Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolysis Worksheet-Igcse
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolysis Worksheet-Igcse
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
TAREK S. ELHAGE
2010
IGCSE - CHEMISTRY
Electrolysis questions + past papers questions
www.chem-exptc.com
U AE AB U DH AB I
www.chem-exptc.com
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
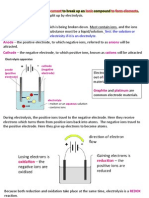
1. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN salt (compound) the product at the CATHODE
is:
A. Non metal
B. Metal
C. Sodium
D. Chlorine
2. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN salt (compound) the product at the ANODE is:
A. Non metal
B. Metal
C. Sodium
D. Chlorine
3. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN sodium chloride ( NaCl ) the product at the
anode and the cathode are:
Anode Cathode
A. Sodium Chloride
B. Sodium chlorine
C. Chlorine Sodium
D. chloride sodium
4. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN lead iodide (
2
PbI ) the product at the anode
and the cathode are:
Anode Cathode
A. hydrogen iodine
B. iodine lead
C. lead iodide
D. lead iodine
5. Circle the correct answer concerning the properties of halogens
Chlorine Bromine Iodine
A. Green, solid Green, solid Red brown, solid
B. Green, gas Red brown, gas Pale pink, liquid
C. Green, liquid Red brown, liquid Pale pink, liquid
D. Green, gas Red brown, liquid Pale pink, solid
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
6. During the electrolysis of a CONCENTRATED
) (aq
CuSO
4
the product at the
CATHODE is:
A.
) ( g
H
2
B.
) ( g
O
2
C.
) ( g
SO
2
D. Red brown deposit ( )
) (s
Cu
7. During the electrolysis of a DILUTE
) (aq
CuSO
4
the products at the CATHODE and
the ANODE are:
cathode anode
A.
) ( g
O
2
) (s
Cu
B.
) ( g
H
2
) ( g
O
2
C.
) (s
Cu
) ( g
O
2
D.
) (s
Cu
) ( g
SO
2
8. The colour of the universal indicator in a neutral medium is .
A. Blue
B. Red
C. Green
D. Violet
9. When a few drops of the universal indicator are added to the acid
) (aq
HCl , the
expected colour is
A. Blue
B. Red
C. Green
D. Violet
10. An acid reacts with metal to produce
A. Salt + water
B. Salt + base
C. Salt + hydrogen
D. Water + carbon dioxide
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
11. Name the products of the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid
(i) At cathode: .
(ii) At anode:
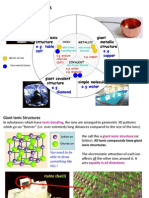
12. Which of the following does NOT contain ions?
(a) Aqueous hydrogen chloride
(b) Gaseous hydrogen chloride
(c) Solid potassium nitrate
(d) Molten potassium chloride
13. Which of the following does NOT contain free ions?
(a) Aqueous hydrogen chloride
(b) Aqueous ammonia
(c) Solid potassium nitrate
(d) Molten potassium chloride
14. When aqueous
4(aq) 2
SO H solution is electrolysed using inert carbon
electrodes, the substance formed at anode is
(a) hydrogen gas
(b) Oxygen gas
(c) Copper (II) ion
(d) Copper deposit
15. When aqueous
4(aq) 2
SO H solution is electrolysed using inert carbon electrodes, the
substance formed at cathode is:
(a) hydrogen gas
(b) Oxygen gas
(c) Copper (II) ion
(d) Copper deposit
16. When aqueous
4(aq) 2
SO H solution is electrolysed using inert carbon electrodes, the
substance formed at anode is a:
(a) Gas that burns with pop sound
(b) Gas that relights a glowing splint
(c) Brown gas
(d) Pink solid
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
17. The diagram shows the electrolysis of a molten compound X.
What is compound X?
A. Copper (II) Chloride
B. Lead(II) bromide
C. Sodium chloride
D. Sodium bromide
18. The diagram shows the electrolysis to electroplate nickel with different metals
Which nickel electrodes are plated with a metal?
A- 1 only
B- 1 and 3 only
C- 2 only
D- 2 and 4 only
electrode Carbon
gas brown
of bubbles
X compound Molten
+
electrode Carbon
metal Silvery Molten
heat
Ni Ni Ni
Ni
1 2 3
4
Aqueous
Chloride sodium
Aqueous
sulphate (II) Copper
+
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
19. Metal X is low in the reactivity series and it is liberated by electrolysis of its
bromide.
Metal X is 1 and the bromide is 2 .
Which words correctly complete gaps 1 and 2?
1 2
A.
B.
C.
D.
Lead
Lead
Sodium
Sodium
In solution
molten
In solution
molten
20. Copper and hydrogen can each be formed by electrolysis.
At which electrodes are these elements formed?
copper hydrogen
A.
B.
C.
D.
anode
anode
cathode
cathode
anode
cathode
anode
cathode
21. Two elements X and Y form ionic compounds, XBr
2
and Y
2
O
3
. The
compounds are separately melted and electricity is passed through the
liquids.
What are the products at the cathodes?
A. bromine and oxygen
B. bromine and Y
C. oxygen and X
D. X and Y
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
22. Which change can take place during electrolysis?
A. lead(IV) oxide lead(II) oxide + oxygen
B. concentrated hydrochloric acid hydrogen + chlorine
C. sodium hydroxide + nitric acid sodium nitrate + water
D. lead(II) nitrate + sulphuric acid lead(II) sulphate + nitric acid
23. What is the charge on an anode and the type of element formed at such an
electrode?
charge on anode type of element formed
A.
