Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Database Administration (DBA)
Database Administration (DBA)
Uploaded by
James R Msonda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesDatarabase Administration
Original Title
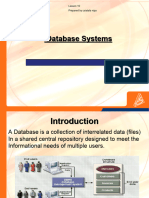
Database
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDatarabase Administration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesDatabase Administration (DBA)
Database Administration (DBA)
Uploaded by
James R MsondaDatarabase Administration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Database Administration (DBA)
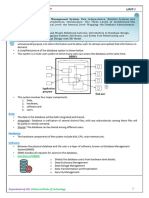
DBA is a resource that supervises both the
database and the use of the DBMS.
DBA is usually a group, but sometimes it
refers to the database administrator.
Figure 8.1
Responsibilities of DBA
Policy Formulation and
Implementation
Access Privileges
Users should access the database only in ways
in which they are entitled.
Security
Access restrictions ensure that the database is
secure.
Passwords, encryption, and views implement
security.
Effective password protection is critical.
Planning for Disaster
Databases can be harmed from hardware
and software malfunctions, and outsides
forces like floods and power outages.
DBAs must take active role in formulating
disaster recovery plans.
Figure 8.8
Disaster Recovery
Archives
An archive is a place where corporate data is kept.
Information in an archive is removed from the
database and stored in the archive for future
reference.
Archives are usually kept in a mass-storage device
like a disk, tape, CD, or a DVD.
It is important such archives be kept off-site to
allow recovery should disaster strike
Data Dictionary Management
Essentially the catalog, but it contains a
wider range of information, including
information on tables, fields, indexes, and
programs.
The DBA manages and updates the data
dictionary, which establishes naming
conventions for tables, fields, etc., and data
integrity rules.
Additional responsibilities of DBA
Training
DBA gives training on the DBMS and how to
access the database
DBMS Support
The DBA is charged with all aspects of a
DBMS, including selection and management
DBA must evaluate each prospective DBMS
using a checklist like that shown in
Figure 8.10.
Additional Responsibilities of DBA
Database design
DBA is responsible for tuning the design, i.e.,
making changes that improve system
performance.
You might also like
- Database AdministratorDocument34 pagesDatabase AdministratorTech_MXNo ratings yet
- DBMS Final NotesDocument30 pagesDBMS Final NotesUmair MalimNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Database AdministratorDocument34 pagesWeek 1 Database AdministratorWaleed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dbms NotesDocument224 pagesDbms NotesMukesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DBMSDocument32 pagesChapter 1 DBMSAishwarya Pandey100% (1)
- ER and NormalizationDocument158 pagesER and NormalizationTulipNo ratings yet
- Database Administration (DBA)Document9 pagesDatabase Administration (DBA)Hugo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Database Components: by Shafillullah Lecturer ICS/ITDocument15 pagesWeek 2 - Database Components: by Shafillullah Lecturer ICS/ITMuhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Database Administration (DBA)Document9 pagesDatabase Administration (DBA)Johann SanoNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument14 pagesNetworkingمحمد الحميديNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Document31 pagesUnit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Madhu RayaproluNo ratings yet
- Dbms Unit 1-1Document87 pagesDbms Unit 1-1Raghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023Document19 pages2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023konkimalla ganeshNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document111 pagesModule 1Ronit ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Database Management SystemDependra SinghNo ratings yet
- File Processing Versus DatabasesDocument12 pagesFile Processing Versus Databasesapi-297547878No ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Database Management SystemDharshanNo ratings yet
- 02.advantages of Database ApproachDocument14 pages02.advantages of Database ApproachMadhuNo ratings yet
- Database Administration and ManagementDocument16 pagesDatabase Administration and ManagementbilalNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument373 pagesDBMSTushar PatelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SudhaDocument129 pagesModule 1 SudhaRupith Kumar .NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DBMSDocument22 pagesLecture 1 DBMSAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Review Question CHDocument6 pagesReview Question CHnour ghanaymNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument17 pagesDatabase Management SystemsHaidarNo ratings yet
