d. Cannot decide
86. Golden Exports wants to set up its sea-
food processing plant at a location that
would enable it to effectively ship the
processed sea food to four distribution
centers across the country. The following
table gives the quantities to be shipped and
the coordinates for the four distribution
centers. Using the center of gravity
method, identify the X and Y coordinates
of the optimal location for Golden Exports
to set up its processing plant. (3 points)
Distribution
Center
X Y Quantity
(in tons)
A 5.5 7 60
B 8 12 90
C 12 6 110
D 15 11 100
a. 7.56, 8.99
b. 10.75, 9.06
c. 9.06. 10.75
d. 8.99, 7.56
Paper I - Model Test 2
Time: 3 Hours Total Points: 100
1. A Kanban system uses different types of
cards to initiate material transactions.
Which of the following Kanban cards
authorizes a materials handling agent to
move the tray to a specified destination?
a. Conveyance authorization card
b. Production authorization card
c. Vendor authorization card
d. Dual-card Kanban system
2. The materials flow is divided into three
different overlapping functions -
production control, inventory control, and
the materials handling function. Which of
the following is not a task associated with
the inventory control function in materials
management?
a. Checking the quantity and quality of the
incoming material and generating
receiving reports
b. Checking the quantity and quality of the
products in the production process
c. Storing and protecting finished goods
d. Auditing finished goods inventory
3. There are many factors that directly
influence the materials handling function.
Which of the following is not such a
factor?
a. Type of plant layout
b. Type of production process used
c. Nature of materials and material handling
equipment used
d. Quality of material
4. If an operator performs a sequence of tasks
using a robot, it stores the sequence in its
memory and performs the same tasks in
the same sequence to produce same/similar
products. Which category of robots, based
on the nature of their operations, is
referred to here?
a. Playback robots
b. Numerical control robots
c. Variable-sequence robots
d. Physically operated robots
5. Which of the following actions is not
associated with a conveyance authorization
card issued by a production worker from a
workstation in a production facility?
a. A material tray is filled with required
material in the inventory
b. A vendor immediately fills up the
inventory with required quantity
c. A material with filled material is sent to
the production worker
d. All of the above
6. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of the Kanban system?
a. The Kanban system follows the open loop
system
b. The Kanban system requires initial
inventory to begin an operation
c. In the Kanban System, cards are used to
initiate transactions
d. All inventory items are stored in single
trays
7. The Kanban system was developed by
Toyota Motor Company, Japan. Which of
the following factors determine the
number of Kanbans?
a. Time and cost of a set-up
b. Demand rate of a product
c. Number of units that can be stored
d. Number of workstations in a production
system
8. Materials handling equipment is of two
types - fixed path equipment and variable
path equipment. Identify the correct
combination from the following.
Answer all the questions.
Each question carries one point, unless specified otherwise.
Operations Management
150
i. Mobile cranes : Fixed path equipment
ii. Forklift : Variable path equipment
iii. Industrial tractors : Fixed path equipment
iv. Conveyor : Fixed path equipment
a. ii and iv
b. i and iii
c. ii, iii, iv
d. ii and iv
9. The components of an MRP system can be
divided as inputs, processing, and outputs.
Which of the following is not part of the
outputs of an MRP system?
a. Purchase commitment report
b. Performance reports
c. Planned orders
d. Bill of materials
10. What basic information does a master
production schedule contain?
a. Required quantities and delivery dates of
final products
b. Required quantities and delivery dates of
all sub-assemblies
c. Inventory on hand for each final product
d. Scheduled receipts for each final product
11. An MRP system takes some inputs,
processes them, and gives certain outputs.
Which of the following is not considered
an input?
a. Master production schedule
b. Planning report
c. Bill of materials
d. Inventory records file
12. In which step of MRP information
processing, all the parts required to
produce a product are identified and the
production or purchase activity of the
respective parts is determined by working
backwards?
a. Explosion
b. Netting
c. Offsetting
d. Consolidation of material requirements
13. What does the Master production schedule
contain?
i. Cumulative lead-time requirements for
activities such as procurement
ii. Activity-wise time-phase requirements
iii. The number of units of finished products
required
iv. List of materials along with the quantity
required
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, iv
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, ii, iii
14. Besides inadequate employee training and
involvement, and use of inaccurate and
obsolete data, the success of an MRP
system usually depends on the product
environment. What does an appropriate
product environment require?
i. An organization needs to purchase many
items, a majority of which are components
and parts
ii. The demand pattern of items should be
dependent in nature
iii. Demand for items should be irregular in
timing
iv. The lead times for purchase of these items
should be inconsistent
a. i, ii, and iii
b. i, iii, and iv
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. ii and iv
15. Scheduling varies depending on the type of
operation. Which type of labor-intensive
scheduling allows employees to choose
their work hours, but on condition that
they put in a specified number of hours in
a period?
a. Flextime approach
b. Flextour approach
c. Staggered times approach
d. Part-time approach
16. One of the methods that service firms can
adopt to meet customer demand under
situations of limited availability of service
facilities is through a reservation system.
Which of the following statements is not
true about a reservation system?
Part B
151
a. Helps manage demand by adjusting price
for services
b. Helps meet customer demand successfully
by scheduling multiple resources and
facilities together
c. Allows firms to discontinue unprofitable
business operations
d. Helps firms in situations where customer
demand exceeds service capacity
17. Which of the following scheduling
activities aims at reducing costs by
minimizing the idle time of the machines
and reducing inventory?
a. Routing
b. Loading
c. Dispatching
d. Backward scheduling
18. Service operations scheduling is quite
different from product operations
scheduling. Which of the following is not
true about service operations scheduling?
a. Appointment system is a scheduling
method used in service operations
b. Service operations are scheduled according
to demand
c. Service operations are scheduled according
to inventory requirements
d. Service operations are scheduled according
to the first in, first serve rule
19. Many tourist resorts reduce room tariffs
during the off-season to maintain the flow
of visitors. Which of the following
methods is the service provider using to
reduce the gap between demand and
supply of services?
a. Appointment system
b. Reservation system
c. Strategic product pricing
d. Routing
20. If there are 3 machines A, B & C, and n
jobs have to be processed on these
machines, which of these conditions need
to be satisfied to use Johnsons sequencing
rules?
i. The smallest processing time on machine
A should be greater than or equal to the
largest processing time on machine B
ii. The smallest processing time on machine
C should be greater than or equal to the
largest processing time on machine A
iii. The smallest processing time on machine
A should be less than or equal to the
largest processing time on machine B
iv. The smallest processing time on machine
C should be less than or equal to the
largest processing time on machine B
a. Only i
b. i and iii
c. ii and iv
d. i and iv
21. Assigning specific jobs to each work
center for the planning period is associated
with _________.
a. Loading
b. Routing
c. Dispatching
d. Mapping
22. In which of the following personnel
scheduling approaches are employees
given an option to select their work hours
from a list of available shifts?
a. Flexitime approach
b. Flextour approach
c. Compressed work week
d. Staggered times approach
23. Which scheduling activity is associated
with the process of releasing job orders to
production workers according to the
planned schedule?
a. Routing
b. Queuing
c. Dispatching
d. Backward scheduling
24. Expand SAP.
a. Systems Analysis and Programming
b. Strategic Analysis and Programming
c. Systems, Application and Products
d. Strategic Application Programming
Operations Management
152
25. Why is integration of data considered most
critical in ERP implementation?
i. It increases data redundancy
ii. It increases connectivity between
departments
iii. It helps in smooth flow of information
between departments
iv. It ensures availability of right information
a. i, ii, iii
b. i, ii, iv
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
26. The key activity of _____________ is to
monitor the implementation process
continuously in order to identify
deviations, cost overruns, resource
requirements, etc., during ERP
implementation.
a. Project member
b. Project leader
c. Project team
d. Steering committee
27. Which of the following concepts can be
linked to the development of ERP?
i. MRP
ii. Inventory Management
iii. Purchase Management
iv. MRP II
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iv
28. Process mapping helps in detailing the
processes used in business transactions.
Process mapping is used in which of the
following stages of ERP implementation?
a. Identify the needs of the ERP package
b. Evaluate the asis situation of the
business
c. Evaluation of available ERP packages
d. Implementation of ERP package
29. SCM enablers are a group of carefully
conceived and defined behaviors and
approaches that allow, encourage, and
reinforce a firms commitment to high
performance SCM practices. Which of the
following is not an SCM enabler?
a. Compensation and benefits
b. Measurement
c. Design
d. Periodic review
30. Which of the following components of
SCM forms a blue print for supply chain
operations?
a. SCM leadership
b. Operational planning
c. SCM strategy
d. Order-to-delivery process
31. Alignment is an SCM enabler. What
should the management of an organization
do to ensure better alignment in the
organization?
a. Develop policies that reward low cost
purchases and intense negotiations
b. Strive for cross-functional interaction
c. Set goals and objectives that support
successful supplier relationships
d. Set up organization-wide and continuous
communication systems
32. Which of the following is not true about
demand chains?
a. A player in the demand chain can develop
products at any point of time
b. Meeting consumer demand in time is given
paramount importance
c. Alliances develop between channel
partners who can best satisfy customer
needs
d. The players in a demand chain are
different from those in the traditional
supply chain
33. Electronic supply chain management
(ESCM) involves business-to-business
integration through the Internet. Identify
the advantages of implementing ESCM for
a firm.
i. Increase in inventory levels
ii. Cost savings
iii. Reduction in cycle time
iv. Reduction in procurement costs
a. i, ii, and iii
b. i, ii, and iv
Part B
153
c. i, iii, and iv
d. ii, iii, and iv
34. Which of the following components of
SCM include functions like commodity
planning, supplier capacity planning,
planning for supplier evaluation,
certification processes, etc.?
a. Operational planning
b. Order-to-delivery process
c. Business relationship management
d. Human resources management
35. Which of the following characteristics is
not associated with JIT?
a. Reduction in paperwork
b. Purchase in small lots with frequent
deliveries
c. Many suppliers for a given part/component
with short-term contracts
d. Standardized packaging for all part types
36. JIT manufacturing has an open
management style. What does this mean?
a. Workers are free to implement whatever
methods they like
b. Suggestions of workers are not collected
and implemented by the management
c. Suggestions of workers are collected,
evaluated, tested, and implemented by
management
d. Top management provides suggestions that
are evaluated and implemented by workers
37. Which of the following elements help
build long-term relationships between the
firms practicing JIT and their suppliers?
i. Trust
ii. Communication
iii. Product design
iv. Linearity of production
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iv
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. i, iii, and iv
38. The frequency of buying material is high
for JIT firms as they stock less inventory
This requires closer supplier ties, a
characteristic of a JIT system. Which of
the following cannot be true in this
scenario?
a. JIT firms select suppliers located away
from the plant
b. JIT firms need to maintain long-term
relationships with suppliers
c. Suppliers should be reliable in terms of
delivery
d. Suppliers should be paid their dues
(invoice amounts) regularly without delay
39. JIT does not focus on one of the
following. Identify.
a. Eliminating external demand variations
b. Reducing unreliable delivery of raw
materials
c. Reduction of inventory
d. Reducing excessive set-up times
40. Identify the sequence used to implement
the suggestions of workers to improve
quality in the organization.
a. Collection evaluation selection
testing approval implementation
b. Collection selection evaluation
testing approval implementation
c. Selection collection evaluation
testing approval implementation
d. Selection collection testing
evaluation approval implementation
41. The cost of quality can be divided into
three major categories - cost of prevention,
cost of detection/appraisal, and cost of
failure. Which of the following is a
prevention cost?
a. Disposition of defective items
b. Equipment maintenance
c. Quality training
d. Warranty charges
42. Which of the following indicates labor
productivity?
i. Goods produced /material consumed
ii. Goods produced /man hours spent
iii. Goods produced /power consumed
iv. Customers handled /number of attendants
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
Operations Management
154
c. iii and iv
d. ii and iv
43. Match the following functions of quality
with the appropriate description.
i. Durability
ii. Serviceability
iii. Performance
iv. Reliability
p. The probability of a products failure in a
time period
q. The operational life of a product
r. Indicates the ability of a products primary
operating characteristics
s. Concerned with how readily a product can
be serviced back into operational mode
a. i/q, ii/s, iii/r, iv/p
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/p, ii/q, iii/s, iv/r
d. i/p, ii/r, iii/q, iv/s
44. The cost of quality can be divided into
different categories. Investments in
machinery and vendor certification are
associated with which of the following
costs?
a. Prevention costs
b. Detection costs
c. Failure costs
d. Appraisal costs
45. ABC Company manufactures cheese and
each packet should weigh 32 gm. The
quality supervisor wants to develop a
process control chart. He takes five
samples of six boxes each and weighs
them. The upper and lower control limits
for the x-bar chart are 34.34 and 33.86
respectively. The upper and lower control
limits for the range are 1.00 and 0.00,
respectively. Based on the following data,
select the statement that best describes the
situation.
Sample Mean Range
1 33.9 1
2 34.1 0.8
3 34.0 1.2
4 34.2 0.3
5 34.0 0.3
a. Sample 1 is outside the control limits.
Further investigation is warranted
b. Sample 3 is outside the control limits.
Further investigation is warranted
c. Samples 1 & 3 are outside the control
limits. Further investigation is warranted
d. All samples are within limits and the
packaging process is in-control
46. A company can compete on different
quality functions. Which function of
quality is measured as the mean time
between failures?
a. Features
b. Reliability
c. Durability
d. Serviceability
47. To provide a clean and conducive work
environment and enable efficient and
effective progress of the core functions of
an organization is an objective of
____________.
a. Quality management
b. Facilities management
c. Maintenance management
d. Inventory management
48. Which of the following is a suitable
strategy a firm can adopt to avoid loss of
control when outsourcing facilities
management activities?
a. Outsource all activities to a singe vendor
b. Outsource different tasks to different
vendors
c. Prefer outsourcing rather than out-tasking
d. Outsource core activities to a single vendor
49. An oil mill contains oil extractors with
many moving parts. The maintenance
inspector on a routine visit finds there is
leakage of lubricant in one machine. What
type of maintenance will the maintenance
inspector take up?
a. Irregular preventive maintenance
b. Predictive maintenance
c. Periodic maintenance
d. Remedial maintenance
50. What do you understand by opportunity
maintenance?
Part B
155
a. Maintenance done when a machine is
running
b. Maintenance carried out when a machine
has broken down
c. Maintenance carried out when a machine
is idle and waiting for the next job
d. Maintenance done at regular intervals of
time
51. The activity of cleaning facilities to keep
them neat and tidy falls under which of the
following services of facilities
management?
a. Janitors services
b. Reprographics
c. Landscaping
d. Waste management
52. Identify the goals of maintenance
management from the following.
i. Preserve the value of the firms machinery
ii. Use maintenance personnel and equipment
efficiently
iii. Minimize availability of machinery for
production process
iv. Eliminate accidents by regular inspection
a. i, ii, and iii
b. ii, iii, and iv
c. iii, iv, and i
d. i, ii, and iv
53. Managers use many terms as part of
networks in project management. In this
context, what is the term used for an
outcome of an activity or group of
activities?
a. Project
b. Event
c. Critical path
d. Node
54. Automated systems are less customizable
in terms of the number of possible
products that can be manufactured when
compared to manually operated systems.
Which of the following overcomes this
disadvantage?
a. CAD
b. CAM
c. FMS
d. JIT
55. Globalization provides many new
opportunities for expansion of
organizations. The BPO industry is
flourishing in India due to availability of
low-cost English-speaking graduates.
Which of the following types of global
competitive advantage does India have?
a. Comparative advantage
b. Economies of scale
c. Proprietary product knowledge
d. All of the above
56. Which of the following formulae correctly
represents the expected time?
a.
=
n
1 i
i
iP
b.
cp
2
E D
Z
=
c.
2
6
o
t
p
t
d.
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t
e
t
+ +
=
57. Which of the following is true about an
FMS?
a. An FMS requires very less capital to
install
b. Different products with similar
components and manufacturing processes
can be manufactured
c. It has a greater response time
d. It requires many part-time workers
58. Coca-Cola markets its products through
mega advertising campaigns and event
sponsorship in most of the countries it
operates. This is an example of which of
the following?
a. Economies of scale in production
b. Economies of scale in purchase
c. Economies of scale in marketing
d. All of the above
59. Raw materials form a major part of costs
incurred by an organization. They are
classified under which of the following
heads in the balance sheet of a firm?
Operations Management
156
a. Current assets
b. Current liabilities
c. Fixed assets
d. Fixed liabilities
60. Give the correct relationship between
material costs and its effect on profitability
of a firm.
a. Profitability increases with rising material
costs
b. Profitability decreases with increase in
material costs
c. Profitability decreases with drop in
material costs
d. Material costs do not affect profitability
61. The components of an MRP system can be
divided into inputs, processing and
outputs. Which of the following is not
associated with any of these components
of an MRP system?
a. Bill of materials
b. Inventory records file
c. Master production schedule
d. Layout planning
62. _______________ contains the list of
materials along with the quantity required
to produce one unit of a product.
a. Master production schedule
b. Demand forecast
c. Bill of materials
d. Inventory records file
63. Which of the following is not a standard
measure of schedule performance to
evaluate priority rules?
a. Meeting due dates of customers or
downstream operations
b. Minimizing flow time
c. Maximizing work-in-progress inventory
d. Minimizing idle time of machines
64. Which of the following is an aid to
monitor jobs in-process?
a. First-in first-serve
b. Gantt chart
c. Johnson's rule
d. Slack time remaining
65. ERP packages are evaluated to identify the
package that will provide a comprehensive
solution to the given organizations
requirements. The type of industry it is
designed for is one of the factors to be
considered. Which of the following terms
represents this factor?
a. Global presence
b. Modularity
c. Price
d. Target market
66. Small and medium sized organizations
usually purchase individual modules of the
ERP package due to high costs. Which
characteristic of evaluating ERP packages
is discussed here?
a. Target market
b. Investment in R&D
c. Modularity
d. Ease and cost of implementation
67. Which of the following SCM enablers
discusses effective decision-making in the
organization?
a. Participation/involvement
b. Design
c. Measurement
d. Periodic review
68. In which of the following, products dont
necessarily originate from manufacturers
and any player in the supply chain can
develop them at any point?
a. Supply chain management
b. Demand chain management
c. Inventory management
d. Production management
69. In which approach do people working in
similar type of operations meet regularly to
discuss work-related problems and ways to
improve work quality?
a. Quality circles
b. Suggestion programs
c. Project teams
d. JIT purchasing
70. Under the JIT manufacturing system, firms
strive to reduce inventory and wastage to
the minimum possible extent. What kind
of supplier relationships do firms adopting
a JIT system maintain?
Part B
157
a. Short-term relationship with a large
number of suppliers
b. Short-term relationship with a few
suppliers
c. Long-term relationship with a large
number of suppliers
d. Long-term relationship with few suppliers
71. Which of the following is not a function of
quality of a product?
a. Features
b. Reliability
c. Durability
d. Productivity
72. The cost of quality can be divided into
different categories. Investments in
machinery and vendor certification are
associated with which of the following
costs?
a. Prevention costs
b. Detection costs
c. Failure costs
d. Appraisal costs
73. Which of the following is not a duty of the
facilities manager carrying out tasks in-
house?
a. Acting as change managers in situations
where existing processes or infrastructure
are modified
b. Developing good relationships with
service providers
c. Measuring the work performance of
facilities management teams
d. Reviewing techniques used to reduce costs
& raising maintenance levels in facilities
74. Which of the following is not an activity
under preventive maintenance?
a. Checking for safety in the work
environment
b. Carrying out periodical preventive
maintenance
c. Order replacement of broken down
machines
d. Allocating budgets to upgrade facilities
75. Which of the following correctly defines a
critical path of a project?
a. It is a task which must be finished in order
to complete the project
b. It is the outcome of an activity or a group
of activities
c. It is the longest path of interrelated
activities in a project with zero slack time
d. It is the minimum amount of time in which
an activity can be completed.
76. The minimum amount of time required to
complete a project is termed ___________.
a. Optimistic time
b. Pessimistic time
c. Expected time
d. Most likely time
77. CNC machines can perform variety of
tasks based on instructions embedded in
them. This technology is part of which of
the following?
a. Flexible manufacturing system
b. Computer aided manufacturing
c. Computer aided design
d. Computer integrated manufacturing
78. There are certain impediments to
globalization that can block an
organization from globalizing its activities.
Which of the following examples fall
under institutional impediments?
a. Government regulations to use locally
produced components
b. Utilizing extra capacity to make products
that can be exported
c. Necessity to produce customized products
in every market
d. Dealing with different people with varying
preferences, work styles, etc.
(Questions 79 to 81) V S Rao (Rao) is the
supervisor of Choudhary Iron Works, which
manufactures customized windows for
households. Five customers submitted orders at
the beginning of the week. Using the specific
scheduling data given below, answer the
following three questions.
