Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis of Beams & Trusses: Hemant Sonawadekar
Uploaded by
hemantkle2uOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Beams & Trusses: Hemant Sonawadekar
Uploaded by
hemantkle2uCopyright:
Available Formats
by
HEMANT SONAWADEKAR
Assistant Professor
Department of Civil Engineering
KLE Dr MSSCET, Belgaum.
ANALYSIS OF
BEAMS & TRUSSES
Beams - usually long, straight, prismatic members designed to
support loads applied at various points along the member.
Beam can be subjected to concentrated loads or distributed
loads or combination of both.
INTRODUCTION
Different types of Supports
Roller Support
Hinge Support
Fixed Support
Various Types of Beams
Beams are classified according to way in which they are
supported.
Reactions at beam supports are determinate if they involve
only three unknowns. Otherwise, they are statically
indeterminate.
CONTD
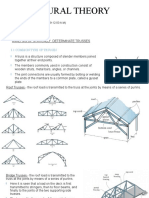
A truss consists of straight members connected at joints. No member is
continuous through a joint. And can carry only axial forces in nature.
Bolted or welded connections are assumed to be pinned together. Forces
acting at the member ends reduce to a single force and no couple. Only two-
force members are considered
TRUSSES
When forces tend to
pull the member apart,
it is in tension. When
the forces tend to
compress the member,
it is in compression.
Members of a truss are slender and not capable of supporting
large lateral loads. Loads must be applied at the joints.
Method of Joints
Method of Sections
Graphical Method
Different Methods to Analyse
Trusses
You might also like
- StructureDocument54 pagesStructureAnoushka BansalNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory - Plane TrussesDocument10 pagesStructural Theory - Plane TrussesJasper Kenneth PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument12 pagesAnalysis of StructuresFabie BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument39 pagesAnalysis of StructuresVimbainaishe MutsvairoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument39 pagesAnalysis of StructuresKenias NdunaNo ratings yet
- Unit4 PDFDocument29 pagesUnit4 PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- MEC-107: Basic Engineering Mechanics Unit-4 Analysis of StructuresDocument29 pagesMEC-107: Basic Engineering Mechanics Unit-4 Analysis of StructuresAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Truss AnalysisDocument11 pagesTruss AnalysisAdrian ParasNo ratings yet
- Truss by RJ AliDocument18 pagesTruss by RJ AliAli AhsanNo ratings yet
- CIVL 3121 Trusses - Introduction 1/7: Analysis of Truss Structures Analysis of Truss StructuresDocument7 pagesCIVL 3121 Trusses - Introduction 1/7: Analysis of Truss Structures Analysis of Truss StructuresNiroj MaharjanNo ratings yet
- MEE 233 - Truss - FrameDocument11 pagesMEE 233 - Truss - Frameleebrown21082003No ratings yet
- VEctor Active StructuresDocument32 pagesVEctor Active StructuresAstha GoyalNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Analysis of StructureDocument42 pagesModule 5 - Analysis of StructureJazmine ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document4 pagesLec 4Muhammad Suhaib Uz Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Space Frame and TrussDocument6 pagesDifference Between Space Frame and TrussKhalida ParveenNo ratings yet
- Analysis For External Reactions and Internal Stress Resultants of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument5 pagesAnalysis For External Reactions and Internal Stress Resultants of Statically Determinate StructuresJanice RamonNo ratings yet
- EM-I - Lec-6. TrussesDocument48 pagesEM-I - Lec-6. TrussesFAISAL TaseenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document2 pagesUnit 1saivedha25No ratings yet
- TOS I Topic 1Document12 pagesTOS I Topic 1Daisy OgollaNo ratings yet
- 04 Analysis of External Reactions and Internal Stress of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument6 pages04 Analysis of External Reactions and Internal Stress of Statically Determinate StructuresDaniela EmbornalNo ratings yet
- Introduction Trusses PDFDocument12 pagesIntroduction Trusses PDFLoraine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Spardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresDocument18 pagesSpardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresSpradha Mehta100% (1)
- Analysis of StructuresDocument2 pagesAnalysis of StructuresElle HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- hdt16 Eng Struc1Document7 pageshdt16 Eng Struc1ruben madridejosNo ratings yet
- Ayush Kishore 21410005 Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesAyush Kishore 21410005 Physics ProjectAYUSH KISHORENo ratings yet
- Teori Dasar StrukturDocument32 pagesTeori Dasar StrukturPAK RINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Structural TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Structural TheoryServando III UyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document38 pagesLecture 5Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Shear Force and Bending Moment PresentationDocument20 pagesLesson 3 Shear Force and Bending Moment PresentationTashNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Beams Loads and Stresses - MACALINTALDocument2 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Beams Loads and Stresses - MACALINTALROMELYN MACALINTALNo ratings yet
- 3-Analysis of StructuresDocument42 pages3-Analysis of StructuresJoylyn BeranNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument46 pagesStructural Analysisongica jamesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument15 pagesAnalysis of StructuresFabie BarcenalNo ratings yet
- ES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesDocument15 pagesES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesErikNo ratings yet
- Types of Structural Load in BeamsDocument10 pagesTypes of Structural Load in BeamswynsangasparNo ratings yet
- TosDocument11 pagesToswynsangasparNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document19 pagesLecture 8Hashir ToheedNo ratings yet
- Structural Matrix Analysis (CEET526) Lecture 1Document21 pagesStructural Matrix Analysis (CEET526) Lecture 1TrishaAndresNo ratings yet
- Types of Beams and Support ReactionsDocument8 pagesTypes of Beams and Support ReactionsayingbaNo ratings yet
- TRuss PDFDocument8 pagesTRuss PDFAlok SarkarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument93 pagesAdvanced Structural AnalysisRoshan kumar patelNo ratings yet