- The Database Management System DBMSDocument15 pagesThe Database Management System DBMSRichard LumawagNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument9 pagesBasic Conceptsuseless0151No ratings yet
- W2L4 - DBMS ConceptsDocument29 pagesW2L4 - DBMS ConceptsMiguel Carlo GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Islamic Online University: Course: Computer 101Document439 pagesIslamic Online University: Course: Computer 101AzarudeenNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument86 pagesDatabase Management SystemG.K.HarishNo ratings yet
- 214 Lecture 1Document57 pages214 Lecture 1Eniola Joyce AdedejiNo ratings yet
- Module 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument32 pagesModule 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemMadaraNo ratings yet
- DBMS 1Document12 pagesDBMS 1Varun NNo ratings yet
- What Is Database?Document3 pagesWhat Is Database?Apna MianwaliNo ratings yet
- Module 1 DBMSDocument96 pagesModule 1 DBMSreddytejaswini0431No ratings yet
- Database Systems Concepts and Architecture: Dheeba. J/SCOPEDocument27 pagesDatabase Systems Concepts and Architecture: Dheeba. J/SCOPEPuneet PurohitNo ratings yet
- Database AdministratorDocument7 pagesDatabase AdministratorHema AroraNo ratings yet
- DB Lec 06Document11 pagesDB Lec 06hammadrajpoot3366qaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Assignment-1Document3 pagesDBMS Assignment-1darkk0462No ratings yet
- Presentation1 DatabaseDocument49 pagesPresentation1 DatabaseSameedNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam FDS PDFDocument35 pagesMidterm Exam FDS PDFAlthea ManlapazNo ratings yet
- DBMS SlidesDocument127 pagesDBMS SlidesAmit KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Database Management System (DBMS) CO# 1, Session: Session Topic: Database ArchitectureDocument34 pagesDatabase Management System (DBMS) CO# 1, Session: Session Topic: Database ArchitectureGVachaspathi gnaneswarNo ratings yet
- DBMS Module1 Part1Document66 pagesDBMS Module1 Part1gauthamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 DBADocument21 pagesChapter 01 DBAHamza khanNo ratings yet
- Da Tabase Management System: Hassan KhanDocument11 pagesDa Tabase Management System: Hassan KhanHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document47 pagesDBMS Unit 1Faisal Nazir (ANDY)No ratings yet
- UNIT I Database Study MaterialDocument13 pagesUNIT I Database Study Materialsavitha ramuNo ratings yet
- DBA Module 2Document16 pagesDBA Module 2melkamu endaleNo ratings yet
- Data and Database AdministrationDocument19 pagesData and Database AdministrationzeeshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document39 pagesChapter 1YasukeNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument30 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAyush RathoreNo ratings yet
- Role and Responsibilities of DBADocument34 pagesRole and Responsibilities of DBAsimargrewalNo ratings yet
- Database Systems MISDocument22 pagesDatabase Systems MISYonse Epic StoriesNo ratings yet
- RdbmsDocument7 pagesRdbmsadityaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - MDocument40 pagesUnit 4 - Mriyan hussainNo ratings yet
- Ict 141 NotesDocument87 pagesIct 141 Notespheobenyapola11No ratings yet
- CH 08Document34 pagesCH 08Fendy RasidNo ratings yet
- Access Week 1Document15 pagesAccess Week 1Daisy Mangahas BaleriteNo ratings yet
- DBF1Document20 pagesDBF1Hana ʚĩɞNo ratings yet
- Regional Studies in Marine ScienceDocument15 pagesRegional Studies in Marine ScienceAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Reef Check Malaysia BHD: Keywords: Coral Reefs, Survey, Status, Southeast Asia and Reef CheckDocument24 pagesReef Check Malaysia BHD: Keywords: Coral Reefs, Survey, Status, Southeast Asia and Reef CheckAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Taebi Soheila 2012 PDFDocument152 pagesTaebi Soheila 2012 PDFAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Circulation Patterns in A Channel Reef-Lagoon System, Ouano Lagoon, New CaledoniaDocument28 pagesCirculation Patterns in A Channel Reef-Lagoon System, Ouano Lagoon, New CaledoniaAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Utorial: Benthic Terrain Modeler For Arcgis 10.1Document15 pagesUtorial: Benthic Terrain Modeler For Arcgis 10.1Azhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Textural Characterization of Coastal Sediments Along Tamil Nadu Coast, East Coast of IndiaDocument8 pagesSciencedirect: Textural Characterization of Coastal Sediments Along Tamil Nadu Coast, East Coast of IndiaAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet