Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nomenclature,: Standards
Uploaded by
reacharunkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nomenclature,: Standards
Uploaded by
reacharunkCopyright:
Available Formats
STANDARDS, NOMENCLATURE, ABBREVIATIONS 3-5
Table 3-2
continued:
QUANTITY UNITS
ABBREVIA-
TIONS
SYM-
BOLS
DEFINING EQUATIONS
LIGHTINGPHOTOMETRY
Luminosity lumen per watt lm watt
-1
K K =
n/*x
factor
Luminous flux lumen
*lumerg/sec
lm F
^pharos \lumin flm
W
Quantity of light lumen-hour lm-hr
Q Q.
=
J'Fdt {t in hrs)
'luminous *talbot *lm-sec
energy
jphos \lumen-second tlm-sec to \Q
=
y
Fdt (t in sec)
\phosage \lumen-second per
square meter
flm-sec m
-2
w \w
=
1/A
J"
Fit (t in sec)
Illumination footcandles ft-c E E
= dF/dA
lux be (A
= area of surface illumi-
phot ph nated)
*
Illuminance E
\pharosage \lumtns per square
meter
flm m~
2
W \D
= dF/dA
Luminous in- candle c I I
= dF/dos
tensity or can- (oi = solid angle through which
dlepower flux from point source
is radiated)
Brightness candles per unit area c/in
2
B B = dI(dA cos 6)
stilb sb (6
= angle between line of sight
apostilb lm m~
2
and normal to surface con-
sidered)
lambert L
footlambert ft-L B' B' = xdI(dA cos 6)
apparent
footcandle
'Luminance
]Helios \blondel tbl \B \H
= ir(dD/du) cos 4>
(w = solid angle
^
= angle of incidence of cen-
tral ray)
\Heliostnt jblondel per meter tbl m- ]G \o = dH/dr
(r
= distance along central ray)
* p
roposed by the Colorimetry Committee of the O.S.A. (nonstandard).
18
t
Proposed by Moon (nonstandard).
18
Except where indicated the following material has been revised and con-
densed for handbook publication from the standard nomenclature. The
three subdivisions immediately following, on radiation, light, and light
measurement, deal with fundamental concepts.
1. Radiation Terms
Radiant energy travels in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Radiant energy density is radiant energy per unit volume.
Spectral radiant energy is radiant energy per unit wavelength interval AX,
at wavelength X.
Radiant flux is the time rate of flow of radiant energy.
Radiant
flux
density is the ratio of radiant flux at an element of surface
to the area of the element.
You might also like
- Spectmethods PDFDocument47 pagesSpectmethods PDFalexlhhcasNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation FundamentalsDocument61 pagesThermal Radiation FundamentalsGregory SimmonNo ratings yet
- Astronomy 2 Session 2011-12 Observational AstrophysicsDocument37 pagesAstronomy 2 Session 2011-12 Observational AstrophysicsbbteenagerNo ratings yet
- Radiation PDocument34 pagesRadiation PJeevan GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationDocument19 pagesChapter 12 Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationMohsen Khandan BakavoliNo ratings yet
- Week8 InterferometersDocument84 pagesWeek8 InterferometersArijit PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument15 pagesPhotoelectric EffectMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- 03-Some Definitions in Radiometry PDFDocument9 pages03-Some Definitions in Radiometry PDFashishdashore1703No ratings yet
- The Advent of Quantum PhysicsDocument152 pagesThe Advent of Quantum PhysicsMary Grace Magpayo LanwangNo ratings yet
- The Planck Function and Remote Sensing SpectraDocument40 pagesThe Planck Function and Remote Sensing SpectraDidik Setyawarno 198810132015041004No ratings yet
- E3877 Optics FormulasDocument6 pagesE3877 Optics FormulasKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Black BodyDocument5 pagesNotes On Black BodyHamza HanifNo ratings yet
- Light Quantities and UnitsDocument18 pagesLight Quantities and Unitswidi muliaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Visual ExaminationDocument84 pagesFundamentals of Visual Examinationkevin desaiNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing Fundamentals Day2Document48 pagesRemote Sensing Fundamentals Day2Va SuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Radiation DosimetryDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Radiation DosimetryGeoff OwusuNo ratings yet
- (Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentDocument21 pages(Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentJai ChangNo ratings yet
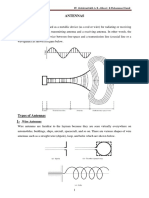
- FUNDAMENTAL PARAMETERS AND FIGURES-OF-MERIT OF ANTENNAS - ch2&ch1Document21 pagesFUNDAMENTAL PARAMETERS AND FIGURES-OF-MERIT OF ANTENNAS - ch2&ch1Abdelrahman Shaban - 53No ratings yet
- Sambalpur University Institute of Information Technology: Antenna Temperature"Document16 pagesSambalpur University Institute of Information Technology: Antenna Temperature"BiswajitNo ratings yet
- Astronomical Instrumentation 1Document28 pagesAstronomical Instrumentation 1Muhammad Nurazin Bin RizalNo ratings yet
- EM radiation fundamentalsDocument12 pagesEM radiation fundamentalsFredrick AwuduNo ratings yet
- Lec20-21 - Compressed SCATTER PDFDocument54 pagesLec20-21 - Compressed SCATTER PDFBobby WardNo ratings yet
- Satellite Remote SensingDocument52 pagesSatellite Remote SensingAnonymous yjF4yygpPbNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Radiometry PhotometryDocument25 pages4.0 Radiometry PhotometrynidharshanNo ratings yet
- Astronomical units and distancesDocument15 pagesAstronomical units and distancesMendoza MenoyNo ratings yet
- Polarized Light ExperimentDocument6 pagesPolarized Light ExperimentmirckyNo ratings yet
- Interpretation and Depth of Schulz1985Document14 pagesInterpretation and Depth of Schulz1985MayaNo ratings yet
