Professional Documents
Culture Documents
India Mecca of Small Car
India Mecca of Small Car
Uploaded by
FRIGHThouseCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
India Mecca of Small Car
India Mecca of Small Car
Uploaded by
FRIGHThouseCopyright:
Available Formats
I NDI A BRAND EQUI TY FOUNDATI ON
www.ibef.org
I BEF
India: Mecca of Small Car
CONTENTS
........................................................................................................................
1. INDIAN AUTOMOBILE: THE SUNSHINE SECTOR
8. MANUFACTURING FACILITIES & THEIR FUTURE INVESTMENTS
10. THE ROAD AHEAD
2. INDIA: THE SMALL CAR HUB
5.1 Indian auto component industry
6.1 Tata Nano: A car for millions
............................................................... 3
................................................................................................. 3
..................................... 6
................................................................................................ 7
..................................................................................................... 7
.................................. 9
................................................................................................................... 13
3. MANUFACTURER AND EXPORTER OF SMALL CARS ......................................................... 4
4. INDIA ADVANTAGE .................................................................................................................... 5
5. INDIA: AN ECOSYSTEM FOR AUTOMOBILE MANUFACTURING
6. PIONEERS OF SMALL CARS ............................................................................. 7
7. GOVERNMENT POLICIES AND REFORMS
9. NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND INITIATIVES ............................................................................. 11
11. REFERENCES ...................................................................................................................... 14
............................................................................. 8
........................................................................................................................
1. Indian Automobile: The sunshine sector
The Indian automobile sector is the seventh largest in the world producing
about 2.6 million cars of the world's 73 million cars produced. According to the
Automotive Component Manufacturers Association of India (ACMA) and Society
of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) estimates, the car production is set
to increase to 4 million by 2015 and to 9 million by 2020. The country is also the
largest manufacturer of motorcycles and the fifth largest producer of
commercial vehicles. In 2009, India became the fourth largest exporter of
automobiles followed by Japan, South Korea and Thailand.
Traditionally, the Indian automobile market has been dominated by the two-
wheeler segment, which accounted for almost 75 per cent of the automobile
sales in the country. However, since 2005, the passenger car market (70 per
cent of which comprises the small car segment) has boomed.
Exhibit 1 shows the demand for passenger car segment to be 3.8 million in the
next 10 years. Small car segment is expected to grow to 2.66 million by 2020.
India: Mecca of Small Car 3
2. India: The small car hub
Exhibit 1: Consumption of cars over the next 10 years In BRIC countries and the share of each country
among the incremental consumption. Consumption forecasts for 2020 were arrived at assuming a
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14 per cent for India and 6 per cent each for China, Brazil and
Russia, as estimated in a study by Ernst & Young.
Source: Organisation Internationale des Constructeurs d'Automobiles (OICA) production statistics,
Redseer Analysis
Consumption Forecasts for
2020
Current consumption (in
2010)
13.4
2.1
1.2
1.0
23.9
2.8
1.6
3.8
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
M
i
l
l
i
o
n
s
China Brazil Russia India
73%
5%
3%
19%
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 4
3. Manufacturer and exporter of small cars
The export market of small cars in India is growing at a rapid pace of average
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 33 per cent over the last five years.
As per the IHS Global Insight Inc estimates, by 2016, India is set to topple
Japan as the world's biggest small car producer, building as many as three
million units. By 2013, 31 per cent of the world's small cars would be from India.
Small cars manufactured in India are being exported to countries such as UK,
Italy, Germany, Netherlands, South Africa, Latin American and other East Asian
countries. The export market is, however, highly fragmented, with countries
such as UK and Italy having 10 per cent share each and countries such as
Netherlands, Germany and South Africa having 5 per cent share each.
Singapore is fast rising as a big market where the demand for Indian cars has
grown seven times over the last four years. Assuming an average growth rate of
40-50 per cent in small car export, by 2014, India will overtake Japan as the
largestexporterof smallcars.
Hyundai, the second largest automotive manufacturer in India, exports 50 per
cent of its India production.