Operations Management
158
Jobs
(In order of
arrival)
Processing
Time
(Days)
Due Date
(Days hence)
A 3 5
B 4 6
C 2 7
D 6 9
E 1 2
79. Rao decides to use Earliest Due Date to
sequence the jobs. Which of the following
sequence will be followed to process the
jobs? (1 point)
a. A-B-C-D-E
b. E-C-A-B-D
c. E-A-B-C-D
d. D-C-B-A-E
80. The average completion time for the
sequence, E-A-B-C-D is (3 points)
a. 2.4 days
b. 7.8 days
c. 5.8 days
d. 7.2 days
81. Calculate the critical ratio for Job A?
(1 point)
a. 0.60
b. 0.50
c. 1.67
d. 0.67
82. For the given three machine and five job
problem, determine the optimum
sequencing for scheduling using Johnsons
sequencing rule. (4 points)
Processing Times (in minutes)
Job
Machine
A
Machine
B
Machine
C
1 23 10 25
2 54 23 65
3 45 18 24
4 41 22 33
5 35 20 46
a. 1, 5, 2, 4, 3
b. 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
c. 3, 2, 5, 4, 1
d. 1, 2, 4, 5, 3
(Question 83 to 88) The network diagram of a
project to install an ERP system in an
organization is given below. The time estimates
for completing the project is also show in the
diagram. Use this information to answer the
following six questions.
83. What is the earliest start time for the
activity 5-6? (1 point)
a. 3 weeks
b. 9 weeks
c. 5 weeks
d. 7 weeks
84. What is the earliest start time for the
activity 6-7? (1 point)
a. 7 weeks
b. 9 weeks
c. 14 weeks
d. 15 weeks
8
6
1 2
5
4
3
6
7
4
2
3
3
5
9
2
Part B
159
85. For which of the following activities the
latest finish time is 15 weeks? (1 point)
a. 2-5
b. 4-5
c. 5-7
d. 5-6
86. For which of the following activities the
latest starting time is 14 weeks? (1 point)
a. 5-7
b. 2-5
c. 5-6
d. 4-5
87. Which of the following activities has zero
slack time? (1 point)
a. 1-4
b. 4-5
c. 5-7
d. 5-6
88. Identify the correct critical path from
among the given options. (1 point)
a. 1-2-5-7
b. 1-4-5-6-7
c. 1-2-3-5-6-7
d. 1-2-3-5-7
(Questions 89 to 92) To manufacture a type of
bolt, a firm requires two machines A & B.
There were seven jobs from seven different
customers who ordered seven different types of
bolts. The processing times (in minutes) of
these jobs on machines A & B are given in the
following table. Use this information to answer
the following four questions.
Job A B C D E F G
Mach
ine A
30 50 45 25 60 40 55
Mach
ine B
25 60 35 20 30 30 40
89. Determine the optimum sequence to
process these five jobs using Johnsons
sequencing rule. (1 point)
a.
D F C B G E A
b.
D E C B G F A
c.
D E C G B F A
d.
D F G B C E A
90. Calculate the total lapsed time for the
seven jobs based on the optimum
sequence. (3 points)
a. 305 minutes
b. 330 minutes
c. 325 minutes
d. 315 minutes
91. What is the idle time on Machine A?
(1 point)
a. 20 minutes
b. 25 minutes
c. 30 minutes
d. 15 minutes
92. What is the total idle time on Machine B?
(2 point)
a. 75 minutes
b. 80 minutes
c. 85 minutes
d. 90 minutes
This section contains answers and explanations for the model tests.
Paper I
Part B: Answers and Explanations
Answers and Explanations
Paper I - Model Test 1
1. (c) Lower initial investment
The high cost of installation and level of maintenance for automated machines has been a major
deterrent in the use of technology in the production process.
2. (b) Frederick W. Taylor
Frederick W. Taylor in his book Principles of Scientific Management introduced the concept of
scientific management in the field of operations management. Taylor proposed a systematic
approach called the shop system and implemented it in Midvale Steel Works, where he worked,
to improve labor efficiency. Henry Ford later introduced scientific management concepts in the
moving assembly line for production of cars. Adam Smith recognised the importance of division of
labor in his book The Wealth of Nations. Elton Mayo conducted Hawthorne stdies that
highlighted the importance of human dimensions and not just planning and control of materials
and machines.
3. (a) Shop system
Taylor introduced the concept of scientific management. According to this, scientific rules
governed worker productivity and it was the prerogative of the management to study and apply
these rules in operations. Taylor proposed a systematic approach called the shop system and
implemented it in Midvale Steel Works to improve labor efficiency.
4. (a) Produce-to-stock policy
In the produce-to-stock policy, products are produced well in advance and are stored in
warehouses, from where they are distributed in accordance with customer orders.
5. (d) i/s, ii/p, iii/q, iv/r
Production flexibility is the ability of an organization to produce different products on short notice.
Low cost process involves producing products at lower costs when compared to competitors.
Product variety refers to an organizations ability to produce different products to cater to different
customer segments. Quality is where the company produces higher quality products when
compared to its competitors.
6. (c) Maturity stage
As the sales become stagnant in the maturity stage, organizations focus on eliminating unnecessary
costs and increasing efficiency in production processes. These strategies prevent the erosion of
profit margins.
7. (a) Core competence
Having superior engineering personnel and producing high quality products is considered a core
competency. Unique selling proposition is a verbal or visual message communicated by a
company, through advertising, about a specific attribute of its product absent in competitors.
Producing a product at cheaper costs than competitors, and flexibility in production processes are
examples of core competence.
8. (b) Process-focused systems
Process-focused systems are highly flexible systems which can be easily modified to support other
product designs. Therefore, by using these systems one can produce different products via different
processes.
Operations Management
164
9. (b) Decrease the value of
Overreacting to the most recent demand implies that the demand forecasted is very optimistic.
Therefore to reduce the forecasted demand, the value of should be reduced.
10. (a) F
t
= D
t-
1+(1-) F
t
-1
In first order exponential smoothing method, the demand forecast for next period is given by the
equation, F
t
= D
t-1
+ (1) F
t-1
11. (c) It always lies between 0 and 1
The value of exponential smoothing constant alpha () always lies between 0 and 1, which can be
mathematically expressed as, 0 1.
12. (a) Only i
Tracking signal is a measure of accuracy that assesses the precision with which forecasting
methods are able to predict demand. Determination of forecasting errors helps operations managers
plan their functional activities in a way that minimizes the effect of forecasting errors. The least
square method is used to generate a regression model by assigning data to a single line. Nominal
group technique is a qualitative method of forecasting demand.
13. (a) Simple moving average method
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) technique forecasts demand on the basis of the average
demand calculated from actual demand in the past. The SMA method is effective only when a
product does not experience fluctuation in demand over a period of time and the past demand for
the product is not seasonal. Historical analogy is a qualitative method and is judgmental in nature.
The other two methods have in-built features to tackle the fluctuations in demand.
14. (c) Tracking signal value nearer to zero indicates low forecast accuracy
All the statements are correct except for option c. A tracking signal nearer to zero indicates that
the forecast is more accurate.
15. (c) A maximum of two decision variables
The graphical method is applicable only to problems in which a maximum of two decision
variables are involved. If it is more than two, the graph becomes difficult to represent and more
complex and it becomes harder to identify the feasible region.
16. (b) Additivity
The objective function and constraints include several decision variables. Here, it is assumed that
the total value of the objective function and each constraint is equal to the sum of individual
contributions from each decision variable. It means that the model does not consider any
synergistic or anti-synergistic effects among decision variables while calculating the total value for
the objective function.
17. (d) Constraint inequalities are taken as equations and are plotted on the graph
Constraints usually come with inequalities. To plot them on a graph, they should first be converted
into equations. Two coordinates for each constraint are obtained to plot each constraint as a line on
the graph.
18. (c) Vogels approximation method
The first step in Vogels approximation method is to calculate the difference between least cost
and the next least cost in a row or column. This difference is called penalty. Then the row or
column with largest penalty value is identified and a quantity is assigned to the least cost in that
row. This process is continued until demand is met.
Part B
165
19. (a) North-West corner method
The North-West corner method assigns the maximum possible quantity of products to the top left
corner cell of the transportation problem. After the allocation, supply and demand numbers are
adjusted. The other two methods, excluding the stepping stone method, are used to test the solution
for optimality and focus on costs while allocating.
20. (a) An optimal solution is possible only when coefficients of variables have certain or
definite problems
It is assumed that all the constants have certain values. This is because the solution for a linear
programming problem can be assumed as optimal only when the coefficients of variables have
certain or definite values.
21. (a) Assembly chart
Assembly charts provide a comprehensive account of the entire production process. They provide
an overall view of the movement of components and sub-assemblies in the production system.
22. (b) Higher fixed costs and lower variable costs
Product focused systems need high initial costs (fixed costs); however operating variable costs
remain low due to limited scope for product variety.
23. (d) Facility layout
While demand, resource availability, and allocation of resources are inputs to a process plan,
facility layout is an output of the process plan, i.e. facility layout is designed based on the process
plan.
24. (b) Vertical integration
Vertical integration refers to the extent to which the production and distribution functions are
brought under the ownership of the organization. Hence, the degree of vertical integration
determines the extent to which a product and its components are produced internally.
25. (d) Line flow production system
Product focused production is also called line-flow production system.
26. (b) Group technology
Product-focused production produces standardized products with prime focus on product rather
than on processes. Process-focused production focuses on the process to produce the product. But,
both these concepts are used in group technology. The product mentioned in the question uses both
the types and thus, comes under group technology. Job shop production, on the other hand,
involves producing customized products.
27. (a) To provide smooth workflow of materials and ensure operational efficiency
The main objective of a facility layout is to ensure smooth work flow and maximize efficiency in
the production process.
28. (c) China
As the company has opted for a labor intensive process requiring more manpower, it could prefer
developing nations like China where it can utilize the vast manpower available at low cost.
29. (b) Cost-profit-volume analysis
Break-even analysis is also called as cost-profit-volume analysis. While break-even analysis and
quality factor analysis are used in location decisions, ABC analysis is used in inventory
management. Value analysis is used in purchase management and product design.
Operations Management
166
30. (b) Product layout
Product layouts, also called flow-shop layouts or straight-line layouts, involve arrangement of
equipment or machines in the same sequence by which a product is made.
31. (b) Process layout
Process layouts, also known as functional layouts or job-shop layouts, involve grouping all similar
equipment or functions. Grouping technology layout is a variant of product layout. A fixed
position layout involves movement of all machines and men while the product remains stationary.
32. (a) Higher transportation costs of raw materials
When a steel manufacturing facility is located near the port, a compromise has to be made on the
transportation cost of raw materials. This is because iron ore mines (raw material for steel) are
generally located away from the seacoast.
33. (c) Higher flexibility in job rotation
Flexibility in shifting people from one job to other is not possible as workers specialize in certain
activities. In the absence of a worker, it is difficult to shift workload to other available workers as
they may not possess the required skills or expertise.
34. (c) i/q, ii/s, iii/p, iv/r
Job identification describes the department under which the job falls, the number of workers
needed, reporting authority, etc. A job title should reflect the purpose and responsibilities of a job.
Job duties include duties and responsibilities associated with the job in a summarized form. Job
specification describes the skills and qualifications required to perform it competently.
35. (a) Task identity
Task identity defines clearly the tasks that are needed to complete the main job.
36. (d) Top management
The difficulty in defining jobs varies at different levels. While jobs of assembly line workers and
supervisors are easy to define, it is difficult to define the other two. Of middle managers and top
management, it is most difficult to define the jobs for the latter as their duties and responsibilities
cannot be fixed. They need to be performed in different ways to meet the unanticipated and
dynamic business situations.
37. (b) To maximize worker inputs in terms of time and physical effort
Objectives of job design are to boost employee motivation, to achieve performance standards and
to match skills and abilities of each worker with job requirements. Job design refers to the process
through which tasks are structured to improve efficiency and productivity of workers. It should
minimize worker inputs (time and physical effort) and maximize their output.
38. (b) Extent of motivation needed
Skill varieties include range of skills, level of skills, abilities and talent of the individual for the
post, etc. Motivation levels are not considered a part of skill requirement. Though not included in
the skill sets for a job, workers need to be motivated to work efficiently and effectively.
39. (d) Work sampling
Work sampling is a technique to analyze work by making several observations, usually taken at
random, to see the relative frequency with which various activities are carried out.
40. (a) The time consumed by an average worker, working at average speed, to perform a
specific task under normal operating conditions
The time consumed by an average worker, working at average speed, to perform a specific task
under normal operating conditions is generally referred to as time standard, work standard, or
standard.
Part B
167
41. (c) Job identification observation pace rating computing normal time & allowances
computing standard time
Time study starts with job identification. Observations are then taken, workers are pace rated and
normal time is computed along with time for allowances, if any. Finally, the standard time is
computed.
42. (c) Work standard
The time consumed by an average worker, working at an average speed, to perform a specific task
under normal operating conditions is generally referred to as time standard, work standard, or just
standard.
43. (b) They help reduce machine utilization
Work standards help improve machine utilization rather than reducing it.
44. (c) Pre-determined Motion Time Study
Pre-determined Motion Time Study (PMTS) is the technique of setting work standards for work
measurement. All other options are optimal models used for formulating aggregate plans.
45. (a) Long-range planning
Long-range planning focuses on a period of over one year and is generally carried out annually.
Process planning and strategic capacity planning are examples of long-range planning. Medium-
range planning focuses on a period of six to 12 months. Examples of medium range planning are
aggregate planning, master production scheduling, and materials requirement planning. Short-
range planning focuses on a period less than six months. Order and workforce scheduling are
examples of such planning.
46. (d) Maintaining product prices to influence the demand level
Master production scheduling is generally based on the results of demand forecasts. These results
are not always accurate and actual production output is not always the same as the real market
demand. To accommodate imbalances, operations managers modify the master production
schedule. One way is to alter (not maintain) product prices to influence the demand level.
47. (a) i and ii
When a firm achieves economies of scale, the firms per unit cost decreases due to reduction in
fixed costs. But variable costs remain more or less the same irrespective of increase in volume.
Inventory costs are not directly dependent on whether the firm has achieved economies of scale or
not.
48. (a) Quantities and required delivery dates of final products
The master production schedule of make-to-order organizations deals only with end-items or final
products and not components and sub-assemblies.
49. (c) Short -range
Short-range planning focuses on a period of less than six months. Order and workforce scheduling
are examples of such planning.
50. (a) Minimizing total inventory cost
EOQ method is used to identify the order quantity to minimize the total cost i.e. the sum of
ordering and carrying costs.
51. (a) Raw material inventory
Large shipments of raw materials reduce incoming freight costs and material handling costs of a
firm considerably.
Operations Management
168
52. (a) Orders are placed at equal intervals of time
In the fixed order period (P) system, the order period is fixed but order quantity varies with
requirement. The quantity ordered each time depends on the current inventory level or inventory in
hand and future requirements. The fixed order quantity (Q) system assumes that the demand for
inventories over a period of time (i.e., usage rate of materials) is constant and lead-time for
replenishment of inventories is zero (i.e., materials are received immediately after they are
ordered).
53. (a) Stock-out costs
Stock-out costs are penalty costs associated with delay in meeting demand or the firm's inability to
make the product due to shortage of stocks.
54. (b) Q system
In Q system, order quantity (Q) is always constant and the order is placed when the level of
inventory reaches the reorder point. This system is also referred to as the reorder point system.
55. (d) Maintain control over supply chain activities
Only the first three arguments favor buy decisions. Extent of control over supply chain activities
reduces if production is outsourced rather than done in-house.
56. (c) Break-even analysis
Make-or-buy decisions are based on break-even analysis. While making the decisions, costs of
producing in-house as well as costs of purchasing from outside are analyzed. These costs are
dependent on the quantity demanded.
57. (d) Contract negotiation and communication interface
Under contract negotiation and communication interface, the purchase department negotiates with
the suppliers on behalf of the indenting departments (who actually use the material) to purchase the
requirements at the most economical prices.
58. d) Purchase order
Purchase order is the legal document issued by a firm that authorizes suppliers to supply goods. It
represents the buyers obligation to buy materials against specified terms mutually agreed upon
with the seller(s).
59. (a) i, ii, iv
When returns on investment in manufacturing goods are attractive, the firm can go for
manufacturing instead of purchase. Thus, this is not a valid reason for the firm to purchase the
product.
60. (b) Hawthorne studies
Hawthorne Studies were initially conducted to establish a relationship between the influence of the
work environment (say, lighting in the work area) and worker productivity. Later studies paved the
way for in-depth research on behavioral aspects of workers in the work area.
61. (b) Standardized production
Standardized production is undertaken when a company manufactures a limited variety of products
in large batches to reduce costs.
62. (c) Response strategy
The situation mentioned here is an example of responding to daily requirements of the customer.
The speed and flexibility of a supplier to respond to a customers requirements is a competitive
advantage.
Part B
169
63. (d) Regression analysis
Regression is a causal method where the relationship between different variables (influencing the
demand of a product) and their influence on each other is evaluated. It is based on the concept that
forecast is influenced by the occurrence of other events. Data is used to establish the functional
relationship between variables, which is then used to forecast dependent variable values.
64. (b) Close to Zero
The value of a mean forecast error for an unbiased forecast model will be close to zero.
65. (c) Increases to a certain point
When the price of a commodity is reduced, keeping other things constant, the demand for that
commodity increases up to certain level and then remains constant.
66. (b) Economies of scale do not play any role in linear programming
In linear programming problems, it is assumed that the contribution of individual decision
variables in the objective function is proportional to their numeric value. Suppose variable X
j
represents the number of units of product j produced and C
j
is the quantity of raw material utilized
in producing a unit of the product, then producing 10 units of product j consumes 10 times the raw
material quantity C
j
. In other words, the raw material consumption per unit product produced is
constant. This means economies of scale do not play a role in linear programming problems.
67. (b) The value will decrease by C
2
Consider C
2
x
2
. If C
2
= 10 and x
2
= 3, then C
2
x
2
= 30. It X
2
is reduced by one unit (i.e. 3-1=2) then
C
2
x
2
= 20. Hence, when x
2
is decreased by one unit, the objective function will decrease by C
2
.
68. (c) Product-focused production system
Product focused production systems are generally used for mass production where the scope for
product variety is limited.
69. (b) Forward integration
Forward integration is the expansion of ownership of production to the distribution chain and the
market. Backward integration expands the ownership of the production and distribution chain
backwards, i.e., towards the source of supplies.
70. (c) Transportation method
The transportation method of linear programming analyses costs involved in transporting supplies
from different sources and compares such costs for two or more locations. This helps select the
location that gives the least costs.
71. (a) Layouts are permanent and do not change over time
No layout is permanent as they are subject to modifications with changes in product design,
process design, introduction of new products, etc.
72. (d) Grouping technology layout
In a grouping technology layout (also called cellular manufacturing layout), dissimilar machines
are grouped into cells. Each cell functions like a product layout within a larger job shop or process
layout.
73. (a) Job specification
Job description describes the tasks, duties and responsibilities of a job. It includes information
regarding job content, job requirements in terms of necessary and desirable qualifications, work
experience, mental and physical effort involved, scope of responsibilities, nature of reporting
relationships and so on. The qualification mentioned in the job description is called job
specification. Job content is the central aspect of job design. It defines the set of activities to be
performed on the job. Job specialization involves assigning employees to positions that require
specific skill sets.
Operations Management
170
74. (a) The number of workers and reporting authority in a job
Job identification describes the department under which the job comes, number of workers needed,
reporting authority, etc.
75. (b) Work sampling
Work sampling is another work measurement technique similar to pre-determined motion time
data system. The different techniques used in work measurement are time study, historical
analysis, standard data, work sampling and predetermined motion time data systems.
76. (a) Back-order strategy
To maintain smooth operations, organizations use the back-order strategy, in which current order
commitments are fulfilled in the future. Back-order strategy assumes that customers are willing to
wait for delivery at a later date.
77. (b) Cumulative demand and cumulative output capacity
Graphical method for aggregate output planning is a two-dimensional model used to relate
cumulative demand to cumulative output capacity.
78. (c) 19,550 units
We use the formula:
F
2007
= D
2006
+ (1) F2006
F
2007
= 0.1 x 20,000 + (1-0.1) x 19,500
= 2,000 + 17,550
= 19,550 units
79. (d) F
3
W
1
The penalty for column W
1
is 6, which is the highest. In this column 8 is the least cost (in cell F
3
W
1
). Hence F
3
W
1
would be first cell to which quantity should be allocated.
80. (a) 10,100
Factory/Warehouse
W
1
W
2
W
3
Supply
14 20 11
F
1
250
250
17 11 16
F
2
150 200
350
8 9 13
F
3
200 100
300
Demand 200 250 450
Step 1: First, we consider the cell where the unit cost of transportation is the least; i.e. the cell (F
3
,
W
1
) with a cost of Rs. 8.
Step 2: The possible number of goods that can be assigned to the cell (F
3
, W
1
) is 200.
Step 3: Next, we move to the cell where the next higher unit cost of transportation exists and
assign the possible number of goods.
Step 4: The process is continued till the entire goods are assigned.
The number of occupied cells is 5, that is equal to the value of (m+n-1), i.e. (3+3-1). So, the
solution obtained is a feasible solution.
Therefore, the cost associated with the solution is
= (8x200) + (9x100) + (11x150) + (11x250) + (16x200)
= 1,600 + 900 + 1,650 + 2,750 + 3,200
= Rs.10,100
Part B
171
81. (c) Rs.25,000
Annual order cost = fixed cost per order (C
o
) x number of orders in the year
= C
o
x (annual demand/units ordered per order)
= 5,000 x (1,000,000 /200,000)
= 5,000 x 5
= Rs. 25,000.