B.
C.
D.
negative
negative
positive
positive
metal
non-metal
metal
non-metal
24. The diagram shows how to cause a chemical change in a molten compound.
What is this process used for?
A. removal of oxides from metals
B. extraction of metal from its ore
C. neutralisation of industrial waste
D. production of fertilisers
electrodes
compound molten
heat
- +
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
25. A molten compound is electrolysed. Two atoms of X are deposited at the
negative electrode at the same time as three atoms of Y are deposited at the
positive electrode.
These results show that:
X is a ..1..;
Y is a ..2..;
the formula of the compound is 3 .
How are gaps 1, 2 and 3 correctly completed?
1 2 3
A.
B.
C.
D.
metal
metal
non-metal
non-metal
non-metal
non-metal
metal
metal
X
3
Y
2
X
2
Y
3
X
3
Y
2
X
2
Y
3
26. In which electrolysis are chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide all
produced?
aqueous sodium chloride
molten sodium chloride
A.
B.
C.
D.
27. Metallic and non-metallic elements can both be extracted by electrolysis.
Which element is produced at the negative electrode (cathode)?
A. bromine
B. chlorine
C. oxygen
D. hydrogen
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
28. The electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride makes three
products.
Which products are shown at the correct electrodes?
anode (+ve)
cathode (ve)
A.
B.
C.
D.
chlorine
sodium hydroxide
hydrogen
chlorine
sodium hydroxide
chlorine
sodium
hydrogen
29. The diagram shows that two gases are formed when concentrated
hydrochloric acid is electrolysed between inert electrodes.
Which line correctly describes the colours of the gases at the electrodes?
anode (+ve) cathode (ve)
A.
B.
C.
D.
colourless
colourless
yellow-green
yellow-green
colourless
yellow-green
colourless
yellow-green
acid ic hydrochlor
ed concentrat
ve - ve +
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
30. The diagram shows the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide.
What is seen at each electrode?
electrode X electrode Y
A.
B.
C.
D.
brown gas
brown metal
green gas
silvery metal
silvery metal
green gas
brown metal
brown gas
31. The following electrolysis circuit is set up, using inert electrodes P, Q, R and
S.
At which of the electrodes is a Group VII element produced?
A. P only B. P and R C. Q only D. Q and S
X electrode
Y electrode +
heat
bromide ) ( lead molten II
P Q R S
+ +
Concentrated
hydrochloric acid
Molten
Lead (II) bromide
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
32. The following electrolysis circuit is set up, using inert electrodes
At which electrode is a metal deposited?
33. The diagram shown is not complete.
What should be shown at X when the solution has been electrolysed for some
time?
X
ed concentrat
acid ic hydrochlor
2
Cl
2
Cl
2
Cl
2
H
2
H
2
H
2
H
2
O
A B C D
Molten
Lead (II) bromide
Concentrated
aqueous
sodium chloride
A B C D
+ +
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
34. Which product is manufactured by electrolysis?
A. aluminium
B. copper(II) sulphate
C. steel
D. sodium chloride
35. The diagram represents the electrolysis of brine (aqueous sodium
chloride).
What are products X and Y?
X Y
A.
B.
C.
D.
hydrogen
hydrogen
oxygen
oxygen
aqueous sodium hydroxide
hydrochloric acid
aqueous sodium hydroxide
hydrochloric acid
Y
X
brine chlorine
+
-
negative
electrode
porous
wall
positive
electrode
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
36. Define
(a) Electrolysis
...
(b) Electrolyte (liquid)
...
(c) Conductor (metal)
...
(d) Anode
...
(e) Inert electrode
...
37. In electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride
2
MgCl using graphite electrodes
(a) Give t he formul a of t he ions present
(b) What i s observed at
Anode , cat hode ..
(c) Name the product at
Anode .., cathode ...
(d) Wri te the i oni c equat ion t o show changes at
Anode:
Cathode: .......
(e) Draw a l abel ed diagram and indi cat e the direction of el ectron flow
(f) How are
e removed from outer circuit and where?
...
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
38. Name the products at electrodes, during the electrolysis ( using inert electrodes) of
(a) di lut e sulphuric aci d solution
) ( 4 2 aq
SO H
39. In the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide
) ( 2
PbBr
l
using Graphite
electrodes
i. at anode , ii . at cathode
(b) dilut e pot assi um ni trat e soluti on
) ( 3 aq
KNO
(i ) at anode , (i i). at cathode .
(c) Copper (II) sul phat e soluti on
) ( 4 aq
CuSO
i. at anode., ii. at cat hode .
(d) concent rat ed
) (aq
HCl
at anode , ii. at cathode.
(e) Concentrat ed
) (aq
NaCl
i. at anode, ii. at cat hode
(i ) What is observed at anode? ....
(i i ) Name the product at anode? ....
(i i i ) Writ e t he i oni c equation that t akes pl ace at anode.
. .
(i ) What is observed at cat hode? .
(i i ) Name the product at cathode? .
(i i i ) Writ e t he i oni c equation that t akes pl ace at cathode.
. .
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(a) What happens to the ammeter readi ng i f heat i s removed? Why?