Exhibit 2: Exports of small cars from India and Japan over the last 5 years
For years 2011-12 to 2013-14 small car exports were estimated by assuming a Compound
Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 40 per cent -50 per cent for India, justified by the growing
demand for Indian small cars worldwide, big investments in the small car industry by the
foreign manufacturers. Japan`s Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is assumed as 5 per
cent, justified by the increasing production costs and costlier small exports.
Source: Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) website, JAMA (Japan automobile
manufacturers association), Redseer Analysis
0.14
0.19
0.42
0.44
0.66
0.91
1.26
1.29
1.47
0.87 0.88 0.93
0.98
1.03
2005-06 2007-08 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
India Japan
M
i
l
l
i
o
n
s
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 5
4. India Advantage
What an Indian engineer promises to do with one, my engineer tells me we
need five to complete - Carl Ghosn, Renault Nissan, CEO
India is not just a low-cost production destination, but also a leader in
engineering services. The Global CEO of Renault - Nissan, Carl Ghosn, quoted,
What an Indian engineer promises to do with one, my engineer tells me we
need five to complete, highlighting the innovation and cost advantage which
Indian engineers are able to bring to the table.
Factors Indian Advantage
Demand for small cars
As per McKinsey estimates, by 2025, the Indian middle-class is
expected to grow from 50 million to 550 million. This, when
combined with Indian middle-class propensity for low- cost fuel-
efficient cars, the demand for small cars in India is all set to
continue growing at a blistering pace.
Advantage Indian
Low cost production
Raw material costs (Steel) and labour costs in India are cheaper
giving a cost advantage in production. As per the wage cost index,
with South Korea normalised to 100, Indian hourly wage cost is just
18.7 in comparison to other BRIC countries like China (29.2.), Russia
(53.3) and Brazil(65.8)
Strong engineering
services background and
fluency in English
India churns out the secondlargest number of Engineering
graduates, after the US -- Approximately 300,000 engineers
graduate from more than 1,400 colleges in India, an advantage that
few countries can compete with. It has a huge Englishspeaking
population base of 72 million people.Indians with strong IT and
Engineering skills provide an opportunity for the foreign players
entering India to develop R&D centres for new technologies like
`parking space measurement' (PSM) devices, automatic wipers,
speed-sensitive automatic door locking systems, Anti-lock Breaking
System (ABS), Adaptive dampers, Ride control etc.
Better IP protection
Indian Patents Act 1970 has been amended thrice in the last 10
years to stay up-to-date with the TRIPs agreement. As per the
International Property Rights Index (IPRI) 2011 report, IP
protection provided in India is ranked better than other BRIC
countries and has given a greater confidence for foreign players to
launch their proprietary models in India.
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 6
Location advantage
India being a peninsular region has a trade advantage in exporting
cars to European countries such as UK, Germany and Italy and
importing raw materials from Japan.
Strong auto component
industry
Auto components manufactured in India are perceived to be 10-15
times cheaper than those in Europe and US with global quality
standards. The current $28 billion auto component industry is set to
grow four-fold to $110 billion industry drawing investments from
foreign players like Bosch and Delphi in India. Indian auto
component industry now has strong local players and growing
foreign players, making it conducive for becoming the hub of small
cars.
Well established local
Original Equipment
Manufacturers (OEMs)
Indian Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) have been on the
forefront of innovation and have benefitted from their heavy
investments in R&D. Local OEMs such as Tata Motors have
developed indigenous capabilities in designing and manufacturing
small cars such as Indica in 1999 and Nano in 2009. These players
are now gearing up to compete in the global markets.
Exhibit 3: Factors of India Advantage
5. India: An ecosystem for automobile manufacturing
The experience of indigenous small car development, excellence in
manufacturing sector, strong auto component industry are the three major
pillars that form the ecosystem of the small car industry in India.
India is ranked second in manufacturing competence, according to a report
`2010 Global Manufacturing Competitiveness Index' by Deloitte and the US
Council on Competitiveness. This can be attributed to a healthy growth of the
Indian manufacturing sector, expertise in low-cost auto component
manufacturing, increasing talent pool of scientists, researchers & engineers,
English-speaking workforce, low labour costs and protection of intellectual
property (IP) rights.