82. (d) Rs.50,000
Holding cost per order is calculated as the product of holding cost per unit and average inventory.
Average inventory is the average of lowest inventory level and highest inventory level. Lowest
inventory level in EOQ model is zero and highest is quantity order (Q).
Holding cost per order = holding cost per unit x [(Q+0)/2]
= 10 x (10,000/2)
= 10 x 5,000
= Rs.50,000
83. (b) Rs.250,000 and Rs.100,000
Total cost of making the product is equal to the unit variable cost (V) times the number of units
demanded (Q) plus the fixed costs.
Total Cost
make
= Variable cost + Fixed cost = VQ + F
= 25 x 2,000 + 200,000
= Rs. 250,000
Total cost of buying is the product of price per unit (P) and the number of units procured (Q), i.e.
Total Cost
buy
= P Q = 50 x 2,000
= Rs. 100,000
84. (a) Rs.550,000 and Rs.700,000
Demand at the end of first year = 2,000 units
Demand at the end of second year = 4,000 units
Demand at the end of third year = 8,000 units
Total demand for the next three years = 2,000 + 4,000 + 8,000 = 14,000 units
Total cost of making the product is equal to the unit variable cost (V) times the number of units
demanded (Q) plus the fixed costs.
Total Cost
make
= Variable cost + Fixed cost = VQ + F
Total cost to make 14000 units = (25 x 14,000) + 200,000
= Rs.550,000
Total cost of buying is the product of price per unit (P) and the number of units procured (Q), i.e.
Total Cost
buy
= P Q.
Total cost to buy 14000 units = 14,000 x 50
= Rs. 700,000
Hence, it is profitable to make this component in-house in the long run.
Operations Management
172
85. (b) Make
Option A: Buy the components for all the five years
The cost incurred for buying the components = 25,000 50 = Rs.1,250,000
Option B: Make the components in-house for all the five years
The cost incurred in making the components in-house = (25,000 30) + 200,000 = 750,000 +
200,000 = Rs.950,000.
Option C: Buy the components for the first two years and make for the remaining three years
The given situation can also be represented algebraically as follows:
Let n be the demand for the first two years during which the company has decided to buy the
components. Then, the number of units for the remaining 3 years would be (25,000-n) units.
The total cost would be = One-time Fixed Cost + Variable Cost of buying n units + Variable Cost
of producing (25,000-n) units
i.e., Total Cost = 200,000 + (n 50) + [(25,000 n) 30]
= 200,000 + 50n + 750,000 30n
= Rs.950,000 + 20n
Therefore, the total cost of (Rs.950,000 + 20n) is more than the cost of making the components in-
house which is Rs.950,000.
Option D (cannot decide) is irrelevant in the given context as one can calculate the costs under
different conditions and select the best one.
Conclusion:
In the given situation, the fixed cost is a one-time fixed cost, which would be incurred even if one
unit of the component is made in-house. Once this fixed cost is incurred, every unit that is bought
with a variable cost of Rs.50 per unit adds (Rs.50 Rs.30) = Rs.20 to the total cost, as compared to
the option of making that unit in-house. So, there is no benefit in switching to in-house production
at any interim point of time.
Over the five-year period, it is clear that Option B costs less than Option A or Option C. Hence,
making the components in-house is the best decision.
86. (b) 10.75, 9.06
Distribution
Center
X Y Quantity
(in tons) (Q)
QX QY
A 5.5 7 60 330 420
B 8 12 90 720 1080
C 12 6 110 1320 660
D 15 11 100 1500 1100
Total 360 3870 3260
X
c
= QX/Q = 3870/360 = 10.75
Y
c
= QY/Q = 3260/360 = 9.06
Answers and Explanations
Paper I - Model Test 2
1. (a) Conveyance authorization card
A Kanban system uses three types of cards to initiate material transactions: production
authorization card, vendor authorization card, and conveyance authorization card. A conveyance
authorization card authorizes a materials handling agent to move the tray to a specified destination.
This specifies the products name, its identification number, and delivery destination.
2. (a) Checking the quantity and quality of the incoming material and generating receiving
reports
Checking the quantity and quality of the incoming material and generating receiving reports is a
function of the purchasing/receiving department which falls under the production control. The
other three options are associated with inventory control. Inventory control is used to minimize the
overall cost of production.
3. (d) Quality of material
Some factors that influence the materials handling function are - type of plant layout, type of
production process used, nature of materials and the material handling equipment used. Quality of
material used can be a factor affecting the quality of finished product but it does not directly
influence the material handling function.
4. (a) Playback robots
Playback robots can store a sequence of operations in the memory. Initially, an operator performs
operations using a robot. The robot stores all those activities (in the same sequence) in its memory
and repeats them to produce similar types of products on its own subsequently.
5. (b) A vendor immediately fills up the inventory with the required quantity
A conveyance card only authorizes the material handling agents to fill material trays with required
material from the inventory and bring it back to the production worker. It does not authorize the
vendor to replenish inventory. A vendor authorization card is used to signal the vendor to replenish
inventory.
6. (a) The Kanban system follows the open loop system
Kanbans operate in closed loops and they continue to operate until the materials manager
withdraws them.
7. (b) Demand rate of a product
The number of Kanbans can be altered according to the estimated demand for a product. If the
demand for the product increases, a larger number of Kanbans are used to meet the increased
demand. Similarly, the number of Kanbans can be reduced if the demand for the product
decreases.
8. (a) ii and iv
Trucks, forklifts, mobile cranes, and industrial tractors are examples of variable-path materials-
handling equipment. A conveyor is an example of fixed path equipment.
9. (d) Bill of materials
Bill of materials is associated with the inputs of an MRP system.
Operations Management
174
10. (a) Required quantities and delivery dates of final products
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) file contains information about when and how many units
of finished products are required. It also gives the available cumulative lead-time for purchasing,
receiving, fabricating, and assembling.
11. (b) Planning report
While master production schedule, bill of materials, and inventory records file are inputs to a MRP
system, planning report is an output.
12. (a) Explosion
The first step in the MRP information processing is explosion where the end product is
disassembled into components. Explosion starts from the time a product is required and proceeds
backward to determine each production or purchasing activity that is necessary to make each
higher-level item in the product structure chart.
13. (d) i, ii, iii
The list of materials along with the quantity required to produce one unit of a product is part of the
Bill of Materials (BOM). The other three alternatives are part of the master production schedule.
14. (a) i, ii, and iii
The success of an MRP system usually depends on the product environment. The system is useful
only when an organization needs to purchase many items, a majority of which are components and
parts. The demand pattern of these items should be dependent in nature and irregular in timing.
Moreover, the lead times for purchase of these items should be consistent (not inconsistent).
15. (a) Flextime approach
Under the flextime approach, employees are given the option of choosing their work timings,
provided a specific number of hours are completed in a time period, say a week.
16. (a) Helps manage demand by adjusting the price for services
Flexibility in setting price for services is not a characteristic of reservation systems. Strategic
product pricing is a scheduling approach that helps a firm respond to shifts in demand.
17. (b) Loading
The activity of loading aims at minimizing costs by reducing machine idle time, the amount of
work-in-process inventory, etc. Loading includes the task of sequencing jobs so that the machine
idle times are minimized and jobs are completed within the least time possible.
18. (c) Service operations are scheduled according to inventory requirements
Service operations are scheduled according to demand rather than inventory requirements. Hence,
they follow the first in, first serve rule of scheduling. The appointment system is one such method
using this rule.
19. (c) Strategic product pricing
Strategic product pricing is a method that helps firms adjust to shifts in demand. The reservation
system allows many customers to use the service at a time by dedicating multiple resources to
provide the service. Appointment systems are used to control customer flow at the individual level.
Routing is a scheduling activity that explains the sequence of operations and processes to be
followed to produce a particular product.
20. (a) Only i
In an n-job and three-machine sequencing problem, three machines; A, B and C, are involved, and
each job is processed in the order ABC. In this procedure, we should ensure that -- the smallest
processing time on machine A should be greater than or equal to the largest processing time on
machine B or the smallest processing time on machine C should be greater than or equal to the
largest processing time on machine B.
Part B
175
21. (a) Loading
Loading is the process of assigning specific jobs to each work center depending on its capacities.
22. (d) Staggered times approach
Staggered times indicate that employees can choose their work hours from a list of available shifts.
23. (c) Dispatching
Dispatching is the process of releasing job orders to workers to go ahead with the production
process. In this activity, an operations manager releases job orders in accordance with the planned
sequence.
24. (c) Systems, Application and Products
The expansion of SAP is Systems, Application and Products in data processing.
25. (c) ii, iii, iv
Integration of data across departments helps in better connectivity and smooth flow of information.
It reduces data redundancy and ensures availability of right information to the concerned
department or personnel.
26. (d) Steering committee
The key activity of the steering committee is to monitor the implementation process continuously
in order to identify deviations, cost overruns, resource requirements, etc, during ERP
implementation.
27. (d) i and iv
ERP extends the functionality of MRP and MRP II systems to provide complete business
solutions. MRP systems are used in manufacturing to automate inventory management and
production processes. MRP II is an extension of MRP providing an interface with other functional
domains. As a result, it is able to achieve a high degree of integration with other automated
processes.
28. (b) Evaluate the asis situation of the business
The listing of processes in business transactions is done while evaluating the as-is situation of the
business. Hence, process mapping is done in this stage of ERP implementation.
29. (a) Compensation and benefits
The six enablers of SCM are: Customer-supplier focus, design, measurement,
participation/involvement, periodic review, and alignment.
30. (c) SCM strategy
SCM strategy forms a blueprint for supply chain operations that support and are consistent with the
manufacturing and marketing objectives of the organization.
31. (a) Develop policies that reward low cost purchases and intense negotiations
Good alignment is achieved through effective planning and execution in conjunction with cross-
functional interaction, effective information systems and organization-wide continuous
communication systems. Besides, the company leadership should strive to set goals, objectives and
strategies that support successful supplier relationships. For example, if the management rewards
the purchasing department for obtaining products at low prices from suppliers, it might hamper the
development of long-term relationships or partnerships with suppliers.
Operations Management
176
32. (d) The players in a demand chain are different from those in the traditional supply
chain
In a demand chain, meeting customer demand in time is given paramount importance. Alliances
are made between demand chain partners who can best meet customer requirements. The players
in todays emerging demand chains are the same as those in traditional chains, but their respective
roles and responsibilities have changed.
33. (d) ii, iii, and iv
The advantages of ESCM are many, including timely order-processing, improved inventory
tracking and management, more accuracy in order fulfillment, support for JIT manufacturing, cost
savings, reduction in cycle time, reduction in procurement costs, etc. ESCM results in an
extended organization that encapsulates suppliers activities. The extended organization
structure provides instant information about the status of inventory levels to suppliers. Therefore,
there is no need to carry high inventory.
34. (a) Operational planning
The operational planning component defines the operational requirements for maintaining a supply
chain. These requirements are specified in terms of tasks, resource requirements and
measurements. The functions under operational planning include commodity planning, supplier
capacity planning, planning for supplier evaluation, certification processes, etc.
35. (c) Many suppliers for a given part/component with short-term contracts
JIT encourages a firm to maintain fewer suppliers with long-term relationships
36. (c) Suggestions of workers are collected, evaluated, tested, and implemented by the
management
The open management style should not imply that workers are free to implement whatever
methods they like. Instead, existing procedures should be continued until a better way is suggested,
tested and approved. Suggestions by workers to improve processes are first collected and evaluated
by the management. The selected suggestions are tested practically to determine how much better
they are compared to the existing process. If the suggested process proves better than the existing
one, the management approves it for implementation.
37. (b) i, ii, and iv
Building effective partnerships in a JIT system depends on four elements - trust, communication,
linearity of production, and time to make changes. The design of a product has no direct bearing on
the extent of relationship with the suppliers.
38. (a) JIT firms select suppliers located away from the plant
Firms practicing JIT systems should have suppliers at close proximity. This enables easy
transportation and consistent delivery in the face of frequent purchases of material.
39. (a) Eliminating external demand variations
External demand variations cannot be eliminated by using the JIT system. By using JIT principles,
firms can reduce wastage that arises during the production process such as the waste of
overproduction, of time spent in waiting, in transportation and movement, in processing, in
keeping excess inventory and in defective parts.
40. (a) Collection evaluation selection testing approval implementation
Suggestions made by workers for improving processes are first collected and evaluated by a firms
management. The suggestions selected are tested practically to determine how much better the new
process is, compared to the existing process. If the suggested process proves better than the
existing one, the management approves it for implementation.
Part B
177
41. (c) Quality training
Prevention costs include investments made in machinery, technology and education/training
programs to reduce defects. It also includes costs to administer the firms quality program, data
collection and analysis, and vendor certification. Equipment maintenance is a detection or
appraisal cost. Disposition of defective items is an internal failure cost and warranty charges are an
external failure cost.
42. (d) ii and iv
Goods produced /man hours spent indicate the number of goods produced by a worker in an
hour, which is a measure of labor productivity in manufacturing concerns. Similarly customers
handled /number of attendants indicates average number of customers handled per attendant,
which is a measure of labor productivity in service industries.
43. (a) i/q, ii/s, iii/r, iv/p
Durability is the operational life of a product. Serviceability is concerned with how readily a
product can be serviced back into operational mode. Performance indicates the ability of a
products primary operating characteristics. Reliability is the probability of a product failing in a
time period.
44. (a) Prevention costs
Prevention costs are costs incurred by a company to prevent defective goods and services from
being produced and/or delivered to customers. This category includes investments made in
machinery, technology, and education/training programs to reduce defects. It also includes costs to
administer the firms quality program, data collection and analysis, and vendor certification.
45. (b) Sample 3 is outside the control limits. Further investigation is warranted
Range of Sample 3 is 1.2, which is more than the upper control limit of 1.00. Hence, sample 3 is
outside the upper limit and requires further investigation.
46. (b) Reliability
Reliability is usually measured as the mean time between failures (MTBF) or the failure rate per
unit of time or any other measure of use.
47. (b) Facilities management
The primary objective of facilities management is to provide a clean and conducive work
environment and enable efficient and effective progress of the core functions of an organization, be
it manufacturing, distribution, or research. Maintenance management is a primary function
associated with facilities management.
48. (b) Outsource different tasks to different vendors
It is important to outsource as well as out-task activities to retain control over vendors. Total
dependence on a single vendor is not advised. The basic objective of outsourcing is to enable a
company to focus on core competencies.
49. (a) Irregular preventive maintenance
Irregular preventive maintenance includes tasks like repairs, overhauls, and cleaning of spills.
These activities are carried out when a casual inspection of a machine reveals the need for
servicing before the next periodic preventive maintenance.
50. (c) Maintenance carried out when a machine is idle and waiting for the next job
Opportunity maintenance is carried out when the equipment is idle or it has been stopped. These
maintenance activities are not scheduled beforehand. If the equipment is idle, it is inspected, and
requisite repair or maintenance tasks are carried out.
Operations Management
178
51. (a) Janitors services
Janitors services involve housekeeping in the interior and exterior of buildings and manufacturing
facilities.
52. (d) i, ii, and iv
The functions of maintenance management are: preserve the value of the firms machinery and
other assets, use maintenance personnel and equipment efficiently, maximize the availability of
machinery for production process, eliminate or reduce accidents by regular inspection and plan and
schedule maintenance work to reduce breakdowns.
53. (b) Event
An event is the outcome of an activity or group of activities. It represents the completion of some
activities and the beginning of some others in the network.
54. (c) FMS
FMS (flexible manufacturing system) is a form of flexible automation in which several machine
tools are linked to a material-handling system. A central computer controls all aspects of the
system which is effective in producing different items that have similar processing requirements.
55. (a) Comparative advantage
The comparative advantage of a country can be defined as its ability to produce goods and services
cheaper than other countries. Organizations generally globalize their operations to take advantage
of these opportunities.
56. (d)
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t
e
t
+ +
=
Expected time represents the mean activity time of the optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely
times. Expected time is calculated by using the equation,
( )
6
p
t
m
4t
o
t
e
t
+ +
=
Option a gives the formula for mean time between failures. Option b gives the formula for the
probability of completing the project within the desired completion period. Option c represents
activity time variances.
57. (b) Different products with similar components and manufacturing processes can be
manufactured
In comparison with traditional automated systems, the flexible manufacturing system (FMS) offers
many advantages such as reduced direct labor, shorter response time, consistent product and better
control over manufacturing processes. It also helps a firm manufacture different products having
similar components and manufacturing processes.
58. (c) Economies of scale in marketing
Organizations can also obtain economy of scale in their marketing function. Here, the company
either uses the same salespeople or same promotion strategy or both for promoting its products in
different markets.
59. (a) Current assets
Raw materials fall under current assets because they are converted into finished products within a
short span of time after their purchase. They do not remain in the same form for long periods of
time. Further, the raw materials can be liquidated quickly.
Part B
179
60. (b) Profitability decreases with increase in material costs
As material costs are variable costs, a small decrease in these costs will lead to an increase in
profitability and a small increase will lead to a decrease in profitability.
61. (d) Layout planning
Layout planning is not a component of MRP. It is associated with facility layout planning.
62. (c) Bill of materials
A bill of materials lists out all the materials used to manufacture a product. It also specifies the
number of different materials required to produce one unit of the end product.
63. (c) Maximizing work-in-progress inventory
Maximizing work-in-progress inventory falls under inventory control and cannot be taken as a
metric for evaluating job priority rules.
64. (b) Gantt chart
A Gantt schedule chart describes the progress of jobs in equal intervals of time. Johnsons rule
helps firms sequence jobs so as to minimize processing time. The other two options are types of
dispatching rules associated with scheduling activities.
65. (d) Target market
When selecting an ERP package, the type of industry process or discrete it is designed for,
should also be considered. If the package is designed for a particular target market and the
organization falls under that market, it reduces the customization efforts as it is likely that the ERP
package will already have several industry-specific features.
66. (c) Modularity
Many organizations, especially small and medium-sized ones, may not want to purchase a
complete package in one instance. They may prefer to implement the package in modules. In such
cases, the modularity of the package, i.e., the availability of the package in separate modules
should be examined.
67. (a) Participation/involvement
Participation/involvement is an SCM enabler, which discusses the participation of all stakeholders
of the organization in the decision-making process. The knowledge of employees and suppliers
should also be considered while arriving at decisions. This makes the decision-making process
more effective.
68. (b) Demand chain management
In a demand chain, products dont necessarily originate from manufacturers. Any player in the
supply chain can develop them at any point. The products developed are based on consumer
research and information gathered by any supply chain partner.
69. (a) Quality circles
There are about 6 to 10 people in a quality circle who work in similar types of operations in a
manufacturing facility. The members of quality circles are generally shop floor workers or
supervisors. They gather at regular intervals to discuss ways to improve quality of work and help
each other gain knowledge.
70. (d) Long-term relationship with few suppliers
Firms that practice JIT production systems require reliable suppliers who can supply high-quality
components and materials in the required quantities. Therefore, JIT firms maintain long-term
business relationships with a few select suppliers
Operations Management
180
71. (d) Productivity
Productivity is not a function of quality. It is a measure of operational or employee effectiveness.
A company can compete on eight different quality functions: (1) Performance, (2) Features, (3)
Reliability, (4) Conformity, (5) Durability, (6) Serviceability, (7) Aesthetics, and (8) Perceived
quality.
72. (a) Prevention costs
Prevention costs are costs incurred by a company to prevent defective goods and services from
being produced and/or delivered to customers. This category includes investments made in
machinery, technology and education/training programs to reduce defects. It also includes costs to
administer the firms quality program, data collection and analysis and vendor certification.
73. (b) Developing good relationships with service providers
When facilities management is done in-house, external vendors do not come into the picture and so
there is no need to manage contracts with vendors
74. (c) Order replacement of broken down machines
Fixing up and/or replacement of broken down machines is part of break-down maintenance and
not of preventive maintenance.
75. (c) It is the longest path of interrelated activities in a project with zero slack time
The critical path is the longest path of interrelated activities with zero slack time. The critical path
consists of all those activities, which if delayed will result in the delay of project completion.
76. (a) Optimistic time
Optimistic time is the minimum amount of time required for an activity to be completed. It is
possible to complete a project within the optimistic time only when all the project conditions are
satisfactory.
77. (b) Computer aided manufacturing
Computer Numeric Controlled (CNC) machines store operation instructions in their on-board
computers which in turn control their operations. These machines can perform variety of tasks
based on instructions embedded in them.
78. (a) Government regulations to use locally produced components
Some institutional impediments are: tariffs and duties, which may limit the benefits achieved by
economies of scale in production, quantitative quotas and other similar restrictions, preferential
procurement from local organizations by government and quasi-government entities, government
pressure to use locally produced components or to engage in local R&D, preferential tax treatment
and labor policies and corporate laws, tax laws or other policies of the local government.
79. c) E-A-B-C-D
E has the earliest due date of 2 days. A follows with 5 days, B with 6 days, C with 7 days, and D
with 9 days.
80. (a) 2.4 days
Jobs
(In order of arrival)
Processing
Time (Days)
Due Date
(Days hence)
Flow Time Delay
E 1 2
0 + 1 = 1 1 2 = 0
A 3 5 1 + 3 = 4 4 5 = 0
B 4 6 4 + 4 = 8 8 6 = 2
C 2 7 8 + 2 = 10 10 7 = 3
D 6 9 10 + 6 = 16 16 9 = 7
Average completion time = (0+0+2+3+7) /5 = 12/5 = 2.4 days.