.
(b) How are el ectrons removed from the outer circui t? and why?
40. In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride ) gBr (
2
M , using inert electrodes
(a) Give t he formul ae of the ions present:
. . . . .
(b) what is observed at each el ectrode
at anode . . . .
At cathode. . . . . .
(c) what are the product s at the el ectrodes
at anode . . . .
At cathode. . . . . .
(d) Wri te the i oni c equat ion whi ch t akes pl ace at
- At Anode: . . . . . . . . . .
- At Cathode: . . . . . . . .
41. In the electrolysis of sulphuric acid ) SO (
4(aq) 2
H , using inert electrodes
(a) Give t he formul ae of the ions present: . . . . . .
(b) Which ions move to the positive electrode (anode): . .
(c) Which ions move to the negative electrode (cathode): . . .
(d) Name the product at anode: . . . . . .
(e) Wri te the i oni c equat ion whi ch t akes pl ace at
- At Anode: . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(f) Name the product at cathode: . . . . .
(g) Write the ionic equation which takes place at cathode
At Cathode: . . . . . . . . .
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
42. The following diagram shows electroplating of a an iron spoon with copper
(a) The met al of whi ch X is made is. . . .
(b) Is X made anode or cat hode? . . . . . .
(c) Is t he spoon anode or cat hode? . . .
(d) A suitable electrolyte is .
(e) In case we need t o el ectropl at e t he spoon with sil ver,
suggest a suit able
(i) Anode . . . .
(ii) Elect rol yt e . .
43. In purification of copper
(a) Impure copper is made . . . . .
(b) Pure copper is made cathode . . .
(c) The used elect rol yt e is . . . . . .
(d) The formed sli me (sl udge) has economi c i mportance because
. . . .
. . . .
Spoon
X
e electrolyt
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
44. The diagram shows a method for obtaining pure copper from impure
copper.
1- Name each of the following substances
a) Substance A ..
b) Substance B
c) Substance C .
d) Substance D .
e electrolyt
positive
Electrode
) ( Anode
negative
Electrode
) ( cathode
A
B
D C
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
45. Ex t r a c t i o n o f Al umi num
(a) Label the letters A to D
(b) Give the name of the main aluminum ore.
(c) Why should aluminum ore be treated with sodium hydroxide before electrolysis?
..
(d) Name the substance in which aluminum oxide is dissolved in the above
electrolysis process.
(e) Explain why the substance in part (4) is added to aluminum oxide.
(f) Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction which takes place at the
cathode.
.
+
C
B
A
Molten Aluminum
collecting on the bottom
D
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(g) Which electrode has to be frequently replaced during the process? Explain your
answer.
.
.
46. Zinc is extracted from its ore, zinc blende ,by reduction with carbon after being roasted
with air
a) Complete the following two equations for the reactions involved in this process
.. ZnS + ... .. ZnO + .
2
SO
ZnO + ... Zn + .
2
CO
b) Give one use of Zinc.
47. (a)Name the 3 products obtained by electrolysis of
) ( aq
KBr using inert electrodes
. .
(a) How is
2
Br obt ained from
) ( aq
KBr ?
. . . . .
. . . . . . . .
(b) How is
2
I obt ained from
) ( aq
NaI ?
. . . . . . . .
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
48. In the electrolysis cell of concentrated
) (aq
NaCl
(a) Name the products at
Anode ....., cathode ....
(b) Name the solution flows out of the cell.
(c) How is sodium hydroxide obtained from concentrated
) (aq
NaCl ?
.
..
..
.
(d) How is chlorine gas obtained from
) (aq
NaCl solution?
..
..
(e) (a) Name the 3 products of the electrolysis of concentrated
) (aq
KBr .
....,
.......,
.
(f) Write the ionic equations taking place at
(i) anode:.. ..
(ii) Cathode: .... ....
Porous
Wall
+
) (Brine
(aq)
NaCl Conc.
Anode Cathode
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
49. Like Copper, nickel can be refined by electrolysis.
Label the diagram to show the purification of nickel in the laboratory
50. The diagram below shows an apparatus in which the electrolysis of aqueous sodium
sulphate containing litmus solution was carried out.
When the current was passed through the solution, the solution around the anode
turned red and the solution around the cathode turned blue. Gas A was found to
relight a glowing splint and gas B, when ignited, burned with pop.
(a) Give the formula of the four ions in aqueous sodium sulphate
.
. [2]
(b) Which ion caused the litmus to turn red?
.. [1]
(c) Which ion caused the litmus to turn blue?
. [1]
+
A
Direct
Current
B
Electrodes Platinium
Gas
Gas
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(d) (i) Complete the table below
Name of gas Name of electrode at which
gas is produced
Gas A
Gas B
(ii) Write an equation to show the formation of gas B.
.
.
(iii) At which electrode has oxidation taken place?
.
.. [4]
(e) If the experiment is repeated using deionised water without sodium sulphate
dissolved in it, no reaction occurs.
(i) Explain why there is no reaction?
.
(ii) Explain why the addition of sodium sulphate to deionised water allows a reaction
to take place.
.
.
.
. [2]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
51. Calcium may be prepared by the electrolysis of molten calcium chloride
2
CaCl .
(i) How would you convert lime (calcium oxide) into anhydrous calcium
chloride?
.
(ii) What element are the anodes made from?