Despite the recession, Indian manufacturing industry has grown at a healthy
rate of 9.5 per cent over the last five years, As per the CII-ASCON survey, 41 out
of 121 sectors in the manufacturing industry are estimated to grow over 20 per
cent, spearheaded by growth rates in vehicle (33.2 per cent), and passenger car
(32.5 per cent) segments in 2010-11.
........................................................................................................................
5.1 Indian auto component industry
Indian auto components are 10-15 times cheaper than European and North
American components which form the primary export markets. As per
Automotive Component Manufacturers Association of India (ACMA) estimates,
by 2020, the auto component industry is set to grow four-fold, i.e.to a $113
billion industry.
Exports form a significant $5 billion of the present $28 billion auto component
industry. The growing domestic demand and the manufacturing cost advantage
are drawing huge investments and collaborations with global players in this
sector. For example, foreign players like Volkswagen and Renault - Nissan are
having tie-ups for component sharing with local players like Maruti-Suzuki and
are making use of the strong Indian supplier base. Toyota plans to invest $107
million to make engines and gearboxes for its new small car, Etios, in India. JK
Tyres & Industries will be setting up a $326 million plant in Chennai for tyre
manufacturing.
India: Mecca of Small Car 7
6. Pioneers of small cars
Maruti-Suzuki launched its first small car, Maruti-800, for India in 1983. In less
than 5 years, it indigenised over 70 per cent to reduce production costs and
followed greater indigenisation levels of 85-90 per cent in its future models of
Zen, WagonR, etc.
Tata Motors launched the first indigenously designed and manufactured Tata
Indica in 1999. In 2009, the company indigenously developed the world's
cheapest small car Tata Nano. Having developed two indigenous small cars,
India can now claim to have the expertise and experience of end-to-end
development of small cars.
6.1 Indian auto component industry
The Indian small car industry underwent a ground-breaking change when the
Indian car maker Tata Motors came up with a car that captured the imagination
of the world. Tata Motors looked at the huge price gap between the two-
wheelers and cars as a potential opportunity to launch a new car. It innovated
and improvised the entire value chain of car production, from design,
development, and manufacturing to supply and marketing. If we look at the cost
savings accounted for in Tata's Nano car, 63 per cent of savings were achieved
........................................................................................................................
through low-cost designs. Tata Motors revolutionised the supply chain by
bringing in suppliers like Bosch and Delphi in the early stage design and
making them full partners in the Nano innovation by developing low-cost
components.
iii
The Auto Policy of 2002 allowed 100 per centForeign Direct Investments (FDIs)
without any restrictions on foreign players to collaborate with domestic players
to set up their facilities.
iv
American and European countries drafted strict emission standards to control
their environment pollution. The government drafted the National Auto Fuel
Policy in 2003 to promote car exports to these markets. This policy focuses on
introducing and implementing emission standards such as Bharat stage III and
stage IV in India. Compulsory implementation of these stricter emission
standards has guided local and foreign automobile players to invest in R&D of
technology to produce more fuel-efficient cars.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) set up by the government has led to the
formation of automobile and automotive hubs in and around cities like Chennai,
Gurgaon and Pune.
The government drafted the Automotive Mission Plan 2006 -2016 together with
the establishment of world-class testing, homologation and certification
facilities along with nine state-of-the-art R&D centres under National
Automotive Testing & R&D Infrastructure Development Project (NATRiP) by
making investments of about $360 million. This has given the Indian industry an
edge over the newly emerging automotive destinations.
India: Mecca of Small Car 8
7. Government policies and reforms
Indian Government has set up the National Automotive Testing and R&D
Infrastructure Project (NATRiP) with investments of around 360 million USD
Further, to mitigate the impact of R&D expenses on the automobile prices, the
Finance Minister had raised the weighted tax deduction to 200 per cent on the
expenditure incurred by companies on in-house R&D activities, from the
existing 150 per cent as part of the Union Budget 2010-11. All these policy
initiatives have led to the spiralling R&D expenditure and have set the
framework for India emerging as a small car hub.