Part B
181
81. (c) 1.67
Critical ratio for Job A = Actual Time Remaining/Work Remaining = 5/3 = 1.67
82. (a) 1, 5, 2, 4, 3
As the least time on machine A is greater than or equal to greatest time on machine B, Johnsons
sequencing rule can be applied to this problem.
Now, we simplify the machine problem into a two machine problem using two fictitious machines
G and H where G
i
= A
i
+ B
i
and H
i
= B
i
+ C
i
. (i represents job number).
Job Processing Times (in minutes)
G
i
= A
i
+ B
i
H
i
= B
i
+ C
i
1 33 35
2 77 88
3 63 42
4 63 55
5 55 66
Job 1 has the least processing time on machine G (33 minutes). It is placed at the beginning of the
sequence. The job with least processing time on machine H is placed at the end of the sequence.
Here too, job 1 has the least processing time of 35 minutes. As it is already placed at the
beginning, the next job with least processing on machine H is taken (job 3 with 42 minutes) and is
placed at the end of the sequence. Again, on machine G, the job with least processing time from
the remaining available jobs (job 5 with 55 minutes) is selected and placed at the beginning as the
second job in the optimum sequence. Now only jobs 2 and 4 are remaining. Of these, on machine
H, job 4 has the least processing time (55 minutes) and it is placed just before job 3. Thus, the
remaining job is job 2 and it is placed in the middle of the sequence.
Hence the optimum sequence is 1, 5, 2, 4, 3
(working table)
Activities Duration
(weeks)
(D)
Earliest
Starting
Time (E)
Earliest
Finish
Time (E+D)
Latest Finish
Time
(L)
Latest
Starting Time
(L-D)
Float
(L-D)-E
1-2 3 0 3 3 0 0
1-4 3 0 3 4 1 1
2-3 4 3 7 7 3 0
2-35 2 3 5 9 7 4
2-5 4 3 7 7 3 0
3-5 2 7 9 9 7 0
4-5 5 3 8 9 4 1
53-6 6 9 15 15 9 0
53-7 9 9 18 23 14 5
4-3 5 3 8 9 4 1
5-3 2 7 9 9 7 0
6-7 8 15 23 23 15 0
Operations Management
182
The earliest time can be calculated by using forward pass computation. The earliest start time for
an event is given by the earliest starting time plus activity duration of the preceding activity. (The
earliest start time for an activity (a-b) is given by the earliest expected occurrence time of the event
a). For instance, earliest start time for the activity 1-2 would be earliest expected occurrence time
for event 1. The earliest event time for the starting event is taken as zero. Therefore, the earliest
start time for the first activity is 0 or E
1
= 0.
(working diagram)
Step 1: In the given network diagram, the first event is followed by two events 2 and 4. Using
forward pass computation: E
2
= E
1
+D
1-4
= 0+3 = 3, E
3
= E
1
+D
1-2
= 0+3 = 3. In this way, we can
compute the earliest start time for the remaining activities. The earliest finish times can be
calculated by adding the duration of each activity to the respective earliest start times. Therefore,
earliest finish time of the activity 1-2 is 0 + 3 = 3 weeks. In this way we obtain earliest finish times
for all the activities. If two or more activities converge into the succeeding activity, the greatest
value among them is taken as the earliest start time for the activity. For example, in the network
diagram, three activities converge at event 5 and the possible values of earliest start time are 9
(from activity 3-5), 5 (from activity 2-5), and 8 (from activity 4-5). As 9 is the largest value, the
earliest start time for event 5 is taken as 9 (E5 = 9).
Step 2: Computation of latest finish times can be done by using backward pass computation.
Backward pass begins from the end node, and proceeds towards the first node. The latest finish
time for the last activity is equal to the earliest finish time of the last activity. Therefore, L
7
= E
7
=
23, L
6
= L
7
D
6-7
= 23 - 8 = 15. If there are more than two activities originating from an event,
then the lowest value of the latest finishing times should be considered. In case of event 5 from the
diagram, the possible latest finishing times (L5) can be 14 and 9. As 9 is smaller than 14, we take
L5 = 9. Similarly, for event 1, the possble L1 values are 0 and 1. 0 is taken as L1 as it is smaller
than 1. (If zero does not figure in the possible values, then there is a error in the problem).
Step 3: Critical paths can be identified by calculating the float or slack values, as shown in the
working table. The float value of each activity can be calculated by using either starting time or
finish time. In the working table the float values are the difference between latest start time (L-D)
and earliest start time (E). All the activities which have float as zero are part of the critical path.
Hence, in this problem, the critical path is 1-2-3-5-6-7.
83. (b) 9 weeks
The earliest start time for the activity 5-6 is 9 weeks. (Refer the working table and diagram
followed by the explanation).
8 6
1 2
5
4
3
6
7
4
2
3
3
5
9
2 E1 = 0
L1 = 0
E4 = 7
L4 = 7
E2 = 3
L2 = 4
E3 =3
L3 = 3
E5 = 9
L5 = 9
E6 = 15
L6 =15
E7 = 23
L7 = 23
Part B
183
84. (d) 15 weeks
The earliest start time for the activity 6-7 is 15 weeks. (Refer the working table and diagram
followed by the explanation).
85. (d) 5-6
The latest finish time is 15 weeks for activity 5-6. (Refer the working table and diagram followed
by the explanation).
86. (a) 5-7
The latest start time is 14 weeks for activity 3-7. (Refer the working table and diagram followed by
the explanation).
87. (d) 5-6
Activity 5-6 has zero slack time. Activities 1-4, 4-5, 5-7 have a slack time of 1, 1, and 5
respectively. (Refer the working table and diagram followed by the explanation).
88. (c) 1-2-3-5-6-7
The critical path is the longest path in the network with zero slack time. Here 1-2-3-5-6-7is the
critical path. (Refer the working table and diagram followed by the explanation).
89. (a)
D F C B G E A
The least processing time on machine A is for job D (25 minutes). It is placed at the beginning of
the sequence. The job with least processing time on machine B is placed at the end of the
sequence. Here job A has the least processing time of 25 minutes and is placed at the end of the
sequence. (Though job D has a lower processing time of 20 minutes, it cannot be taken as it is
already placed at the beginning of the sequence). This process is continued to get the optimum
sequence.
90. (b) 330 minutes
Machine 1 Machine 2 Optimum
Job-
sequence
Time in Processing
Time
Time out Time in Processing
Time
Time out
D 0 25 25 25 20 45
F 25 40 65 65 30 95
C 65 45 110 110 35 145
B 110 50 160 160 60 220
G 160 55 215 220 40 260
E 215 60 275 275 30 305
A 275 30 305 305 25 330
Total lapsed time at the end of seven jobs is 330 minutes.
91. (b) 25 minutes
Total idle time on machine A is the difference between the time when the last job in the optimum
sequence is completed on machine B and the time when the last job is completed on machine A. It
is 330 305 = 25 minutes
Operations Management
184
92. (d) 90 minutes
Total idle time on machine B = (Time taken by Machine A to complete the first job in the
optimum sequence) + [(time when k
th
job starts on machine B) (time when (k-1)
th
job finishes
on machine B)].
= 25 + [(65-45) + (110-95) + (160-145) + (220-220) + (275-260) + (305-305)]
= 25 + [20 + 15 +15 + 0 +15 + 0]
= 90 minutes
Paper II
Part B: Model Tests
Paper II - Model Test 1
Time: 3 Hours Total Points: 100
1. Decisions on scheduling weekly
production of products can be categorized
under which type of decisions of
operations managers?
a. Strategic decisions
b. Tactical decisions
c. Operational decisions
d. All of the above
2. _________ is a computer controlled
warehouse system that automates inflow
and outflow of materials from the
warehouse and shop floor on the basis of
production requirements.
a. AS/RS
b. CAD
c. FMS
d. CAM
3. Many technologies have been developed to
support the production process and
increase efficiencies. Identify the one that
has minimized worker involvement in the
production process during manufacturing.
a. Manufacturing information systems
b. Computer-aided manufacturing
c. Linear Programming
d. Automated storage and retrieval systems
4. Availability of raw materials and nearness
to markets are some of the factors that are
considered while making decisions
regarding plant location. Which
component of operations strategy deals
with decisions such as plant location?
a. Allocation of resources to strategic
alternatives
b. Technology selection and process
development
c. Product design and development
d. Facility planning
5. State Bank of India has the biggest
network of branches and ATMs across
India. This can lead to which type of
competitive advantage for SBI?
a. Low cost production process
b. Product variety and facility size
c. Convenience and location
d. All of the above
6. Which of the following products are
generally produced under the produce-to-
order policy?
a. Refrigerators
b. Ballpoint pens
c. Aircraft
d. Television
7. Identify the relationship between the net
present value (NPV) and profitability of a
project.
a. The greater the NPV, the greater will be
the profitability
b. The greater the NPV, the lesser will be the
profitability
c. Profitability cannot be judged with NPV
d. The lesser the NPV, the greater will be the
profitability
8. Time series data may help forecasters
identify various demand characteristics of
a product except one of the following.
Identify it.
a. Random variations
b. Seasonality
c. Trend
d. Maximization
9. Qualitative methods are subjective and
judgmental in nature. Which of the
following is a qualitative method of
forecasting?
a. Simple moving average
b. Regression analysis
c. Delphi method
d. Exponential smoothing
Answer all the questions.
Each question carries one point, unless specified otherwise.
Operations Management
188
10. The value of the tracking signal explains
the nature of demand. Which of the
following statements correctly states this
relationship?
a. A positive tracking signal indicates that
demand is overestimated
b. A positive tracking signal indicates that
demand is underestimated
c. A negative tracking signal indicates that
estimated demand is equal to actual
demand
d. A negative tracking signal indicates that
demand is underestimated
11. A relationship exists between dependent
and independent variables of demand.
Which of the following techniques is
appropriate when such relationships exist?
a. Qualitative methods
b. Moving average method
c. Causal methods
d. Least squares method
12. For any product, there are six major
forecast components: base demand,
seasonal factors, trends, cyclical factors,
promotions and the irregular component.
Which component gives the long-term
pattern of movement of demand over a
period of time?
a. Trend component
b. Seasonal component
c. Cyclical component
d. Base demand
13. Time series methods are divided into static
and adaptive methods. Identify the odd one
out.
a. Simple moving average method
b. Weighted moving average method
c. Basic time series forecasting method
d. Exponential smoothing method
14. The simplex method can be applied to
problems where the number of decision
variables is more than two. However,
inequalities in the constraint equation are
converted to equalities. How is this done?
a. Introduce objective functions
b. Introduce slack variables
c. Introduce decision variables
d. Introduce constraints
15. Linear programming is used to arrive at
decisions on product mix, transportation,
allocation of resources, etc. What are the
possible constraints for a transportation
decision in linear programming?
i. Market
ii. Destination requirements
iii. Inventory space
iv. Capacity
a. only iii
b. only ii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iv
16. Which among the following is not a
method used in developing an initial
feasible solution for a transportation
problem?
a. North-West corner method
b. Least cost method
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Stepping stone method
17. Which among the following is not a major
component of a constrained optimization
model?
a. Decision variables
b. Objective functions
c. Constraints
d. Optimal solution
18. What should be the possible action if
production capacity is more than the
requirement (demand) in a transportation
problem, to balance it?
a. An existing warehouse is subtracted
b. A dummy warehouse is added
c. An existing origin is subtracted
d. A dummy origin is added
19. Which among the following methods does
not consider either least cost or penalties
for assigning products to the cells in the
table of a transportation problem?
a. Least cost method
b. North-West corner method
c. Vogels approximation method
d. Both a & c
20. Which of the following is a disadvantage
of process-focused production system?
Part B
189
a. Highly skilled employees
b. Greater flexibility
c. Lower initial investments
d. Use of general purpose equipment
21. Non-productive activities like storage,
delay, transport, input etc, are also
included in the process chart. Match the
following activities with the appropriate
symbols.
i. Storage
ii. Delay
iii. Transport
iv. Input
p. ()
q. (D)
r. ()
s. ()
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/s, iv/r
c. i/q, ii/p, iii/r, iv/s
d. i/p, ii/r, iii/s, iv/q
22. There are various types of process designs
that are generally used by organizations. In
which type of process design, products or
services tend to flow along linear paths
without backtracking or side tracking?
a. Product-focused systems
b. Process-focused systems
c. Group technology
d. All the above
23. Logan Rubber manufactures synthesized
rubber caps that are used by many
companies as a component in their
products. When Logan Rubber wanted to
add a new rubber-based product to their
product mix, they realized that the present
machinery could not be used to produce it.
As a result, they decided to install new
machinery. What production system did
Logan have that prevented it from using
the existing machinery for the new
product?
a. Job shop production system
b. Cellular manufacturing system
c. Batch production system
d. Product-focused system
24. Product/service flexibility refers to the
ability of the production system to shift
quickly from producing one product to
another. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of a production system with
product/service flexibility?
a. It uses general purpose equipment
b. It requires a multi-skilled workforce
c. Employees have to be trained to perform
different jobs
d. Employ part-time workers to meet the
demand
25. Product-focused systems are characterized
by product design and batch size. Which of
the following statements correctly explains
these two aspects?
a. High diversity in product design and large
batch size
b. High diversity in product design and small
batch size
c. Low diversity in product design and large
batch size
d. Low diversity in product design and small
batch size
26. Which of the following types of layout is
used when the product manufactured is
bulky, heavy, or fragile?
a. Product layout
b. Process layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Group technology layout
27. A majority of the companies
manufacturing fire crackers are
manufactured in and around Sivakasi in
Tamil Nadu. Which factor would have
affected the selection of Sivakasi as an
ideal location for manufacturing fire
crackers?
a. Proximity of markets
b. Availability of transportation facilities
c. Arid and dry climate with minimal rainfall
d. Availability of services
28. Highly skilled workers are required for
which of the following layouts?
a. Process layout
b. Product layout
c. Fixed position layout
d. Hybrid layout
Operations Management
190
29. Center of Gravity method is used to
evaluate and find the optimal location for a
distribution center. What is the basic aim
of this method?
a. To reduce procurement costs
b. To reduce production costs
c. To reduce transportation costs
d. To reduce inventory costs
30. In which of the following methods used
for selection of a location, are different
factors assigned weightages?
a. Break-even analysis
b. Point-rate method
c. Transportation method
d. None of the above
31. Two dimensional scaled down drawings of
equipment and machinery is used to
determine the best layout for a facility.
This is a feature of which model used to
develop a layout?
a. Graphic and schematic analysis
b. CRAFT model
c. Load distance model
d. Line balancing
32. ___________ investigates job content, the
physical conditions in which the job is
carried out, and the qualifications
necessary to carry out job responsibilities.
a. Job description
b. Job analysis
c. Job profile
d. Job specification
33. The Job Characteristics Model developed
by Richard Hackman and Greg Oldham
includes five characteristics. They are skill
variety, task identity, task significance,
autonomy, and feedback. Flexibility and
discretion is related to which of the
following?
a. Task identity
b. Task significance
c. Autonomy
d. Feed back
34. The self-esteem of an employee is
enhanced when an important responsibility
is delegated. This is associated with which
type of feasibility?
a. Technical feasibility
b. Economical feasibility
c. Behavioral feasibility
d. Political feasibility
35. Identify the correct statement?
a. Job description is part of job evaluation
b. Job description is part of job identification
c. Job specification is part of job description
d. All of the above
36. Which of the following work measurement
techniques use statistical tools to arrive at
the standard time to perform a task?
a. Time study
b. Employee self timing
c. Historical analysis
d. Work sampling
37. Which of the following work measurement
techniques uses a stop-watch to measure
time and establish a time standard?
a. Time study
b. Pre-determined motion time study
c. Work sampling
d. Standard data
38. Developing a good job design is not
sufficient to achieve objectives. Certain
pre-requisites need to be satisfied for the
job design to be successful. Which of the
following is not such a pre-requisite?
a. Machinery and equipment to be in good
working condition
b. Sufficient buffer stock of material and
components
c. Good working conditions
d. High motivation
39. Which of the following statements
correctly describes the relationship
between tasks to be performed and skills
acquired by an employee in an
organization?
a. Fewer the number of specific tasks
performed, higher the skill proficiency and
efficiency of the employee
b. Greater the number of tasks performed,
higher the skill proficiency and efficiency
of the employee
Part B
191
c. Fewer the number of tasks performed,
lower the skill proficiency and efficiency
of the employee
d. There is no relationship between the
number of tasks performed and the skill
proficiency and efficiency of the employee
40. Which of the following work measurement
techniques are extensively used to measure
worker performance in indirect labor
jobs (jobs involving machine or
automation)?
a. Historical analysis
b. Work sampling
c. Pre-determined Motion Time Study
d. Standard data
41. One of the primary applications of work
sampling is to find the percentage of time
an employee or equipment was occupied,
or left idle. What is the name given to this
application of work sampling?
a. Ratio delay
b. Performance measurement
c. Time standards
d. Employee self-timing
42. Which of the following is an assumption
taken for back-order strategy used in
aggregate planning?
a. Customers are willing to pay more for
product delivery
b. Customers are willing to wait for product
delivery
c. Customers are not willing to pay in case of
delay in product delivery
d. None of the above
43. Which of the following is not associated
with aggregate planning?
a. Making best use of resources to meet
market demand
b. Minimizing production costs
c. Making appropriate changes in production
rates and workforce levels to improve
profits
d. Expanding plant capacity to meet future
demand
44. It is important to determine adequate
production capacity to meet forecast
demand levels and to determine whether or
not sub-contracting and/or overtime has to
be used. This activity is associated with
which of the following?
a. Capacity planning
b. Aggregate planning
c. Scheduling
d. Demand forecasting
45. Which of the following is a type of
heuristic model used for aggregate
planning?
a. Management coefficient model
b. Linear programming
c. Computer simulation model
d. Linear decision rules
46. The term rolling through time is
associated with which of the following
activities in operations management?
a. Location decisions
b. Master production schedule
c. Inventory management
d. Job design
47. Which of the following does not directly
signify the service capacity of an
organization?
a. Total beds in a hospital
b. Total seats in an aircraft
c. Total rooms in a hotel
d. Total drafts issued by a bank in a day
48. Inventories can be direct or indirect.
Identify indirect inventory from the
following.
i. Raw material
ii. Stationery
iii. Work-in-progress
iv. Lubricants
a. i and ii
b. iii and iv
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
49. In the EOQ model, reorder level is set to
the number of units used in the lead time.
What is the formula for reorder point?
a. Reorder point = Annual demand x Lead
time
b. Reorder point = Lead time x Total costs
c. Reorder point = Lead time x Average daily
demand
d. Reorder point = Lead time x Ordering
costs
Operations Management
192
50. FSND is a type of classification of
inventory. On what basis are items
classified under FSND?
a. Turnover
b. Consumption value
c. Importance in usage
d. All of the above
51. In which of the following types of
inventory classification are items classified
based on their importance in the
production process?
a. ABC
b. VED
c. FSND
d. Both a & c
52. Purchase indents for raw materials usually
originate in which department of a
manufacturing organization?
a. Purchase
b. Finance
c. Production
d. Marketing
53. Identify the correct sequence of steps in
the supplier selection process.
a. Request for quotations Evaluation of
suppliers Develop a list of suppliers
Supplier selection
b. Develop a list of suppliers Evaluation of
suppliers Request for quotations
Supplier selection
c. Develop a list of suppliers Request for
quotations Evaluation of suppliers
Supplier selection
d. Develop a list of suppliers Request for
quotations Supplier selection
Evaluation of suppliers
54. Most organizations develop a set of rules
and guidelines to ensure that purchasing
personnel conduct business ethically.
Which of the following statements is not
to be considered a purchasing rule by a
firm?
a. The organizations interest should be kept
in mind while purchasing
b. Selection of suppliers should be based on
individual discretion
c. All purchasing activities should be
conducted honestly and truthfully
d. All purchasing commitments (payments of
bills, etc) should be completed on time
55. Which of the following activities are
performed by people involved in making
purchase decisions?
i. Price negotiation
ii. Giving feedback to sales personnel of
suppliers
iii Building long-term relationships
iv. Giving indents to concerned departments
a. i, ii, and iii
b. ii, iii, and iv
c. i, iii, and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
56. Operations management involves the
functions of planning, organizing,
controlling, directing, and coordinating in
production systems, which help in
converting the resource inputs into
products or services. Activities that
compare work progress to schedule, and
inventory level to targets fall under which
function of operations management?
a. Planning
b. Directing
c. Coordinating
d. Controlling
57. What does the ratio between the quantity
of output produced and the quantity of
input used in an organization indicate?
a. Product quality
b. Productivity
c. Product variety
d. Profitability
58. What do you understand by the term
production flexibility?
a. Ability to produce large quantities of
products
b. Ability to produce different varieties of
products
c. Ability to produce a single product
d. None of the above
59. Identify the qualitative forecasting method
in which the member experts are allowed
to discuss and arrive at a consensus.
Part B
193
a. Delphi method
b. Nominal group technique
c. Brainstorming
d. Executive committee consensus
60. What is the relationship between the time
frame and accuracy of demand forecast in
simple moving average technique?
a. The greater the time period, the greater the
accuracy
b. The lesser the time period, greater the
accuracy
c. Accuracy of demand is independent of
time period
d. The greater the time period, the lesser the
accuracy
61. The demand of Product A for six
consecutive months is given as 50, 53, 54,
55, 53, and 52. Calculate the demand for
Product A for the seventh month using the
simple moving averages method. Assume
the time period to be a three month moving
average.
a. 52.33
b. 54.00
c. 53.33
d. 55.00
62. Which of the following can be an objective
of a transportation problem?
a. Allocating resources to the production
process
b. Minimizing production costs
c. Minimizing transportation costs
d. Maximizing capacity
63. Under what condition can one say that a
transportation problem is balanced?
a. Supply should be greater than demand
b. Supply should be equal to demand
c. Supply should be less than demand
d. There is no condition
64. If an ice cream factory plans to meet the
peak demand during summer season,
which of the following steps could it
possibly take?
i. Employ additional workforce on part-time
basis
ii. Make existing employees work overtime
iii. Recall the workforce laid-off previously
iv. Employ multi-skilled employees
a. i and ii
b. ii and iv
c. i, ii, and iv
d. i, ii, and iii
65. What is the Line flow production system
also referred to as?
a. Product-focused systems
b. Process-focused systems
c. Group technology
d. None of the above
66. If in an assembly line more than a single
product is to be made, which model can be
used to study workflow in terms of
different workstation sizes, task variations,
etc?
a. Line balancing
b. Mixed-model line balancing
c. Load distance model
d. CRAFT model
67. Which of the following location-evaluation
methods uses expert panels, namely
strategic panel, forecasting panel and
coordinating panel, while deciding on
optimal plant location?
a. Point rate method
b. Center of gravity method
c. Analytic Delphi method
d. Break-even analysis
68. Break-even analysis is a graphical and
algebraic representation of relationships
among volume of output, costs and
revenues. What is the other commonly
used term for break-even analysis?
a. Quality factor analysis
b. Cost-volume-profit analysis
c. ABC analysis
d. Value analysis
Operations Management
194
69. Many factors have to be considered as part
of job design. The basic question Where
is the job performed? describes one of the
following. Identify.
a. The tasks to be performed
b. The geographic location of the job
c. Method of performing the job
d. Qualities of workers who perform the job
70. The Job Characteristics Model developed
by Richard Hackman and Greg Oldham
includes five characteristics. They are skill
variety, task identity, task significance,
autonomy, and feedback. Which of the
following defines details of tasks needed to
complete/perform a job?
a. Task identity
b. Task significance
c. Autonomy
d. Feed back
71. Rajdhani Enterprises Ltd. asks its
employees to fill up a time sheet for
different tasks undertaken and respective
time spent on each task in a given period.
Which of the following methods of work
measurement has the company
implemented?
a. Work sampling
b. Time study
c. Employee self-timing
d. Pre-determined Motion Time Study
72. What term is used to signify maximum
output that can be produced in a given
production system in a given time period?
a. Productivity
b. Capacity
c. Quality
d. Inventory
73. Which of the following types of plans
helps define how resources can be used in
the best way to meet the market demand
for a product, minimize the production
costs, make appropriate changes in
production rates and workforce levels to
improve profits, improved customer
service, and utilization of resources?
a. Inventory plan
b. Aggregate plan
c. Capacity plan
d. Material requirement plan
74. What is the optimum criterion for selecting
the best economic order quantity?
a. Annual ordering costs are minimum
b. Annual carrying costs are minimum
c. Total annual costs are minimum
d. Annual inventory costs are minimum
75. Stock-out costs are assumed to be absent
in which of the following inventory
systems?
a. Q system
b. P system
c. EOQ
d. Fixed Order Quantity system
76. Who generally issues a purchase indent?
a. User department
b. Purchase department
c. Vendor
d. Top management
77. Which of the following is not mentioned
in a quotation?
a. Price per unit
b. Delivery schedule
c. Terms and conditions
d. Name of the user department
78. What precedes a typical make-or-buy
decision?
a. Value analysis
b. ABC analysis
c. Break-even analysis
d. Vendor analysis
(Questions 79 to 81) The desired daily output
for an assembly line is 1000 units. The
assembly line operates for a period of 480
minutes a day. The process involves the tasks
as shown in the figure. Answer the following
three questions.
Part B
195
79. Calculate the cycle time. (1 point)
a. 4.8 seconds
b. 28.8 seconds
c. 0.48 seconds
d. 2.88 seconds
80. Calculate the number of workstations that
are theoretically required? (2 points)
a. 7
b. 6
c. 4
d. 5
81. If the actual number of work stations
required is 6 in number, then what is the
efficiency of the assembly line? (1 point)
a. 0.93
b. 0.95
c. 0.98
d. 0.94
(Question 82 to 86) In a production facility, a
worker is capable of producing 4 metal frames
per day. Assume the time taken for producing
each metal frame is the same.
Given: Hiring costs = Rs. 2000, Layoff costs =
Rs. 2500, Current employee strength = 50
Aggregate demand for next four months is
given in the following table.
Jun Jul Aug Sep
Demand 5150 5000 4800 4660
Working
Days
24 25 23 24
Answer the following five questions from the
above information.
82. For which of the given months, the
production capacity exceeds demand?
(1 point)
a. June
b. July
c. August
d. September
83. How many extra workers are required to
meet the demand for the month of June
(1 point)
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
84. What is the total cost incurred by the
organisation for hiring/laying off workers
in the month of June? (1 point)
a. 2000
b. 4000
c. 6000
d. 8000
85. Calculate the total cost incurred by the
organisation for hiring/laying off workers
in August to meet the demand during the
month without any shortage. (2 points)
a. 2,000
b. 6,000
c. 4,000
d. 8,000
A
B F
H
D E
G
I
11 sec
45 sec
50 sec
9 sec
15 sec
16 sec
6 sec
9 sec
9 sec
C
Operations Management
196
86. What is the layoff cost incurred by the
organisation in the month of September
assuming number of workers available to
be 52? (2 points)
a. 6000
b. 8000
c. 7500
d. 8500
87. The extent of sales of a product depends
on many variables. Assume that sales of a
bulldozer increases with increase in the
sales promotion expenditure. Given below
are the sales figures over a period of six
months along with the sales promotion
expenditure incurred by a distributor of
heavy equipment.
Sales
(in units)
33 35 40 30 32 30
Sales
promotion
expenses
(in Rs.
lakhs)
7 5 14 8 9 6
Calculate the sales promotion expenditure
needed to achieve sales of 40 units using the
least square method. (5 points)
a. 10.83
b. 33.33
c. 11.97
d. 15.67
(Questions 88 & 89) Alpha Stabilizers Ltd
purchases electrical switches at Rs.20 per unit.
Annual demand for this component is 10000
units. The ordering costs and carrying costs per
unit are Rs.250 and Rs.5 respectively and lead
time for inventory replenishment is 4 days.
Assume the number of working days in a year
as 300. Answer the following two questions.
88. Using this data calculate the EOQ
(1 point)
a. 1000
b. 2236
c. 5000
d. 2000
89. What is the reorder point for Alpha
Stabilizers? (2 points)
a. 100 units
b. 133 units
c. 33 units
d. 150 units
90. The profit before tax of SP Chemicals was
Rs.25 million for 2006, which is 10% of
the overall sales. Cost of materials
accounted for 40% of the sales. What
would be the change in profit if the cost of
materials decreased by 5%.? (3 points)
a. 20% increase
b. 25% increase
c. 20% decrease
d. 25% decrease
Paper II - Model Test 2
Time: 3 Hours Total Points: 100
1. Which of the following is not true about a
single card Kanban system?
a. Only the conveyance card is used
b. Some initial inventory is available
c. The number of trays used are dependant on
the lot size of production
d. The system is useful in execution of
repetitive operations
2. Which of the following is not a task
performed by the purchase department?
a. Processing requisitions for materials
b. Identifying and selecting suppliers
c. Negotiating with suppliers
d. Maintain inventory of the purchased
material till usage
3. Which of the following applications
performed by robots are more relevant in
materials management?
a. Processing
b. Pick-and-place
c. Inventory stocking and picking
b. Both b & c
4. Which of the following Kanban cards
specifies quantity of material ordered?
a. Vendor authorization card
b. Product authorization card
c. Conveyance card
d. Both b & c
5. Which of the following statements
describes the limitations of a Kanban
system?
i. Excessive dependence on people involved
in the process
ii. The failure of a vendor to supply the
required amount of materials
iii. Reduction of work-in-process
iv. A missing Kanban card
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i, ii, and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
6. Materials managers use several techniques
to carry out their tasks. Which among the
following is not a technique used by
materials managers in the movement of
materials?
a. Kanban Systems
b. JIT System
c. Value Analysis
d. ABC Analysis
7. What is the relationship between the
number of Kanban cards used and the
demand for a product?
a. Number of cards decrease with increase in
demand for a product
b. Number of cards increase with rise in
demand for a product
c. Number of cards increase with decrease in
demand for a product
d. There is no relationship between the
number of cards and demand for a product
8. Which of the following is not true about
the MRP system?
a. Planning and implementation time for
MRP systems can take years
b. Data entry requirements and file
maintenance are time consuming
c. The set up time is low
d. Over dependence on forecasts and
estimated lead time
9. An MRP system works based on the
demand for the end product. Which of the
following is not true about MRP?
a. It is a backward scheduling process
b. It helps coordinate orders from external
and internal sources
Answer all the questions.
Each question carries one point, unless specified otherwise.
Operations Management
198
c. It is responsible for the purchase of
required material
d. It generates a schedule of all items
required for production
10. In which of the following each type of
material held by the firm is recorded with
detailed specifications of the availability at
the beginning of a time period along with
expected arrivals during the time period?
a. Bill of materials
b. Primary report
c. Inventory records file
d. Secondary report
11. An output of MRP system that specifies
the quantity of inventory that is required in
a specific time bracket is called
__________.
a. Planned orders
b. Order releases
c. Exception reports
d. Performance reports
12. Identify the input to the MRP system that
contains information about whether a
particular item is produced internally or
purchased from external sources.
a. Master production schedule
b. Demand forecast
c. Bill of materials
d. Inventory records file
13. Netting in MRP information processing is
used to calculate net product requirement.
Identify the correct formula to calculate
this.
a. Net Requirement = Gross Requirement +
On hand inventory Quantity on order
b. Net Requirement = Gross Requirement +
On hand inventory + Quantity on order
c. Net Requirement = Gross Requirement
On hand inventory Quantity on order
d. Net Requirement = Gross Requirement
On hand inventory + Quantity on order
14. Which of the following is not true about
the forward scheduling method?
a. Actual production activities start after
receiving a job order
b. Work-in-process inventory level is high in
this method
c. Jobs are assigned according to the latest
available time slot at a work center
d. Mostly used in operations in which
customized products are manufactured
15. Which of the following is not true about
backward scheduling?
a. Backward scheduling is calculated from
earliest start time forward
b. Jobs are assigned the latest time slots
c. Backward scheduling is done when
demand can be anticipated beforehand
d. Work-in-process inventory is low as they
are used within a short time
16. Which of the following dispatching rules
do firm use when they want to maximize
the number of completed jobs and reduce
the number of jobs in waiting?
a. Longest processing time
b. Shortest processing time
c. First in, first serve
d. Slack time remaining
17. Service firms can adopt various methods to
meet customer demand under situations of
limited availability of service facilities.
Which system is used by an operations
manager to control customer arrival
timings so that the firms resources can be
utilized to the fullest extent?
a. Appointment system
b. Reservation system
c. Strategic product pricing
d. Routing
18. Identify the statements that correctly
describe the characteristics of Gantt
charts?
i. They are useful only when work centers
are less in number
ii. It considers break-down in production
iii. It does not consider human performance
iv. It does not provide clarity in
communicating job information
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iii
Part B
199
19. Several methods are used for scheduling
operations in an organization. Based on
which factors are scheduling methods
selected?
i. Volume of production
ii. Nature of operations
iii. Inventory in store
iv. All of the above
a. Only i
b. i and ii
c. i and iii
d. Only iv
20. Scheduling of operations is different for
different types of operation. Which of the
following operations is used to produce
goods and services in low volumes?
a. Job operations
b. Repetitive operations
c. Labor-intensive operations
d. Service operations
21. Gantt charts are simple bar charts that can
be used to schedule any type of operation.
Identify the different types of Gantt charts
from the following.
i. Workload charts
ii. Scheduling charts
iii. X-chart
iv. R-chart
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iv
d. iv and i
22. A firm is involved in five types of jobs.
Each must be processed on three
machines, A, B and C in the order ABC.
The processing time of each job (in hours)
on the three machines is given below.
Identify the optimum sequence using
Johnsons rule.
Processing Times
Job
A B
C
1 23 10 25
2 54 25 65
3 45 18 24
4 41 22 33
5 35 20 46
a. 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
b. 3, 2, 5, 4, 1
c. 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
d. Cannot be determined
23. Identify the correct definition of a
business process.
a. A set of unrelated tasks performed to
achieve a defined business outcome
b. A set of logically related tasks performed
to achieve an unknown outcome
c. A set of logically related tasks performed
to achieve a defined business outcome
d. A set of unrelated tasks performed to
achieve an unknown business outcome
24. Gap analysis helps identify the areas that
are not handled by the standard system.
Which of the following gaps can be dealt
with by a project team?
a. Gaps that can be eliminated with minimal
programming
b. Gaps that require extensive rework and
additional resources
c. Gaps that cannot be handled by the system
d. All of the above
25. Which dimension of quality talks about a
products primary operating
characteristics?
a. Performance
b. Reliability
c. Durability
d. Conformance
26. Proper communication optimizes the
implementation process, but overstating or
understating the functionalities of the ERP
package do not fetch desired results.
Which of the following can be a
consequence of overstating functionalities?
a. Unrealistic expectations from employees
about the benefits of ERP
b. Employees would be unprepared for the
changes required for ERP implementation
c. Employees will be aware of the effects of
ERP implementation on their jobs
d. All of the above
27. Four key drivers help determine not only
responsiveness and effectiveness, but also
the strategic fit of the supply chain. Which
of the following is not one among them?
Operations Management
200
a. Inventory
b. Decision-making
c. Facilities
d. Information
28. Enablers are responsible for overall
performance of the SCM. Which of the
following enablers emphasize that the
goals of various business units of an
organization should match corporate
goals?
a. Customer-supplier focus
b. Design
c. Alignment
d. Measurement
29. What does the SCM enabler period
review focus on?
a. Evaluation of performance of processes,
programs, and systems
b. Involvement of suppliers in decision-
making
c. To understand and react to customer
requirements fast
d. Develop products, services, and business
processes that satisfy the requirements of
both customers and suppliers
30. ESCM or electronic supply chain
management involves business-to-business
integration through the Internet. Which of
the following is not an advantage of
ESCM?
a. Increase in cost savings
b. Increase in cycle time
c. Reduction in inventory levels
d. Reduction in procurement costs
31. Which of the following SCM enablers
discusses effective decision-making in the
organization?
a. Participation/involvement
b. Design
c. Measurement
d. Periodic review
32. According to the demand chain concept,
which member(s) assume the role of
monitoring changes in consumer
preferences?
a. Retailer
b. Manufacturer
c. Wholesaler
d. All of the above
33. JIT manufacturing focuses on which of the
following conditions?
i. Continuous improvement
ii. High performance levels in all operational
areas
iii. Maintaining consistent quality
iv. High volumes of output
a. Only i
b. i and ii
c. i, ii, and iii
d. i, ii, iii, and iv
34. Which of the following is not an
advantage gained by a firm implementing
JIT?
a. Minimal inventory storage and
maintenance costs
b. Reduction in production cycle time
c. Reduction in formal paper work
d. Steady and continuous demand for
material
35. Sheetal Plastic Company adopts the JIT
manufacturing system and maintains
smaller lot sizes of inventory. Identify the
advantages of maintaining smaller lots
over larger lots.
i. Increases set-up frequency
ii. Reduces lead times
iii. Achieves uniform loads
iv. Reduces cycle inventory
a. i and ii
b. i, ii, and iii
c. ii, iii, and iv
d. iv, i, and ii
36. Many JIT firms follow group technology
layouts where several types of machines
are placed in distinct cells with each
machine in a cell performing a single
operation repeatedly. Which of the
following is not a benefit of group
technology layouts?
a. Movement of material is minimized
b. Reduced need for material handling
equipment
Part B
201
c. Reduced total materials handling costs
d. Reduced speed of production
37. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of the JIT system?
a. Uniform workstation loads
b. Large lot sizes
c. Quick and economic set-ups
d. Flexible facilities
38. The break-down of one machine in a JIT
manufacturing system can lead to stoppage
of the entire production line, which proves
to be very costly for the firm. To avoid
such situations, the firm has to regularly
take up preventive maintenance. Which of
following does not assist in easy
preventive maintenance measures in a JIT
production unit?
a. Complex equipment design and non-
standardized replacement parts
b. Collection of information about frequency
and causes of machine failure
c. Replacement of worn-out parts regularly
during frequent checks
d. Purchase of spare parts required for
maintenance beforehand
39. Which of the following is not a measure of
an input to produce an output?
a. Tons of coal consumed
b. Kilowatt of power consumed
c. Number of personnel worked
d. Meters of cloth produced
40. Identify the function of quality directly
related to the reputation of the firm.
a. Conformity
b. Aesthetics
c. Serviceability
d. Perceived quality
41. For most products and services, it is not
possible to test final outputs. In this
scenario, to improve efficiency of
inspections, they should be carried out at
different stages of production. Which
among the following is not an ideal time to
carry out such an inspection?
a. Before commencement of operations that
can cover up defects
b. After commencement of operations that
are likely to provide outputs with defects
c. After the commencement of irreversible
processes
d. After finished products are ready for
delivery
42. Match the following control charts with
their respective utilities.
i. X-chart
ii. R-chart
iii. P-chart
iv. C-chart
p. Illustrates the central tendency of
inspected samples
q. Shows variability in terms of precision and
accuracy of a process in manufacturing
r. Helps find the proportion of defective
items in a selected sample
s. Illustrates the total number of defects in an
item
a. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/r, iii/q, iv/s
c. i/q, ii/p, iii/r, iv/s
d. i/q, ii/r, iii/p, iv/s
43. A firm has to incur costs as part of quality
control. The costs include cost of
inspection and the cost of an undetected
fault. Which of the following is not a cost
arising due to undetected faults?
a. Customer complaints
b. Product replacement costs
c. Cost of product recall programs
d. Inspection labor costs
44. Each type of control chart is used for a
different purpose. Which type of control
chart details the central tendency of
inspected samples?
a. X-chart
b. R-chart
c. P-chart
d. C-c hart
45. Companies outsource the facilities
management function due to many
reasons. Which among the following is not
a valid reason for this?
a. To reduce costs
b. To improve the control of tasks
c. To focus on core competency
d. To improve quality of tasks performed
Operations Management
202
46. Compressors in a certain manufacturing
plant have to be serviced after every 200
hours of operation. This is an example of
___________.
a. Irregular preventive maintenance
b. Predictive maintenance
c. Periodic maintenance
d. Remedial maintenance
47. What are the other names for remedial
maintenance?
i. Breakdown maintenance
ii Irregular maintenance
iii Corrective maintenance
iv. Condition monitoring
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
48. In which of the following stages of a
bathtub curve is the failure rate constant
and to some extent predictable?
a. Early failure stage
b. Adult stage
c. Wear out stage
d. Both a & c
49. Bharti Engineering Ltd takes up preventive
maintenance for its machinery every 2
months though the service manual advices
maintenance once in 3 months for effective
performance. What can be the possible
negative consequences of such a practice
for Bharti?
i. Preventive maintenance costs increase
ii. Down time of machinery can decrease
iii. Frequent stalling of work
iv. Productivity can increase
a. i and iii
b. ii, iii, and iv
c. iii, iv, and i
d. i and iv
50. Which stage in a Bathtub Curve is also
known as burn-in stage?
a. Early failure stage
b. Adult stage
c. Wear out stage
d. Useful life stage
51. _________________ is the amount of time
that an activity can be delayed beyond its
earliest start time without extending the
project duration.
a. Latest start time
b. Expected start time
c. Slack time
d. Most likely time
52. Match the following systems used in
production with their respective features.
i. CNC machines
ii. CIM
iii. FMS
iv. AI
p. A flexible system capable of producing
different types of products
q. Performs a variety of tasks based on the
instructions fed to the onboard computer
r. Computer systems capable of reasoning
and decision making
s. Integrates designing, manufacturing, and
controlling functions
a. i/q, ii/r, iii/p, iv/s
b. i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
c. i/q, ii/s, iii/p, iv/r
d. i/q, ii/p, iii/s, iv/r
53. There are certain impediments to
globalization that can block an
organization from globalizing its activities.
