Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths PMR Form 3 Notes
Uploaded by
AkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths PMR Form 3 Notes
Uploaded by
AkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTES AND FORMULAE
PMR MATHEMATICS
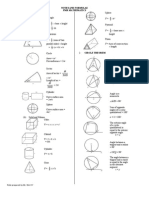
1. SOLID GEOMETRY
(a) Area and perimeter
Triangle
A =
2
1
base height
=
2
1
bh
Trapezium
A =
2
1
(sum of two
parallel sides) height
=
2
1
(a + b) h
Circle
Area = r
2
Circumference = 2r
Sector
Area of sector =
!"
r
2
#ength of arc =
!"
2r
C$linder
Cur%e surface area
= 2rh
Sphere
Cur%e surface area =
&r
2
(b) Solid and 'olume
Cube(
' = x x x = x
Cuboid(
' = l b h
= lbh
C$linder
V = r
2
h
Cone
V =
1
r
2
h
Sphere
V =
&
r
)$ramid
V =
1
base area
height
)rism
V = Area of cross section
length
2. CIRCLE THEOREM
Angle at the centre
= 2 * angle at the
circumference
x = 2y
Angles in the same
segment are e+ual
x = y
Angle in a
semicircle
ACB = ,"
o
Sum of opposite
angles of a c$clic
+uadrilateral = 1-"
o
a + b = 1-"
o
The e.terior angle
of a c$clic
+uadrilateral is
e+ual to the interior
opposite angle.
b = a
Angle between a
tangent and a radius
= ,"
o
OPQ = ,"
o
The angle between a
tangent and a chord
is e+ual to the angle
in the alternate
segment.
x = y
Note prepared by Mr. Sim KY
/f PT and PS are
tangents to a circle0
PT = PS
TPO = SPO
TOP = SOP
. POLYGON
(a) The sum of the interior angles of a n sided pol$gon
= (n 1 2) 1-"
o
(b) Sum of e.terior angles of a pol$gon = !"
o
(c) 2ach e.terior angle of a regular n sided pol$gon =
n
"
!"
(d) 3egular pentagon
2ach e.terior angle = 42
o
2ach interior angle = 1"-
o
(e) 3egular he.agon
2ach e.terior angle = !"
o
2ach interior angle = 12"
o
(f) 3egular octagon
2ach e.terior angle = &5
o
2ach interior angle = 15
o
&. FACTORISATION
(a) xy + xz = x(y + z)
(b) x
2
y
2
= (x y)(x + y)
(c) xy + xz + ay + az
= x (y + z) + a (y + z)
= (y + z)(x + a)
(d) x
2
6 &x 6
= (x 6 )(x 6 1)
5. EXPANSION OF ALGERBRAIC
EXPRESSIONS
(a)
2.
2
1 !. 6 . 1 = 2.
2
1 5. 7
(b) (. 6 )
2
= .
2
6 2 * * . 6
2
= .
2
6 !. 6 ,
(c) (. 1 $)(. 6 $) = .
2
6 .$ 1 .$ 1 $
2
= .
2
1 $
2
!. LAW OF INDICES
(a) x
m
x
n
= x
m 6 n
(b) x
m
x
n
= x
m 1 n
(c) (x
m
)
n
= x
m n
(d) x
-n
=
n
x
1
(e)
n
x x
n
=
1
(f)
m n
x x
n
m
) ( =
(g) x
0
= 1
4. ALGEBRAIC FRACTION
2.press
2
1 1"
2 !
k
k k
as a fraction in its simplest
form.
Solution(
2 2
1 1" 1 (1" )
2 ! !
k k k
k k k
=
=
2 2 2 2
1" & 1" 2( 5) 5
! ! !
k k k k k
k k k k
+
= = =
-. LINEAR EQUATION
8i%en that
1
5
(n 6 2) = n 1 20 calculate the %alue
of n.
Solution(
1
5
(n 6 2) = n 1 2
5 *
1
5
(n 6 2) = 5(n 1 2)
n 6 2 = 5n 1 1"
2 6 1" = 5n 1 n 2n = 12 n = !
,. SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS
(a) Substitution 9ethod(
$ = 2. 1 5 ::::::::(1)
2. 6 $ = 4 ::::::::(2)
Substitute (1) into (2)
2. 6 2. 1 5 = 4 &. = 12 . =
Substitute . = into (1)0 $ = ! 1 5 = 1
(b) 2limination 9ethod(
Sol%e(
. 6 2$ = 5 ::::::::::(1)
. 1 2$ = 4 ::::::::::(2)
(1) 6 (2)0 &. = 120 . =
Substitute into (1) , 6 2$ = 5
2$ = 5 1 , = 7&
$ = 72
1". ALGEBRAIC FORMULAE
8i%en that ; 1 (m 6 2) = m0 e.press m in terms of
;.
Solution(
; 1 (m 6 2) = m ; 1 m 1 2 = m
; 1 2 = m 6 m = &m
m =
2
&
k
Note prepared by Mr. Sim KY
11. LINEAR INEQUALITIES
1. Sol%e the linear ine+ualit$ . 1 2 < 1".
Solution(
. 1 2 < 1" . < 1" 6 2
. < 12 . < &
2. #ist all integer %alues of . which satisf$ the
linear ine+ualit$ 1 = . 6 2 > &
Solution(
1 = . 6 2 > &
Subtract 20 1 7 2 = . 6 2 1 2 > & 1 2
71 = . > 2
. = 710 "0 1
. Sol%e the simultaneous linear ine+ualities
&p 1 = p and p 6 2
1
2
p
Solution(
&p 1 = p &p 1 p = p =
p = 1
p 6 2
1
2
p * 20 2p 6 & p
2p 1 p 7& p 7&
The solution is 7& = p = 1.
12. STATISTICS
9ean =
sum of data
number of data
9ean =
sum of(fre+uenc$ data)
sum of fre+uenc$
0 when the data
has fre+uenc$.
9ode is the data with the highest fre+uenc$
9edian is the middle data which is arranged in
ascending?descending order.
1. 0 0 &0 !0 -
9ean =
& ! -
&.-
5
+ + + +
=
9ode =
9edian = &
2. &0 50 !0 -0 ,0 1"0 there is no middle number0
the median is the mean of the two middle
numbers.
9edian =
! -
2
+
= 4
2. A pictograp uses s$mbols to represent a set of
data. 2ach s$mbol is used to represent certain
fre+uenc$ of the data.
@anuar$
Aebruar$
9arch
3epresents 5" boo;s
. A !ar cart uses horizontal or %ertical bars to
represent a set of data. The length or the height of
each bar represents the fre+uenc$ of each data.
&. A pi" cart uses the sectors of a circle to represent
the fre+uenc$?+uantiti$ of data.
A pie chart showing the fa%ourite drin;s of a group
of students.
1. TRIGONOMETRY
TBA SBC CAC
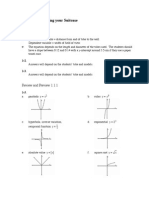
1&. GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS
(i) #inear function.
(ii) Duadratic function.
(iii) Cubic function.
(i%) 3eciprocal
y =
a
x
15. GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTIONS
Note prepared by Mr. Sim KY
E "F &5F !"F
sin E G
2
2
2
1
=
2
cos E
2
2
2
2
1
=
G
tan E
1
=
1 H
adIacent side
h$potenuse
opposite
side
A B
C
tan =
side adIacent
side opposite
sin =
h$potenuse
side opposite
cos =
h$potenuse
side adIacent
y = x
y = 1x
y = x
2
y = 1 x
2
y = x
3
y = 1 x
3
x
y
O
x
y
O
y = :
a
x
1!. SCALE DRAWINGS
Scale of a drawing =
The length of drawing
The length of the actual obIect
14. LINES AND ANGLES
1-. COORDINATES
1. Jistance ( ) ( )
2
1 2
2
1 2
$ $ . . =
2. 9idpoint0
( )
+ +
=
2 2
2 1 2 1
y y
,
x x
y , x
1,. TRANSFORMATIONS
1. Translation
x
y
2. 3eflection
. 3otation
(i) centre of rotation
(ii) angle of rotation
(iii) direction of rotation : e.ample( ,"
"
cloc;wise ?