(iii) At which electrode is the calcium obtained?
(iv) Name the other substance produced during this electrolysis.
.
+
+
Graphite anode Graphite anode
Graphite
Molten Calcium
Chloride
Steel Cathode
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
52. Lithium is extracted by the electrolysis of its molten chloride.
(i) Lithium chloride is an ionic compound. Explain why it conducts electricity in
molten state but not in the solid state.
.. [2]
(ii) How is electricity conducted in the part of the circuit labeled
A to B
C to D ... [2]
(iii) What would be the products of the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous
lithium chloride?
. [3]
B
+
D
C
A
B A to circuit of Part
Electrodes
Lithium Molten
chloride
Carbon
D C to circuit of Part
heat
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
53. Chemistry is concerned with the transfer of electrons and energy.
(a) During electrolysis, electrical energy is supplied,
electrons move in the external circuit and ions
move in the electrolyte. The diagram
shows the electrolysis of molten
potassium bromide.
(i) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the direction of the
electrons in the external circuit. [1]
(ii) Is the following reaction exothermic or endothermic? Give a reason for
your choice.
2
Br 2K 2KBr +
[2]
(iii) Electrons are removed from the external circuit. Howe and where is this
done?
[1]
Circuit External
supply Power
Electrodes
potassium Molten
bromide
heat
+
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(iv) The results of experiments on electrolysis are shown in the following table.
Complete the table; the first has been completed as an example.
Electrolyte Electrodes Change at
cathode
Change
at anode
Change to
electrolyte
Molten
potassium
bromide
Carbon Potassium
metal formed
Bromine
formed
Used up
Aqueous
copper (II)
sulphate
Copper Stays the same
Carbon hydrogen
gas evolved
Chlorine
formed
Potassium
hydroxide formed
[4]
54. The diagram shows the electrolysis of Lead (II) bromide,
2
PbBr
(a) Explain why solid lead (II) bromide does not conduct electricity.
..
(b) Balance the equations for the reactions that take place at each electrode.
(i) ...
Br
2
Br +
e
(ii)
+ 2
Pb + .
e Pb
(c) Identify the brown fumes shown in the above diagram
..
(d) Define reduction in terms of electrons
..
metal Silvery
bromide (II) Lead Molten
fumes Brown
Heat
+
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
55. A metallic cup can be coated in silver by electrolysis. The process is called
electroplating
(a) Identify the metal from which the used electrode is made.
(b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte that could be used. ....
(c) Should the cup be made anode or cathode? ...
56.
The diagram shows the apparatus used to electrolyse lead(II) bromide.
(a) The wires connected to the electrodes are made of copper.
Explain why copper conducts electricity.
..................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
(b) Explain why electrolysis does not occur unless the lead(II) bromide is
molten.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(c) The reactions occurring at the electrodes can be represented by the
equations shown in the table.
Complete the table to show the electrode (A or B) at which each reaction
occurs, and the type of reaction occurring (oxidation or reduction).
electrode Metal
Cup
electrolyte
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
Paper3
57. The electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride produces three
commercially important chemicals; hydrogen, chlorine and sodium hydroxide.
(a)The ions present are Na
+
(aq), H
+
(aq) ,Cl
(aq) and OH
(aq).
(i)Complete the ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode (cathode).
. + . [1]
(ii)Complete the ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode).
. - . [1]
(iii)Explain why the solution changes from sodium chloride to sodium hydroxide.
... [1]
(b) (i) Why does the water supply industry use chlorine?
... [1]
(ii)Name an important chemical that is made from hydrogen.
... [1]
(iii)Sodium hydroxide reacts with fats to make soap and glycerine
What type of compound are fats?
... [1]
Nov-2008
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
1. Copper is purified by electrolysis.
(a) Complete the following.
The positive electrode (anode) is made from.
The negative electrode (cathode) is made from
The electrolyte is aqueous [3]
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode).
..... [2]
(c) (i) Give two reasons why copper is used,
in electric wiring, ..
... [2]
in cooking utensils., ..
... [2]
(ii) Give another use of copper.
... [1]
[Total: 10]
May-2008
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
1. Zinc is extracted from zinc blende, ZnS. Zinc blende is heated in air to give
zinc oxide . part of the zinc oxide reacts with sulphuric acid to give aqueous
zinc sulphate. This is electrolysed with inert electrodes (the electrolysis is
the same as that of copper (II) sulphate with inert electrodes).
ions present: Zn
2+
(aq)
2
4
SO (aq) H
+
(aq) OH
-
(aq)
(i) Zinc forms at the negative electrode (cathode). Write the equation for this
reaction.
... [1]
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode).
... [1]
(iii) The electrolyte changes from aqueous zinc sulphate to
... [1]
(a) Give two uses of zinc.
1......
2. .... [2]
Nov-2007
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(a) Cell reactions are both exothermic and redox. They produce electrical
energy as well as heat energy.
(i) The diagram shows a simple cell.
Which substance in this cell is the reductant and which ion is the oxidant?
reductant zinc
oxidant hydrogen ions [2]
(ii) How could the voltage of this cell be increased?
magnesium instead of zinc or increase concentration of acid
or copper instead of iron ( increase the reactivity difference)
..[1]
(ii) What is the important large scale use, relating to iron and steel, of this
type of cell reaction?
sacrificial protection or stop iron/steel rusting [1]
or galvanising
[1]
voltmeter
iron
electrode
zinc
electrode
bubbles of
hydrogen form
becomes
thinner
dilute
sulphuric acid
V
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(b) Cells can be set up with inert electrodes and the electrolytes as oxidant
and reductant.