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 9
The government also showed special focus on small cars in the Budget
Proposal 2010-11 by promoting the manufacturing of fuel-efficient and hybrid
cars. The government also announced tax breaks and proposed the setting up
of a `National Mission for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles.'
v
8. Manufacturing facilities & their future investments
The India advantage for small car has drawn huge investments in the
manufacturing and R&D facilities by local and foreign OEMs over the last
decade. Many foreign players are now doing in-house development,
manufacture, and exports of small cars from India.
Chennai is now being called the `Detroit of the South' because big players such
as Ford, Hyundai, Renault - Nissan, Daimler and BMW have opened up
manufacturing plants and R&D houses.
vi
Exhibit 4 shows the current picture of India in its role as a manufacturer,
developer and exporter of small cars.
Car manufacturers
Flagship small cars
launched in India
Manufactured in India Developed in India
Exported to other
Countries
Maruti - Suzuki Maruti 800, Alto, Zen
Hyundai
Santro, i10, i20
Ford Figo
Volkswagen Polo
Renault - Nissan Micra
Chevrolet Beat, Spark, Aveo U-VA
Fiat Palio, Punto
Tata Motors Indica, Nano
Skoda Fabia
Toyota Etios
Already being exported
Planning to export
Exhibit 4: A snapshot of car manufacturers and their flagship small cars in India
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 10
Exhibit 5: Hubs of small car manufacturing for various OEMs and investments planned by
them for the next 2-3 years
Global car manufacturers made huge investments in setting up manufacturing
plants and increasing production capacities of small car to meet the growing
domestic demand and export demands.
Exhibit 5 shows the location-wise investments and the production capacity
increments. Many global players such as Volkswagen, Mercedes- Benz and
BMW, alongside domestic players such as Bajaj, have realised the potential of
small and cheaper cars in the Indian market. These players have plans to make
huge infrastructure investments to produce their small cars for India. Tata
Motors, on the other hand, is modifying Nano to suit the needs of the global
market.
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 11
Exhibit 6: Investments made till year 2010 and investments planned (for the next 5 years 2010-
2015) by major small car players in India
Exhibit 6 compares the key investments made by major car manufacturers till
year 2010 with future investment plans for the next five years. Players such as
Tata Motors and Maruti - Suzuki plan to double their investments in the next five
years (2010-2015)
9. New Technologies and Initiatives
In 1999, the Indian small car industry showcased its innovation in car design and
new technologies by building the completely indigenised Tata Indica. The
Bangalore based Reva Electric Car Company, launched the first ever electric
car REVA, the world'smass produced electric car in 2001.
Tata Nano is an excellent example of innovation using light-weight technologies
to produce a fuel-efficient and low-cost car. Tata Motors is now shifting gears to
the electric versions of Nano and Indica and has plans to launch these hybrids
in India by 2011.
Advanced technologies used in the cars exported to Europe are now being
developed in India itself. For example, Nissan Micra provides features such as
reversing sensors, new `parking space measurement' (PSM) devices,
Billion USD
........................................................................................................................
automatic wipers and speed-sensitive automatic door-locking system etc,
which are developed in India for exporting to Europe.
New technologies in batteries are made available to the Indian markets, which
are expected to further boost the electric car market in India.
India: Mecca of Small Car 12
Exhibit 7: New Car launches and Investments
1
Car manufacturers New investments/plans
Maruti- Suzuki
Plans to set up a third plant worth $411.45 million in Manesar with
a capacity of 2,50,000 units
Tata Motors
Is collaborating with a Canadian company for second-generation
gearless Nano and preparing to launch the electric version of Tata
Indica Vista
Toyota
Is set to launch Etios, with a localisation level of 70 per cent.
Invested $107 million for manufacturing auto components of Etios.