Restrictions through tariffs and duties to
control MNCs operating in a country come
under which type of impediments?
a. Economic impediment
b. Managerial impediment
c. Institutional impediment
d. None of the above
54. Which category of robots, based on the
nature of their operations, is capable of
perceiving the environmental conditions of
the workplace and making suitable
decisions using onboard computers?
a. Playback robots
b. Numerical control robots
c. Variable-sequence robots
d. Intelligent robots
Part B
203
55. Which of the following combinations of
cards are used in a dual Kanban system?
a. Vendor authorization card and conveyance
authorization card
b. Product authorization card and conveyance
authorization card
c. Vendor authorization card and product
authorization card
d. Product authorization card, vendor
authorization card and conveyance
authorization card
56. What should a manufacturing firm
producing three different products that
require the same raw materials for two of
them do while planning?
a. Develop a materials requirement plan for
each product
b. Develop a consolidated materials
requirement plan for products using same
type of materials
c. Avoid developing any materials
requirement plan for products using same
type of materials
d. Develop a materials requirement plan only
for the product using raw materials that are
not common
57. Which of the following outputs of MRP
system authorizes the purchase department
to go ahead with the purchase of material
as planned?
a. Planned orders
b. Order releases
c. Exception reports
d. Planning reports
58. Forward scheduling is a scheduling
method. Which of the following is not a
feature of forward scheduling?
a. Production activities start when the job
order is received
b. Scheduling is done from the date of
production
c. Start & finish times are determined by
using earliest time slots
d. Work-in-process inventory is very low
59. Gantt charts are simple bar charts that can
be used to schedule any type of operation.
Identify the different types of Gantt charts.
i. Workload charts
ii. Scheduling charts
iii. X-chart
iv. R-chart
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iv
d. iv and i
60. Identify problems encountered during a
typical ERP implementation process?
i. Executing complex tasks
ii. Setting several milestones
iii. Communication breakdown
iv. Rushed deadlines
a. i, ii and iii
b. i, iii and iv
c. ii, iii and iv
d. i, ii, iii, iv
61. Which of the following statements are true
about Business Process Reengineering
(BPR)?
i. It advocates the complete overhaul of
business processes in an organization
ii. It advocates the complete overhaul of
processes in the manufacturing department
of an organization
iii. It reduces costs and improves business
practices
iv. It helps increase productivity
a. i and iv
b. iii and iv
c. ii, iii, iv
d. i, iii, iv
62. What dimension of quality measures the
degree to which a product is manufactured
to the pre-specified specifications?
a. Reliability
b. Serviceability
c. Aesthetics
d. Conformance
63. Which of the following is not a benefit of
JIT purchasing?
a. Increased responsiveness and flexibility
b. Reduction in product design time
c. Reduction in cost of scrapped inventory
d. Administrative efficiency
Operations Management
204
64. Which of the following statements best
describes total quality control?
a. Quality of the product is a concern of the
quality control department
b. Only the quality control department is
responsible for improving product quality
c. Quality can be increased by changing
product design rather than meeting
customer requirements
d. Quality can be enhanced through
collective efforts of all departments
65. The maximum average outgoing quality
for any acceptance plan is the average
outgoing quality limit (AOQL), which
indicates the point at which the AOQ
reaches the critical level. Identify the true
statement pertaining to the AOQ.
a. Products above the AOQL are shipped to
suppliers
b. Products above the AOQL are not shipped
to customers
c. The entire lot of products is accepted when
defects exceed the critical point
d. Extent of inspection decreases when AOQ
crosses the AOQL
66. What action does a firm take when average
outgoing quality (AOQ) of a product
crosses average outgoing quality level
(AOQL)?
a. Products are shipped to customers
b. Products are retained and inspected
c. Products are sent to production department
for changes
d. Products are shipped to suppliers
67. What is a Type I error in quality control?
a. Probability of rejecting the lot at AQL
b. Customers face the risk of receiving a lot
with minor defects
c. A risk that a bad lot will be rejected
d. Probability of accepting the lot at AQL
68. Identify the service under facilities
management that involves duplication of
printed material.
a. Housekeeping
b. Plumbing
c. Reprographics
d. Horticulture
69. Which of the following is not a
consequence of poor maintenance of
machinery?
a. Productivity of the firm would be affected
b. Production costs would decrease
c. Safety would be adversely affected,
leading to more accidents
d. Quality of output would come down
70. Maintenance of material handling
equipment falls under which of the
following?
a. Mechanical maintenance
b. Civil maintenance
c. Electrical maintenance
d. Preventive maintenance
71. What are the other names for remedial
maintenance?
i. Breakdown maintenance
ii Irregular maintenance
iii Corrective maintenance
iv. Condition monitoring
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
72. Which of the following reasons has led to
the initial stage of the bathtub curve
gradually losing importance?
a. Firms use new equipment
b. Failure rates in the first stage are
accurately measured
c. Zero failures in the first stage have become
common
d. Equipment manufacturers dispatch
equipment only after the burn-in period is
over
73. The process of reducing the time of the
project by reducing the scheduled time of
some of the activities is called project
crashing. Which among the following is
not a crash strategy?
a. Reducing the workforce
b. Additional capacity installation
c. Subcontracting
d. Overtime
Part B
205
74. Identify the correct formula to calculate
the time-cost ratio in project crashing.
a.
( )
( ) Crash time time Normal
cost Crash cost Normal
b.
( )
( ) Crash time time Normal
cost Normal cost Crash
c.
( )
( ) cost Normal cost Crash
time Normal e Crash tim
d.
( )
( ) time Normal e Crash tim
cost Crash cost Normal
75. Which one of the following is a
networking method?
a. Center of gravity method
b. Critical path method
c. Graphical method of linear programming
d. Economic order quantity method
76. Automated systems are less customizable
in terms of the number of possible
products that can be manufactured when
compared to manually operated systems.
Which of the following overcomes this
disadvantage?
a. CAD
b. CAM
c. FMS
d. JIT
77. Robotics is an automation technology
based on two related technologies. What
are they?
i. Numeric control
ii. Computer Aided Manufacturing
iii. Computer Integrated Manufacturing
iv. Teleoperator
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iv
78. The difference in approaches between
national and global goals and management
necessitates changes in several key
strategic operational decisions. Which of
the following strategic decisions basically
involves scanning of macro-economic
factors, information on market size, and
capability of the subsidiary?
a. Selection of markets
b. Product development
c. Allocation of resources
d. Choice of technology
79. Preferential procurement from local
organizations by government and quasi-
government entities comes under which of
the following impediments to
globalization?
a. Economic impediment
b. Managerial impediment
c. Institutional impediment
d. Both a & c
(Question 80 to 82) Bill of materials for product A is given below showing the lead times and
required quantities. Use this information to answer the following three questions.
A
LT = 2
D (4)
LT = 4
C (1)
LT = 2
B (4)
LT = 1
E (3)
LT = 2
Operations Management
80. How many units of D are required to
produce 5 units of Product A? (1 point)
a. 5 units
b. 10 units
c. 20 units
d. 30 units
81. How many units of E are required to
produce 5 units of Product A? (1 point)
a. 15 units
b. 60 units
c. 70 units
d. 120 units
82. If a time-phased product structure is
drawn, how many weeks will be required
to produce the product A? (2 points)
a. 3 weeks
b. 4 weeks
c. 5 weeks
d. 6 weeks
83. The unit price of a product is Rs 150, the
unit variable cost Rs 125, and the fixed
cost Rs 50,000. What should be the
demand for the product so that the
manufacturer can reach break-even point?
(1 point)
a. 2000 units
b. 1500 units
c. 4000 units
d. 2750 units
(Question 84 to 87) Standard Binders is a
photocopying and binding firm. It undertakes
photocopying and binding works in large
quantities. The firm got five orders on a certain
day and their processing times in the
photocopying and binding machines
respectively (in minutes) are as given below.
Use this information to answer the following
four questions.
Job A B C D E
Photocopying
machine
40 100 50 30 90
Binding
machine
25 60 45 30 40
84. Determine the optimum sequence to
process these five jobs using Johnsons
sequencing rules. (2 point)
a.
D E C B A
b.
D C E B A
c.
D C B E A
d.
D B E C A
85. Calculate the total elapsed time for the
jobs using the optimum sequence D-C-E-
B-A. (5 points)
a. 300 minutes
b. 330 minutes
c. 355 minutes
d. 335 minutes
86. What is the total time idle time on
photocopying machine? (1 point)
a. 40 minutes
b. 25 minutes
c. 50 minutes
d. 55 minutes
87. What is the total idle time on binding
machine? (2 points)
a. 135 minutes
b. 155 minutes
c. 100 minutes
d. 125 minutes
(Questions 88 to 90) P-Chart is used to control
the proportion of defective items being made
by a production process. Use the data to answer
the following three questions. The table gives
the number of defects in 5 samples where each
sample contains 20 items.
Sample 1 2 3 4 5
Number of defects 4 3 6 5 4
88. What is the average proportion of
defective items for the given data?
(2 points)
a. 0.154
b. 0.144
c. 0.220
d. 0.166
Part B
207
89. What is the upper control limit for the P-
chart to be developed using this data?
(2 points)
a. 0.642
b. 0.4978
c. 0.625
d. 0.674
90. Calculate the lower limit for the same
P-chart. (2 points)
a. 0.22
b. 0.334
c. 0
d. 0.565
Paper II
Part B: Answers and Explanations
Answers and Explanations
Paper II - Model Test 1
1. (c) Operational decisions
Operational decisions are short-term decisions and have a time-frame of a few days or a week.
They address problems and requirements at the operational level, which include scheduling weekly
production and assigning jobs/responsibilities to workers, etc.
2. (a) AS/RS
AS/RS is a computer controlled warehouse system that automates inflow and outflow of materials
from the warehouse and shop floor on the basis of production requirements. CAD is a specialized
software used for designing products and processes. FMS relates to flexible manufacturing where
large quantities of products with similar processing requirements can be produced. Computer-
aided manufacturing (CAM) is a specialized computer system, which translates CAD information
into instructions for numerically controlled automated machines.
3. (b) Computer Aided Manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is a specialized computer system, which translates CAD
(Computer Aided Design) information into instruction for numerically controlled automated
machines. The use of CAM in manufacturing has minimized worker involvement in production.
Manufacturing information systems were used for planning and controlling operations. These
provided comprehensive information regarding production (such as demand forecasts, purchasing,
inventories, etc.) to operations managers. Automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS) is a
computer-controlled warehouse system that automates inflow and outflow of materials from the
warehouse and shop floor on the basis of production requirements. Linear programming is an
operations research technique.
4. (d) Facility planning
Facility planning deals with location of the facility and its layout. Decisions regarding facility
location are based on the accessibility to raw materials and nearness to markets. Allocation of
resources deals with the allotment of existing resources like men, machines, material, etc, to
different strategic alternatives. Technology selection and process development deals with selection
of the most suitable technology for producing products and product design and development is
used to develop new products.
5. (c) Convenience and location
If SBI offers the facility of easy accessibility for customers (especially in services industry), this is
a competitive advantage and offers convenient service delivery. Low cost production process
involves lowering costs of production to values smaller than those incurred by competitors.
Product variety and facility size implies a wide product mix covering customer needs in all market
segments.
6. (c) Aircraft
Aircraft are manufactured after taking orders from customers. This is because different airline
customers require different type of interior and exterior finish.
7. (a) The greater the NPV, the greater will be the profitability
The greater the NPV value of the project, the better is its profitability. In cases where multiple
projects are compared, the project with the largest NPV is selected.
Operations Management
212
8. (d) Maximization
Time series data can reveal random variations, seasonality changes, and trends in demand for a
product. However, since time series analysis depends on past data, it can only extrapolate that data
to the future. Hence, the data cannot tell when there is maximum demand.
9. (c) Delphi method
Delphi method is an interactive learning process that involves a group of experts responding to a
questionnaire. The results obtained are compiled to formulate a new questionnaire, which is again
submitted to the group. The other three options are types of quantitative methods. (Simple moving
average and exponential smoothing are part of time series methods while regression analysis is a
causal method).
10. (b) A positive tracking signal indicates that demand is underestimated
A positive tracking signal indicates that demand is underestimated while a negative tracking signal
indicates that demand is overestimated.
11. (c) Causal methods
If a relationship exists between the different variables under review, causal methods (such as
regression analysis) are used.
12. (a) Trend component
The trend component gives long-term pattern of movement of demand over a period of time.
The trend may be positive, negative, or neutral.
13. (c) Basic time series forecasting method
While simple moving average, weighted moving average and exponential smoothing are adaptive
forecasting techniques. Static forecasting methods are also called as basic time series forecasting
techniques.
14. (b) Introduce slack variables
Slack variables are introduced in each constraint equation as an idle source to convert inequalities
to equalities.
15. (b) ii only
Market, capacity, and inventory space are constraints associated with production plan decisions.
Destination requirements are a constraint for transportation decisions.
16. (d) Stepping stone method
While methods mentioned in options (a), (b), and (c) can be used to develop the initial feasible
solution, the stepping stone method is used to test the solution for optimality.
17. (d) Optimal solution
A constrained optimization model consists of three major components decision variables,
objective function, and constraints. All these are used to find an optimal solution for the model.
18. (b) A dummy warehouse is added
In an unbalanced problem, a dummy warehouse is added if production capacity is more than the
requirement. A dummy origin is added if production capacity is less than the requirement, with
desired quantity to make it a balanced problem.
19. (b) North-West corner method
In the North-West Corner Method, allocation of products starts at the north-west corner (or the top
left corner) of the transportation table. Here, least cost or penalties are not considered while
allocating products.
Part B
213
20. (a) Highly skilled employees
Unlike product-focused production systems, process-focused production systems need highly
skilled employees.
21. (a) i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
The symbols for non-productive activities in the process chart are storage (), delay (D), transport
(), and input () respectively.
22. (a) Product-focused systems
In this type of process design, products or services tend to flow along linear paths without
backtracking or side tracking. Items follow a similar production sequence, which can be anything
from a pipeline (for oil) to an assembly line (for televisions or radios).
23. (d) Product-focused system
A product-focused production system is appropriate for a non-differentiated product. However, it
is inflexible and impractical to alter the equipment to make it possible to produce other products.
Thus, Logan was using a product-focused system.
24. d) Employ part-time workers to meet the demand
The characteristics of a production system with product/service flexibility include use of general-
purpose equipment and multi-skilled employees. The employees have to be trained so that they can
perform different types of jobs. Employing part-time workers to meet the additional demand
requirements is characteristic of a production system having volume flexibility.
25. (c) Low diversity in product design and large batch size
Product focused systems are more assembly line and continuous production systems, which
produce products in bulk quantities. Hence, they have large batch sizes. Also, such systems have
very narrow scope for modifying the product design.
26. (c) Fixed position layout
This layout involves movement of men, machines, and equipment to the product, which remains
stationary. The product here may be bulky, large, heavy, or fragile. This type of layout is generally
used in ship manufacturing.
27. (c) Arid and dry climate with minimal rainfall
Sivakasi has an arid and dry climate. Therefore the material used to manufacture fire crackers does
not absorb moisture and become damp. Besides, a dry climate helps easy storage of finished
products as production is carried out round the year and maximum consumption is during the
festival season.
28. (a) Process layout
Workers in process layouts must be highly skilled as they need to handle a variety of jobs to
produce a variety of products.
29. (c) To reduce transportation costs
The center of gravity method is used to find optimal location for a distribution center that
minimizes total transportation costs. This method takes into account factors like markets, cost of
goods, and cost of transportation. The center of gravity method aims at minimizing total shipping
cost, i.e., cost incurred for shipping from distribution centers to different shipping points.
Operations Management
214
30. (b) Point-rate method
Under the point-rate method, weightages are allotted to different factors under consideration.
Companies have several objectives of various importance levels while selecting a site or location.
Companies assign weightage to these objectives in the form of points. Potential sites are evaluated
with respect to every factor a company is seeking and points are allotted accordingly to each
factor. The superior site is the one that finishes with more points.
31. (a) Graphic and schematic analysis
In graphic and schematic analysis, templates and two-dimensional cutouts of equipment drawn to
scale are used as layout-planning tools. Templates are moved about within a scaled model of the
walls and columns of a facility to identify the best layout through trial and error.
32. (b) Job analysis
Job analysis investigates job content, physical conditions in which the job is done, and
qualifications necessary to carry out the job responsibilities.
33. (c) Autonomy
The autonomy in a job indicates flexibility, independence, and discretion available to employees
performing the job.
34. (c) Behavioral feasibility
Behavioral feasibility considers employees perceptions about themselves and about others in the
work environment. Hence, when an employee is delegated an important responsibility, it has a
positive effect on self esteem.
35. (c) Job specification is part of job description
Job identification, job specification, and job evaluation are components of job description.
36. (c) Historical analysis
Historical analysis uses statistical tools like arithmetic mean and others to find the standard time
from the given historical data.
37. (a) Time study
Time study is used to identify time standards for a particular job performed by a competent worker
under standard conditions. To record time taken by each worker to finish the job, a stop-watch is
used.
38. (d) High motivation
Machinery and equipment in good running condition, sufficient stock of material for production,
good working conditions for employees are some pre-requisites for the success of any job design.
Improved productivity and motivation are a consequence of job design.
39. (a) Fewer the number of specific tasks performed, higher the skill proficiency and
efficiency of the employee
The lower the number of tasks an employee performs, the greater will be the skill proficiency and
efficiency of the employee. This is because the individual becomes a specialist in performing these
tasks.
40. (b) Work sampling
Work sampling technique is used extensively to measure the performance of workers involved in
indirect labor jobs (like driving a pay loader to feed raw materials). It can also be adopted in
service organizations like schools and hospitals.
Part B
215
41. a) Ratio delay
Ratio delay, performance measurement, and time standards are primary applications of work
sampling. Ratio delay refers to the activity time percentage for an employee or equipment. Ratio
delay shows the percentage of time an employee or equipment was occupied or idle.
42. (b) Customers are willing to wait for product delivery
Back-order strategy assumes that customers are willing to wait for product delivery.
43. (d) Expanding plant capacity to meet future demand
Aggregate plans define how resources can be best employed to meet market demand for the given
products. The objective of an aggregate plan is to minimize production costs, make appropriate
changes in production rates and workforce levels, and to improve profits, customer service, and
resource utilization. Expansion of plant capacity is a separate long-term operations plan, which
does not come under aggregate planning, a medium-term plan.
44. (a) Capacity planning
Capacity planning is important to determine adequate production capacity to meet the forecasted
demand levels. Capacity planning is also used by organizations when deciding on issues like
whether or not to use sub-contracting or overtime to achieve production goals.
45. (a) Management coefficient model
The management coefficient model is a heuristic model which uses the regression method to
identify capacity requirements based on the managements past decisions. The other three are
types of optimal models used for aggregate planning are similar to the heuristic model.
46. (b) Master production schedule
Forecasted demand and actual demand for a product may differ significantly due to unexpected
events. Transactions, records and reports developed as part of MPS are updated and reviewed
continuously to accommodate differences. This process of continuous reviewing and updating is
called rolling through time.
47. (d) Total drafts issued by a bank in a day
Service capacity can be measured in terms of number of beds in hospital, number of seats an
aircraft has, or number of clients an executive can service in a day. But, the number of total drafts
issued by a bank in a day does not directly signify service capacity. It is rather dependant on the
number of customers demanding that particular service.
48. (d) ii and iv
Inventories can be direct or indirect. Direct inventories include goods that play an important role in
manufacturing of a product and become part of the finished product. Direct inventories include raw
material, work-in-progress goods, etc. Indirect inventories include goods necessary to run the
production process but do not become part of the end product. For example, lubricants, grease,
oils, stationery, etc.
49. (c) Reorder point = Lead time x average daily demand
Lead time is defined as the product of demand per unit time and lead-time. Unit time and lead-time
are expressed in the same units. Reorder Point = d
LT, where d = Average daily demand, and LT
= Lead time.
50. (a) Turnover
Under FSND classification, goods are classified on the basis of turnover. F items are fast moving,
S items are slow moving items, N items are non-moving items and D items are dead items or the
items that have not been issued for a few years.
Operations Management
216
51. (b) VED
VED classification is based on the importance of a particular item in the production process. Under
VED, items critical for production are classified as V (vital). Items important in the production
process but not critical are classified as E (essential) and items, not essential and not influencing
the production process are classified as D (desirable).
52. (c) Production
The production department primarily issues purchase indents as and when the need for more raw
material arises.
53. (c) Develop a list of suppliers Request for quotations Evaluation of suppliers
Supplier selection
In the supplier selection process, the first step is to prepare a list of probable suppliers and then ask
them to submit quotations for products that the firm intends to purchase. When quotations are
submitted, they are evaluated and analyzed in detail. Finally, the actual supplier(s) is/are selected.
54. (b) Selection of suppliers should be based on individual discretion
No undue favor should be taken from or given to suppliers. Selection of suppliers should be based
solely on merit and not on individual discretion.
55. (a) i, ii, and iii
The duties of purchase department members involved in making purchase decisions include
negotiating with suppliers, building long term relationships with them and providing feedback to
sales representatives. Accepting indents from user departments (not issuing indents) is also an
activity handled by the purchase department.
56. (d) Controlling
Controlling refers to comparing actual results with set standards or benchmarks. Activities part of
controlling include comparing work progress to schedule, actual labor hours to standards, costs to
budget, inventory level to targets, and inspection of quality levels.
57. (b) Productivity
Productivity is the ratio of output produced to input consumed.
58. (b) Ability to produce different varieties of products
Production flexibility refers to the production of different varieties of products. A production
system which is flexible can utilize its machinery and equipment to produce another product at
short notice (usually a day or two or a week) and is referred to as flexible production system.
59. (b) Nominal group technique
Under nominal group technique, experts are allowed to meet, give their opinions and/or ideas, and
discuss and debate on the issue to come to a consensus. In Delphi method, experts do not meet
with each other while giving opinions/ideas. In executive committee consensus method, line
managers use the information and suggestions given by the staff to arrive at a consensus regarding
the forecast. Brainstorming generally involves employee participation at all levels without
invitation only for experts.
60. (a) The greater the time period, the greater the accuracy
The greater the moving average period the forecast value is less vulnerable to random variations. A
larger moving average period is taken when fluctuations in demand are minimal. This is done to
erase the random variations in demand to the maximum extent possible.
Part B
217
61. (c) 53.33
In the three-month simple moving average technique, the forecast for the fourth month will be the
average of the preceding three months. Thus, the forecast for month 4 is the average demand for
the product A during month 1, 2 & 3. Similarly, the forecast for month 5, 6 and 7 can be
calculated. Thus, by using moving averages for three months, we obtain the demand for the month
7 as 53.33 as given in the table.
Month 1 50
Month 2 53
Month 3 54
Month 4 55 52.33
Month 5 53 54.00
Month 6 52 54.00
Month 7 53.33
62. (c) Minimizing transportation costs
In its most general form, the transportation problem has a number of origins and a number of
destinations. A certain quantity of a commodity is produced or manufactured at each origin and
transported to destinations, each with specific requirements. The objective of a transportation
problem is to meet the requirements of customers at the destination with supply from the origin,
while ensuring that transportation costs are minimal.
63. (b) Supply should be equal to demand
A transportation problem can be either balanced or unbalanced. It is said to be balanced if the
quantity of goods produced (supply) is equal to total requirement (demand) of all warehouses.
Otherwise, the problem is said to be unbalanced.
64. (d) i, ii and iii
The ice cream factory needs to have volume flexibility in the production system. The extra
workforce that is required to increase production can be obtained from outside subcontractors, by
paying overtime allowance to the existing workforce, by temporary recruitment of part-time
workers, or by recalling the workforce previously laid off. Employing multi-skilled employees is
necessary to gain product/service flexibility in the production system. .
65. (a) Product-focused systems
Product-focused systems are also called as Line flow production systems. They are used mostly
in production departments that are organized according to the type of product or service being
produced.
66. b) Mixed-model line balancing
Line balancing and mixed-model line balancing are used in developing a product layout. Load
distance and CRAFT model are used to develop a process layout. Line balancing is considered for
only a single product in an assembly line. For multiple products, manufacturers consider mixed-
model line balancing. Mixed model lines involve multiple lot sizes, lot sequencing, different set up
times for each lot, differing workstation sizes along the line and task variations that make it very
difficult to design.
67. (c) Analytical Delphi method
Analytic Delphi Method helps managers take complex multi-location decisions. This method
requires participation of a coordinating panel, forecasting panel, and strategic panel.
Operations Management
218
68. (b) Cost-volume-profit analysis
Break-even analysis is also called as cost-profit-volume analysis. While break-even analysis and
quality factor analysis are used in location decisions, ABC analysis is used in inventory
management. Value analysis is used in purchase management and product design.
69. (b) The geographic location of the job
The question Where the job has to be performed? helps clarify the location of a particular job i.e.,
whether it is in a particular department, division or geographic location.
70. (a) Task identity
Task identity defines clearly the identifiable tasks needed to complete the main task.
71. (c) Employee self-timing
Employee self-timing is a technique used by managements where employees are asked to record
the time taken to perform different activities or tasks. This is a simple and cost effective way of
work measurement.
72. (b) Capacity
Capacity indicates the maximum output that can be produced in a given production system. If a
factory is said to have production capacity of 100 units per hour, it means that under optimal
conditions, the factory will be able to produce a maximum of 100 units per hour.
73. (b) Aggregate plan
Aggregate plans define how resources can be best employed to meet market demand for the given
products. The objective of an aggregate plan is to minimize production costs, make appropriate
changes in production rates and workforce levels and to improve profits, customer service, and
utilization of resources.
74. (c) Total annual costs are minimum
Operations managers compute total annual costs for various order quantities and then select the
economic order quantity where total annual cost is minimum. Ordering and carrying costs are
components of total costs.
75. (c) EOQ
Under the EOQ model, inventory is assumed to be replenished about the time it becomes zero.
Hence, there would be no shortage of materials on a continuing basis. Costs will be minimal. As
shortage of materials is not allowed, stock-out costs of inventory have a role to play in the
computation of EOQ.
76. (a) User department
The user department that utilizes material or goods issues purchase indents. They are issued to the
purchase department, which requests for quotations from vendors for the materials.
77. (d) Name of the user department
The name of the user department is present in the purchase indent or requisition and not in the
suppliers quotation. The latter usually contains price per unit, delivery schedule, mode of
transportation, special terms and conditions, etc.
78. (c) Break-even analysis
Make-or-buy decisions are based on break-even analysis, where costs of producing in-house as
well as costs of purchasing from outside are analyzed. These costs are dependent on the quantity
demanded.
Part B
219
79. (b) 28.8 seconds
day per Output
day per time Operation
time Cycle = =(480 x 60)/1000= 28.8 seconds
80. (b) 6
Total time required for all the tasks (T) = 45 + 11 + 6 + 9 + 50 + 15 + 16 + 9 + 9 = 170 seconds
N
t
= T / Cycle time
= 170/28.8
= 5.9
Theoretically, 6 workstations are required at the minimum.
81. (c) 0.98
Efficiency of the assembly line = Sum of the tasks of the processes / (Actual number of
workstations x cycle time)
= 170 / (6 x 28.8)
= 0.98
82. (d) September
Production capacity from the given details are:
June - 50 x 4 x 24 = 4800, July - 50 x 4 x 25 = 5000, August = 50 x 4 x 23 = 4600, September - 50
x 4 x 24 = 4800. Hence, the production capacity for September of 4800 is more than the estimated
demand at 4660 units.
83. (d) 4
If 50 workers can produce 4800 units in 24 days, then to produce 5150 units in the same period the
number of workers required are (5150 x 50)/4800 = 53.65 = 54
Extra workers required = 54 50 = 4
84. (d) 8000
If 50 workers can produce 4800 units in 24 days, then to produce 5150 units in the same period,
the number of workers required are (5150 x 50)/4800 = 53.65 = 54. Extra workers required are
54 50 = 4. As 4 extra workers were hired to meet the demand and hiring costs for each worker is
Rs.2000, total cost incurred by the organization is, 4 x 2000 = Rs.8,000.
85. (b) 6,000
50 workers in 23 days can produce 4600 units (50x4x23). But the demand is 4800 units which
means that additional workers are required to produce the extra 200 units. The number of
additional workers required are (50 x 200) / 4600 = 2.17
To meet the demand completely (without any shortage), 3 workers are required.
Hence, hiring costs = 3 x 2000 = Rs.6,000
86. (c) 7500
52 workers in 24 days can produce 4992 units which implies a surplus of 332 units. Hence number
of workers to be laid-off is (52 x 332)/4992 = 3.45 (3 workers approx)
Hence, cost of lay-off = 3 x 2,500 = Rs.7500
Operations Management
220
87. (c) 11.97
Bulldozer sales in
units (X)
Sales promotion
expenses (Y)
XY X
2
33 7 231 1089
35 5 175 1225
40 14 560 1600
30 8 240 900
32 9 288 1024
30 6 180 900
200 49 1674 6738
The linear equation is Y = a + bX.
b =
2
X) ( - )
2
X
Y) ( X) ( XY) n(
( n
= 6(1674) (200)(49)) / 6(6738) 40000)
= (10044 9800) / (40428 40000)
= 244 / 428
= 0.57
To calculate a, the formula is = X b Y
Where Y =
n
Y
and X =
n
X
Y = 49/6 = 8.17
X = 200/6 = 33.33
Hence, a = 8.17 (0.57 x 33.33)
= 8.17 19
= -10.83
Substituting a and b in Y = a + bX
Y = -10.83 + 0.57(40)
= 22.8 10.83
= 11.97
Hence to achieve sales of 40 bulldozers the distributor has to spend Rs.11.97 lakhs on sales
promotion.
88. (a) 1000
EOQ =
h
C
D
o
2C
Where, C
o
is the ordering cost
D is the demand
C
h
is the carrying cost
By substituting the respective values,
EOQ =
( )( )
5
10000 250 2
we get EOQ as 1000 units.
Part B
221
89. (b) 133 units
Reorder point = daily demand x lead time
Daily demand = yearly demand / number of working days
= 10000/300
= 33.33
Reorder point = 33.33 x 4
= 133 units (approx)
90. (a) 20% increase
Sales = Rs.250 million (10% of sales is the profit of Rs.25 million)
Material cost = 40% of sales (250 million) = Rs.100 million
5% of Rs.100 crores = Rs.5 million.
If the material costs decreases by Rs.5million, the same amount would add to the profit before tax
i.e. the profit would be Rs.30 million. The change in profit before tax would be (5/25) x 100 = 20
%. Thus, a 5% reduction in material costs would increase the profit before tax by 20%.
Answers and Explanations
Paper II - Model Test 2
1. (c) The number of trays used is dependant on the lot size of production
The single card Kanban system is more useful in executing repetitive operations. Also, trays used
in this system should be standardized to the lot size in production. For example, if a firm produces
one television at a time, a tray should contain only the parts required to manufacture one
television. If it produces ten televisions at a time, the tray should contain materials required to
produce ten televisions.
2. (d) Maintain inventory of the purchased material till usage
Maintain inventory of the purchased material is the task of raw material inventory department and
not that of the purchase department.
3. (b) Pick-and-place
The two basic types of applications where robots are used are processing and pick-and-place. In
a processing application, the robot works as a tool by performing a job on a product (cutting,
screwing, etc.) that moves to the robot. In a pick-and-place application, the robot moves the
product (e.g. loading and unloading of materials). The pick-and-place application is more relevant
in materials management.
4. (a) Vendor authorization card
A vendor authorization card specifies the product name, vendor name and quantity of material
ordered. When this card is issued, it authorizes a vendor to supply the required materials in the
specified quantity.
5. (c) i, ii, and iv
The limitation of the Kanban system is that it depends excessively on the people involved. The
failure of a vendor to supply the required amount of materials and missing a Kanban are serious
threats to the success of the system. Reduction of work-in-process and raw materials stores is a
benefit derived through the effective use of Kanban system.
6. (c) Value analysis
Value analysis is a technique used by purchase managers to identify and rank components based
on the level of importance in operations during the purchase of materials and components.
7. (b) Number of cards increase with increase in demand for a product
The number of cards can be altered according to the estimated demand for a product. If the
demand for the product increases, a larger number of Kanban cards are used to meet it. Similarly,
the number of Kanbans can be decreased with less demand for the product.
8. (c) The set up time is low
MRP Systems require longer set up times.
9. (c) It is responsible for the purchase of required material
An MRP is a backward scheduling process which generates a schedule of all the items required for
production of the end product. It helps in coordinating orders from external and internal sources.
External sources are purchase orders and internal sources are jobs. However, it is not in the scope
of MRP to oversee the purchase process of these materials.
Part B
223
10. (c) Inventory records file
The inventory records file is computerized with a complete record of each material held in the
inventory. It contains information about inventory levels i.e., levels at the beginning of the
planning horizon and the details of the expected arrivals of inventory during that period.
11. (a) Planned orders
Planned orders specify the quantity of inventory required in a time bracket. It includes information
about all inventory requirements during the planning period. Planned orders and order releases are
part of primary report outputs. Exception and performance reports come under secondary report
outputs.
12. (c) Bill of materials
Bill of materials contains information about whether a particular item is produced internally or
purchased from external sources. The purchase or production lead-time to acquire the item is also
mentioned in the bill of materials.
13. (c) Net Requirement = Gross Requirement - On hand inventory - Quantity on order
In netting, the net product requirements are calculated by subtracting the available units of item
and the quantity on order from gross product requirement. Net Requirement = Gross Requirement
- On hand inventory - Quantity on order.
14. (c) Jobs are assigned according to the latest available time slot at a work center
Using forward scheduling, the operations manager determines the start and finish times for jobs to
be done by assigning them to the earliest available time slots at the work center.
15. (a) Backward scheduling is calculated from earliest start time forward
Backward scheduling starts from due date of the order and works backwards. Jobs are assigned the
latest time slots and as a job is finished, the material is immediately sent to the next workstation for
process. Thus, work-in-process inventory is reduced. Backward scheduling is done for goods and
services whose demand can be forecast or anticipated beforehand.
16. (b) Shortest processing time
Here, jobs are processed in the shortest time. Under this rule, jobs with shorter processing times
get completed earlier than jobs with longer processing time. This rule ensures that minimum
number of jobs are left for processing.
17. (a) Appointment system
Appointment systems are used to control customer flow at the individual level. The system works
only when the service is provided to a single individual or few individuals at a time. Reservation
system is used to provide service to a large number of individuals at a time. Routing explains the
sequence of operations and processes to be followed to produce a particular product.
18. (d) i and iii
Gantt charts provide ease and clarity in communicating important job information, but they do not
take into account hurdles like production breakdown and human performance. They are useful
only when the number of work centers is limited, job times are long, and job routings are short.
19. (b) i and ii
Selection of the scheduling method depends mainly on production volume and the nature of the
operation. While scheduling is done, it is assumed that required inventory is already present in
store so that a stock-out situation does not arise and hinder the production process.
Operations Management
224
20. (a) Job operations
Job operations are used to produce goods and services on the basis of customer orders while
repetitive operations, also known as continuous operations, are used to mass produce goods and
services. Labor intensive operations involve using a large number of workers to produce high
volumes. In general, service operations are done on the first in-first serve principle.
21. (a) i and ii
Gantt charts are simple bar charts used to schedule any kind of operation. Workload charts and
scheduling charts are two types of Gantt charts. X-chart and R-chart are used in quality control.
22. (d) Cannot be determined
For a 3 machine and n job problem, Johnsons sequencing rule is applicable only when one of the
following two conditions are satisfied: (i) Smallest time on Machine A should be greater than or
equal to greatest time on Machine B or (ii) Smallest time on Machine C should be greater than or
equal to greatest time on Machine B. In this problem, both conditions are not satisfied. Hence,
Johnsons sequencing rule cannot be applied for determining the optimum sequence.
23. (c) A set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome
According to Davenport and Short, a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed
to achieve a defined business outcome
24. (a) Gaps that can be eliminated with minimal programming
Gaps that can be eliminated with minimal programming fall under the purview of project teams
and they can take corrective action to fill those gaps. However, gaps that require extensive rework
and gaps that cannot be handled by the system are dealt with by the steering committee.
25. (a) Performance
A products primary operating characteristics relates to its basic performance.
26. (a) Unrealistic expectations from employees about the benefits of ERP
Communication should not overstate or understate the functionalities of the system. Overstating
functionalities would raise employees expectations unrealistically, while understating them might
leave employees unprepared for the changes required for ERP implementation.
27. (b) Decision-making
Four key drivers of supply chain performance are inventory, transportation, facilities and
information. They help in overall decision making in the supply chain management.
28. (c) Alignment
Alignment here refers to the matching of corporate and business unit goals. It also includes
consistency in processes, actions, and decisions across business units to support the supply chain
management processes.
29. (a) Evaluation of performance of processes, programs, and systems
Periodic review involves measurement of performance at periodic intervals. It focuses on
evaluation of performance of processes, programs, and systems periodically and contributes to
continuous improvement. The basic objective of the customer-supplier focus is to prepare an
organizations processes to understand and react to customer requirements fast. Decision-making
is covered by the participation/involvement enabler and process design is covered by the design
enabler.
30. (b) Increase in cycle time
Under ESCM, cycle time is actually reduced. Other advantages of ESCM include increase in cost
savings, reduction in inventory levels, and reduction in procurement costs.
Part B
225
31. (a) Participation/involvement
Participation/involvement is an SCM enabler, which discusses the participation of all stakeholders
of the organization in the decision-making process. The knowledge of employees and suppliers
should also be considered while arriving at decisions. This makes the decision- making process
more effective.
32. (d) All of the above
In a demand chain, every member should monitor consumer preferences. Due to growth in
technologies like the Internet, consumers have begun to use multiple channels to procure goods
and services. Due to marketing practices like direct marketing, tele-marketing, etc, consumers are
now interacting with different entities in the purchasing process. So, every member of the demand
chain, whether they design, manufacture, market, sell, or transport a specific product, needs to
monitor consumer needs and wants.
33. (c) i, ii, and iii
Just-in-time manufacturing focuses on continuous improvement in all processes, and maintains
consistent performance (in terms of quality) in operations. JIT manufacturing does not focus on
producing large volumes of output, but on reducing inventory levels as well as wastage in
production facilities while making products.
34. (d) Steady and continuous demand for material
Firms practicing JIT enjoy certain advantages. The inventory is reduced to almost zero, reducing
the maintenance costs of inventory. Long-term relationship with suppliers enables firms to get the
required materials just-in-time for production. The cycle time also comes down. The long-term
relationship also reduces the otherwise considerable amount of paperwork and provides steady
supply of materials. Steady and continuous demand for the material is an advantage for suppliers
of the firm but not for the firm implementing JIT.
35. (c) ii, iii, and iv
While reduced lead times, achieving uniform loads and reduced cycle inventory are advantages,
increased set-up frequency is a disadvantage. Due to maintenance of small lot sizes, purchase
orders should be placed frequently and inventory should be regularly replenished.
36. (d) Reduced speed of production
Grouping of machinery into cells reduces material movement and the need for material handling
equipment, which in turn cuts overall the materials handling costs. This will lead to speedy
production and quicker deliveries.
37. (b) Large lot sizes
Firms that follow JIT type of manufacturing system maintain inventory in the smallest possible lot
sizes. This is required as small lot sizes reduce cycle inventory (the excess of inventory, above the
safety stock, that is carried between two orders), cut lead times and also help in achieving a
uniform workload. JIT manufacturing systems follow uniform workstation loads where material is
fed to the workstation uniformly and uniform output is produced across different workstations.
Besides, these firms have flexible facilities and quick and economic set-ups.
38. (a) Complex equipment design and non-standardized replacement parts
Simple design equipment and standardized replacement parts make the work of preventive
maintenance easier, while complex designs delay maintenance. Non-standardized parts can
increase delays in terms of procurement and usage.
39. (d) Meters of cloth produced
While options (a), (b), and (c) are examples of inputs, option (d) is an example of output.
Operations Management
226
40. (d) Perceived quality
Perceived quality is directly related to the reputation of the firm that manufactures the product.
Total information about the various quality aspects of a product is usually not available, especially
when it is a new product. So, customers rely heavily on the firms reputation and past performance
of its products when attaching a value to its new products.
41. (c) After the commencement of irreversible processes
It is not possible to inspect products that are in the middle of an irreversible process. To improve
the efficiency of inspections they should be carried out: after operations most likely to produce
faulty items, before costly operations commence, before operations that can mask defects, when
the finished product is ready for delivery, and before undertaking assembly operations that cannot
be undone.
42. (a) i/p, ii/q, iii/r, iv/s
X-Chart illustrates the central tendency of inspected samples. R-Charts show the variability of the
process. A process is said to be in control when both accuracy (mean) and precision are in control.
P-Chart is employed to find proportion of defective items in a selected sample. C-Chart is used to
illustrate the total number of defects in an item when it may have more than one defect.
43. (d) Inspection labor costs
The first three options are costs of undetected faults while the last is an inspection cost.
44. (a) X-chart
X-chart and R-chart come under control charts for variables. X-chart illustrates the central
tendency of inspected samples while R-chart (range chart) shows process variability.
45. (b) To improve the control of tasks
The facilities management function is outsourced to focus on core competencies, reduce costs,
improve the efficiency and quality of tasks. Loss of control is one of the costs associated with
outsourcing.
46. (c) Periodic maintenance
Periodic maintenance implies servicing equipment at regular intervals of time or at regular usage
intervals. The given case falls under the latter.
47. (c) i and iii
Remedial maintenance is also called corrective or breakdown maintenance.
48. (b) Adult stage
In the adult or useful life stage, failure rate is constant, and to some extent, predictable. Proper
maintenance of equipment can ensure longevity of this stage. Most causes of failure during this
stage are attributed to external causes or accidents, for example, a mistake by an operator or usage
of improper materials.
49. (a) i and iii
Taking up preventive maintenance activities over and above the required number of times can
cause delays in production and increase maintenance costs. Down time of machines will rise,
leading to stalling of work, and decrease in productivity.
50. (a) Early failure stage
The early failure stage is characterized by more equipment failure. This can be due to faulty design
or improper installation. This stage is also called as burn-in stage.
Part B
227
51. (c) Slack time
Slack time refers to the amount of time by which an activity can be delayed beyond its earliest start
time without extending the project duration, provided that the activity and other activities take their
estimated durations. It is a measure for determining the criticality of an activity.
52. (c) i/q, ii/s, iii/p, iv/r
Computer Numeric Controlled (CNC) machines can perform a variety of tasks based on the
instructions fed to the onboard computer. Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) systems
integrate design, manufacture and control functions. Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) is a
flexible production system capable of producing different types of products. Artificial intelligence
(AI) allows computer systems with capabilities of reasoning and decision making.
