Professional Documents
Culture Documents
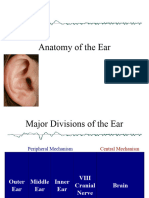
Laboratory Guidance, Ear
Laboratory Guidance, Ear
Uploaded by
jr1111Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Guidance, Ear
Laboratory Guidance, Ear
Uploaded by
jr1111Copyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Guidance
Histology of Ear
Histology Department
Medical Faculty
University of Sumatera Utara
2008
Objectives:
To know the structure of outer, middle,
and inner ear
To know the structure of equilibrium and
hearing receptor
Be able to understand how sound waves
travel to the inner ear and how they are
transformed
Questions?
What is the function of the auditory ossicles, tympanic
membrane, tensor tympani, and stapedius muscles?
How are sound waves transformed into pressure on the
fluid of the inner ear?
What fluid flows through the membranous labyrinth?
What fluid flows through the bony labyrinth?
How do the hair cells get stimulated by the sound
waves? What specializations are on their surface and
what is the role of the tectorial membrane?
Look at the difference in supportive cells adjacent to the
inner and outer hair cells. How could this arrangement
aid in the contactile ability of the outer hair cells?
What is the function of the stria vascularis?
Histology Slides
Auricle (pinna)
Meatus Acusticus Externus (Meatus A.E.)
Macula
Crista Ampularis
Cochlea
Auricle (Pinna)
Skin
Cartilage
Meatus Acusticus Externus
Epithelial tissue
Lamina propria
Sebaceous glands
Ceruminous glands
Cartilage/Bone
Macula
Neuroepithelium
Receptors: Hair cells
Supporting cells
Crista Ampullaris
Neuroepithelium
Hair Cells
Supporting cells
Cupula
Cochlea
Scala vestibuli
Scala tympani
Scala media
Organ of Corti
Striae vascularis
Spiral prominence
Limbus
The End
You might also like
- Navajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFDocument44 pagesNavajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFgerald nacinopaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Hearing and EarDocument10 pagesThe Physiology of Hearing and EarMustafam98No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument20 pagesAnatomy of EarMalsawma PolarisNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Projectsoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- ENT Notes PDFDocument66 pagesENT Notes PDFBob Jenson100% (1)
- Patients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossDocument3 pagesPatients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossminaNo ratings yet
- 2303 Final Exam Q&A 2023Document39 pages2303 Final Exam Q&A 2023dietubrowNo ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Referat Delayed Speech FixDocument23 pagesReferat Delayed Speech FixmutiaraptrcNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- OAE Pediatrician BookletDocument22 pagesOAE Pediatrician BookletKalpana ParajuliNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - BSci - BSN 1 F - Worksheet 7.5Document10 pagesGroup 2 - BSci - BSN 1 F - Worksheet 7.5Aiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument27 pagesAnatomy of Earkaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Document126 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Minlik-alew Dejenie89% (18)
- Tugas Inggris KMB MGG 1-3Document6 pagesTugas Inggris KMB MGG 1-3Julia Wibawa HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ReadingDocument32 pagesJurnal ReadingEva Ratnasari DinNo ratings yet
- W1-1 Review of Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and Nose and Other Important Face and Neck Structures - LectureDocument126 pagesW1-1 Review of Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and Nose and Other Important Face and Neck Structures - LectureDhandepatil PavanKumarNo ratings yet
- 2 The Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and HearingDocument15 pages2 The Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and HearingiwanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Ear, Eye, Nose and ThroatDocument101 pagesAssessment of Ear, Eye, Nose and ThroatMuhammad100% (1)
- Auditory Function: Physiology and Function of The Hearing SystemDocument27 pagesAuditory Function: Physiology and Function of The Hearing SystemRana Sabouni TabariNo ratings yet
- Ent and OptalmologyDocument138 pagesEnt and OptalmologyFan Eli100% (3)
- Case Method Sense of Hearing Group 3Document24 pagesCase Method Sense of Hearing Group 3NASYWANo ratings yet
- Auditory SenseDocument3 pagesAuditory SenseFranchezka GuintoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & HistologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy & Histologykhizar naseemNo ratings yet
- Report 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimDocument3 pagesReport 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimAiman D.No ratings yet
- Submitted By, Adersh. T Natural Science, Reg. No. 13375002Document16 pagesSubmitted By, Adersh. T Natural Science, Reg. No. 13375002vincentksooranadNo ratings yet
- Os TemporaleDocument1 pageOs TemporaleLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument72 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediavishalsidankarNo ratings yet
- Auditory DisordersDocument19 pagesAuditory DisordersJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument17 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMichael FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Human EarDocument3 pagesHuman EarRON PAULO OGALESCONo ratings yet
- Otic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINDocument27 pagesOtic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINJames AchuNo ratings yet
- Auditory System: Human Outer Ear and CultureDocument5 pagesAuditory System: Human Outer Ear and CulturejennyrosepamatNo ratings yet
- Hearing SenseDocument13 pagesHearing SenseLuis NietoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EarDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of EarAriguna WijayaNo ratings yet
- Auditory PerceptionDocument29 pagesAuditory Perceptionayushbhakta2003No ratings yet
- Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument25 pagesChronic Tympanomastoiditispatriciaberedo100% (1)
- The Human EarDocument10 pagesThe Human Earvenkat kandukuriNo ratings yet
- Sample Discriptive Process 2Document5 pagesSample Discriptive Process 2Acatech CabNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment EarsDocument42 pagesHealth Assessment EarsMary Jane M. MorenoNo ratings yet
- How Hearing Loss Can OccurDocument2 pagesHow Hearing Loss Can OccurFaridah AlatasNo ratings yet
- 8 KandleDocument7 pages8 KandleKezia KurniaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy / Physio of The EarDocument58 pagesAnatomy / Physio of The EarRA100% (1)
- Section15 Chapter8EarAnatomyDocument29 pagesSection15 Chapter8EarAnatomyBudi Darmawan DiswanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Ear.Document14 pagesAnatomy of Ear.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Human EarDocument38 pagesHuman Earshervlad75% (4)
- Ear Anatomy - TranscriptDocument5 pagesEar Anatomy - TranscriptSabeel KhalidNo ratings yet
- Section16 Chapter9AuditoryFunctionDocument27 pagesSection16 Chapter9AuditoryFunctionBudi Darmawan DiswanNo ratings yet
- Ear Trauma PDFDocument14 pagesEar Trauma PDFAnggi CalapiNo ratings yet
- Ear Trauma: Kylee Eagles,, Laura Fralich,, J. Herbert StevensonDocument14 pagesEar Trauma: Kylee Eagles,, Laura Fralich,, J. Herbert StevensonInggitaDarmawanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1672293009500025 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1672293009500025 Main273046236No ratings yet
- 8 - Physiology of HearingDocument38 pages8 - Physiology of HearingHealthNo ratings yet
- O To SclerosisDocument44 pagesO To Sclerosismajhi.jhalak19No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EAR: Dr. M. Irfan Butt Mcps - FcpsDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EAR: Dr. M. Irfan Butt Mcps - FcpsRupak GhimireNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Speech PerceptionDocument92 pagesSpeech PerceptionestrellaNo ratings yet