,"
"
anticloc;wise
&. 2nlargement
(i) centre of enlargement
(ii) scale factor
k =
obIect of side ing correspond the of length
image of side a of length
k
2
=
area of image
area of obIect
Note prepared by Mr. Sim KY
x
y
x = y
!
= !
a
b
x + y = "#0
$
You might also like
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moivre in SummationDocument18 pagesDe Moivre in SummationFarhan Ellahi0% (1)
- Kvpy SB SolutionsDocument34 pagesKvpy SB Solutionsricky24x7No ratings yet
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- Maths PMR Form 3 NotesDocument4 pagesMaths PMR Form 3 NotesMichael Lopez100% (2)
- SPM MATHS FORMULA GUIDEDocument9 pagesSPM MATHS FORMULA GUIDENurAinKhalidNo ratings yet
- SPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsDocument9 pagesSPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsPatrick PhuahNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Mathematics Ellipse SolutionsDocument10 pagesIIT-JEE Mathematics Ellipse SolutionsPremNo ratings yet
- KVPY Paper 2012 Class XII Part I QuestionsDocument25 pagesKVPY Paper 2012 Class XII Part I QuestionsVishank RustagiNo ratings yet
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Document27 pagesInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceNo ratings yet
- MCR3U Final Exam Review (June2010)Document6 pagesMCR3U Final Exam Review (June2010)Erin Guerrero100% (1)
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocument9 pagesFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Maximizing Your IIT JEE Score With Proven TechniquesDocument14 pagesMaximizing Your IIT JEE Score With Proven TechniquesKashish ManochaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Take PrintDocument17 pagesFiitjee Take PrintPraks SaxenaNo ratings yet
- MATH Formulas PDFDocument33 pagesMATH Formulas PDFAnonymous 0Mduljho100% (3)
- ALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSDocument33 pagesALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSLala Hala100% (3)
- MHT CET 2016 Version 11Document16 pagesMHT CET 2016 Version 11JitNo ratings yet
- Some Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in MathematicsDocument12 pagesSome Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in Mathematicsparchure123No ratings yet
- ENGMATTITLEDocument7 pagesENGMATTITLEVignesh RavishankarNo ratings yet
- IIT Sts Vii/Mpc/P (Ii) /solns: Paper Ii Solutions Mathematics Physics ChemistryDocument22 pagesIIT Sts Vii/Mpc/P (Ii) /solns: Paper Ii Solutions Mathematics Physics ChemistryKAMAL KANT KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Precalculus Review: For Problems 1 Through 3, Let P (1, 3) and Q (5, - 3)Document7 pagesPrecalculus Review: For Problems 1 Through 3, Let P (1, 3) and Q (5, - 3)shannonhu519No ratings yet
- Narayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Document53 pagesNarayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Pranjal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PC Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument29 pagesPC Chapter 1 SolutionsvincentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document184 pagesChapter 7Christopher BreedenNo ratings yet
- Math Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Document21 pagesMath Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- MATH2117 Exam 2008s2 SolnDocument14 pagesMATH2117 Exam 2008s2 Solns3208510No ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Differential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDifferential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Maths PMR Form 3 NotesDocument4 pagesMaths PMR Form 3 NotesAkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Module on Directed NumbersDocument22 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Module on Directed NumbersslpheyNo ratings yet
- Plan-J Math Form 3 2014Document5 pagesPlan-J Math Form 3 2014AkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaNo ratings yet
- 1 CewtDocument1 page1 CewtAkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaNo ratings yet
- Plan-J Math Form 2 2014Document8 pagesPlan-J Math Form 2 2014AkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaNo ratings yet
- Senarai Semak PJK Ting 1 2013Document2 pagesSenarai Semak PJK Ting 1 2013cody_lee_8No ratings yet
- Form1 Mat 3Document35 pagesForm1 Mat 3patkhsheng@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Geometry Shapes PropertiesDocument3 pagesGeometry Shapes PropertiesAkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)