The potassium manganate(VII) is the oxidant and the potassium iodide is the
reductant.
(i) Describe the colour change that would be observed in the left hand beaker.
pink or purple [1] to colourless or decolourised [1]
NOT red NOT clear
[2]
(ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in the right hand beaker.
2I
2e I
2
[2]
May-2006
voltmeter
carbon
electrode
(inert)
carbon
electrode
(inert)
electron flow
Potassium
iodide(aq)
Potassium
manganate(VII)(aq)
salt bridge
(allows ions to move from
one beaker to another)
V
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(i) The electrolysis of molten strontium chloride produces strontium metal and
chlorine. Write ionic equations for the reactions at the electrodes.
negative electrode (cathode) ....
positive electrode (anode) ... [2]
(ii) One of the products of the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous strontium
chloride is chlorine. Name the other two.
.. [2]
Nov-2005
(i ) hydrochl ori c aci d [ 1]
(i i ) Sr
2 +
+ 2e = Sr [ 1]
2Cl
2e = Cl 2 [ 1] or 2Cl
= Cl 2 + 2e
(i i i ) hydr ogen [ 1] and st ront i um hydr oxi de [ 1] [ 2] Nov-2005
(b) Aqueous copper(II) sulphate solution can be electrolysed using carbon
electrodes. The ions present in the solution are as follows.
Cu
2+
(aq),
2
4
SO (aq), H
+
(aq), OH
(aq)
(i) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode (cathode).
............................................................................................................[1]
(ii) A colourless gas was given off at the positive electrode (anode) and the
solution changes from blue to colourless.
Explain these observations.
............................................................................................................
............................................................................................................[2]
(c) Aqueous copper(II) sulphate can be electrolysed using copper electrodes. The
reaction at the negative electrode is the same but the positive electrode
becomes smaller and the solution remains blue.
(i) Write a word equation for the reaction at the positive electrode.
............................................................................................................[1]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(ii) Explain why the colour of the solution does not change.
............................................................................................................
............................................................................................................[2]
(iii) What is the large scale use of this electrolysis?
............................................................................................................[1]
May-2004
(b) (i) Cu2+ + 2e = Cu [1]
(ii) gas is oxygen [1]
(copper(II) sulphate) changes to sulphuric acid [1]
or copper ions removed from solution
(c) (i) copper atoms - electrons = copper ions [1]
accept correct symbol equation
(ii) concentration of copper ions does not change or [1]
amount or number of copper ions does not change
copper ions are removed and then replaced [1]
or copper is transferred from anode to cathode
(iii) refining copper or plating (core) [1]
or extraction of boulder copper
May-2004
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
1. Copper is purified by electrolysis.
(a) Complete the following.
The positive electrode (anode) is made from.
The negative electrode (cathode) is made from ..
The electrolyte is aqueous [3]
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode).
....... [2]
(c) (i) Give two reasons why copper is used,
in electric wiring, ....
... [2]
in cooking utensils., ....
.... [2]
(ii) Give another use of copper.
... [1]
[Total: 10]
May-2008
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
2. Lead bromide was placed in a tube and connected to an electrical circuit as shown below.
The lead bromide was heated until molten. A brown gas was given off.
(a) State one other expected observation.
..[1]
(b) (i)Suggest a suitable material to make the electrodes.
.....[1]
(ii)Indicate on the diagram the negative electrode (cathode). [1]
(c) Name the brown gas. At what electrode will the gas be given off?
Name ....
electrode ....[2]
(d) Why is this experiment carried out in a fume cupboard?
....[1]
May-June - 2004
d.c.power supply
LEAD
BROMIDE
TOXIC
bulb
heat
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
3. The diagram shows the apparatus used to find out the effect of an electric current on a
concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(a) On the diagram label the electrodes [1]
(b) Give three observations when the circuit is switched on.
1.
2.
3..[3]
(c) (i)Name the product at the positive electrode (anode).
..[1]
(ii)State a test for this product and the result of the test.
test..[1]
result .[1]
May-June-2006
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
4. Impure copper is extracted from the ore. This copper is refined by
electrolysis.
(a) Name;
the material used for the positive electrode (anode),
...... [1]
the material used for the negative electrode (cathode),
.[1]
a suitable electrolyte.
.[1]
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode.
.[1]
(c) One use of this pure copper is electrical conductors, another is to make
alloys.
Name the metal that is alloyed with copper to make brass.
.[1]
Nov-2005
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
5. The diagram shows the apparatus used to pass an electric current through concentrated
hydrochloric acid.
(a) Label the electrodes. [1]
(b) Give two observations when the current is switched on.
1....
2... [2]
(c) Give a test for the product at the negative electrode (cathode).
test ....
result .... [2]
oct-Nov-2005
chlorine hydroge
n
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
6. Electricity was passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride containing
Universal Indicator.
(a) Suggest a suitable material for the electrodes.
carbon/graphite/any unreactive metal e.g. platinum/nickel...[1]
Three observations were noted:
1- Bubbles of gas seen immediately at the negative electrode.