- 110 Basic RadiationDocument12 pages110 Basic RadiationLTE002No ratings yet
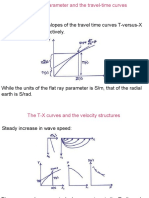
- P and P Are The Slopes of The Travel Time Curves T-versus-X and T-Versus-, RespectivelyDocument38 pagesP and P Are The Slopes of The Travel Time Curves T-versus-X and T-Versus-, RespectivelyKiswanto Habib IhsaniNo ratings yet
- Awp Notes SvewDocument110 pagesAwp Notes SvewPallavi ChNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Radiowave Propagation OverviewDocument55 pagesIntroduction to Radiowave Propagation OverviewRenato MangilaNo ratings yet
- Material Characterization TechniquesDocument28 pagesMaterial Characterization TechniquesAmal ShajiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Parameters of AntennaDocument19 pagesFundamental Parameters of Antennaihab411No ratings yet
- Radiation 1Document13 pagesRadiation 1Mukesh BohraNo ratings yet
- Subject Code: Asc 372 Subject Title: Heat TransferDocument11 pagesSubject Code: Asc 372 Subject Title: Heat TransferSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics 2Document36 pagesFiber Optics 2ekramul98131No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Document10 pagesUltrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)SITI NURFATIHA JAMIANNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation: Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesSolar Radiation: Lecture NotesPHjecrisNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Ch3 PhotonsDocument17 pagesLecture6 Ch3 PhotonsKenny H G Jiménez100% (1)
- Radiant Heat TransferDocument20 pagesRadiant Heat TransferAnonymous ioNuZrgNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & ENERGY STUDIES LASER PHYSICS NOTESDocument3 pagesUNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & ENERGY STUDIES LASER PHYSICS NOTESmanindra kumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing BasicsDocument55 pagesThermal Infrared Remote Sensing Basicssoumitra karNo ratings yet
- Antenna Radiation PatternDocument59 pagesAntenna Radiation PatternIdrees MohammedNo ratings yet
- Quantities and units in optical radiationDocument2 pagesQuantities and units in optical radiationZvonko DamnjanovicNo ratings yet
- Ley de Wien Y Rayleigh-Jean: Daniel Rodríguez (2151933) Laura Aguilar (2154300)Document12 pagesLey de Wien Y Rayleigh-Jean: Daniel Rodríguez (2151933) Laura Aguilar (2154300)DANIEL ESTEBAN RODRÍGUEZ TORRESNo ratings yet
- COLORIMETRY: MEASURING LIGHT & COLORDocument26 pagesCOLORIMETRY: MEASURING LIGHT & COLORKathy Mae DumoghoNo ratings yet
- Radiation SlidesDocument44 pagesRadiation SlidesGourav PundirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Part 1Document59 pagesChemistry Notes Part 1SharleneNo ratings yet
- Presented at The 103rd Convention 1997 September 26-29 New YorkDocument9 pagesPresented at The 103rd Convention 1997 September 26-29 New YorkMiguel PérezNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics Part IDocument62 pagesWave Optics Part IAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 Radiation Heat TrasferDocument16 pagesLAB 3 Radiation Heat TrasferMastura Ahmad Termizi89% (19)
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 83-97, 2011Document15 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 83-97, 2011narico37No ratings yet
- CH 7Document60 pagesCH 7Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- PPT - RadiationDocument40 pagesPPT - Radiationarik chattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Tables for the Energy and Photon Distribution in Equilibrium Radiation Spectra: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 35From EverandTables for the Energy and Photon Distribution in Equilibrium Radiation Spectra: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 35No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- PZU EDUKACJA INSURANCE TERMSDocument19 pagesPZU EDUKACJA INSURANCE TERMSreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Supplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesDocument65 pagesSupplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1461)Document1 pageEn (1461)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Supplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesDocument65 pagesSupplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNamereacharunkNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response Quick Guide MY: 2014Document2 pagesEmergency Response Quick Guide MY: 2014reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1453)Document1 pageEn (1453)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1463)Document1 pageEn (1463)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1460)Document1 pageEn (1460)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1462)Document1 pageEn (1462)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1452)Document1 pageEn (1452)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1455)Document1 pageEn (1455)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1454)Document1 pageEn (1454)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1457)Document1 pageEn (1457)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1456)Document1 pageEn (1456)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1389)Document1 pageEn (1389)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1450)Document1 pageEn (1450)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1388)Document1 pageEn (1388)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1390)Document1 pageEn (1390)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1387)Document1 pageEn (1387)reacharunkNo ratings yet