- Types of TrussesDocument15 pagesTypes of Trussesprabhu81No ratings yet
- Internal Loading Notes Week 3Document1 pageInternal Loading Notes Week 3Harry GaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Structural AnalysisCNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 23 Trusses IntroDocument17 pagesLecture # 23 Trusses IntroAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Structure 1 - Chapter 3Document35 pagesStructure 1 - Chapter 3ljlubrhf rjnNo ratings yet
- Pin Jointed SystemsDocument24 pagesPin Jointed SystemsAbu BakarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A TrussDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of A TrussManish RaturiNo ratings yet
- Determinacy of Structures: Prepared By: Engr. Precious Princess T. Saba InstructorDocument14 pagesDeterminacy of Structures: Prepared By: Engr. Precious Princess T. Saba InstructorDjonraeNarioGalvezNo ratings yet
- Module 3 TOSDocument10 pagesModule 3 TOSPrince IbanezNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument30 pagesAnalysis of Structurescontrax8No ratings yet
- Structure AnaylsisDocument13 pagesStructure AnaylsisHassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 7 PDFTravis ShivleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Handout - Edited PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 3 Handout - Edited PDFTTTNo ratings yet
- Nota Structure-TrussDocument8 pagesNota Structure-TrussSiti NurfatinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Truss PDFDocument8 pagesBasics of Truss PDFKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics I CHAP 4Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics I CHAP 4nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Ce 8502 Structural AnalysisDocument2 pagesCe 8502 Structural AnalysisROOPA100% (1)
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Prepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum FekheraldinDocument55 pagesPrepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum Fekheraldinhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Seismic Fragilities For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Consideration of IrregularitiesDocument13 pagesSeismic Fragilities For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Consideration of IrregularitiesmohamedNo ratings yet
- Objective of A Pushover AnalysisDocument3 pagesObjective of A Pushover Analysishemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Seismic Safety Assessment of Existing Masonry Infi LL Structures in NepalDocument2 pagesSeismic Safety Assessment of Existing Masonry Infi LL Structures in Nepalhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Effect of Torsional Irregularity On Earthquake BehaviourDocument7 pagesInvestigation of The Effect of Torsional Irregularity On Earthquake Behaviourhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- RRM DykeDocument1 pageRRM Dykehemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes in Structural ModelingDocument5 pagesCommon Mistakes in Structural Modelinghemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Prasad Patil Raju Honule - Plinth BeamDocument1 pagePrasad Patil Raju Honule - Plinth Beamhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: G. Uva, F. Porco, A. FioreDocument13 pagesEngineering Structures: G. Uva, F. Porco, A. Fiorehemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Strong Column Weak Beam Mixed StructuresDocument6 pagesStrong Column Weak Beam Mixed StructuresSigfridoLogesNo ratings yet
- V3i5 1163 PDFDocument18 pagesV3i5 1163 PDFhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Studies On Vertically Irregular RC Infilled Frame BuildingsDocument1 pageStudies On Vertically Irregular RC Infilled Frame Buildingshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Studies On Vertically Irregular RC Infilled Frame BuildingsDocument1 pageStudies On Vertically Irregular RC Infilled Frame Buildingshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Seismic Analysis of Masonry Infill RC Buildings With PDFDocument9 pagesNonlinear Seismic Analysis of Masonry Infill RC Buildings With PDFhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Masonry Infilled Frame Structures: State-Of-The-Art Review of Numerical ModellingDocument28 pagesMasonry Infilled Frame Structures: State-Of-The-Art Review of Numerical ModellingRosa valero gutierrezNo ratings yet
- 119TOBCTJDocument8 pages119TOBCTJকিশলয়No ratings yet
- Damping in Structures: 18.1 ConceptsDocument12 pagesDamping in Structures: 18.1 Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Prestress: 12.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument12 pagesPrestress: 12.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass: 3.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument16 pagesCentre of Mass: 3.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear WallsDocument8 pagesNonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear Wallsakif-benzer-6764No ratings yet
- Objective of A Pushover AnalysisDocument3 pagesObjective of A Pushover Analysishemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Pendulums: 15.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument14 pagesPendulums: 15.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- V3i5 1163 PDFDocument18 pagesV3i5 1163 PDFhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Vibration Reduction: 19.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument12 pagesVibration Reduction: 19.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Theory and Practice: 24.1 Preliminary CommentsDocument12 pagesTheory and Practice: 24.1 Preliminary Commentshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Human Body Models in Structural Vibration: 20.1 ConceptsDocument12 pagesHuman Body Models in Structural Vibration: 20.1 Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Effect of Different Cross Sections: 4.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument12 pagesEffect of Different Cross Sections: 4.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Bending: 6.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument12 pagesBending: 6.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration: 16.1 Definitions and ConceptsDocument22 pagesFree Vibration: 16.1 Definitions and Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Damping in Structures: 18.1 ConceptsDocument12 pagesDamping in Structures: 18.1 Conceptshemantkle2uNo ratings yet