2- Bubbles of gas formed after some time at the positive electrode.
3- The solution turned blue around the negative electrode and colourless near the
positive electrode.
(b) Give a test to show that the gas observed in 1 is hydrogen.
Test lighted splint (1) .....[1]
result pops(1) ..[1]
(c) Suggest why bubbles of gas were not seen immediately in 2.
gas dissolves (in the solution) o.w.t.t.e [1]....
..[2]
(d) (d)What causes the colour change in 3 at
the negative electrode, alkali/(sodium) hydroxide (1)..[1]
the positive electrode? chlorine/bleach (1) not chloride or chlorine ions..[1]
Concentrated
aqueous sodium
chloride and
universal indicator
negative
electrode
positive
electrode
carbon
rods
+
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
7. A constant current was passed through aqueous copper(II) sulphate using inert
electrodes as shown in the diagram below. Copper was deposited at one of the
electrodes.
A
variable
resistor
+
D E
aqueous
copper(II) sulphate
(a) Name a suitable material for the inert electrodes. [1]
(b) At which electrode was copper deposited, D or E? [1]
(c) What was seen at the other electrode?
............................................................................................................................................[1]
(d) What was the colour of the electrolyte
(i) at the start of the experiment,
...................................................................................................................................
(ii)at the end of the experiment?
...................................................................................................................................
[2]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
8. A metal cup can be coated in silver by electrolysis. The cup must be very clean and
also rotated during the process, which is known as electroplating.
(a) Should the metal cup be the anode or the cathode?
.............................................................................................................................[1]
(b)Identify the metal from which the electrode is made.
..............................................................................................................................[1]
(c) Suggest a suitable electrolyte that could be used to electroplate this cup.
..............................................................................................................................[2]
(d)Suggest why the cup must be
(ii) very clean,
...........................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................[1]
(iii) rotated during the electrolysis.
...........................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................[1]
2 (a) cathode / negative [1]
(b) silver [1]
(c) silver nitrate (1) solution (1) [2] // any silver salt not Cl
-
, I
-
(d) (i) silver will not coat / stick or similar [1]
(ii) to give even coating / all of it gets coated [1] [Total 6]
electrolyte
metal electrode
cup
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
9. A student electrolysed lead bromide and aqueous sodium chloride in the apparatus
shown below.
Each of the electrodes is labelled with a letter.
(a) Why was it necessary for lead bromide to be molten?
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(b) (i)What was produced at electrode A?
...................................................................................................................................
(ii) What was the appearance of this product?
...................................................................................................................................
(iii) What was produced at electrode B?
...................................................................................................................................
(iv) Where did this product collect?
...................................................................................................................................
[4]
D C B A
+ -
carbon
electrodes
carbon
electrodes
molten
lead bromide
aqueous
sodium chloride
heat
+ - + -
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(c) Gases were produced at electrodes C and D. In each case name the gas and give
a test to confirm its presence.
(i) the gas produced at C ...............................................................................
test for this gas .........................................................................................................
(ii) gas produced at D ,,....................................................................................
test for this gas .........................................................................................................
[4]
(d) What change should be made so that sodium is produced at one of the
electrodes?
..........................................................................................................................................[1]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
10. The apparatus below was used to electrolyse water.
(a) (i) Why was a small volume of sulphuric acid added to the water?
.......................................................................................................................
(ii) Name the gas collected in tube X and give a test for this gas.
gas ............................................................................................................................
test ............................................................................................................................
(iii) Name the gas collected in tube Y and give a test for this gas.
gas ............................................................................................................................
test ........................................................................................................................[5]
(aq) SO H
4 2
electrodes graphite
Y X
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(b) State how the volume of gas collected in tube X compares with the volume of gas
collected in tube Y.
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c) Name a gas that may be used to sterilise water and give a test for this gas.
gas ...................................................................................................................................
test .............................................................................................................................. [2]
(d) A student added a small piece of sodium and a small piece of iron to separate samples
of water. What observations were made?
sodium ..............................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
iron ...................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [3]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
11. A student electrolysed concentrated aqueous sodium chloride using the apparatus
below.
The solution also contained litmus solution.
(a) (i)Name the gas produced at the anode (positive electrode).
......................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Suggest what happened to the colour of the solution around the anode as the
electrolysis proceeded.
........................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Why did this change take place?
..................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) (i)Name the gas produced at the cathode (negative electrode).
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Give a test for this gas.
........................................................................................................................................ [1]
Carbon
anode
Carbon
anode
aqueous sodium
chloride containing
some litmus solution
+
-
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(iii) What happened to the colour of the solution around the cathode as the electrolysis
proceeded?
.............................................................................................................................. [1]
(iv) Why did this change take place?
.............................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) The solution was replaced by a dilute solution of an acid. Suggest which acid
would produce the same gases as those produced with concentrated aqueous sodium
chloride.
(d) Under what conditions does the electrolysis of sodium chloride produce sodium at one of
the electrodes?
[Total: 9]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
12. The diagram shows a cell that can be used to make electrical energy.
(a) Explain why distilled water is not used as the electrolyte.
............................................................................................................................................[1]
(b) This table shows the results when rods of three metals, X, Y and Z, are used in separate
experiments.
All the metals are less reactive than magnesium.