Plans to ramp up production capacity in India by ten-fold to make
India a hub for Toyota manufacturing
Bajaj & Renault-Nissan
Formed an alliance for developing low cost car and setting up a
manufacturing plant in Pune
General Motors
Plans to launch another small car and to export small cars to
Bhutan, Nepal and Sri Lanka
Honda
Plans to launch its small car in India, Nepal, Sri Lanka by end of
2011. Plans to start production at Greater Noida
Renault - Nissan
Shifted the production of exported Micra cars from United Kingdom
to India
Ford
Invested $500 million on its Chennai plant to make it the hub for
small car production
As a part of the NATRiP, International centre for Automotive Technology (ICAT)
was set up in Manesar that provides R&D and support services for automotive
design, test and validation. The global component manufacturers like Bosch,
Valeo, Caterpillar, General Motors, Ford, Cummins etc, have set up their R&D
facilities in India.
........................................................................................................................
India: Mecca of Small Car 13
10. The road ahead
The growing demand for small cars globally and the India advantage have
established the subcontinent as the hub of small cars. The Indian small car
industry now has the expertise and experience to innovate further and make
affordable cars for the highly untapped rural segments. Moreover, with the ever
-increasing oil prices, hybrid vehicles and electric cars seem to be the way
ahead. India, which has the expertise of developing electric car `REVA' as early
as 2001 should leverage the quality talent pool, best in-house R&D facilities,
auto component systems and government support (setting up of National
Mission for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) to focus on being the leader in the
electric car segment.
........................................................................................................................
11. References
India: Mecca of Small Car 14
i
http://www.business-standard.com/india/news/india-to-be-small-car-hub-
by-2013/334005/
ii
http://www.livemint.com/2009/09/07214652/Cheaper-labour-helps-India-ove.html
iii
http://www.businessweek.com/innovate/content/mar2009/
id20090318_012120_page_2.htm
iv
http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2002-03-05/news/27350234_1_auto-
policy-minimum-capitalisation-three-wheelers
v
http://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/article1498167.ece
vi
http://online.wsj.com/article/
SB10001424052748704111704575354853980451636.html?mod=googlenews_wsj
........................................................................................................................
DISCLAIMER
India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF) engaged RedSeer Management
Consulting Private Limited to prepare this presentation and the same has
been prepared by RedSeer Management Consulting Private Limited in
consultation with IBEF. All rights reserved. All copyright in this presentation
and related works is solely and exclusively owned by IBEF. The same may
not be reproduced, wholly or in part in any material form (including
photocopying or storing it in any medium by electronic means and whether
or not transiently or incidentally to some other use of this presentation),
modified or in any manner communicated to any third party except with the
written approval of IBEF.
This presentation is for information purposes only. While due care has been
taken during the compilation of this presentation to ensure that the
information is accurate to the best of RedSeer Management Consulting
Private Limited's and IBEF's knowledge and belief, the content is not to be
construed in any manner whatsoever as a substitute for professional advice.
RedSeer Management Consulting Private Limited and IBEF neither
recommend nor endorse any specific products or services that may have
been mentioned in this presentation and nor do they assume any liability or
responsibility for the outcome of decisions taken as a result of any reliance
placed on this presentation.
Neither RedSeer Management Consulting Private Limited nor IBEF shall be
liable for any direct or indirect damages that may arise due to any act or
omission on the part of the user due to any reliance placed or guidance
taken from any portion of this presentation.