53. (c) Institutional impediment
Impediments to globalization can be economic, managerial, or institutional. Some institutional
impediments are: tariffs and duties which may limit benefits achieved by economy of scale in
production, quantitative quotas and other similar restrictions, preferential procurement from local
organizations by government and quasi-government entities, governmental pressure to use locally
produced components or insistence on local R&D, preferential tax treatment and labor policies and
corporate laws, tax laws or other policies of the local government.
54. (d) Intelligent robots
Intelligent robots are capable of perceiving environmental conditions of the workplace through
tactile or visual perception (or both) and can make necessary and suitable decisions by using the
on-board computers they are equipped with.
55. (a) Vendor authorization card and conveyance authorization card
A dual Kanban system uses two Kanbans and they include Vendor authorization card and
Conveyance authorization card.
56. (b) Develop a consolidated materials requirement plan for products using same type of
materials
Manufacturing firms that produce multiple products and have common material requirements for
two or more products must consolidate the individual material requirements and form a single
master material requirements plan for the two products.
57. (b) Order releases
Order release documents empower the purchase department to procure a specific quantity of
inventory items required within a specified period.
58. (d) Work-in-process inventory is very low
In forward scheduling, production activities start when job orders are received and scheduling is
done from the date of production. Start and finish times of each job is determined by assigning the
earliest possible time slots for the jobs. As a result, jobs get finished before the requirement at their
respective work stations. They get accumulated as work-in-process inventory. Hence, work-in-
process inventory is high in forward scheduling.
59. (a) i and ii
Gantt charts are simple bar charts used to schedule any kind of operation. Workload charts and
scheduling charts are two types of Gantt charts. X-chart and R-chart are used in quality control.
60. (d) i, ii, iii, iv
As typical implementation of a ERP project exceeds one year, experts suggest having several
deliverables or milestones. A single milestone leads to problems in ERP implementation.
Operations Management
228
61. (d) i, iii, iv
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) advocates the complete overhaul of the existing systems
and processes in the entire organization (irrespective of departments) in order to increase
productivity, reduce costs and improve business practices.
62. (d) Conformance
Conformance is defined as that dimension of quality which is measured as the degree to which a
product is manufactured to the pre-specified specifications.
63. (b) Reduction in product design time
Reduction in product design time is not a benefit of JIT purchasing. This mainly focuses on
inventory management-related issues leading to increase responsiveness and supply flexibility. It
also improves administrative efficiency.
64. (d) Quality can be enhanced through collective efforts of all departments
It is not just the firms quality control department that is responsible for ensuring product quality.
High quality can be attained only through the collective and coordinated efforts of all departments
of the firm.
65. (b) Products above the AOQL are not shipped to customers
Products are rejected if the AOQ crosses the AOQL. They are retained and not sent to customers.
Such rejected lots of products would be inspected completely and defects removed.
66. (b) Products are retained and inspected
Products are rejected if the AOQ crosses the AOQL. They are retained and not sent to the
customers. Such rejected lots of products would be inspected 100% and the defects removed
completely.
67. (a) Probability of rejecting the lot at AQL
In any sampling plan, there is always a risk that a good lot will be rejected - this is the producers
risk. This is termed as Type I error.
68. (c) Reprographics
Reprographics refers to reproducing or duplicating printed material using various kinds of printing
presses and high speed copiers.
69. (b) Production costs would decrease
The probable consequences of poor maintenance of facilities are: productivity of the firm would be
affected and reduced, production costs would rise, safety would be hit, leading to more accidents,
and output quality would come down.
70. (a) Mechanical maintenance
Mechanical maintenance includes maintenance of the firm's machines and equipment such as
furnaces, boilers, compressors, material handling equipment, transport vehicles, etc. Civil
maintenance includes building construction and maintenance; maintenance of service facilities like
water filters, air conditioning, plumbing, etc. Electrical maintenance covers electrical and
electronic equipment such as generators, motors, electrical installations, lighting, telephone
systems, etc. Preventive maintenance is a type of maintenance operation.
71. (c) i and iii
Remedial maintenance is also called corrective or breakdown maintenance.
Part B
229
72. (d) Equipment manufacturers dispatch equipment only after the burn-in period is over
The bathtub curve may not always be an effective indicator of the failure rate of equipment. For
example, present day manufacturers dispatch equipment only after the burn in period is over, so
that they can identify and rectify problems before it reaches end-users. So, the initial stage of the
bathtub curve will not be applicable to such machines.
73. (a) Reducing the workforce
To crash a project, one needs to utilize the services of additional resources and/or maximize the
services of existing resources. Hence instead of reducing the workforce, it can be increased to
reduce the expected time of project completion.
74. (b)
( )
( ) Crash time time Normal
cost Normal cost Crash
Time-cost ratio helps in identifying those activities which are to be crashed in a project. The
activities with smallest time-cost ratio on the critical path have to be identified and crashed.
75. (b) Critical path method
Networking methods/techniques are used in project management in scheduling operations such
that wastage in terms of time and material is minimized. Popular networking methods include
Critical Path Method (CPM) and Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT).
76. (c) FMS
FMS (flexible manufacturing system) is a form of flexible automation in which several machine
tools are linked to a material-handling system. A central computer controls all aspects of the
system which is effective in producing different items that have similar processing requirements.
77. (d) i and iv
Robotics is an automation technology that has received considerable attention since 1960s. It is
based on two related technologies: numerical control and teleoperators. Numerical control (NC) is
a method of controlling machines by means of numbers coded on punched paper, tape or other
media. Teleoperator is a mechanical manipulator that is controlled by an individual from a remote
location.
78. (a) Selection of markets
When a global organization decides to select a new market (which can be a new country or a new
area in an existing country), it has to analyze the macro-economic factors, market information,
capabilities of the subsidiary with which it is tying up, etc.
79. (c) Institutional impediment
Rules and regulations framed by different national governments hinder the process of
globalization. They come under institutional impediments. Preferential procurement from local
organizations by government and quasi-government entities is one type of rules and regulations
that might be framed by governments to hinder the expansion of global corporations.
80. (c) 20 units
4 units of D are required to produce 1 unit of A. It implies that 20 units (5 x 4) of D will be
required to produce 5 units of A.
81. (b) 60 units
3 units of E are required to produce 1unit of B and 4 units of B are required to produce 1 unit of A.
Hence to produce 5units of A, 60 units (3 x 4 x 5) of E are required.
Operations Management
230
82. (d) 6 weeks
Lead time of E is 2 weeks, but lead time of D is 4 weeks. Hence, at the end of 4 weeks, products B
( 3 weeks), and product C & D ( 4 weeks) will be ready to produce A. It takes 2 weeks to produce
A using B, C and D. Therefore the total time to produce A will be 6 weeks (4 + 2).
83. (a) 2000 units
BEP (in number of units) = fixed cost / (unit price variable cost per unit)
= 50000 / (150-125)
= 2000 units
84. (c)
D C B E A
From the given data, least processing time on the photocopying machine is for job D and on the
binding machine for job A. Using Johnsons sequencing rules, place job D at the beginning and job
A at the end of the sequence. Repeat the process with the remaining jobs. The optimum sequence
is D-C-B-E-A.
85. (d) 335 minutes
Photocopying Machine Binding Machine Job
Sequence
Time in Processing
Time
Time out Time in Processing
Time
Time out
D 0 30 30 30 30 60
C 30 50 80 80 45 125
B 80 100 180 180 60 240
E 180 90 270 270 40 310
A 270 40 310 310 25 335
The total elapsed time is 335 minutes.
86. (b) 25 minutes
Total idle time on photocopying machine is the difference between the time when the last job in
the optimum sequence is completed on binding machine and the time when the last job is
completed on photocopying machine.
= 335 310 = 25 minutes
87. (a) 135 minutes
Total idle time on binding machine = (Time taken by photocopying machine to complete the first
job in the optimum sequence) + [(time when k
th
job starts on binding machine) (time when
(k-1)
th
job finishes on binding machine)].
= 30 + [(80-60) + (180-125) + (270-240) + (310-310)]
= 30 + [20 + 55 + 30]
= 135 minutes
88. (c) 0.220
Fraction defective for each sample is given by
p = c /n (number of defectives /sample size)
Part B
231
Fraction defective for Sample 1 = 4/20 = 0.2
Fraction defective for Sample 2 = 3/20 = 0.15
Similarly, calculate the fraction defective for all five samples as given in the following table.
Sample Fraction Defective
1 0.20
2 0.15
3 0.30
4 0.25
5 0.20
Total 1.10
Average = 1.10/5 = 0.220
89. (b) 0.4978
UCL=
P
+3
n
) P (1 P
where
P
is the average proportion of defects, and n the number of samples.
UCL = 0.22 + 3
20
) 22 . 0 0.22(1
UCL = 0.22 + 3(0.0926)
UCL = 0.4978
90. (c) 0
LCL=
P
- 3
n
) P (1 P
where
P
is the average proportion of defects and n the number of samples.
LCL = 0.22 - 3
20
) 22 . 0 0.22(1
LCL = 0.22 - 3 (0.0926)
LCL = - 0.0578
As negative value cannot be considered while counting defects, LCL is assumed to be zero.
You might also like
- AquaStar 125vp ManualDocument28 pagesAquaStar 125vp ManualAllynna Valentine McCleod100% (2)
- Water Supply Project SpecificationDocument33 pagesWater Supply Project SpecificationHimawan Sutardjo100% (1)
- Course Outline Quality Management and Six Sigma 2020 - IIM SirmaurDocument4 pagesCourse Outline Quality Management and Six Sigma 2020 - IIM SirmaurAjay SutharNo ratings yet
- QSP ENG 01 New Product DevelopmentDocument6 pagesQSP ENG 01 New Product DevelopmentOM BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Production & Operation ManagementDocument13 pagesProduction & Operation Managementmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- 1-Production and Operations Management and Competitive AdvantageDocument29 pages1-Production and Operations Management and Competitive AdvantageJayant ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Introduction To Retailing - 1628856313Document45 pagesUNIT I Introduction To Retailing - 1628856313puspa Raj upadhayayNo ratings yet
- ch07 Operation Management Roberta Russell & Bernard W. TaylorDocument47 pagesch07 Operation Management Roberta Russell & Bernard W. TaylorkiruthigNo ratings yet
- 12mba32 Om NotesDocument68 pages12mba32 Om NotessanthoshNo ratings yet
- Operations Management in Business StrategiesDocument5 pagesOperations Management in Business StrategiesMaverick CardsNo ratings yet
- SCM Bullwhip EffectDocument21 pagesSCM Bullwhip EffectvksdsatmNo ratings yet
- Push-Pull Strategy Operational ManagementDocument48 pagesPush-Pull Strategy Operational ManagementShridhar PadyanaNo ratings yet
- SchedulingDocument30 pagesSchedulingJo Jo100% (1)
- Lec 05Document42 pagesLec 05Naeem Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- IE-L1-Presentation New - Work Study and Job DesignDocument93 pagesIE-L1-Presentation New - Work Study and Job Designsanjeewa herathNo ratings yet
- Operations Management 18769 PDF PDFDocument278 pagesOperations Management 18769 PDF PDFneckoalNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument80 pagesOperations ManagementgopalsakalaNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument369 pagesOperations ManagementJoaoPinto100% (3)
- Production AnalysisDocument21 pagesProduction AnalysisAnshul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Operational ManagementDocument31 pagesOperational ManagementEllaNo ratings yet
- Chap001 OSCMDocument15 pagesChap001 OSCMAdyanto PutraNo ratings yet
- MPS & MRPDocument41 pagesMPS & MRPdeliciousfood96No ratings yet
- Production Operation Management NotesDocument11 pagesProduction Operation Management NotesLords PorseenaNo ratings yet
- Focussed FactoryDocument13 pagesFocussed FactoryjcspaiNo ratings yet
- Note LogisticsDocument24 pagesNote LogisticsMohammad Halis AzhanNo ratings yet
- L 7 Comparative AdvantageDocument16 pagesL 7 Comparative AdvantageFiyanshu TambiNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument153 pagesInventory ManagementlalitbadheNo ratings yet
- 7894 Final GR 2 Paper 5 Cost Managementyear 2005Document60 pages7894 Final GR 2 Paper 5 Cost Managementyear 2005Tlm BhopalNo ratings yet
- Agile ManufacturingDocument12 pagesAgile ManufacturingAswin SankarNo ratings yet
- Operation Management - Overview - Strategy - Challenges and Emerging Trends 2019Document101 pagesOperation Management - Overview - Strategy - Challenges and Emerging Trends 2019TaMiL HiTzNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Management FadsDocument112 pagesThe Handbook of Management FadsOscar Fernando Guzman Quintero100% (1)
- Chapter 8: Distribution Strategies: AnswerDocument9 pagesChapter 8: Distribution Strategies: AnswerLinh LêNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument11 pagesOperations Managementajeet sharmaNo ratings yet
- BullWhip EffectDocument17 pagesBullWhip EffectSaurabh Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Supplier Assesment SCMDocument22 pagesSupplier Assesment SCMNiranjan ThiruchunapalliNo ratings yet
- Modern ProductionOperations Management (Elwood S. Buffa and Rakesh K. Sarin)Document856 pagesModern ProductionOperations Management (Elwood S. Buffa and Rakesh K. Sarin)Indah AswadiNo ratings yet
- MB0044 Production & Operations ManagementDocument319 pagesMB0044 Production & Operations Managementnirmalgupta31100% (3)
- Lean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResDocument47 pagesLean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResrikiNo ratings yet
- Introduction SCMDocument55 pagesIntroduction SCMUsama Jahangir BabarNo ratings yet
- D - Lean Leadership PDFDocument6 pagesD - Lean Leadership PDFIkramullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Using A Simulation Game Approach To Teach Pull andDocument8 pagesUsing A Simulation Game Approach To Teach Pull andPiereSalasNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDABMDocument60 pagesInventory ManagementDABMbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials Management BookDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Materials Management Bookka5227No ratings yet
- Age of LogisticsDocument136 pagesAge of LogisticsManu JosephNo ratings yet
- MA Exam Paper May 2010Document23 pagesMA Exam Paper May 2010MsKhan0078No ratings yet
- Scheduling of OperationsDocument26 pagesScheduling of OperationsVijay JainNo ratings yet
- FoundationBook2016e Version PDFDocument241 pagesFoundationBook2016e Version PDFsusie andersonNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking: Aka, Types, Tools, DisadvantagesDocument6 pagesBenchmarking: Aka, Types, Tools, DisadvantagesFaisal WaqasNo ratings yet
- Atlas Inc. Is A Toy Bicycle Manufacturing Company Producing A Five-Inch Small Version of TheDocument3 pagesAtlas Inc. Is A Toy Bicycle Manufacturing Company Producing A Five-Inch Small Version of ThevarunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Production Planning and ControlDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Production Planning and ControlDr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-NaimiNo ratings yet
- IGNOU MBA MS-94 Solved Assignment Dec 2012Document11 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-94 Solved Assignment Dec 2012Varinder AnandNo ratings yet
- Essential Operations Management Case Study AnswersDocument69 pagesEssential Operations Management Case Study Answerswaqas724No ratings yet
- Capacity Utilization For Product Mix Using Operation Based Time Standard EvaluationDocument6 pagesCapacity Utilization For Product Mix Using Operation Based Time Standard EvaluationInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Production Management - BBA NotesDocument6 pagesProduction Management - BBA Notesmadhuphd131650% (2)
- Me403.01 - Production and Operations Management - Lab ManualDocument33 pagesMe403.01 - Production and Operations Management - Lab ManualTUSHAR VALANo ratings yet
- SAP B1 On Cloud - Accounting Information Systems OutlineDocument2 pagesSAP B1 On Cloud - Accounting Information Systems OutlineChristine Jane LaciaNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management QBDocument13 pagesProduction and Operations Management QBSuchitra PrajinNo ratings yet
- Operations & Supply Chain Management-TYBBADocument6 pagesOperations & Supply Chain Management-TYBBAANSH AHUJANo ratings yet
- Operations Management & Strategic Management: Study NotesDocument332 pagesOperations Management & Strategic Management: Study NotesKunal MishraNo ratings yet
- Bknmu Bba Sem-V Syllabus (New) 2020Document28 pagesBknmu Bba Sem-V Syllabus (New) 2020Pradip MehtaNo ratings yet
- PM Book - FinalDocument372 pagesPM Book - FinalThu Hà Phan ThịNo ratings yet
- Affliated Institutions: Anna University of Technology Chennai CHENNAI 600 113Document34 pagesAffliated Institutions: Anna University of Technology Chennai CHENNAI 600 113Maha RajaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: B.B.A. Iii Sem Subject - Operations ManagementDocument46 pagesSyllabus: B.B.A. Iii Sem Subject - Operations Managementharshbhatt100% (1)
- Discriminant Function AnalysisDocument16 pagesDiscriminant Function AnalysisVignesh AngurajNo ratings yet
- Cluster Analysis With SPSSDocument8 pagesCluster Analysis With SPSSVignesh AngurajNo ratings yet
- Cluster AnalysisDocument5 pagesCluster AnalysisPuscas EmanuelaNo ratings yet
- Dubai Debt CrisisDocument24 pagesDubai Debt CrisisVignesh AngurajNo ratings yet
- Companies Bill 2009 24aug2009Document261 pagesCompanies Bill 2009 24aug2009Vignesh AngurajNo ratings yet
- Lec # 13.5 Power Factor CorrectionDocument49 pagesLec # 13.5 Power Factor CorrectionAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Kaled, A. - Modelling and Theoretical Analysis of Laminar Flow and Heat TransferDocument21 pagesKaled, A. - Modelling and Theoretical Analysis of Laminar Flow and Heat TransferElios SequiNo ratings yet
- LG 42ln5390 Manual de Usuario PDFDocument88 pagesLG 42ln5390 Manual de Usuario PDFJorge Valencia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Pricelist ChallengerDocument4 pagesPricelist ChallengerMichaelben Michaelben50% (4)
- Pelton Turbine ExperimentDocument6 pagesPelton Turbine ExperimentvedNo ratings yet
- Torrent - Strong, Fast Balance Discovery in The Lightning NetworkDocument7 pagesTorrent - Strong, Fast Balance Discovery in The Lightning NetworkANDREW KIMANINo ratings yet
- SM-A730F DS SVC Guide - F PDFDocument27 pagesSM-A730F DS SVC Guide - F PDFsafi alsafiNo ratings yet
- A320NEO-B12-0009.2, NEO 36 Diffs, R4 170817Document80 pagesA320NEO-B12-0009.2, NEO 36 Diffs, R4 170817simsimsom100% (2)
- Edc Question Bank R20 2021Document5 pagesEdc Question Bank R20 2021khadarskb19No ratings yet
- Service Pack Upgradation: LogshippingDocument2 pagesService Pack Upgradation: LogshippingJoshua PrakashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Ashwani MishraDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Ashwani MishraAshwani MishraNo ratings yet
- Hilti - CS Cash Sale - 32303743Document1 pageHilti - CS Cash Sale - 32303743John SabandoNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Flow Pattern Maps For Macrochannels: October 2015Document48 pagesTwo-Phase Flow Pattern Maps For Macrochannels: October 2015akinhaciNo ratings yet
- C BOOKnewDocument187 pagesC BOOKnewMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Yabai Toggle WindowDocument3 pagesYabai Toggle WindowBinay BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- Write UpDocument2 pagesWrite Upvu2cw.radioNo ratings yet
- Logistics J Operations and Supply Chain ManagementDocument35 pagesLogistics J Operations and Supply Chain ManagementArjay B. CenizaNo ratings yet
- Cấp Trường Pxc4, Pxc5 & Pxc7Document26 pagesCấp Trường Pxc4, Pxc5 & Pxc7Lap Vo NhuNo ratings yet
- Detail Usage Statement: Keterangan IstilahDocument1 pageDetail Usage Statement: Keterangan Istilahrafi anasNo ratings yet
- Simple Step by Step Procedure For Text File To Email With File Conversion in PI 7.1Document24 pagesSimple Step by Step Procedure For Text File To Email With File Conversion in PI 7.1fziwenNo ratings yet
- Europe COmpaniesDocument62 pagesEurope COmpaniesTom MasterNo ratings yet
- Which of Following Is Shared Structure of A Set of Similar Objects?Document5 pagesWhich of Following Is Shared Structure of A Set of Similar Objects?20UCS128Debajeet DasNo ratings yet
- Ts 133127v170500p Lawful InterceptionDocument162 pagesTs 133127v170500p Lawful InterceptionPAVAN KUMAR GUDAVALLETINo ratings yet
- Refsheet 2nd Namhae Bridge CH enDocument1 pageRefsheet 2nd Namhae Bridge CH en王小波No ratings yet
- 1perception of The Students of Negatives Effect of Online Classes in Saint Nicholas Catholic School of MarivelesDocument10 pages1perception of The Students of Negatives Effect of Online Classes in Saint Nicholas Catholic School of MarivelesEmman Hipol0% (1)
- Baumer BHF ENCODERDocument4 pagesBaumer BHF ENCODERAgus SalimbasukiNo ratings yet
- Cni (1) .PDF Orignal ElisaDocument1 pageCni (1) .PDF Orignal ElisaTapita HEBANGNo ratings yet