Place the metals in order of reactivity
most reactive magnesium
least reactive
rod 1 rod 2 Voltmeter reading / V
magnesium
X 2.72
magnesium
Y 0.78
magnesium
Z 1.10
Magnesium
rod
voltmeter
rod of metal X, Y or Z
electrolyte
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
(c) A student places a rod of magnesium in aqueous silver nitrate.
(i) Write an ionic equation, with state symbols, for the reaction which happened.
...................................................................................................................................
(ii) What would you expect to see after the reaction had been taking place for some time?
...............................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................[3]
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
13. This reaction can be used to generate electricity in a cell.
(a) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between zinc and aqueous copper(II) sulphate.
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) Drawn an arrow on the diagram to show the direction of the flow of electrons in the wire.
[1]
(c) The voltage of the cell was measured when the following metals were used as electrode 2.
copper iron lead zinc
Complete the table by entering the metals in the correct order.
(d) When metal M was used as electrode 2, it produced a higher voltage than zinc.
Suggest a name for metal M.
........................................................................................................................................................ [1]
meter reading / V metal
1.10
0.78
0.21
0.00
copper
electrode
electrode 2
(Zinc)
aqueous copper (II)
sulphate
V
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
14. The diagram shows a cell for purifying copper.
(a) Describe what you would observe during this electrolysis and write the equations for the
reactions at the electrodes.
(b) The electrodes and the electrolyte conduct electricity.
(i) Explain how the structure of metals allows copper electrodes to conduct electricity. [1]
(ii) Explain why solid copper(II) sulphate does not conduct electricity but an aqueous
solution of copper(II) sulphate does conduct.
(c) Describe how the apparatus shown in the diagram could be modified in order to electroplate
an iron object, such as a knife, with nickel.
(d) Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Bronze is less malleable than pure copper. Use ideas
about the structure of metals and alloys to explain why bronze is less malleable than pure copper.
Pure copper
cathode
impure copper
anode
Electrolyte
(aqueous copper (II)
sulphate
+ -
Electrolysis-Past papers questions
15. An electric current can be generated by a simple electrochemical cell such as the one
shown.
(a) Explain why the flow of electrons is in the direction shown in the diagram. [2]
(b) Suggest why silver nitrate would not be a good electrolyte to use in this cell. [1]
magnesium copper
Electrolyte
(magnesium sulphate)
V
You might also like
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (34)
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901275% (4)
- Electrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesElectrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- Tips For Chemistry ATPDocument4 pagesTips For Chemistry ATPŁílać Mónşťeŕ SublininalsNo ratings yet
- Metals IGCSE NotesDocument27 pagesMetals IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsDocument27 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsChemistryKlipz100% (14)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Conductors and Electrolysis ReactionsDocument31 pagesElectrolytic Conductors and Electrolysis ReactionsSanchita Sarkar100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Oxygen, Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Oxygen, Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideChemistryKlipz75% (4)
- O'Levels Chemistry NotesDocument15 pagesO'Levels Chemistry NotesShahzaib Saqib60% (5)
- Olevels Chemistry Notes - Pure ChemistryDocument82 pagesOlevels Chemistry Notes - Pure ChemistryMarcusNg100% (10)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesDocument4 pagesPhysics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesVernon67% (3)
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9From EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IGCSE Electrochemistry NotesDocument14 pagesIGCSE Electrochemistry Notestettehsackey100% (12)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Extraction and Uses of MetalsDocument21 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Extraction and Uses of MetalsChemistryKlipz90% (10)
- IGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesChemistryKlipz100% (24)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Acids Bases and SaltsDocument13 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Acids Bases and SaltsChemistryKlipz100% (11)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Bonding (Ionic, Covalent and Metallic)Document19 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Bonding (Ionic, Covalent and Metallic)ChemistryKlipz93% (41)
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids, Ester, Macromolecules, Polymer, Polyethene, Polythene, Homologous SeriesDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids, Ester, Macromolecules, Polymer, Polyethene, Polythene, Homologous SeriesOpen200993% (28)
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- N (A) Science (Chem) CHP 13b Preparation of SaltsDocument4 pagesN (A) Science (Chem) CHP 13b Preparation of SaltshamsterishNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument25 pagesIGCSE ChemistryDeyala Mark82% (17)
- Electrolysis BreakdownDocument14 pagesElectrolysis BreakdownBaryaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse ElectrolysisDocument86 pagesEdexcel Igcse ElectrolysisshoshoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisDocument20 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0Document11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0ChemistryKlipz100% (4)
- O LVL Chem Definitions ListDocument6 pagesO LVL Chem Definitions Listacsbr4science170% (10)
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- Notes To Study For Chemistry Paper 6Document8 pagesNotes To Study For Chemistry Paper 63abood51467% (6)