India: Mecca of Small Car 15
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Managing PeopleDocument14 pagesManaging PeopleAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- SCHNEIDERS (00102) Peridic Billing Statement Ending 03.15.2017 - RedactedDocument1 pageSCHNEIDERS (00102) Peridic Billing Statement Ending 03.15.2017 - Redactedlarry-612445No ratings yet
- APDocument54 pagesAPAndangNo ratings yet
- Delhi Doctor DataDocument8 pagesDelhi Doctor DataJagsonpal Medical InsightsNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management CH 08Document13 pagesStrategic Management CH 08Khadra NuurNo ratings yet
- Solution To Case 32 by Jim DemelloDocument7 pagesSolution To Case 32 by Jim DemelloRefi Reyhandi Mahardhika100% (2)
- IELTS Akash Confirmation ReceiptDocument1 pageIELTS Akash Confirmation ReceiptAkashNo ratings yet
- Club-Mahindra Case StudyDocument9 pagesClub-Mahindra Case StudyAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- Future of India Post - Rural DimensionDocument5 pagesFuture of India Post - Rural DimensionAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix and Its Significance in Product Mix Analysis - NCK Pharma Solution Private Limited - Powered by Comm100 PDFDocument6 pagesBCG Matrix and Its Significance in Product Mix Analysis - NCK Pharma Solution Private Limited - Powered by Comm100 PDFAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- Application of Statistical Techniques in IndustryDocument7 pagesApplication of Statistical Techniques in IndustryAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- IIFT GK CompendiumDocument80 pagesIIFT GK CompendiumAkhilesh Menon100% (1)
- JERASIA-Annual Report 2016 PDFDocument111 pagesJERASIA-Annual Report 2016 PDFmizzaldamaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Product Life Cycle of CRT TELEVISION Course Title: International Business Course Code: Bus-305Document7 pagesAssignment On Product Life Cycle of CRT TELEVISION Course Title: International Business Course Code: Bus-305Syed InshanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Rakindo KovaiDocument1 pageRakindo KovaiRagumuthukumar AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- International Business Machines Corporation: Type Traded AsDocument4 pagesInternational Business Machines Corporation: Type Traded AsSoyi PsNo ratings yet
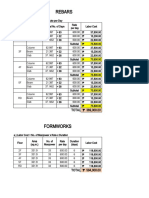
- Labor FormatDocument2 pagesLabor FormatJohnNo ratings yet
- WP 93 LucarelliDocument86 pagesWP 93 Lucarellirabbu14No ratings yet
- Dar Vs Carriedo DigestDocument2 pagesDar Vs Carriedo DigestJennica Gyrl G. Delfin100% (3)
- Icag Past QuestionDocument5 pagesIcag Past QuestionAdam AliuNo ratings yet
- Reflective EssayDocument3 pagesReflective Essayapi-340281541No ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy Tab A7 Invoice - 27 May 2022Document1 pageSamsung Galaxy Tab A7 Invoice - 27 May 2022Saransh KejriwalNo ratings yet
- OD328636244353646100Document3 pagesOD328636244353646100ankit ojhaNo ratings yet
- Pesco Online BillsDocument1 pagePesco Online BillsAziz0346100% (1)
- Patrakar SadanDocument4 pagesPatrakar SadanRKM RKMNo ratings yet
- Corporate Law #3:for Whose ActsDocument11 pagesCorporate Law #3:for Whose Actssup3rst8rNo ratings yet
- Roland Berger Trends Trucks TrailerDocument56 pagesRoland Berger Trends Trucks TrailerAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Vishesh FormDocument4 pagesVishesh FormVijaySengarNo ratings yet
- Dashboard Templates-Fix (1) NewDocument11 pagesDashboard Templates-Fix (1) NewdindajelantikNo ratings yet
- Reading - Towill & Christopher Developing Market Specific Supply Chain StrategiesDocument29 pagesReading - Towill & Christopher Developing Market Specific Supply Chain StrategiesSasha KingNo ratings yet
- 34 Resolution (Annual Budget 10% SK Fund 2020)Document3 pages34 Resolution (Annual Budget 10% SK Fund 2020)anabel0% (1)
- International Economics and Trade Theory Chapter 15 QuizDocument3 pagesInternational Economics and Trade Theory Chapter 15 QuizMeghana1205No ratings yet
- Paramount Surgimed LTD - Policy IssuedDocument8 pagesParamount Surgimed LTD - Policy IssuedBOC ClaimsNo ratings yet
- BOCW Welfare Cess Rules, 1998Document10 pagesBOCW Welfare Cess Rules, 1998EricKankarNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Exploration & Production POLICY 2012: Government of Pakistan Ministry of Petroleum & Natural ResourcesDocument54 pagesPetroleum Exploration & Production POLICY 2012: Government of Pakistan Ministry of Petroleum & Natural ResourcesabdullahiqbalNo ratings yet
- MGX80 Gearless 20171 3Document3 pagesMGX80 Gearless 20171 3HƯNG NGUYỄN THANHNo ratings yet