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- 2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersDocument10 pages2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Energy ChangesDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Energy ChangesChemistryKlipz100% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry Notes: Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Notes: Organic CompoundsFasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument70 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesCrystal Wong93% (40)
- O Level Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesO Level Chemistry Practice Questionschong5675% (12)
- GCSE/IGCSE Chemistry Question Bank With AnswersDocument347 pagesGCSE/IGCSE Chemistry Question Bank With AnswersVenkatesh Rao93% (67)
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Calculations Workbook IgcseDocument29 pagesChemical Calculations Workbook IgcsehannahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Document4 pagesWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Secondary 2 Science NotesDocument43 pagesSecondary 2 Science Noteszach0% (1)
- Chemistry IGCSE Paper 6 Revision GuideDocument16 pagesChemistry IGCSE Paper 6 Revision GuideLucas SilvaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Definitions - Learn Key TermsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Definitions - Learn Key Termsjenifer100% (1)
- GCE O Level Pure Chemistry 507302 Suggested Answers 2016Document5 pagesGCE O Level Pure Chemistry 507302 Suggested Answers 2016DjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ATP study tipsDocument3 pagesChemistry ATP study tipsAbdul HannanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument40 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Notestasha100% (5)
- Chemistry Practical TipsDocument18 pagesChemistry Practical TipsK K Chamath Aachinthya64% (11)
- Revision Checklist For O Level Chemistry 5070 FINALDocument32 pagesRevision Checklist For O Level Chemistry 5070 FINALAminah Faizah Kaharuddin67% (6)
- Paper 4Document418 pagesPaper 4Ahmad asa100% (1)
- O Level Physics ATP NotesDocument8 pagesO Level Physics ATP NotesAll in one 474728No ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For Information Technology PhilippinesDocument8 pagesThesis Topics For Information Technology PhilippinesClaudia Acosta100% (2)
- Roles of advertisement and media in marketing five star hotelsDocument20 pagesRoles of advertisement and media in marketing five star hotelsMohitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Accounting 1: Chapter OneDocument15 pagesBasic Structure of Accounting 1: Chapter OneSeid KassawNo ratings yet
- PRIA FAR - 016 Share-Based Payments (PFRS 2) Notes and SolutionDocument4 pagesPRIA FAR - 016 Share-Based Payments (PFRS 2) Notes and SolutionEnrique Hills RiveraNo ratings yet
- EQPS MAF451 - July2020Document10 pagesEQPS MAF451 - July2020Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- DMS (Next Gen Dealer Management Systems DMS)Document13 pagesDMS (Next Gen Dealer Management Systems DMS)Ulfa AkhilNo ratings yet
- SBLC Monetizing MOUDocument9 pagesSBLC Monetizing MOUDinni Resa75% (4)
- Quant Process NotesDocument27 pagesQuant Process NotesDanie100% (1)
- Employee Satisfaction Result Period 2023Document15 pagesEmployee Satisfaction Result Period 2023Doppy LianoNo ratings yet
- Compact Printed Circuit Heat ExchangerDocument3 pagesCompact Printed Circuit Heat ExchangerNur Amanina50% (2)
- GSM Based Smart Irrigation Systems PDFDocument7 pagesGSM Based Smart Irrigation Systems PDFMohamed RafiNo ratings yet
- Progressive Development Corporation v. Quezon CityDocument1 pageProgressive Development Corporation v. Quezon Cityfranzadon100% (1)
- API-EBS Comparison TableDocument5 pagesAPI-EBS Comparison TableantozzNo ratings yet
- Rovshan Oguz Group LLC Hse Plan June 2011Document10 pagesRovshan Oguz Group LLC Hse Plan June 2011vladNo ratings yet
- A Study of the Scrap Metal Trade in KumasiDocument82 pagesA Study of the Scrap Metal Trade in KumasiNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- New Central Bank Act I. Creation, Responsibilities, and Corporate Powers of The Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas (BSP)Document6 pagesNew Central Bank Act I. Creation, Responsibilities, and Corporate Powers of The Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas (BSP)MarrenSalvadorNo ratings yet
- Delta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: Automation For A Changing WorldDocument52 pagesDelta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: Automation For A Changing WorldelkimezsNo ratings yet
- WTO Philippines Spirits AnalysisDocument11 pagesWTO Philippines Spirits Analysisodin_siegreicher100% (1)
- (Offline) Rundown Awarding AiseefDocument4 pages(Offline) Rundown Awarding AiseefFanji HastomoNo ratings yet
- Taxes in India: An Overview of Direct and Indirect TaxationDocument26 pagesTaxes in India: An Overview of Direct and Indirect TaxationGyaneshwariNo ratings yet
- @raniaayamin TikTok Report by Analisa - IoDocument8 pages@raniaayamin TikTok Report by Analisa - IoAizz D'Tech AbeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Discharge Machine (Edm) PDFDocument65 pagesElectrical Discharge Machine (Edm) PDFsujayan2005100% (3)
- AUD 1206 Case Analysis RisksDocument2 pagesAUD 1206 Case Analysis RisksRNo ratings yet
- Proof of Cash CelticsDocument3 pagesProof of Cash CelticsCJ alandyNo ratings yet
- The Wallace Group - TypedDocument4 pagesThe Wallace Group - TypedMohammed ImaniNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - BRENT SCHOOL v. RONALDO ZAMORADocument3 pagesCase Digest - BRENT SCHOOL v. RONALDO ZAMORAAnton Ric Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- BDPR3103 Final Exam AnswerDocument5 pagesBDPR3103 Final Exam AnswerGayathri PathmanathanNo ratings yet
- Qualities of an Effective Internal AuditorDocument2 pagesQualities of an Effective Internal AuditorLINA GABRIELA MENDEZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Logistics Expenses - Seminar Paper II.Document8 pagesLogistics Expenses - Seminar Paper II.PetraNo ratings yet
- Company Introduction Marketing Plan OfHCG & HMGDocument29 pagesCompany Introduction Marketing Plan OfHCG & HMGwk babar100% (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldFrom EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (289)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)